码上生花,ECharts 作品展示赛正式启动!>>> ![]()
微服务概述
前言
为什么要使用微服务?
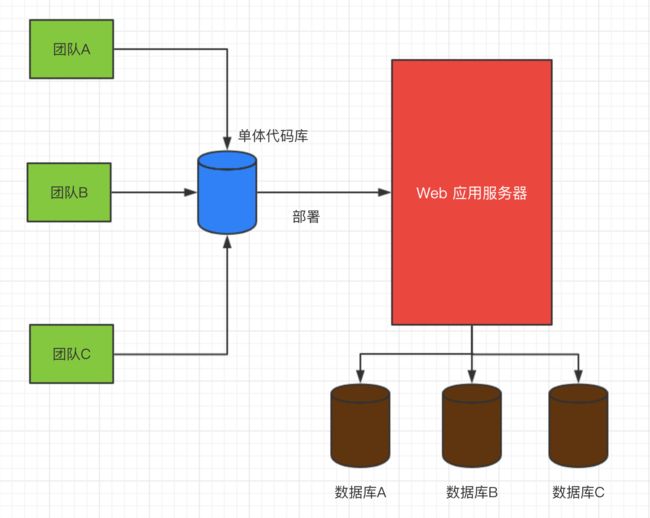
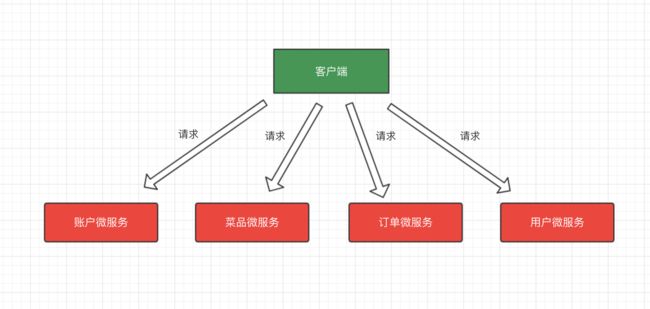
传统的 Java Web 都是采用单体架构的方式来进行开发、部署、运维的,所谓单体架构就是将 Application 的所有业务模块全部打包在一个文件中进行部署。但是随着互联网的发展、用户数量的激增、业务的极速扩展,传统的单体应用方式的缺点就逐渐显现出来了,给开发、部署、运维都带来了极大的难度,工作量会越来越大,难度越来越高。
因为在单体架构中,所有的业务模块的耦合性太高,耦合性过高的同时项目体量又很大势必会给各个技术环节带来挑战。项目越进行到后期,这种难度越大,只要有改动,整个应用都需要重新测试,部署,极大的限制了开发的灵活性,降低了开发效率。同时也带来了更大的安全隐患,如果某个模块发生故障无法正常运行就有可能导致整个项目崩溃,单体应用的架构如下图所示。
单体应用存在的问题
- 随着业务的发展,开发变得越来越复杂。
- 修改、新增某个功能,需要对整个系统进行测试,重新部署。
- 一个模块出现问题,很可能导致整个系统崩溃。
- 多团队同时对数据进行管理,容易产生安全漏洞。
- 各模块使用同一种技术框架,很难根据具体业务需求选择更合适的框架,局限性太大。
- 模块内容太复杂,如果员工离职,可能需要很长时间才能完成任务交接。
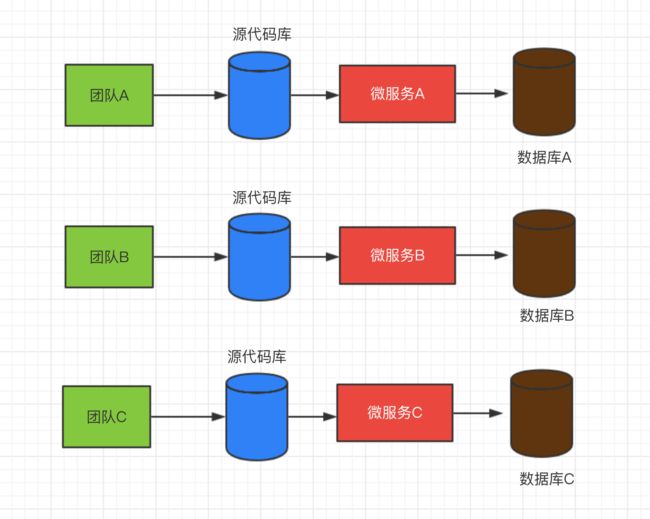
为了解决上述问题,微服务架构应运而生,简单来说,微服务就是将一个单体应用拆分成若干个小型的服务,协同完成系统功能的一种架构模式,在系统架构层面进行解耦合,将一个复杂问题拆分成若干个简单问题。这样的好处是对于每一个简单问题,开发、维护、部署的难度就降低了很多,可以实现自治,可自主选择最合适的技术框架,提高了项目开发的灵活性。
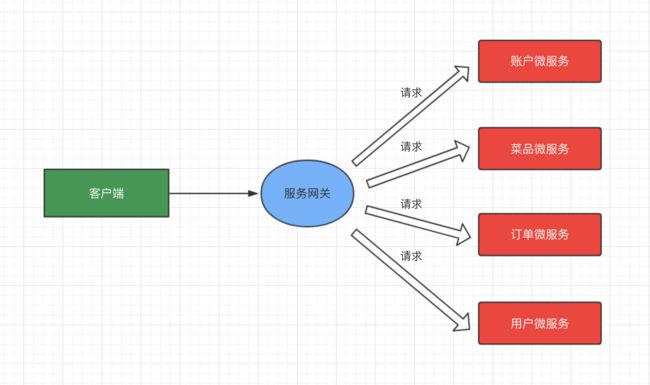
微服务架构不仅是单纯的拆分,拆分之后的各个微服务之间还要进行通信,否则就无法协同完成需求,也就失去了拆分的意义。不同的微服务之间可以通过某种协议进行通信,相互调用、协同完成功能,并且各服务之间只需要制定统一的协议即可,至于每个微服务是用什么技术框架来实现的,统统不需要关心。这种松耦合的方式使得开发、部署都变得更加灵活,同时系统更容易扩展,降低了开发、运维的难度,单体应用拆分之后的架构如下图所示。
微服务的优点
- 各个服务之间实现了松耦合,彼此之间不需要关注对方是用什么语言,什么技术开发的,只需要保证自己的接口可以正常访问,通过标准协议可以访问其他微服务的接口即可。
- 各个微服务之间是独立自治的,只需要专注于做好自己的业务,开发和维护不会影响到其他的微服务,这和单体架构中"牵一发而动全身"相比是有很大优势的。
- 微服务是一个去中心化的架构方式,相当于用零件去拼接一台机器,如果某个零件出现问题,可以随时进行替换从而保证机器的正常运转,微服务就相当于零件,整个项目就相当于零件组成的机器。
任何一种架构方式都有其优势,同时也一定会存在不足,我们需要做的是根据具体的业务场景,选择最合适的架构来进行开发。
微服务的不足
- 各个服务之间是通过远程调用的方式来完成协作任务的,如果因为某些原因导致远程调用出现问题,导致微服务不可用,就有可能产生级联反应,造成整个系统崩溃。
- 如果某个需求需要调用多个微服务,如何来保证数据的一致性是一个比较大的问题,这就给给分布式事务处理带来了挑战。
- 相比较于单体应用开发,微服务的学习难度会增加,对于加入团队的新员工来讲,如何快速掌握上手微服务架构,是他需要面对的问题。
即便是微服务存在这样那样的问题,也不能掩盖这种技术选型在当今互联网环境下的巨大优势,了解完微服务的基本概念、优缺点之后,我们来谈一谈微服务的设计原则。
我们说过微服务就是对应用进行拆分,在软件设计层面进行解耦合,说起来容易做起来难,如何来拆分服务也是一个有难度的挑战,如果拆分的服务粒度太小,导致微服务可完成的功能有限,这种情况反而会增加系统的复杂度。相反如果服务粒度太大,又没有实现足够程度的解耦合,那它本质上就还是单体应用的架构,同样是失去了拆分服务的意义。比较合理的拆分方式是由大到小,提炼出核心需求,搞清楚服务间的交互关系,先拆分成粒度相对较大的服务,然后再根据具体的业务需求逐步细化服务粒度,最终形成一套合理的微服务体系。
微服务设计原则
- 服务粒度不能过大也不能过小,提炼核心需求,根据服务间的交互关系找到最合理的服务粒度。
- 各个微服务的功能职责尽量单一,避免出现多个服务处理同一个需求。
- 各个微服务之间要相互独立、自治,自主开发、自主部署、自主维护。
- 保证数据独立性,各个微服务独立管理其业务模块下的数据,可开放出接口供其他微服务访问数据,但是其他微服务不能直接管理这些数据。
- 使用 REST 协议完成微服务之间的协作任务,数据交互采用 JSON 格式,方便调用与整合。
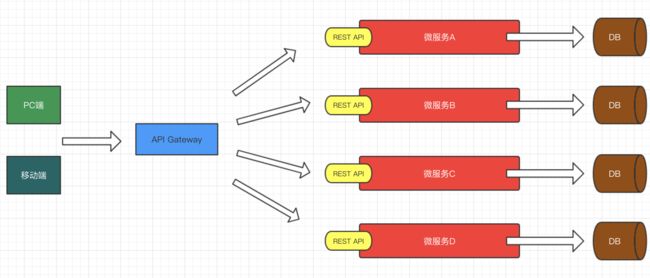
综上所述,微服务的架构设计不是一次成型的,需要反复进行实践和总结,不断进行优化,最终形成一套更为合理的解决方案,微服务架构图如下所示。
微服务架构的核心组件
- 服务治理(服务注册、服务发现)
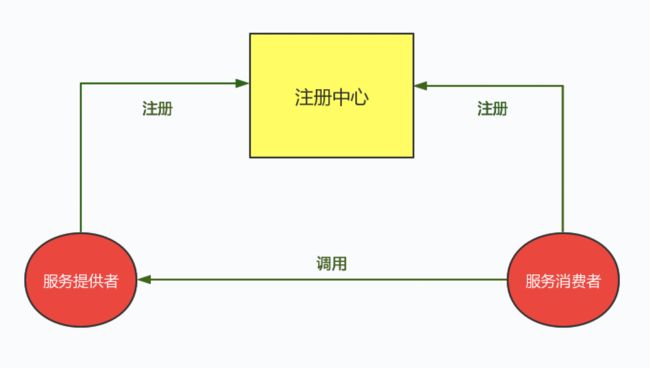
