Docker安装RabbitMq及java对接
一、安装一个RabbitMq服务节点
1.1 安装环境
系统环境:CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)
Docker安装版本:19.03.5
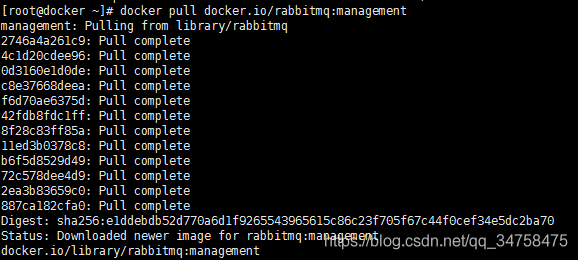
1.2 使用docker下载镜像
# docker pull docker.io/rabbitmq:management1.3 运行镜像
# docker run -d --restart=always -p 15672:15672 --name shop-rabbitmq -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=guest -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=guest -v /var/lib/rabbitmq:/var/lib/rabbitmq rabbitmq:management参数说明:
-d ##后台运行容器
--name ##指定容器名称
-p ##暴露服务运行的端口(15672:控制台Web端口号)
-e 指定环境变量(RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER:默认的用户名;RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS:默认用户名的密码)
rabbitmq配置文件在/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf(这是容器内位置)
RabbitMQ默认端口:
4369 -- erlang发现端口
5672 --client端通信端口,应用访问端口
15672 -- 管理界面ui端口,控制台Web端口号
25672 -- server间内部通信端口
二、安装RabbitMq集群
2.1 安装环境
系统环境:CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)
Docker安装版本:19.03.5
2.2 使用docker下载镜像源
# docker pull rabbitmq:3.6.15-management2.3 安装RabbitMQ容器
# docker run -d --hostname rabbit1 --name myrabbit1 -p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='rabbitcookie' rabbitmq:3.6.15-management# docker run -d --hostname rabbit2 --name myrabbit2 -p 5673:5672 --link myrabbit1:rabbit1 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='rabbitcookie' rabbitmq:3.6.15-management# docker run -d --hostname rabbit3 --name myrabbit3 -p 5674:5672 --link myrabbit1:rabbit1 --link myrabbit2:rabbit2 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='rabbitcookie' rabbitmq:3.6.15-management具体的参数含义,参见上文“启动RabbitMQ”部分。
注意点:
- 多个容器之间使用“--link”连接,此属性不能少;
- Erlang Cookie值必须相同,也就是RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE参数的值必须相同,原因见下文“配置相同Erlang Cookie”部分;
2.4 加入RabbitMQ节点到集群
2.4.1 设置节点1
[root@docker ~]# docker exec -it myrabbit1 bash
root@rabbit1:/# rabbitmqctl stop_app
Stopping rabbit application on node rabbit@rabbit1
root@rabbit1:/# rabbitmqctl reset
Resetting node rabbit@rabbit1
root@rabbit1:/# rabbitmqctl start_app
Starting node rabbit@rabbit1
root@rabbit1:/# exit
exit
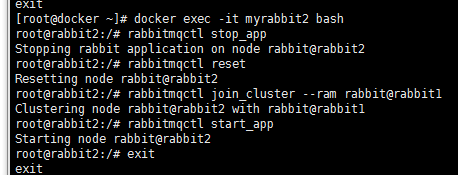
2.4.2 设置节点2,并加入集群
[root@docker ~]# docker exec -it myrabbit2 bash
root@rabbit2:/# rabbitmqctl stop_app
Stopping rabbit application on node rabbit@rabbit2
