不支持目录,截图展示:
[toc]
redis 基础(单机版)
准备环境
centos 6.8
下载
下载redis:官方网站
使用的最新版本是3.2.8版本。
安装gcc
需要安装gcc的环境。
yum install gcc-c++
编译和安装
# 解压
tar xzf redis-3.2.8.tar.gz
cd redis-3.2.8
# 编译
make
# 安装,PREFIX参数指定redis的安装目录。一般软件安装到/usr目录下
make install PREFIX=/usr/local/redis
启动服务端
- 前台启动
cd /usr/local/redis/bin/
./redis-server
- 后台启动
把/root/redis-3.2.8/redis.conf复制到/usr/local/redis/bin目录下
cd redis-3.2.8
cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/
vim /usr/local/redis/bin/redis.conf
修改配置文件:
cd /usr/local/redis/bin/
#后台启动
./redis-server redis.conf
查看redis进程:
ps aux|grep redis
关闭 redis
找到进程,使用:
kill 进程号
启动客户端(Redis-cli)
启动指令
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli
-
默认连接localhost(127.0.0.1)运行在6379端口的redis服务。
指定连接ip 和 端口号
-h:连接的服务器的地址
-p:服务的端口号
#需要保证服务器已经启动
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -h 192.168.25.153 -p 6379
关闭redis:
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli shutdown
Mac 安装
Mac os x下安装Redis很简单通过Brew安装即可。
执行指令安装Redis
brew install redis
结果:
==> Downloading https://homebrew.bintray.com/bottles/redis-3.0.7.yosemite.bottle
######################################################################## 100.0%
==> Pouring redis-3.0.7.yosemite.bottle.1.tar.gz
==> Caveats
To have launchd start redis at login:
ln -sfv /usr/local/opt/redis/*.plist ~/Library/LaunchAgents
Then to load redis now:
launchctl load ~/Library/LaunchAgents/homebrew.mxcl.redis.plist
Or, if you don't want/need launchctl, you can just run:
redis-server /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
==> Summary
/usr/local/Cellar/redis/3.0.7: 9 files, 876.3K
表示安装成功了。那么怎么启动它呢?
启动,在终端直接运行命令
redis-server
Redis 默认端口是6379,你也可以换个端口号启动,
redis-server --port 6380
停止,执行命令
redis-cli shutdown
Redis 基本使用
使用命令行,进行增删改查的 redis 操作。
Redis五种数据类型
String:key-value(做缓存)
Redis中所有的数据都是字符串。命令不区分大小写,key是区分大小写的。Redis是单线程的。Redis中不适合保存内容大的数据。
get、set、
incr:加一(生成id)
Decr:减一
存值取值:
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
PONG
127.0.0.1:6379> set name inke
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
"inke"
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "name"
127.0.0.1:6379>
加一减一:
127.0.0.1:6379> incr countkey
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> incr countkey
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> decr countkey
(integer) 1
查询所有 key
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "countkey"
2) "name"
Hash:key-fields-values(做缓存)
相当于一个key对应一个Map,Map中还有key-value
使用hash对key进行归类。
类似于:[key,Map[key,map]]
-
Hset:向hash中添加内容
- 格式:hset key field value
- field 表示域,一个 key 可以有多个域
Hget:从hash中取内容
向hash中添加内容:
127.0.0.1:6379> hset names test jack
(integer) 1
从hash中取内容
127.0.0.1:6379> hget names test
"jack"
向hash中添加内容:
127.0.0.1:6379> hset names test1 rose
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hset names test2 inke
(integer) 1
获取 key 的所有域
127.0.0.1:6379> hkeys names
1) "test"
2) "test1"
3) "test2"
获取 key 的所有value
127.0.0.1:6379> hvals names
1) "inke"
2) "rose"
3) "inke"
获取所有 key-value
127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall names
1) "test"
2) "inke"
3) "test1"
4) "rose"
5) "test2"
6) "inke"
删除 key的某个域
127.0.0.1:6379> hdel names test1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hkeys names
1) "test"
2) "test2"
List:有顺序可重复
类似于:[key,List[...]]