拆分之后的微服务首先需要完成的工作就是实现服务治理,包括服务注册和服务发现。这里我们把微服务分为两类:提供服务的叫做服务提供者,调用服务的叫做服务消费者。一个服务消费者首先需要知道有哪些可供调用的微服务,以及如何来调用这些微服务。所以就需要将所有的服务提供者在注册中心完成注册,记录服务信息,如 IP 地址、端口等,然后服务消费者可以通过服务发现获取服务提供者的这些信息,从而实现调用。
- 服务负载均衡
微服务间的负载均衡是必须要考虑的,服务消费者在调用服务提供者的接口时,可根据配置选择某种负载均衡算法,从服务提供者列表中选择具体要调用的实例,从而实现服务消费者与服务提供者之间的负载均衡。
- 微服务网关
在一个微服务架构中会包含多个微服务实例,每个微服务实例都有其特定的网络信息,如 IP 地址、端口等,很多时候完成一个需求需要多个微服务来协同工作,那么客户端就需要频繁请求不同的 URL ,不便于统一管理,可以使用微服务网关来解决这一问题,为客户端提供统一的入口,系统内部由网关将请求映射到不同的微服务。
- 微服务容错
前面我们提到过,各个服务之间是通过远程调用的方式来完成协作任务的,如果因为某些原因使得远程调用出现问题,导致微服务不可用,就有可能产生级联反应,造成整个系统崩溃。这个问题我们可以使用微服务的熔断器来处理,熔断器可以防止整个系统因某个微服务调用失败而产生级联反应导致系统崩溃的情况。
- 分布式配置
每个微服务都有其对应的配置文件,在一个大型项目中管理这些配置文件也是工作量很大的一件事情,为了提高效率、便于管理,我们可以对各个微服务的配置文件进行集中统一管理,将配置文件集中保存到本地系统或者 Git 仓库,再由各个微服务读取自己的配置文件。
- 服务监控
一个分布式系统中往往会部署很多个微服务,这些服务彼此之间会相互调用,整个过程就会较为复杂,我们在进行问题排查或者优化的时候工作量就会比较大。如果我们能准确跟踪到每一个网络请求,了解它整个运行流程,经过了哪些微服务、是否有延迟、耗费时间等,这样的话我们分析系统性能,排查解决问题就会容易很多,这就是服务监控。
Spring Cloud
微服务是一种分布式软件架构设计方式,具体的落地框架有很多,如阿里的 Dubbo、Google 的 gRPC、新浪的 Motan、Apache 的 Thrift 等,都是基于微服务实现分布式架构的技术框架,本课程我们选择的框架的是 Spring Cloud,Spring Cloud 基于 Spring Boot 使得整体的开发、配置、部署都非常方便,可快速搭建基于微服务的分布式应用,Spring Cloud 相当于微服务各组件的集大成者,下图来自 Spring 官网。
Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 的关系可大致理解为,Spring Boot 快速搭建基础系统,Spring Cloud 在此基础上实现分布式系统中的公共组件,如服务注册、服务发现、配置管理、熔断器、控制总线等,服务调用方式是基于 REST API,整合了各种成熟的产品和架构。
对于 Java 开发者而言,Spring 框架已成为事实上的行业标准,Spring 全家桶系列产品的优势在于功能齐全、简单好用、性能优越、文档规范,实际开发中就各方面综合因素来看,Spring Cloud 是微服务架构中非常优秀的实现方案,本课程就将为各位读者详细解读如何快速上手 Spring Cloud,Spring Cloud 的核心组件如下图所示,我们会按照图中分布来逐一讲解各个组件的使用,最后会结合一个实战案例将各个组件进行串联,让读者可以将 Spring Cloud 运用在实际开发中。
首先我们来学习服务治理。
服务治理的核心组成有三部分:服务提供者,服务消费者,注册中心。
在分布式系统架构中,每个微服务(服务提供者、服务消费者)在启动时,将自己的信息存储在注册中心,我们把这个过程称之为服务注册。服务消费者要调用服务提供者的接口,就得找到服务提供者,从注册中心查询服务提供者的网络信息,并通过此信息来调用服务提供者的接口,这个过程就是服务发现。
既然叫服务治理就不仅仅是服务注册与服务发现,同时还包括了服务的管理,即注册中心需要对记录在案的微服务进行统一管理,如何来具体实现管理呢?各个微服务与注册中心通过心跳机制完成通信,每间隔一定时间微服务就会向注册中心汇报一次,如果注册中心长时间无法与某个微服务通信,就会自动销毁该微服务。当某个微服务的网络信息发生变化时,会重新注册。同时,微服务可以通过客户端缓存将需要调用的服务地址保存起来,并通过定时任务更新的方式来保证服务的时效性,这样可以降低注册中心的压力,如果注册中心出现问题,也不会影响微服务之间的调用。
服务提供者、服务消费者、注册中心的关联
- 首先启动注册中心。
- 服务提供者启动时,在注册中心注册可以提供的服务。
- 服务消费者启动时,在注册中心订阅需要调用的服务。
- 注册中心将服务提供者的信息推送给服务调用者。
- 服务调用者通过相关信息(IP、端口等)调用服务提供者的服务。
注册中心核心模块:
服务注册表:用来存储各个微服务的信息,注册中心提供 API 来查询和管理各个微服务。
服务注册:微服务在启动时,将自己的信息在保存在注册中心。
服务发现:查询需要调用的微服务的网络信息,如 IP 地址、端口。
服务检查:通过心跳机制与完成注册的各个微服务完成通信,如果发现某个微服务长时间无法访问,则销毁该服务。
Spring Cloud 的服务治理可以使用 Consul 和 Eureka 组件,这里我们选择 Eureka。
什么是 Eureka?