root@rabbit2:/# rabbitmqctl reset
Resetting node rabbit@rabbit2
root@rabbit2:/# rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@rabbit1
Clustering node rabbit@rabbit2 with rabbit@rabbit1
root@rabbit2:/# rabbitmqctl start_app
Starting node rabbit@rabbit2
root@rabbit2:/# exit
exit
参数“--ram”表示设置为内存节点,忽略次参数默认为磁盘节点。
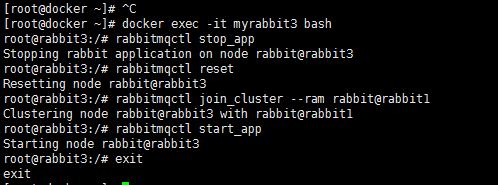
2.4.3 设置节点3,加入到集群:
[root@docker ~]# docker exec -it myrabbit3 bash
root@rabbit3:/# rabbitmqctl stop_app
Stopping rabbit application on node rabbit@rabbit3
root@rabbit3:/# rabbitmqctl reset
Resetting node rabbit@rabbit3
root@rabbit3:/# rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@rabbit1
Clustering node rabbit@rabbit3 with rabbit@rabbit1
root@rabbit3:/# rabbitmqctl start_app
Starting node rabbit@rabbit3
root@rabbit3:/# exit
exit
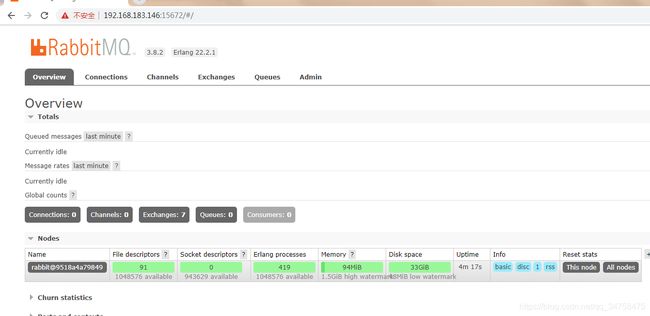
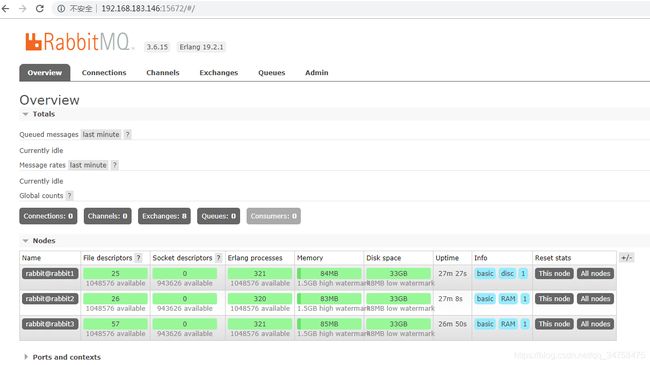
设置好之后,使用http://本机ip:15672 进行访问了,默认账号密码是guest/guest,效果如下图:
启动了3个节点,1个磁盘节点和2个内存节点。
2.5 配置相同Erlang Cookie
有些特殊的情况,比如已经运行了一段时间的几个单个物理机,我们在之前没有设置过相同的Erlang Cookie值,现在我们要把单个的物理机部署成集群,实现我们需要同步Erlang的Cookie值。
因为RabbitMQ是用Erlang实现的,Erlang Cookie相当于不同节点之间相互通讯的秘钥,Erlang节点通过交换Erlang Cookie获得认证。
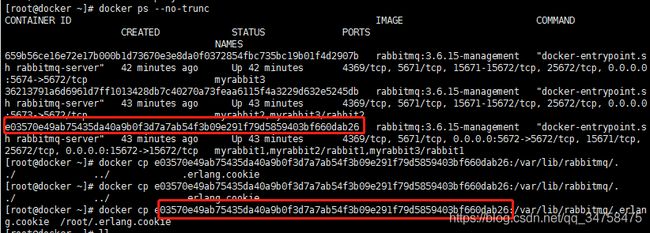
要想知道Erlang Cookie位置,首先要取得RabbitMQ启动日志里面的home dir路径,作为根路径。使用:“docker logs 容器名称”查看,如下图:
现将节点1的cookie值复制到本地:
[root@docker ~]# docker cp e03570e49ab75435da40a9b0f3d7a7ab54f3b09e291f79d5859403bf660dab26:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie /root/.erlang.cookie然后将本地的cookie值复制到节点2和3的服务器:
[root@docker ~]# docker cp /root/.erlang.cookie 36213791a6d6961d7ff1013428db7c40270a73feaa6115f4a3229d632e5245db:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
[root@docker ~]# docker cp /root/.erlang.cookie 659b56ce16e72e17b000b1d73670e3e8da0f0372854fbc735bc19b01f4d2907b:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
三、使用java连接RabbitMQ(直连型交换机)
3.1 使用docker运行RabbitMQ
[root@docker ~]# docker run -d --restart=always -p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672 -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=guest -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=guest rabbitmq:management注意点:
-d:表示后台运行容器
--restart=always:表示随着docker重启服务
-p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672:表示映射端口,以便其他电脑访问