相当于List 集合有个原点,从左 或 从右 添加元素,类似于正负轴。
从左添加元素到 List 集合中
192.168.25.153:6379> lpush list1 a b c d
(integer) 4
从List 开头0 到 结束-1 查询遍历
192.168.25.153:6379> lrange list1 0 -1
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
从右添加元素到 List 集合中
192.168.25.153:6379> rpush list1 1 2 3 4
(integer) 8
从List 开头0 到 结束-1 查询遍历
192.168.25.153:6379> lrange list1 0 -1
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
5) "1"
6) "2"
7) "3"
8) "4"
192.168.25.153:6379>
左边取出一个元素,取完就没有了
192.168.25.153:6379> lpop list1
"d"
192.168.25.153:6379> lrange list1 0 -1
1) "c"
2) "b"
3) "a"
4) "1"
5) "2"
6) "3"
7) "4"
右边取出一个元素,取完就没有了
192.168.25.153:6379> rpop list1
"4"
192.168.25.153:6379> lrange list1 0 -1
1) "c"
2) "b"
3) "a"
4) "1"
5) "2"
6) "3"
192.168.25.153:6379>
Set:元素无顺序,不能重复
类似于:[key,Set[...]]
添加元素
192.168.25.153:6379> sadd set1 a b c c c d
(integer) 4
查询元素
192.168.25.153:6379> smembers set1
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "d"
4) "a"
删除元素
192.168.25.153:6379> srem set1 a
(integer) 1
查询元素
192.168.25.153:6379> smembers set1
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "d"
192.168.25.153:6379>
还有集合运算命令,自学(交集、并集、排序等等...)。
Key命令
设置key的过期时间。
Expire key second:设置key的过期时间
Ttl key:查看key的有效期
Persist key:清除key的过期时间。Key持久化。
设置 Hello 这个 key 的过期时间为 100秒
192.168.25.153:6379> expire Hello 100
(integer) 1
查看 Hello 这个 key 的过期时间,正数是正在倒计时,负数到期或者不存在key等。
192.168.25.153:6379> ttl Hello
(integer) 77
Key持久化,清除key的过期时间
192.168.25.153:6379> Persist key
(integer) 1
192.168.25.153:6379> ttl Hello
(integer) -1
Redis的持久化方案
Redis的所有数据都是保存到内存中的。
Rdb:快照形式,定期把内存中当前时刻的数据保存到磁盘。Redis默认支持的持久化方案。
aof形式:append only file。把所有对redis数据库操作的命令,增删改操作的命令。保存到文件中。数据库恢复时把所有的命令执行一遍即可。
在redis.conf配置文件中配置。
vim /usr/local/redis/bin/redis.conf
搜索 rdb,可以看到以下配置
900秒保存一次(数据变化1次)、300秒保存一次(数据变化10次)、60秒保存一次(数据变化10000次)保存策略。
可能丢失数据,如果缓存丢失数据无所谓,例如查询数据,可以使用这个模式,效率高。
Rdb的配置:
Aof的配置:
vim /usr/local/redis/bin/redis.conf
搜索 rdb,可以看到以下配置
降低丢失数据,可以考虑使用这种方案,每分钟会同步一次缓存到文件中,但是操作磁盘,效率低。
两种持久化方案同时开启使用aof文件来恢复数据库。
redis 进阶(集群版)
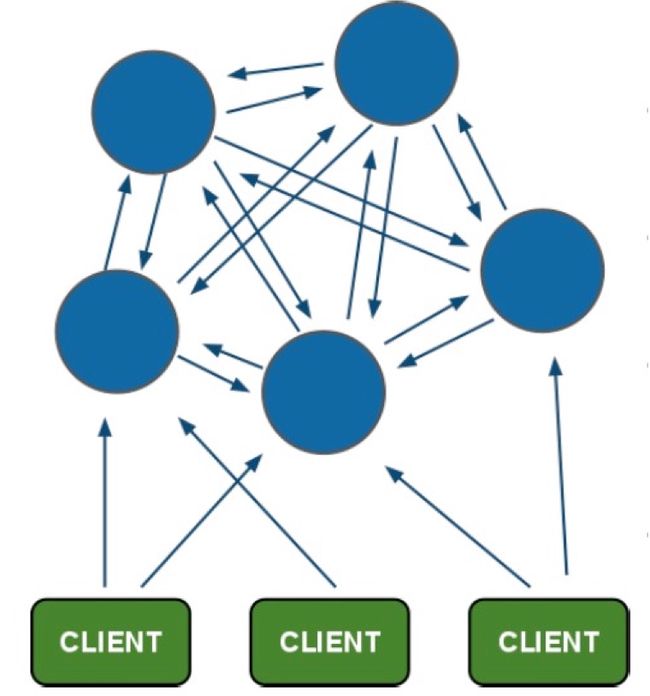
redis-cluster架构图
节点之间互相通信。
redis-cluster投票:容错
投票机制,判断一个节点是否挂了,需要半数以上确认挂了,它才是挂了,如果没有备份机,那么 redis 就不能用了。
架构细节:
- 所有的redis节点彼此互联(PING-PONG机制),内部使用二进制协议优化传输速度和带宽.
- 节点的fail是通过集群中超过半数的节点检测失效时才生效.
- 客户端与redis节点直连,不需要中间proxy层.客户端不需要连接集群所有节点,连接集群中任何一个可用节点即可