Eureka 是 Netflix 开源的基于 REST 的服务治理解决方案,Spring Cloud 集成了 Eureka,即 Spring Cloud Eureka,提供服务注册和服务发现功能,可以和基于 Spring Boot 搭建的微服务应用轻松完成整合,开箱即用,实现 Spring Cloud 的服务治理功能。Spring Cloud 对 Netflix 开源组件进行了二次封装,也就是 Spring Cloud Netflix,Spring Cloud Eureka 是 Spring Cloud Netflix 微服务套件中的一部分,基于 Netflix Eureka 实现了二次封装,实际开发中,我们就使用 Spring Cloud Eureka 来完成服务治理。
Spring Cloud Eureka 的组成
Spring Cloud Eureka 主要包含了服务端和客户端组件:Eureka Server 服务端、Eureka Client 客户端。
Eureka Server,是提供服务注册与发现功能的服务端,也称作服务注册中心,Eureka 支持高可用的配置。
Eureka Client 是客户端组件,它的功能是将微服务在 Eureka Server 完成注册和后期维护功能,包括续租、注销等。需要注册的微服务就是通过 Eureka Client 连接到 Eureka Server 完成注册的,通过心跳机制实现注册中心与微服务的通信,完成对各个服务的状态监控。
简单理解注册中心(Eureka Server)就相当于一个电商平台,服务提供者(Eureka Client)相当于卖家在平台上注册了一个店铺,提供出售商品的服务,服务消费者(另一个Eureka Client)相当于用户在平台上注册账号,然后就可以在平台的各个店铺中购买商品了,同时平台(Eureka Server)还提供管理买家与卖家信息的功能,比如卖家是否在线、可以提供哪些具体服务等等。
接下来我们结合实例进行学习
Spring Cloud Eureka
- Eureka Server,注册中心
- Eureka Client,所有要进行注册的微服务通过 Eureka Client 连接到 Eureka Server,完成注册。
Eureka Server代码实现
- 创建父工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.7.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-dependencies
Finchley.SR2
pom
import
- 在父工程下创建 Module,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml,添加 Eureka Server 相关配置。
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
属性说明
server.port:当前 Eureka Server 服务端口。
eureka.client.register-with-eureka:是否将当前的 Eureka Server 服务作为客户端进行注册。
eureka.client.fetch-fegistry:是否获取其他 Eureka Server 服务的数据。
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone:注册中心的访问地址。
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class,args);
}
}
注解说明:
@SpringBootApplication:声明该类是 Spring Boot 服务的入口。
@EnableEurekaServer:声明该类是一个 Eureka Server 微服务,提供服务注册和服务发现功能,即注册中心。
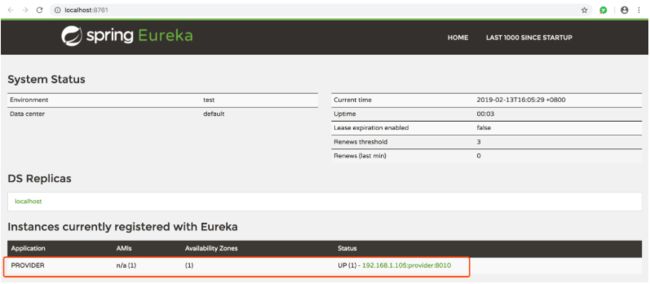
打开浏览器,访问http://localhost:8761,可看到如下界面,注册中心启动成功
Eureka Client 代码实现
上面说到 Eureka Server 是注册中心,分布式系统架构中的所有微服务都需要在注册中心完成注册才能被发现进而使用,我们所说的服务提供者和服务消费者是从业务角度来划分的,实际上服务提供者和服务消费者都是通过 Eureka Client 连接到 Eureka Server 完成注册,现在实现一个服务提供者,并且在 Eureka Server 完成注册,大致思路是先通过 Spring Boot 搭建一个微服务应用,再通过 Eureka Client 将其注册到 Eureka Server,创建 Eureka Client 的过程与创建 Eureka Server 十分相似。
- 创建 Module ,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml,添加 Eureka Client 相关配置
server:
port: 8010
spring:
application:
name: provider
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
属性说明:
spring.application.name:当前服务注册在 Eureka Server 上的名称。
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone:注册中心的访问地址。
eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address:是否将当前服务的 IP 注册到 Eureka Server。
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class,args);
}
}
- 实体类
package com.janeroad.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
- Repository
package com.janeroad.repository;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import java.util.Collection;
public interface StudentRepository {
public Collection findAll();
public Student findById(long id);
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student);
public void deleteById(long id);
}
- RepositoryImpl
package com.janeroad.repository.impl;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class StudentRepositoryImpl implements StudentRepository {
private static Map studentMap;
static {
studentMap = new HashMap<>();
studentMap.put(1L,new Student(1L,"张三",22));
studentMap.put(2L,new Student(2L,"李四",23));
studentMap.put(3L,new Student(3L,"王五",24));
}
@Override
public Collection findAll() {
return studentMap.values();
}
@Override
public Student findById(long id) {
return studentMap.get(id);
}
@Override
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student) {
studentMap.put(student.getId(),student);
}
@Override
public void deleteById(long id) {
studentMap.remove(id);
}
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentHandler {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
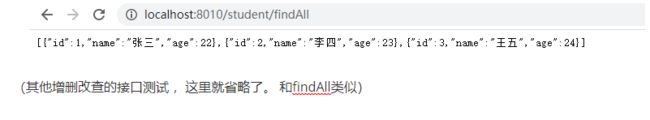
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return studentRepository.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
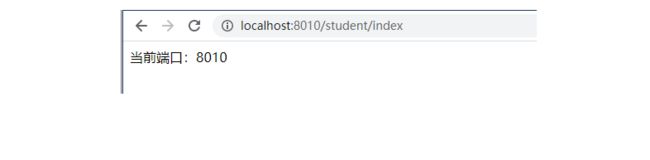
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "当前端口:"+this.port;
}
}
打开浏览器,访问http://localhost:8761,看到如下界面。
运行eurekaclient启动类效果
(其他增删改查的接口测试 ,这里就省略了。 和findAll类似)
RestTemplate 的使用
-
什么是REST
REST是当前比较流行的一种互联网软件架构模型,通过统一的规范完成不同终端的数据访问和交互,REST是一个词组的缩写,全称为代表性状态转移,翻译成中文的意思是资源表现层状态转化。
特色
\1. URL传参更加简洁,如下所示:
- 非RESTful的URL:http://…../queryUserById?id = 1
- RESTful的URL:http://…./queryUserById/1
2.完成不同终端之间的资源共享,RESTful提供了一套规范,不同终端之间只需要遵守该规范,就可以实现数据交互。
Restful具体就是就是一种表现形式,HTTP协议的中部请求类型(GET,POST,PUT,DELETE)分别表示常规操作,即CRUD:
-
获取获取资源
-
POST创造创造资源
-
放置修改属性
-
DELETE用作删除资源
-
什么是RestTemplate
RestTemplate是Spring框架提供的基于REST的服务组件,通过对HTTP请求和响应进行了封装,提供了很多访问远程REST服务的方法,可简化代码开发。
-
如何使用 RestTemplate?