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=guest -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=guest:表示设置RabbitMQ的用户名以及密码
rabbitmq:management:表示运行的镜像以及版本
3.2 使用springboot创建RabbitMq的生产者
3.2.1 创建rabbitmqprovider(生产者项目),项目目录如下:
3.2.2 配置pom.xml文件以及application.yml文件
pom.xml文件配置
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
application.yml文件配置
server:
port: 8021
spring:
#给项目来个名字
application:
name: rabbitmq-provider
#配置rabbitMq 服务器
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.183.146
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#虚拟host 可以不设置,使用server默认host
virtual-host: /注意点:virtual-host:配置的主机名一定要与控制台的Admin配置相同,否则会出现An unexpected connection driver error occured的报错:
3.2.3 创建DirectRabbitConfig类,创建direct exchange(直连型交换机)
package com.qhr.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 9:13
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqprovider
*/
@Configuration
public class DirectRabbitConfig {
//队列 起名:TestDirectQueue
@Bean
public Queue TestDirectQueue() {
return new Queue("TestDirectQueue",true); //true 是否持久
}
//Direct交换机 起名:TestDirectExchange
@Bean
DirectExchange TestDirectExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("TestDirectExchange");
}
//绑定 将队列和交换机绑定, 并设置用于匹配键:TestDirectRouting
@Bean
Binding bindingDirect() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(TestDirectQueue()).to(TestDirectExchange()).with("TestDirectRouting");
}
}
3.2.4 创建SendMessageController类,用于消息推送
package com.qhr.rabbitmqprovider.controller;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 9:16
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqprovider
*/
@RestController
public class SendMessageController {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; //使用RabbitTemplate,这提供了接收/发送等等方法
@GetMapping("/sendDirectMessage")
public String sendDirectMessage() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "test message, hello!";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("messageId",messageId);
map.put("messageData",messageData);
map.put("createTime",createTime);
//将消息携带绑定键值:TestDirectRouting 发送到交换机TestDirectExchange
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("TestDirectExchange", "TestDirectRouting", map);
return "ok";
}
}
3.2.5 运行rabbitmqprovider项目
把rabbitmqprovider项目运行,调用下接口:
因为我们目前还没弄消费者 rabbitmqconsumer,消息没有被消费的,我们去rabbitMq管理页面看看,是否推送成功:
再看看队列:
如图所示,消息已经推送成功了.