- redis-cluster把所有的物理节点映射到[0-16383]slot上,cluster 负责维护node<->slot<->value
Redis 集群中内置了 16384 个哈希槽,当需要在 Redis 集群中放置一个 key-value 时,redis 先对 key 使用 crc16 算法算出一个结果,然后把结果对 16384 求余数,这样每个 key 都会对应一个编号在 0-16383 之间的哈希槽,redis 会根据节点数量大致均等的将哈希槽映射到不同的节点
举例:分配16384 个哈希槽,每个服务器都会自己记录有多少个槽,如果存 key 的值是 hello,计算 hello 的值是500,那么会存放到0-5000的服务器上,这是槽作用均匀分配。
Redis集群的搭建
Redis集群中至少应该有三个节点。要保证集群的高可用,需要每个节点有一个备份机。
Redis集群至少需要6台服务器。
搭建伪分布式。可以使用一台虚拟机运行6个redis实例。需要修改redis的端口号7001-7006
集群搭建环境
使用ruby脚本搭建集群。需要ruby的运行环境。
安装ruby
yum install ruby
yum install rubygems
安装ruby脚本运行使用的包。
[root@localhost ~]# gem install redis-3.0.0.gem
Successfully installed redis-3.0.0
1 gem installed
Installing ri documentation for redis-3.0.0...
Installing RDoc documentation for redis-3.0.0...
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# cd redis-3.0.0/src
[root@localhost src]# ll *.rb
-rwxrwxr-x. 1 root root 48141 Apr 1 2015 redis-trib.rb
搭建步骤
自己没有搭建,有点麻烦,但是记录搭建流程是可行的,现实开发中也是运维搭建后,我们使用而已。
需要6台redis服务器。搭建伪分布式。
需要6个redis实例。
需要运行在不同的端口7001-7006
第一步:创建6个redis实例,每个实例运行在不同的端口。
需要修改redis.conf配置文件。配置文件中还需要把cluster-enabled yes前的注释去掉。
第二步:启动每个redis实例。
第三步:使用ruby脚本搭建集群。
./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.25.153:7001 192.168.25.153:7002 192.168.25.153:7003 192.168.25.153:7004 192.168.25.153:7005 192.168.25.153:7006
创建关闭集群的脚本:
前提是:关闭防火墙。
[root@localhost redis-cluster]# vim shutdow-all.sh
redis01/redis-cli -p 7001 shutdown
redis01/redis-cli -p 7002 shutdown
redis01/redis-cli -p 7003 shutdown
redis01/redis-cli -p 7004 shutdown
redis01/redis-cli -p 7005 shutdown
redis01/redis-cli -p 7006 shutdown
[root@localhost redis-cluster]# chmod u+x shutdow-all.sh
[root@localhost redis-cluster]# ./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.25.153:7001 192.168.25.153:7002 192.168.25.153:7003 192.168.25.153:7004 192.168.25.153:7005 192.168.25.153:7006
>>> Creating cluster
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7001: OK
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7002: OK
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7003: OK
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7004: OK
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7005: OK
Connecting to node 192.168.25.153:7006: OK
>>> Performing hash slots allocation on 6 nodes...