1、创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml。
2、创建实体类
package com.janeroad.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
3、Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class RestHandler {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
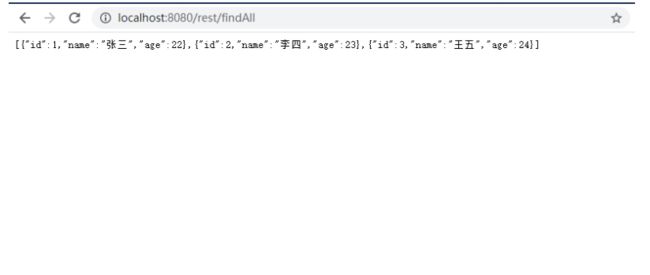
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/findAll",Collection.class).getBody();
}
@GetMapping("/findAll2")
public Collection findAll2(){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/findAll",Collection.class);
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/findById/{id}",Student.class,id).getBody();
}
@GetMapping("/findById2/{id}")
public Student findById2(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/findById/{id}",Student.class,id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.postForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/save",student,null).getBody();
}
@PostMapping("/save2")
public void save2(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/save",student,null);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.put("http://localhost:8010/student/update",student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
restTemplate.delete("http://localhost:8010/student/deleteById/{id}",id);
}
}
4、启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RestTemplateApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RestTemplateApplication.class,args);
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
resttemplate不是一个微服务,就是一个单纯的springboot应用,但是可以调用eurekaclient服务提供者的方法
resttemplate启动效果
服务消费者 consumer
实现一个用户的消费者,调用提供者的相关接口,实现思路是先通过Spring Boot构建一个微服务应用,再通过Eureka Client将其注册到Eureka Server。此时的提供者和消费者从代码的角度看并没有区别,都是Eureka客户端,我们人为地从业务角度对它们进行区分,提供者提供服务,消费者调用服务,具体的实现需要结合RestTemplate来完成,即在服务消费者Consumer中通过RestTemplate来调用服务提供者provider的相关接口。
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8020
spring:
application:
name: consumer
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class,args);
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/consumer")
public class ConsumerHandler {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/findAll",Collection.class).getBody();
}
@GetMapping("/findAll2")
public Collection findAll2(){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/findAll",Collection.class);
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/findById/{id}",Student.class,id).getBody();
}
@GetMapping("/findById2/{id}")
public Student findById2(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/findById/{id}",Student.class,id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.postForEntity("http://localhost:8010/student/save",student,null).getBody();
}
@PostMapping("/save2")
public void save2(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:8010/student/save",student,null);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
restTemplate.put("http://localhost:8010/student/update",student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
restTemplate.delete("http://localhost:8010/student/deleteById/{id}",id);
}
}
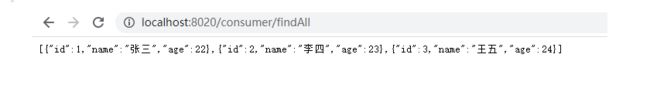
consumer实际上是一个服务消费者,间接地去访问数据
consumer启动效果
其他增删改查的功能展示这里就省略了,可以用postman去测试
服务网关
在分布式项目架构中,我们会将服务进行拆分,不同的微服务负责各自的业务功能,实现软件架构层面的解耦合。但是如果拆分之后的微服务数量太多,是不利于系统开发的,因为每个服务都有不同的网络地址,客户端多次请求不同的微服务需要调用不同的 URL,如果同时去维护多个不同的 URL 无疑会增加开发的成本。
如下图所示,一个外卖订餐系统,需要调用多个微服务接口才能完成一次订餐的业务流程,如果能有一种解决方案可以统一管理不同的微服务 URL,肯定会增强系统的维护性,提高开发效率。
这个解决方案就是 API 网关,API 网关可以对所有的 API 请求进行管理维护,相当于为系统开放出一个统一的接口,所有的外部请求只需要访问这个统一入口即可,系统内部再通过 API 网关去映射不同的微服务。对于开发者而言就不需要关注具体的微服务 URL 了,直接访问 API 网关接口即可,API 网关的结构如下图所示。
如此一来我们就解决了上述问题,开发变得更加简单方便。
- 什么是 Zuul?
Zuul 是 Netflix 提供的一个开源的 API 网关服务器,是客户端和网站后端所有请求的中间层,对外开放一个 API,将所有请求导入统一的入口,屏蔽了服务端的具体实现逻辑,Zuul 可以实现反向代理的功能,在网关内部实现动态路由、身份认证、IP 过滤、数据监控等。我们可以使用 Zuul 来实现微服务网关,Spring Cloud 集成了 Zuul。
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-zuul
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8030
spring:
application:
name: gateway
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
zuul:
routes:
provider: /p/**
属性说明:
zuul.routes.provider:给服务提供者 provider 设置映射
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
@EnableZuulProxy
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class ZuulApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZuulApplication.class,args);
}
}
注解说明:
@EnableZuulProxy:包含了 @EnableZuulServer,设置该类是网关的启动类。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:可以帮助 Spring Boot 应用将所有符合条件的 @Configuration 配置加载到当前 Spring Boot 创建并使用的 IoC 容器中。
- Zuul 自带了负载均衡功能,修改 provider 的代码。
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentHandler {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return studentRepository.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "当前端口:"+this.port;
}
}
服务网关zuul启动效果
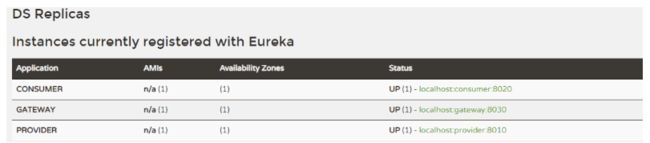
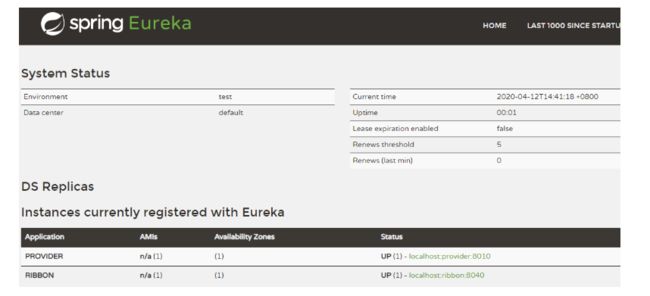
可以看到注册中心多了GATEWAY
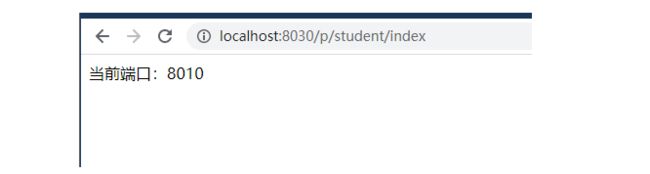
访问8030/p/student/findAll 相当于访问服务提供者 8010/student/findAll,因为配置文件做了相关的映射
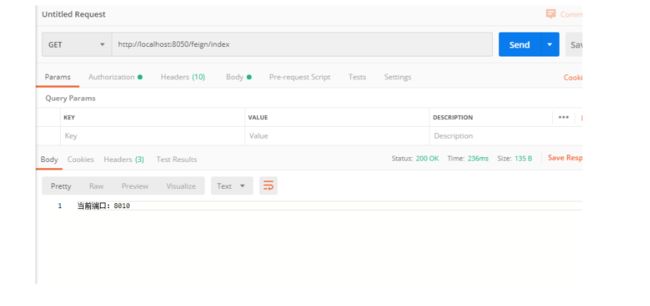
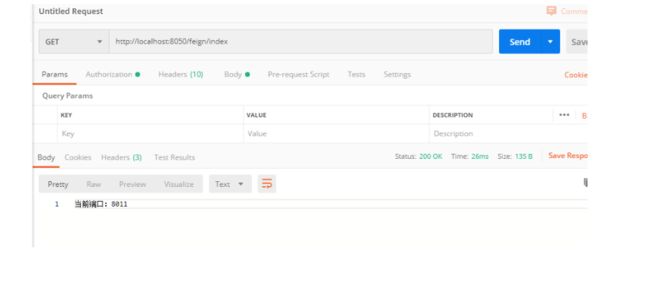
同时 Zuul 自带了负载均衡功能,在EurekaClient中的Handler里面增加一个返回当前服务端口的方法,重启EurekaServer和EurekaClient 然后修改 provider 的端口为 8011,创建一个新的 provider 启动类并启动,最后重新启动 gateway,访问 http://localhost:8761 可以看到有两个provider
访问两次 http://localhost:8030/p/student/index,分别请求了端口为 8010 和 8011 的 provider 微服务,实现了负载均衡。
Ribbon 负载均衡
我们已经通过 RestTemplate 实现了服务消费者对服务提供者的调用,这只是实现了最基本的需求,如果在某个具体的业务场景下,对于某服务的调用需求激增,这时候我们就需要为该服务实现负载均衡以满足高并发访问,在一个大型的分布式应用系统中,负载均衡(Load Balancing)是必备的。
什么是 Ribbon?