3.3 创建rabbitmqconsumer(消费者)项目
3.3.1 创建rabbitmqconsumer(消费者)项目,项目目录如下:
3.3.2 配置pom.xml文件以及application.yml文件
配置pom.xml文件
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
配置application.yml文件
server:
port: 8022
spring:
#给项目来个名字
application:
name: rabbitmq-consumer
#配置rabbitMq 服务器
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.183.146
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#虚拟host 可以不设置,使用server默认host
virtual-host: /
注意点:virtual-host:配置的主机名一定要与控制台的Admin配置相同,否则会出现An unexpected connection driver error occured的报错:
3.3.3 创建DirectRabbitConfig类
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 9:13
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Configuration
public class DirectRabbitConfig {
//队列 起名:TestDirectQueue
@Bean
public Queue TestDirectQueue() {
return new Queue("TestDirectQueue",true);
}
//Direct交换机 起名:TestDirectExchange
@Bean
DirectExchange TestDirectExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("TestDirectExchange");
}
//绑定 将队列和交换机绑定, 并设置用于匹配键:TestDirectRouting
@Bean
Binding bindingDirect() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(TestDirectQueue()).to(TestDirectExchange()).with("TestDirectRouting");
}
}
3.3.4 创建DirectReceiver类,用于接收生产发送的消息
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 10:52
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "TestDirectQueue")//监听的队列名称 TestDirectQueue
public class DirectReceiver {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("DirectReceiver消费者收到消息 : " + testMessage.toString());
}
}
3.3.5 运行rabbitmqconsumer项目
并且比较RabbitMq的控制台页面
之前rabbitmqprovider发送的信息,已经被接收,队列里已经没有消息在等待处理了.然后可以再继续调用rabbitmq-provider项目的推送消息接口,可以看到消费者即时消费消息:
四、配置主题交换机
4.1 配置生产者项目:
4.1.1 在rabbitmqprovider项目里面创建TopicRabbitConfig.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 11:28
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqprovider
*/
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
//绑定键
public final static String man = "topic.man";
public final static String woman = "topic.woman";
@Bean
public Queue firstQueue() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.man);
}
@Bean
public Queue secondQueue() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.woman);
}
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
//将firstQueue和topicExchange绑定,而且绑定的键值为topic.man
//这样只要是消息携带的路由键是topic.man,才会分发到该队列
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(firstQueue()).to(exchange()).with(man);
}
//将secondQueue和topicExchange绑定,而且绑定的键值为用上通配路由键规则topic.#
// 这样只要是消息携带的路由键是以topic.开头,都会分发到该队列
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(secondQueue()).to(exchange()).with("topic.#");
}
}
4.1.2 然后添加多2个接口,用于推送消息到主题交换机:
@GetMapping("/sendTopicMessage1")
public String sendTopicMessage1() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: M A N ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map manMap = new HashMap<>();
manMap.put("messageId", messageId);
manMap.put("messageData", messageData);
manMap.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.man", manMap);
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/sendTopicMessage2")
public String sendTopicMessage2() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: woman is all ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map womanMap = new HashMap<>();
womanMap.put("messageId", messageId);
womanMap.put("messageData", messageData);
womanMap.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.woman", womanMap);
return "ok";
}
4.1.3 生产者配置完成的项目目录:
配置完成,暂时不要运行项目。
4.2 配置消费者项目:
4.2.1 在rabbitmqconsumer项目上,创建TopicManReceiver.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 11:30
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.man")
public class TopicManReceiver {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("TopicManReceiver消费者收到消息 : " + testMessage.toString());
}
}
4.2.2 再创建一个TopicTotalReceiver.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 11:32
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.woman")
public class TopicTotalReceiver {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("TopicTotalReceiver消费者收到消息 : " + testMessage.toString());
}
}4.2.3 同样,加主题交换机的相关配置,TopicRabbitConfig.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 11:34
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
//绑定键
public final static String man = "topic.man";