Using 3 masters:
192.168.25.153:7001
192.168.25.153:7002
192.168.25.153:7003
Adding replica 192.168.25.153:7004 to 192.168.25.153:7001
Adding replica 192.168.25.153:7005 to 192.168.25.153:7002
Adding replica 192.168.25.153:7006 to 192.168.25.153:7003
M: 2e48ae301e9c32b04a7d4d92e15e98e78de8c1f3 192.168.25.153:7001
slots:0-5460 (5461 slots) master
M: 8cd93a9a943b4ef851af6a03edd699a6061ace01 192.168.25.153:7002
slots:5461-10922 (5462 slots) master
M: 2935007902d83f20b1253d7f43dae32aab9744e6 192.168.25.153:7003
slots:10923-16383 (5461 slots) master
S: 74f9d9706f848471583929fc8bbde3c8e99e211b 192.168.25.153:7004
replicates 2e48ae301e9c32b04a7d4d92e15e98e78de8c1f3
S: 42cc9e25ebb19dda92591364c1df4b3a518b795b 192.168.25.153:7005
replicates 8cd93a9a943b4ef851af6a03edd699a6061ace01
S: 8b1b11d509d29659c2831e7a9f6469c060dfcd39 192.168.25.153:7006
replicates 2935007902d83f20b1253d7f43dae32aab9744e6
Can I set the above configuration? (type 'yes' to accept): yes
>>> Nodes configuration updated
>>> Assign a different config epoch to each node
>>> Sending CLUSTER MEET messages to join the cluster
Waiting for the cluster to join.....
>>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 192.168.25.153:7001)
M: 2e48ae301e9c32b04a7d4d92e15e98e78de8c1f3 192.168.25.153:7001
slots:0-5460 (5461 slots) master
M: 8cd93a9a943b4ef851af6a03edd699a6061ace01 192.168.25.153:7002
slots:5461-10922 (5462 slots) master
M: 2935007902d83f20b1253d7f43dae32aab9744e6 192.168.25.153:7003
slots:10923-16383 (5461 slots) master
M: 74f9d9706f848471583929fc8bbde3c8e99e211b 192.168.25.153:7004
slots: (0 slots) master
replicates 2e48ae301e9c32b04a7d4d92e15e98e78de8c1f3
M: 42cc9e25ebb19dda92591364c1df4b3a518b795b 192.168.25.153:7005
slots: (0 slots) master
replicates 8cd93a9a943b4ef851af6a03edd699a6061ace01
M: 8b1b11d509d29659c2831e7a9f6469c060dfcd39 192.168.25.153:7006
slots: (0 slots) master
replicates 2935007902d83f20b1253d7f43dae32aab9744e6
[OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration.
>>> Check for open slots...
>>> Check slots coverage...
[OK] All 16384 slots covered.