Spring Cloud 提供了实现负载均衡的解决方案:Spring Cloud Ribbon,Ribbon 是 Netflix 发布的负载均衡器,而 Spring Cloud Ribbon 则是基于 Netflix Ribbon 实现的,是一个用于对 HTTP 请求进行控制的负载均衡客户端。
Spring Cloud Ribbon 官网地址:
http://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-netflix/multi/multi_spring-cloud-ribbon.html
Ribbon 的使用同样需要结合 Eureka Server,即需要将 Ribbon 在 Eureka Server 进行注册,注册完成之后,就可以通过 Ribbon 结合某种负载均衡算法,如轮询、随机、加权轮询、加权随机等帮助服务消费者去调用接口。除了 Ribbon 默认提供的这些负载均衡算法外,开发者也可以根据具体需求来设计自定义的 Ribbon 负载均衡算法。实际开发中,Spring Cloud Ribbon 需要结合 Spring Cloud Eureka 来使用,Eureka Server 提供所有可调用的服务提供者列表,Ribbon 基于特定的负载均衡算法从这些服务提供者中挑选出要调用的实例,如下图所示。
Ribbon 常用的负载均衡策略有以下几种:
- 随机:访问服务时,随机从注册中心的服务列表中选择一个。
- 轮询:当同时启动两个服务提供者时,客户端请求会由这两个服务提供者交替处理。
- 加权轮询:对服务列表中的所有微服务响应时间做加权处理,并以轮询的方式来访问这些服务。
- 最大可用:从服务列表中选择并发访问量最小的那个微服务。
了解完原理,接下来我们一起实现 Ribbon
- 创建 Module,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8040
spring:
application:
name: ribbon
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RibbonApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RibbonApplication.class,args);
}
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@LoadBalanced:声明一个基于 Ribbon 的负载均衡。
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/ribbon")
public class RibbonHandler {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://provider/student/findAll",Collection.class);
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://provider/student/index",String.class);
}
}
打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:8761,看到如下界面。
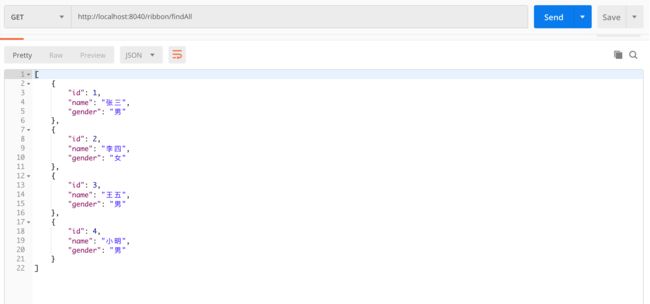
可以看到 Provider 和 Ribbon 已经在注册中心完成注册,接下来用 Postman 工具测试 Ribbon 相关接口,如下图所示。
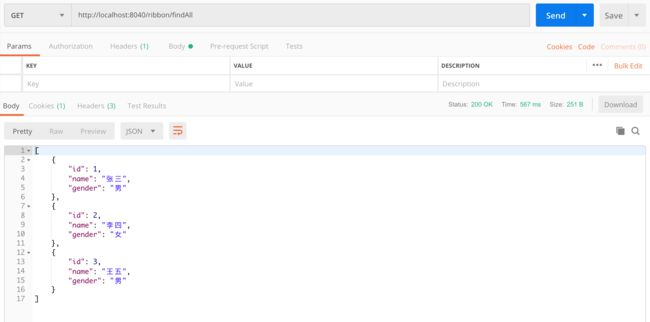
- findAll 接口
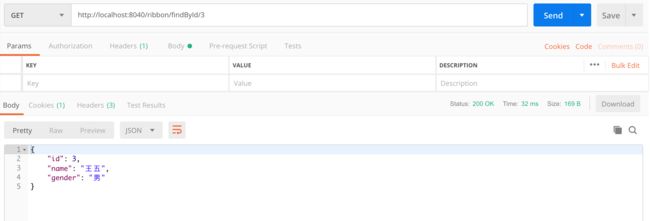
- findById 接口
- save 接口
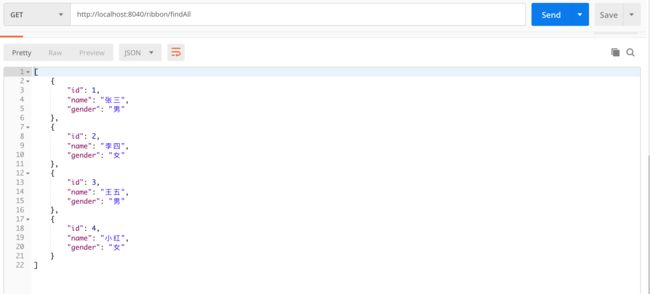
添加完成之后再来查询,调用 findAll 接口,可以看到新数据已经添加成功。
- update 接口
修改完成之后再来查询,调用 findAll 接口,可以看到修改之后的数据。
- deleteById 接口
删除完成之后再来查询,调用 findAll 接口,可以看到数据已经被删除。
接下来测试 Ribbon 的负载均衡,在 RibbonHandler 中添加如下代码
@RequestMapping("/ribbon")
@RestController
public class RibbonHandler {
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://provider/student/index",String.class);
}
}
分别启动注册中心,端口为 8010 的 Provider,端口为 8011 的 Provider、Ribbon。
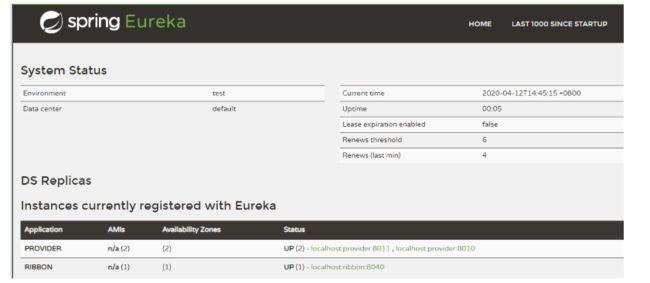
打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:8761,可看到如下界面
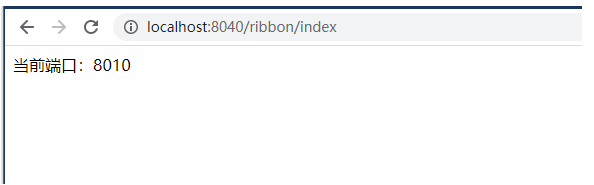
可以看到两个 Provider 和 Ribbon 已经在注册中心完成注册,访问 http://localhost:8040/ribbon/index,交替出现下图所示情况,实现了负载均衡。
Feign
我们使用过功能区+ RestTemplate实现服务调用的负载均衡,在实际开发中,还有另外一种更加便捷的方式来实现相同的功能,这就是Feign,现在就来使用Feign实现服务消费的负载均衡。
什么是Feign
与Ribbon一样,Feign也是由Netflix提供的,Feign是一个提供模版的声明式Web服务客户端,使用Feign可以简化Web Service客户端的编写,开发者可以通过简单的接口和注解来调用HTTP API,进行开发Spring Cloud也提供了Feign的集成组件:Spring Cloud Feign,它整合了Ribbon和Hystrix,具有可插拔,基于注解,负载均衡,服务熔断等多种便捷功能。
在Spring Cloud中使用Feign非常简单,我们说过Feign是一个声明式的Web服务客户端,所以只需要创建一个接口,同时在接口上添加相关注解即可完成服务提供方的接口绑定,相比较于Ribbon + RestTemplate的方式,Feign大大简化了代码的开发,Feign支持多种注释解,包括Feign注解,JAX-RS注解,Spring MVC注解等。Spring Cloud对Feign进行了优化,整合了Ribbon和Eureka,从而让Feign的使用更加方便。
我们说过Feign是一种比Ribbon更加方便好用的Web服务客户端,那么两者有什么具体区别呢?Feign好用在哪里?