public final static String woman = "topic.woman";
@Bean
public Queue firstQueue() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.man);
}
@Bean
public Queue secondQueue() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.woman);
}
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
//将firstQueue和topicExchange绑定,而且绑定的键值为topic.man
//这样只要是消息携带的路由键是topic.man,才会分发到该队列
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(firstQueue()).to(exchange()).with(man);
}
//将secondQueue和topicExchange绑定,而且绑定的键值为用上通配路由键规则topic.#
// 这样只要是消息携带的路由键是以topic.开头,都会分发到该队列
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(secondQueue()).to(exchange()).with("topic.#");
}
}
4.2.4 消费者配置完成的项目目录
4.3 然后把rabbitmqprovider,rabbitmqconsumer两个项目都跑起来
4.3.1 调用sendTopicMessage1接口:
然后看消费者rabbitmq-consumer的控制台输出情况:
TopicManReceiver监听队列1,绑定键为:topic.man
TopicTotalReceiver监听队列2,绑定键为:topic.#
而当前推送的消息,携带的路由键为:topic.man
4.3.2 调用sendTopicMessage2接口
然后看消费者rabbitmq-consumer的控制台输出情况:
TopicManReceiver监听队列1,绑定键为:topic.man
TopicTotalReceiver监听队列2,绑定键为:topic.#
而当前推送的消息,携带的路由键为:topic.woman
运行结果:
4.4 总结
主题交换机,这个交换机其实跟直连交换机流程差不多,但是它的特点就是在它的路由键和绑定键之间是有规则的。
简单地介绍下规则:
* (星号) 用来表示一个单词 (必须出现的)
# (井号) 用来表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词
通配的绑定键是跟队列进行绑定的,举个小例子
队列Q1 绑定键为 *.TT.* 队列Q2绑定键为 TT.#
如果一条消息携带的路由键为 A.TT.B,那么队列Q1将会收到;
如果一条消息携带的路由键为TT.AA.BB,那么队列Q2将会收到;
五、Fanout Exchang 扇型交换机
5.1 配置生产者项目
5.1.1 先在rabbitmqprovIder项目上创建FanoutRabbitConfig.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 14:32
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqprovider
*/
@Configuration
public class FanoutRabbitConfig {
/**
* 创建三个队列 :fanout.A fanout.B fanout.C
* 将三个队列都绑定在交换机 fanoutExchange 上
* 因为是扇型交换机, 路由键无需配置,配置也不起作用
*/
@Bean
public Queue queueA() {
return new Queue("fanout.A");
}
@Bean
public Queue queueB() {
return new Queue("fanout.B");
}
@Bean
public Queue queueC() {
return new Queue("fanout.C");
}
@Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
5.1.2 在SendMessageController类中,添加一个接口用于推送消息
@GetMapping("/sendFanoutMessage")
public String sendFanoutMessage() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: testFanoutMessage ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("messageId", messageId);
map.put("messageData", messageData);
map.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange", null, map);
return "ok";
}
5.1.3 生产者配置完成的项目目录:
5.2 配置消费者项目
5.2.1 在rabbitmqconsumer项目上创建FanoutReceiverA、FanoutReceiverB、FanoutReceiverC三个类
FanoutReceiverA类:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 14:45
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.A")
public class FanoutReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("FanoutReceiverA消费者收到消息 : " +testMessage.toString());
}
}
FanoutReceiverB类:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 14:47
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.B")
public class FanoutReceiverB {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("FanoutReceiverB消费者收到消息 : " +testMessage.toString());
}
}
FanoutReceiverC类:package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 14:54
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.C")
public class FanoutReceiverC {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(Map testMessage) {
System.out.println("FanoutReceiverC消费者收到消息 : " +testMessage.toString());
}
}
5.2.2 创建FanoutRabbitConfig类
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 14:59
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
public class FanoutRabbitConfig {
/**
* 创建三个队列 :fanout.A fanout.B fanout.C
* 将三个队列都绑定在交换机 fanoutExchange 上
* 因为是扇型交换机, 路由键无需配置,配置也不起作用
*/
@Bean
public Queue queueA() {
return new Queue("fanout.A");
}
@Bean
public Queue queueB() {
return new Queue("fanout.B");
}
@Bean
public Queue queueC() {
return new Queue("fanout.C");
}
@Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
5.2.3 由于扇形交换机不需要传递键值,所以没有自动加入队列,我们必须手动在RabbitMQ网页控制台手动添加,如下图所示
注:若无添加队列会报Failed to declare queue(s):[XXX]错误5.2.4 消费者配置完成项目目录
5.3 然后把rabbitmqprovider,rabbitmqconsumer两个项目都跑起来
调用sendFanoutMessage :
查看rabbitmqconsumer项目控制台:六、消息确认回调函数
6.1 在rabbitmq-provider项目的application.yml文件上,加上消息确认的配置项后:
server:
port: 8021
spring:
#给项目来个名字
application:
name: rabbitmq-provider
#配置rabbitMq 服务器
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.183.146
port: 5672
username: test
password: qhr7788995201314.