[root@localhost redis-cluster]#
集群的使用方法
Redis-cli 客户端连接集群。
[root@localhost redis-cluster]# redis01/redis-cli -p 7002 -c
-c:代表连接的是redis集群
也可以使用Redis Desktop Manager 可视化客户端进行管理。
Java客户端连接redis(Jedis)
需要把jedis依赖的jar包添加到工程中。
Maven工程中需要把jedis的坐标添加到依赖。
redis.clients
jedis
2.7.2
推荐添加到服务层。xxxx-Service工程中。
连接单机版
第一步:创建一个Jedis对象。需要指定服务端的ip及端口。
第二步:使用Jedis对象操作数据库,每个redis命令对应一个方法。
第三步:打印结果。
第四步:关闭Jedis
@Test
public void testJedis() throws Exception {
// 第一步:创建一个Jedis对象。需要指定服务端的ip及端口。
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.25.162", 6379);
// 第二步:使用Jedis对象操作数据库,每个redis命令对应一个方法。
jedis.set("test123", "my first jedis test");
String string = jedis.get("test123");
// 第三步:打印结果。
System.out.println(string);
// 第四步:关闭Jedis
jedis.close();
}
连接单机版使用连接池
第一步:创建一个JedisPool对象。需要指定服务端的ip及端口。
第二步:从JedisPool中获得Jedis对象。
第三步:使用Jedis操作redis服务器。
第四步:操作完毕后关闭jedis对象,连接池回收资源。
第五步:关闭JedisPool对象。
@Test
public void testJedisPool() throws Exception {
// 第一步:创建一个JedisPool对象。需要指定服务端的ip及端口。
JedisPool jedisPool = new JedisPool("192.168.25.153", 6379);
// 第二步:从JedisPool中获得Jedis对象。
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
// 第三步:使用Jedis操作redis服务器。
jedis.set("jedis", "test");
String result = jedis.get("jedis");
System.out.println(result);
// 第四步:操作完毕后关闭jedis对象,连接池回收资源。
jedis.close();
// 第五步:关闭JedisPool对象。
jedisPool.close();
}
连接集群版
第一步:使用JedisCluster对象。需要一个Set
第二步:直接使用JedisCluster对象操作redis。在系统中单例存在。
第三步:打印结果
第四步:系统关闭前,关闭JedisCluster对象。
@Test
public void testJedisCluster() throws Exception {
// 第一步:使用JedisCluster对象。需要一个Set参数。Redis节点的列表。
Set nodes = new HashSet<>();
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7001));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7002));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7003));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7004));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7005));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.25.153", 7006));
JedisCluster jedisCluster = new JedisCluster(nodes);
// 第二步:直接使用JedisCluster对象操作redis。在系统中单例存在。
jedisCluster.set("hello", "100");
String result = jedisCluster.get("hello");
// 第三步:打印结果
System.out.println(result);
// 第四步:系统关闭前,关闭JedisCluster对象。
jedisCluster.close();
}
业务逻辑中添加缓存
接口封装
常用的操作redis的方法提取出一个接口,分别对应单机版和集群版创建两个实现类。开发中,我们都是使用单机版,测试再到集群中测试。
接口定义
public interface JedisClient {
String set(String key, String value);
String get(String key);
Boolean exists(String key);
Long expire(String key, int seconds);
Long ttl(String key);
Long incr(String key);
Long hset(String key, String field, String value);
String hget(String key, String field);
Long hdel(String key, String... field);
}
单机版实现类
public class JedisClientPool implements JedisClient {
@Autowired
private JedisPool jedisPool;
@Override
public String set(String key, String value) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String result = jedis.set(key, value);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String result = jedis.get(key);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Boolean exists(String key) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Boolean result = jedis.exists(key);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Long expire(String key, int seconds) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Long result = jedis.expire(key, seconds);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Long ttl(String key) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Long result = jedis.ttl(key);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Long incr(String key) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Long result = jedis.incr(key);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Long hset(String key, String field, String value) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Long result = jedis.hset(key, field, value);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public String hget(String key, String field) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String result = jedis.hget(key, field);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