Ribbon与Feign的区别
关于Ribbon和Feign的区别可以简单地理解为Ribbon是个通用的HTTP客户端工具,而Feign则是基于Ribbon来实现的,同时它更加灵活,使用起来也更加简单,上节课中我们通过Ribbon + RestTemplate实现了服务调用的负载均衡,相比较于这种方式,使用Feign可以直接通过声明式接口的形式来调用服务,非常方便,比Ribbon使用起来要更加完善,只需要创建接口并添加相关注解配置,即可实现服务消费的负载均衡。
Feign的特点
- Feign是一个声明式Web Service客户端。
- 支持Feign注解,JAX-RS注解,Spring MVC注解。
- Feign基于Ribbon实现,使用起来更加简单。
- Feign集成了Hystrix,具有服务熔断功能。
接下来实现Feign
- 创建 Module,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8050
spring:
application:
name: feign
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class FeignApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FeignApplication.class,args);
}
}
- 创建声明式接口
package com.janeroad.feign;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import java.util.Collection;
@FeignClient(value = "provider")
public interface FeignProviderClient {
@GetMapping("/student/findAll")
public Collection findAll();
@GetMapping("/student/index")
public String index();
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.feign.FeignProviderClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feign")
public class FeignHandler {
@Autowired
private FeignProviderClient feignProviderClient;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return feignProviderClient.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return feignProviderClient.index();
}
}
- 服务熔断,application.yml 添加熔断机制。
server:
port: 8050
spring:
application:
name: feign
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
feign.hystrix.enabled:是否开启熔断器。
- 创建 FeignProviderClient 接口的实现类 FeignError,定义容错处理逻辑,通过
@Component注解将 FeignError 实例注入 IoC 容器中。
package com.janeroad.feign.impl;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.feign.FeignProviderClient;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collection;
@Component
public class FeignError implements FeignProviderClient {
@Override
public Collection findAll() {
return null;
}
@Override
public String index() {
return "服务器维护中......";
}
}
- 在 FeignProviderClient 定义处通过
@FeignClient的 fallback 属性设置映射。
package com.janeroad.feign;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.feign.impl.FeignError;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import java.util.Collection;
@FeignClient(value = "provider",fallback = FeignError.class)
public interface FeignProviderClient {
@GetMapping("/student/findAll")
public Collection findAll();
@GetMapping("/student/index")
public String index();
}
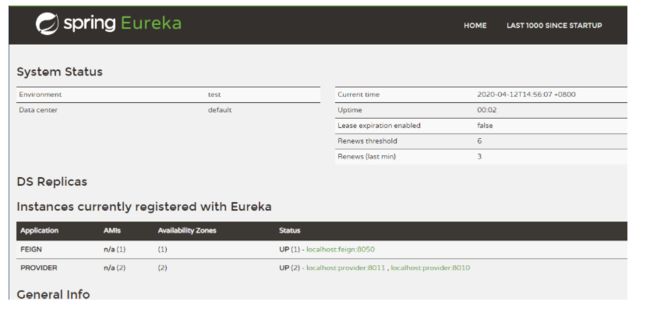
依次启动注册中心,端口为8010的Provider,端口为8011的Provider,Feign
浏览器,访问http:// localhost:8761,看到如下界面
可以看到两个Provider和Feign已经在注册中心完成注册,然后使用Postman工具测试Feign相关接口,如下图所示。
- findAll接口
![]()
- 负载均衡
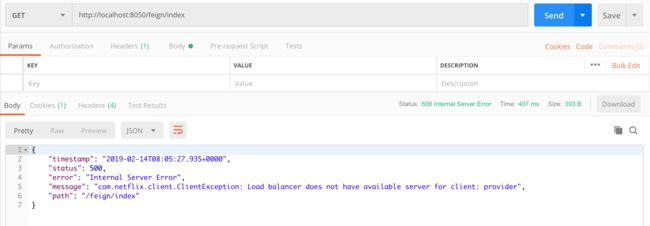
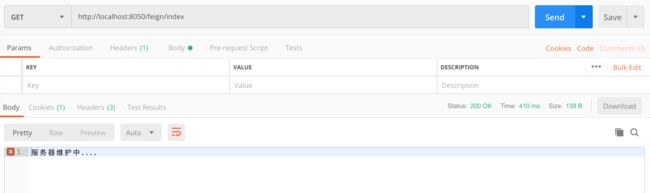
Feign同时提供了容错功能,如果服务提供者Provider出现故障无法访问,直接访问Feign会报错,如下图所示。
很简单这种直接返回错误状态码的交互方式不友好,可以通过容错机制给用户相应的提示信息,而不是错误状态码,从而交互方式更加友好,容错机制非常简单,首先在application.yml中。中添加配置。
server:
port: 8050
spring:
application:
name: feign
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
feign.hystrix.enabled:是否开启熔断器。
创建FeignProviderClient接口的实现类FeignError,定义容错处理逻辑,通过@Component将FeignError实例注入IoC容器。
@Component
public class FeignError implements FeignProviderClient {
@Override
public String index() {
return "服务器维护中....";
}
@Override
public Collection findAll() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Student findById(long id) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void save(Student student) {
}
@Override
public void update(Student student) {
}
@Override
public void deleteById(long id) {
}
}
在FeignProviderClient定义处通过@FeignClient的fallback属性设置映射。
@FeignClient(value = "provider",fallback = FeignError.class)
public interface FeignProviderClient {
}
启动注册中心和Feign,此时没有服务提供者Provider被注册,直接访问Feign接口,如下图所示。
Hystrix 容错机制
上面涉及到 Feign 提供了容错功能,该功能是结合 Hystrix 实现的,现在就来学习 Hystrix 的相关知识。
什么是微服务容错机制?
在一个分布式系统中,各个微服务之间相互调用、彼此依赖,实际运行环境中可能会因为各种个样的原因导致某个微服务不可用,则依赖于该服务的其他微服务就会出现响应时间过长或者请求失败的情况,如果这种情况出现的次数较多,从一定程度上就可以能导致整个系统崩溃,如何来解决这一问题呢?
在不改变各个微服务调用关系的前提下,可以针对这些错误情况提前设置处理方案,遇到问题时,整个系统可以自主进行调整,这就是微服务容错机制的原理,发现故障并及时处理。
什么是 Hystrix?
