OC 是一门复杂的高级语言,正是因为巧妙复杂的结构设计和内存模型,巧妙的运用isa和superClass才赋予这门语言独特的属性和特点。
实例对象的isa 指针类对象,类对象的isa指针指向metaClass,metaClass的isa指针指向基类NSObject.
实例对象没有superClass指针,类对象的superClass指向父类对象,一直到基类的类对象[NSObject class], NSObject的类对象指向nil。
metaClass对象的superClass指向父类的metaClass对象,一直到基类的metaClass对象, NSObject的metaClass对象指向类对象[NSObject class]。
面试
- OC消息机制
- 消息转发机制
- 什么是runtime?
消息机制三大步
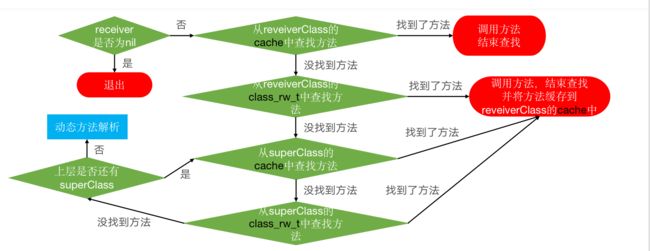
OC中的方法调用,其实都是转换为objc_msgSend函数的调用, objc_msgSend又分为三大阶段:消息分发,动态解析,消息转发; objc_msgSend是汇编实现的因为这个方法调用频次太高了
消息分发
receiver通过isa指针找到receiverClass,receiverClass通过superclass指针找到superClass;
如果是从class_rw_t中查找方法,已经排序的,二分查找;没有排序的,遍历查找;
方法缓存需要用到cache_t cache哈希表;
/***********************************************************************
* lookUpImpOrForward.
* The standard IMP lookup.
* initialize==NO tries to avoid +initialize (but sometimes fails)
* cache==NO skips optimistic unlocked lookup (but uses cache elsewhere)
* Most callers should use initialize==YES and cache==YES.
* inst is an instance of cls or a subclass thereof, or nil if none is known.
* If cls is an un-initialized metaclass then a non-nil inst is faster.
* May return _objc_msgForward_impcache. IMPs destined for external use
* must be converted to _objc_msgForward or _objc_msgForward_stret.
* If you don't want forwarding at all, use lookUpImpOrNil() instead.
**********************************************************************/
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) {//去缓存中查找
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.read();
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
// Drop the read-lock and acquire the write-lock.
// realizeClass() checks isRealized() again to prevent
// a race while the lock is down.
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
runtimeLock.write();
realizeClass(cls);
runtimeLock.unlockWrite();
runtimeLock.read();
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists.
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.去父类中查找
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);//找到之后先缓存到当前类对象的列表中,
goto done; //接着跳到 done:去执行返回IMP
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
//当方法执行到这里的时候说明,方法的实现查找不到,接下来通过_class_resolveMethod会执行第二个阶段了;
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
//如果第二部仍然没有添加方法,接下来通过_objc_msgForward_impcache会执行第三个阶段了;
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}
动态解析
根据类对象或元类对象执行 [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel] 或者[nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel], 我们可以在这个方法里动态添加方法,然后回到消息分发阶段从新执行,所以仍然会把IMP添加到缓存中;
/***********************************************************************
* _class_resolveMethod
* Call +resolveClassMethod or +resolveInstanceMethod.
* Returns nothing; any result would be potentially out-of-date already.
* Does not check if the method already exists.
**********************************************************************/
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
我们会在类对象中动态添加方法
struct method_t {
SEL sel;
char * types;
IMP imp;
};
@implementation MJGoodStudent
-(void)other{
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
void c_other(id self, SEL _cmd){
NSLog(@"");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(test)){
方法1:
struct method_t * otherMethod_t = (struct method_t * )class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
class_addMethod(self, sel, otherMethod_t->imp, otherMethod_t->types);
方法2:
/*
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
class_addMethod(self, sel, method_getImplementation(method), method_getTypeEncoding(method));
*/
方法3:
/*
class_addMethod(self, sel, c_other, "v16@0:8");
*/
return YES;
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
消息转发
如果第二部没有添加方法的实现,会通过第三部进行方法转发:
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
- forwardingTargetForSelector返回一个对象,会在泽恒对象中查找aSelector,然后去调用;
@interface OtherClass : NSObject
-(void)test;
@end
@implementation OtherClass
-(void)test{
}
@end
@implementation MJGoodStudent
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(test)) {
return [[OtherClass alloc] init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- 如果forwardingTargetForSelector没有实现或者返回的Target为nil的话,会执行methodSignatureForSelector获取方法签名, 然后通过forwardInvocation方法得到NSInvocation,可以在forwardInvocation方法中为所欲为:空实现或者重置NSInvocation的target的值;
@interface OtherClass : NSObject
-(void)test;
@end
@implementation OtherClass
-(void)test{
}
@end
@implementation MJGoodStudent
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(test)) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v16@0:8"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
//anInvocation参数顺序:reviver, selector, other arguments
//int age;
//[anInvocation getArgument:&age atIndex:2];
anInvocation.target = [[OtherClass alloc]init];
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[OtherClass alloc]init]];
int res;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&res];
}
面试参考
- OC消息机制
OC中的方法调用,其实都是转换为objc_msgSend函数的调用, objc_msgSend又分为三大阶段:消息分发,动态解析,消息转发;
分别阐述三大步骤
- 消息转发机制
如果没有通过方法动态解析,添加方法的话,说明当前对象没能力处理这个消息,所以会通过消息转发去寻找别的对象。
- 什么是runtime?