@Override
public Long hdel(String key, String... field) {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Long result = jedis.hdel(key, field);
jedis.close();
return result;
}
}
配置:applicationContext-redis.xml
集群版实现类
package cn.e3mall.jedis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster;
public class JedisClientCluster implements JedisClient {
@Autowired
private JedisCluster jedisCluster;
@Override
public String set(String key, String value) {
return jedisCluster.set(key, value);
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
return jedisCluster.get(key);
}
@Override
public Boolean exists(String key) {
return jedisCluster.exists(key);
}
@Override
public Long expire(String key, int seconds) {
return jedisCluster.expire(key, seconds);
}
@Override
public Long ttl(String key) {
return jedisCluster.ttl(key);
}
@Override
public Long incr(String key) {
return jedisCluster.incr(key);
}
@Override
public Long hset(String key, String field, String value) {
return jedisCluster.hset(key, field, value);
}
@Override
public String hget(String key, String field) {
return jedisCluster.hget(key, field);
}
@Override
public Long hdel(String key, String... field) {
return jedisCluster.hdel(key, field);
}
}
Spring的配置:
注意:
单机版和集群版不能共存,使用单机版时注释集群版的配置。使用集群版,把单机版注释。
封装代码测试
@Test
public void testJedisClient() throws Exception {
//初始化Spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/applicationContext-redis.xml");
//从容器中获得JedisClient对象
JedisClient jedisClient = applicationContext.getBean(JedisClient.class);
jedisClient.set("first", "100");
String result = jedisClient.get("first");
System.out.println(result);
}
业务举例:
-
功能分析
- 查询内容列表时添加缓存。
- 查询数据库之前先查询缓存。
- 查询到结果,直接响应结果。
- 查询不到,缓存中没有需要查询数据库。
- 把查询结果添加到缓存中。
- 返回结果。
-
向redis中添加缓存:
- Key:cid
- Value:内容列表。需要把java对象转换成json。
-
使用hash对key进行归类。
- HASH_KEY:HASH
- KEY:VALUE
- KEY:VALUE
- KEY:VALUE
- KEY:VALUE
- HASH_KEY:HASH
注意:添加缓存不能影响正常业务逻辑。
代码实现
CONTENT_KEY是定义在resource.properties定义的常量:
# redis 中缓存的 key
CONTENT_LIST=CONTENT_LIST
/**
* 内容管理Service
* Title: ContentServiceImpl
* Description:
* Company: www.itcast.cn
* @version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class ContentServiceImpl implements ContentService {
@Autowired
private TbContentMapper contentMapper;
@Autowired
private JedisClient jedisClient;
@Value("${CONTENT_LIST}")
private String CONTENT_LIST;
/**
*缓存同步
*对内容信息做增删改操作后只需要把对应缓存删除即可。
*可以根据cid删除。
*/
@Override
public E3Result addContent(TbContent content) {
//将内容数据插入到内容表
content.setCreated(new Date());
content.setUpdated(new Date());
//插入到数据库
contentMapper.insert(content);
//缓存同步,删除缓存中对应的数据。
jedisClient.hdel(CONTENT_LIST, content.getCategoryId().toString());
return E3Result.ok();
}
/**
* 根据内容分类id查询内容列表
* Title: getContentListByCid
* Description:
* @param cid
* @return
* @see cn.e3mall.content.service.ContentService#getContentListByCid(long)
*/
@Override
public List getContentListByCid(long cid) {
//查询缓存
try {
//如果缓存中有直接响应结果
String json = jedisClient.hget(CONTENT_LIST, cid + "");
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(json)) {
List list = JsonUtils.jsonToList(json, TbContent.class);
return list;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//如果没有查询数据库
TbContentExample example = new TbContentExample();
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
//设置查询条件
criteria.andCategoryIdEqualTo(cid);
//执行查询
List list = contentMapper.selectByExampleWithBLOBs(example);
//把结果添加到缓存
try {
jedisClient.hset(CONTENT_LIST, cid + "", JsonUtils.objectToJson(list));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
}
参考自某某培训机构和 csdn 文章