Hystrix 是 Netflix 的一个开源项目,是一个熔断器模型的具体实现,熔断器就类似于电路中的保险丝,某个单元发生故障就通过烧断保险丝的方式来阻止故障蔓延,微服务架构的容错机制也是这个原理。Hystrix 的主要作用是当服务提供者发生故障无法访问时,向服务消费者返回 fallback 降级处理,从而响应时间过长或者直接抛出异常的情况。
Hystrix 设计原则:
- 服务隔离机制,防止某个服务提供者出问题而影响到整个系统的运行。
- 服务降级机制,服务出现故障时向服务消费者返回 fallback 处理机制。
- 熔断机制,当服务消费者请求的失败率达到某个特定数值时,会迅速启动熔断机制并进行修复。
- 提供实时的监控和报警功能,迅速发现服务中存在的故障。
- 提供实时的配置修改功能,保证故障问题可以及时得到处理和修复。
上面演示过了 Hystrix 的熔断机制,现在重点介绍 Hystrix 的另外一个重要功能——数据监控。
Hystrix 除了可以为服务提供容错机制外,同时还提供了对请求的监控,这个功能需要结合 Spring Boot Actuator 来使用,Actuator 提供了对服务的健康监控、数据统计功能,可以通过 hystrix-stream 节点获取监控到的请求数据,Dashboard 组件则提供了数据的可视化监控功能,接下来通过代码来实现 Hystrix 的数据监控。
- 创建 Maven,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
2.0.7.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8060
spring:
application:
name: hystrix
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: 'hystrix.stream'
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.dashboard.EnableHystrixDashboard;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableCircuitBreaker
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class HystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HystrixApplication.class,args);
}
}
注解说明:
@EnableCircuitBreaker:声明启用数据监控
@EnableHystrixDashboard:声明启用可视化数据监控
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import com.janeroad.entity.Student;
import com.janeroad.feign.FeignProviderClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hystrix")
public class HystrixHandler {
@Autowired
private FeignProviderClient feignProviderClient;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection findAll(){
return feignProviderClient.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return feignProviderClient.index();
}
}
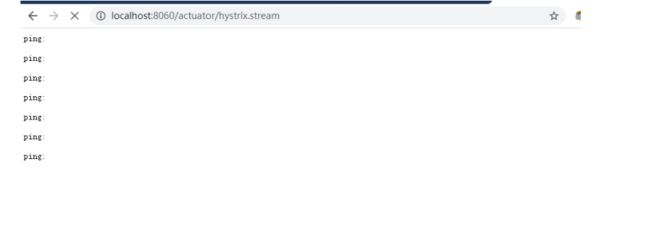
- 启动成功之后,访问
http://localhost:8060/actuator/hystrix.stream可以监控到请求数据, - 访问
http://localhost:8060/hystrix,可以看到可视化的监控界面,输入要监控的地址节点即可看到该节点的可视化数据监控。
依次启动注册中心、Provider、Hystrix,可以直接访问红框中的 URL 来监控数据,在浏览器地址栏输入 http://localhost:8060/actuator/hystrix.stream,可看到如下界面
此时没有客户端请求,所以没有数据,访问 http://localhost:8060/hystrix/index,可看到如下界面
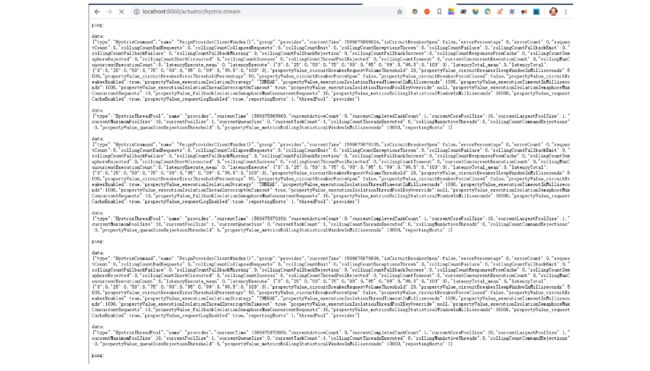
再次访问 http://localhost:8060/actuator/hystrix.stream,可看到如下界面。
显示了监控数据情况,但是这种方式并不直观,通过可视化界面的方式能够更加直观地进行监控数据,添加 Dashboard 即可,pom.xml 添加相关依赖。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard
HystrixApplication 类定义处添加 @EnableHystrixDashboard 注解。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableCircuitBreaker
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class HystrixApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HystrixApplication.class,args);
}
}
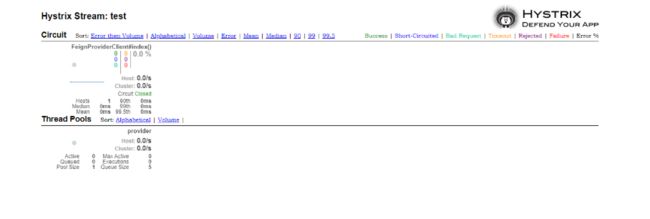
访问 http://localhost:8060/hystrix,可看到如下界面。
在红框处输入 http://localhost:8060/actuator/hystrix.stream 以及 Tiltle,点击 Monitor Stream 按钮,如下图所示
来了到可视化监控数据界面。
Spring Cloud 配置中心
在基于微服务的分布式系统中,每个业务模块都可以拆分为一个独立自治的服务,多个请求来协同完成某个需求,在一个具体的业务场景中某个请求可能需要同时调用多个服务来完成,这就存在一个问题,多个微服务所对应的配置项也会非常多,一旦某个微服务进行了修改,则其他服务也需要作出调整,直接在每个微服务中修改对应的配置项是非常麻烦的,改完之后还需要重新部署项目。
微服务是分布式的,但是我们希望可以对所有微服务的配置文件进行集中统一管理,便于部署和维护,Spring Cloud 提供了对应的解决方案,即 Spring Cloud Config,通过服务端可以为多个客户端提供配置服务。
Spring Cloud Config 可以将配置文件存放在本地,也可以存放在远程 Git 仓库中。拿远程 Git 仓库来说,具体的操作思路是将所有的外部配置文件集中放置在 Git 仓库中,然后创建 Config Server,通过它来管理所有的配置文件,需要更改某个微服务的配置信息时,只需要在本地进行修改,然后推送到远程 Git 仓库即可,所有的微服务实例都可以通过 Config Server 来读取对应的配置信息。
接下来我们就一起来搭建本地 Config Server。我们可以将微服务的相关配置文件存储在本地文件中,然后让微服务来读取本地配置文件,具体操作如下所示。
本地文件系统
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建 application.yml
server:
port: 8762
spring:
application:
name: nativeconfigserver
profiles:
active: native
cloud:
config:
server:
native:
search-locations: classpath:/shared
注解说明
profiles.active:配置文件的获取方式
cloud.config.server.native.search-locations:本地配置文件存放的路径
- resources 路径下创建 shared 文件夹,并在此路径下创建 configclient-dev.yml。
server:
port: 8070
foo: foo version 1
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class NativeConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(NativeConfigServerApplication.class,args);
}
}
注解说明
@EnableConfigServer:声明配置中心。
创建客户端读取本地配置中心的配置文件
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建 bootstrap.yml,配置读取本地配置中心的相关信息。
spring:
application:
name: configclient
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:8762
fail-fast: true
注解说明
cloud.config.uri:本地 Config Server 的访问路径
cloud.config.fail-fase:设置客户端优先判断 Config Server 获取是否正常。
通过spring.application.name 结合spring.profiles.active拼接目标配置文件名,configclient-dev.yml,去 Config Server 中查找该文件。
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class NativeConfigClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(NativeConfigClientApplication.class,args);