#虚拟host 可以不设置,使用server默认host
virtual-host: demo
#消息确认配置项
#确认消息已发送到交换机(Exchange)
publisher-confirms: true
#确认消息已发送到队列(Queue)
publisher-returns: true
6.2 配置相关的消息确认回调函数,RabbitConfig.java:
package com.qhr.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : 邱杭锐
* @Date : 2020/1/9 15:52
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqprovider
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public RabbitTemplate createRabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate();
rabbitTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//设置开启Mandatory,才能触发回调函数,无论消息推送结果怎么样都强制调用回调函数
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
System.out.println("ConfirmCallback: "+"相关数据:"+correlationData);
System.out.println("ConfirmCallback: "+"确认情况:"+ack);
System.out.println("ConfirmCallback: "+"原因:"+cause);
}
});
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
System.out.println("ReturnCallback: "+"消息:"+message);
System.out.println("ReturnCallback: "+"回应码:"+replyCode);
System.out.println("ReturnCallback: "+"回应信息:"+replyText);
System.out.println("ReturnCallback: "+"交换机:"+exchange);
System.out.println("ReturnCallback: "+"路由键:"+routingKey);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}
到这里,生产者推送消息的消息确认调用回调函数已经完毕。可以看到上面写了两个回调函数,一个叫 ConfirmCallback ,一个叫 RetrunCallback;那么以上这两种回调函数都是在什么情况会触发呢? 先从总体的情况分析,推送消息存在四种情况:
①消息推送到server,但是在server里找不到交换机②消息推送到server,找到交换机了,但是没找到队列③消息推送到sever,交换机和队列啥都没找到④消息推送成功那么我先写几个接口来分别测试和认证下以上4种情况,消息确认触发回调函数的情况:
6.2.1 消息推送到server,但是在server里找不到交换机:
在SendMessageController中添加接口:
public String TestMessageAck() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: non-existent-exchange test message ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("messageId", messageId);
map.put("messageData", messageData);
map.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("non-existent-exchange", "TestDirectRouting", map);
return "ok";
}
结果:![]()
结论:
这种情况触发的是 ConfirmCallback 回调函数。
6.2.2 消息推送到server,找到交换机了,但是没找到队列:
在DirectRabbitConfig类中添加:@Bean
DirectExchange lonelyDirectExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("lonelyDirectExchange");
}
在SendMessageController中添加接口:@GetMapping("/TestMessageAck2")
public String TestMessageAck2() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: lonelyDirectExchange test message ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("messageId", messageId);
map.put("messageData", messageData);
map.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("lonelyDirectExchange", "TestDirectRouting", map);
return "ok";
}
结果: 结论: 这种情况触发的是 ConfirmCallback和RetrunCallback两个回调函数.6.2.3 消息推送到sever,交换机和队列啥都没找到
在SendMessageController中添加接口:@GetMapping("/TestMessageAck3")
public String TestMessageAck3() {
String messageId = String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID());
String messageData = "message: non-existent-exchange test message ";
String createTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("messageId", messageId);
map.put("messageData", messageData);
map.put("createTime", createTime);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("non-existent-exchange", "non-existent-routing", map);
return "ok";
}
结果:
结论: 这种情况与①一样触发的是 ConfirmCallback 回调函数。6.2.4 消息推送成功
直接调用sendDirectMessage接口结果: 结论: 这种情况触发的是 ConfirmCallback 回调函数。七、消息确认机制
7.1 三种模式
①自动确认, 这也是默认的消息确认情况。AcknowledgeMode.NONERabbitMQ成功将消息发出(即将消息成功写入TCP Socket)中立即认为本次投递已经被正确处理,不管消费者端是否成功处理本次投递。所以这种情况如果消费端消费逻辑抛出异常,也就是消费端没有处理成功这条消息,那么就相当于丢失了消息。一般这种情况我们都是使用try catch捕捉异常后,打印日志用于追踪数据,这样找出对应数据再做后续处理。 ② 不确认,这个不做介绍③ 手动确认 ,这个比较关键,也是我们配置接收消息确认机制时,多数选择的模式。消费者收到消息后,手动调用basic.ack/basic.nack/basic.reject后,RabbitMQ收到这些消息后,才认为本次投递成功。basic.ack用于肯定确认 basic.nack用于否定确认(注意:这是AMQP 0-9-1的RabbitMQ扩展) basic.reject用于否定确认,但与basic.nack相比有一个限制:一次只能拒绝单条消息