}
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/native")
public class NativeConfigHandler {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Value("${foo}")
private String foo;
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return this.port+"-"+this.foo;
}
}
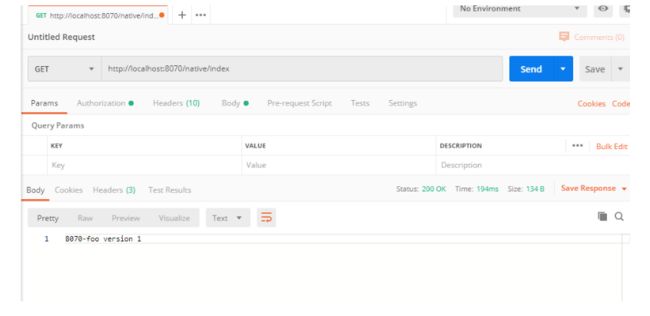
依次启动 NativeConfigServer、ConfigClient,通过 Postman 工具访问 http://localhost:8070/native/index,如下图所示
读取本地配置成功。
Spring Cloud Config 远程配置
前面的操作我们使用了本地Config Server的构建方式,接下来使用远程Config Server的环境搭建,即 将各个微服务的配置文件放置在远程Git仓库中,通过Config Server进行统一管理,我们使用基于Git的第三方代码托管远程仓库GitHub作为远程仓库,实际开发中也可以使用Gitee,SVN或自己建造的私服作为远程仓库,配置服务器的结构如图所示。
接下来我们就来一起建造远程Config Server。
GitHub远程配置文件
首先将配置文件上传到GitHub仓库。
- 创建配置文件,上传至 GitHub
server:
port: 8070
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
spring:
application:
name: configclient
- 创建 Config Server,新建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: configserver
cloud:
bus:
trace:
enable: true
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/JaneRoad/springcloud.git
searchPaths: config
username: 马赛克#自己的账号
password: 马赛克#自己的密码
label: master
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class,args);
}
}
创建 Config Client
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建 bootstrap.yml
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: configclient
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: configserver
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
注解说明
spring.cloud.config.name:当前服务注册在 Eureka Server 上的名称,与远程仓库的配置文件名对应。
spring.cloud.config.label:Git Repository 的分支。
spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled:是否开启 Config 服务发现支持。
spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id:配置中心在 Eureka Server 上注册的名称。
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientApplication.class,args);
}
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloHandler {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return this.port;
}
}
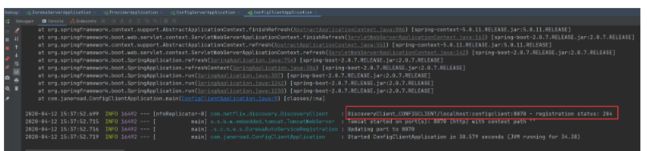
依次启动注册中心,configserver,configclient,如下图所示
通过控制台输出信息可以看到,configclient已经读取到了Git仓库中的配置信息。
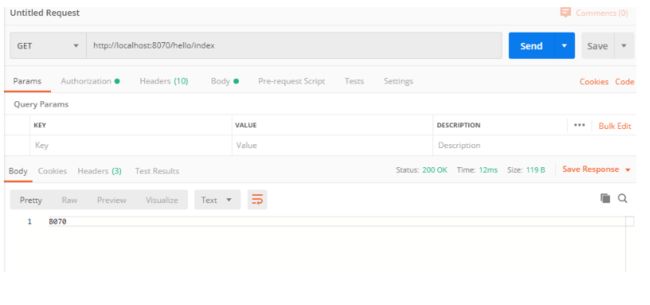
通过Postman工具访问http:// localhost:8070 / config / index,如下图所示
服务跟踪
首先来思考一个问题,为什么要有服务跟踪,我们知道一个分布式系统中往往会部署很多个微服务,这些服务彼此之间会相互调用,整个过程就会较为复杂,我们在进行问题排查或者优化的时候工作量就会比较大。如果能准确跟踪每一个网络请求的整个运行流程,获取它在每个微服务上的访问情况、是否有延迟、耗费时间等,这样的话我们分析系统性能,排查解决问题就会容易很多,我们使用 Zipkin 组件来实现服务跟踪。
什么是 Zipkin
Zipkin 是一个可以采集并且跟踪分布式系统中请求数据的组件,可以为开发者采集某个请求在多个微服务之间的追踪数据,并以可视化的形式呈现出来,让开发者可以更加直观地了解到请求在各个微服务中所耗费的时间等信息。
ZipKin 组件包括两部分:Zipkin Server 和 Zipkin Client,服务端用来采集微服务之间的追踪数据,再通过客户端完成数据的生成和展示,Spring Cloud 为服务跟踪提供了解决方案,Spring Cloud Sleuth 集成了 Zipkin 组件。
接下来我们通过实际代码来完成服务跟踪的实现,首先来实现 Zipkin Server
创建 Zipkin Server
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
io.zipkin.java
zipkin-server
2.9.4
io.zipkin.java
zipkin-autoconfigure-ui
2.9.4
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 9090
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import zipkin.server.internal.EnableZipkinServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZipkinServer
public class ZipkinApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZipkinApplication.class,args);
}
}
注解说明
@EnableZipkinServer:声明启动 Zipkin Server
创建 Zipkin Client
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
2.0.2.RELEASE
- 创建配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8090
spring:
application:
name: zipkinclient
sleuth:
web:
client:
enabled: true
sampler:
probability: 1.0
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9090/
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
属性说明
spring.sleuth.web.client.enabled:设置开启请求跟踪
spring.sleuth.sampler.probability:设置采样比例,默认是 1.0
srping.zipkin.base-url:Zipkin Server 地址
- 创建启动类
package com.janeroad;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ZipkinClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZipkinClientApplication.class,args);
}
}
- Handler
package com.janeroad.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/zipkin")
public class ZipkinHandler {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return this.port;
}
}
依次启动注册中心、Zipkin、ZipkinClient, 打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:9090/zipkin/,可看到 Zipkin 首页,如下图所示
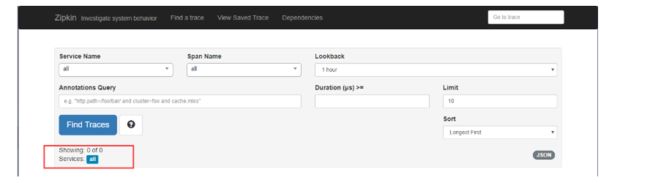
点击 Find Traces 按钮可看到监控数据情况,当前没有监控到任何数据,如下图
通过 Postman 访问 http://localhost:8090/zipkin/index,如下图所示。
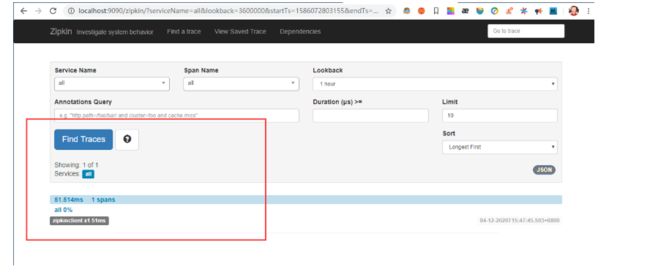
再次刷新 http://localhost:9090/zipkin/,可看到监控数据,如下图所示
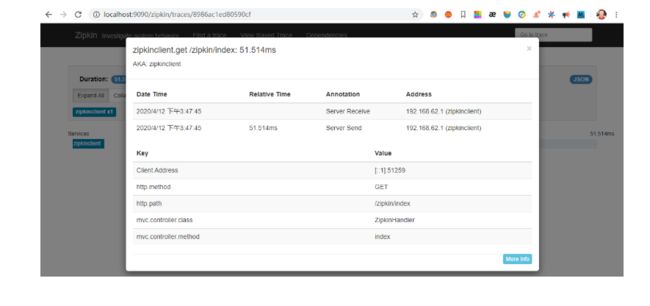
点击可查看详情,如下图所示。