消费者端以上的3个方法都表示消息已经被正确投递,但是basic.ack表示消息已经被正确处理,但是basic.nack,basic.reject表示没有被正确处理,但是RabbitMQ中仍然需要删除这条消息。7.2 在rabbitmqconsumer项目创建MessageListenerConfig.java
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.config;
import com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver.DirectReceiver;
import com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver.FanoutReceiverA;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AcknowledgeMode;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CachingConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.listener.SimpleMessageListenerContainer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author : qhr520
* @Date : 2020/1/9 16:29
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Configuration
public class MessageListenerConfig {
@Autowired
private CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
@Autowired
private DirectReceiver directReceiver;//Direct消息接收处理类
//@Autowired
//FanoutReceiverA fanoutReceiverA;//Fanout消息接收处理类A
@Autowired
DirectRabbitConfig directRabbitConfig;
//@Autowired
//FanoutRabbitConfig fanoutRabbitConfig;
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer simpleMessageListenerContainer() {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer container = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
container.setConcurrentConsumers(1);
container.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(1);
container.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL); // RabbitMQ默认是自动确认,这里改为手动确认消息
container.setQueues(directRabbitConfig.TestDirectQueue());
container.setMessageListener(directReceiver);
//container.addQueues(fanoutRabbitConfig.queueA());
//container.setMessageListener(fanoutReceiverA);
return container;
}
}
7.3 修改DirectReceiver.java类
package com.qhr.rabbitmqconsumer.receiver;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.listener.api.ChannelAwareMessageListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : 邱杭锐
* @Date : 2020/1/9 10:52
* @Version : 01
* @Description :
* @ProjectName : rabbitmqconsumer
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "TestDirectQueue")//监听的队列名称 TestDirectQueue
public class DirectReceiver implements ChannelAwareMessageListener {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception {
long deliveryTag = message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag();
try {
//因为传递消息的时候用的map传递,所以将Map从Message内取出需要做些处理
String msg = message.toString();
String[] msgArray = msg.split("'");//可以点进Message里面看源码,单引号直接的数据就是我们的map消息数据
Map msgMap = mapStringToMap(msgArray[1].trim());
String messageId=msgMap.get("messageId");
String messageData=msgMap.get("messageData");
String createTime=msgMap.get("createTime");
System.out.println("messageId:"+messageId+" messageData:"+messageData+" createTime:"+createTime);
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, true);
// channel.basicReject(deliveryTag, true);//为true会重新放回队列
} catch (Exception e) {
channel.basicReject(deliveryTag, false);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//{key=value,key=value,key=value} 格式转换成map
private Map mapStringToMap(String str) {
str = str.substring(1, str.length() - 1);
String[] strs = str.split(",");
Map map = new HashMap();
for (String string : strs) {
String key = string.split("=")[0].trim();
String value = string.split("=")[1];
map.put(key, value);
}
return map;
}
}