YOLOv5:代码阅读(一):train.py;yaml文件
YOLOv5:代码阅读(一)
文章目录
- YOLOv5:代码阅读(一)
-
- 1.yaml文件
-
- 1.1 从yaml文件中解析yolov5整体基本框架
- 问题:Focus是啥模块?
- 问题:Conv的咋定义的
- 问题:CSPNet是如何实现的
- 问题:SPP的实现
- 问题:head是怎样的
- 问题:如何根据yaml文件生成模型
- 2. train.py[^2]
-
- 问题: yolov5训练方式
- 问题: 训练策略
- 问题: nbs是什么
- ==问题: yolov5用的loss是怎么样的==
- 问题:check_anchor函数
- 问题:使用超参数进化算法[^5]
1.yaml文件
1.1 从yaml文件中解析yolov5整体基本框架
# YOLOv5 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
问题:Focus是啥模块?
Focus源代码:
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
一种下采样方法,该方法将原图尺寸变为原来的一半,即步长设为2,然后将通道变为原来的4倍,这样信息没丢,但是尺度变小了。
问题:Conv的咋定义的
源代码:
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Conv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.Hardswish() if act else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def fuseforward(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
CONV层使用的激活函数是Hardswish;
atuopad是自动填padding的值,在k=1的时候,padding=0,在k=3的时候padding=1
问题:CSPNet是如何实现的
根据源代码:
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(BottleneckCSP, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_) # applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)])
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))))
得到如下图:
先用一层网络(CV1,CV2)将通道降为原来的一半(话说这个真的是CSP吗?),然后分为两个路径,一个路径进行特征提取,另一个不进行(CSP的操作),最后将两个路径concat起来。
倘若该层后面有BN层的话,一般选择bias=False(BN有偏置),而后面没有的时候bias=True。上面的CONV层和CSPNet也是这个规律
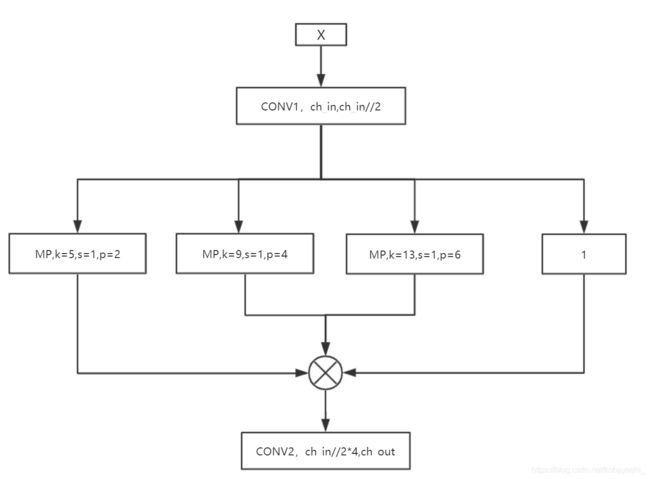
问题:SPP的实现
源代码:
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial pyramid pooling layer used in YOLOv3-SPP
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPP, self).__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))//
首先明确一点,
nn.ModuleList和python的list是一样的,它是一个储存不同 module,并自动将每个 module 的 parameters 添加到网络之中的容器。其次,
[x] + [m(x) for m in self.m]返回值是一个list,torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1)是将list在通道层面合并;当2*padding=k_size+1的时候,特征图输出尺寸不变
最后,SPP是这样的,其中1代表不作变换。
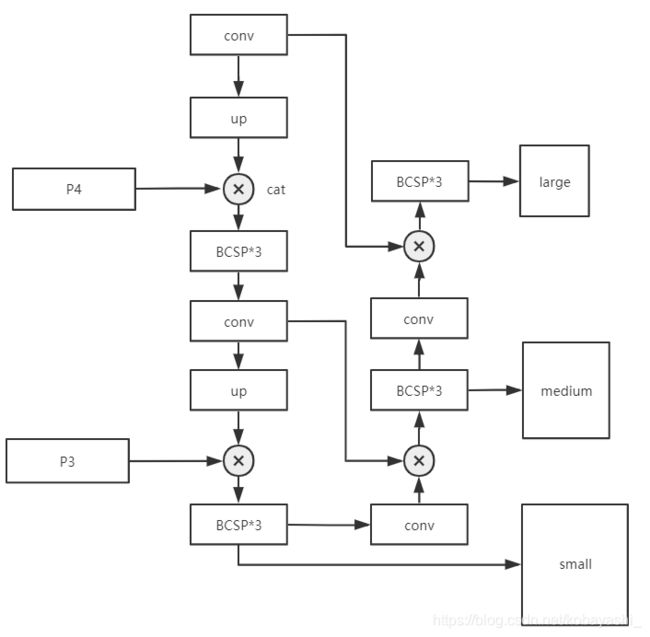
问题:head是怎样的
yolov5使用的head是PANet1
# YOLOv5 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
不过也可以使用FPN
# YOLOv5 FPN head
head:
[[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 10 (P5/32-large)
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 14 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 18 (P3/8-small)
[[18, 14, 10], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
问题:如何根据yaml文件生成模型
生成的代码在yolo.py中。
2. train.py2
问题: yolov5训练方式
main函数。
for _ in range(100): # generations to evolve
if os.path.exists('evolve.txt'): # if evolve.txt exists: select best hyps and mutate
# Select parent(s)
# 选择进化方式
parent = 'single' # parent selection method: 'single' or 'weighted'
# 加载evolve.txt
x = np.loadtxt('evolve.txt', ndmin=2)
# 选取至多前5次进化的结果
n = min(5, len(x)) # number of previous results to consider
x = x[np.argsort(-fitness(x))][:n] # top n mutations
# 根据results计算hyp的权重
w = fitness(x) - fitness(x).min() # weights
# 根据不同进化方式获得base hyp
if parent == 'single' or len(x) == 1:
# x = x[random.randint(0, n - 1)] # random selection
x = x[random.choices(range(n), weights=w)[0]] # weighted selection
elif parent == 'weighted':
x = (x * w.reshape(n, 1)).sum(0) / w.sum() # weighted combination
# Mutate
# 超参数进化
mp, s = 0.9, 0.2 # mutation probability, sigma
npr = np.random
npr.seed(int(time.time()))
# 获取突变初始值
g = np.array([x[0] for x in meta.values()]) # gains 0-1
ng = len(meta)
v = np.ones(ng)
# 设置突变
while all(v == 1): # mutate until a change occurs (prevent duplicates)
v = (g * (npr.random(ng) < mp) * npr.randn(ng) * npr.random() * s + 1).clip(0.3, 3.0)
# 将突变添加到base hyp上
# [i+7]是因为x中前七个数字为results的指标(P, R, mAP, F1, test_losses=(GIoU, obj, cls)),之后才是超参数hyp
for i, k in enumerate(hyp.keys()): # plt.hist(v.ravel(), 300)
hyp[k] = float(x[i + 7] * v[i]) # mutate
# Constrain to limits
# 修剪hyp在规定范围里
for k, v in meta.items():
hyp[k] = max(hyp[k], v[1]) # lower limit
hyp[k] = min(hyp[k], v[2]) # upper limit
hyp[k] = round(hyp[k], 5) # significant digits
# Train mutation
# 训练
results = train(hyp.copy())
# Write mutation results
"""
写入results和对应的hyp到evolve.txt
evolve.txt文件每一行为一次进化的结果
一行中前七个数字为(P, R, mAP, F1, test_losses=(GIoU, obj, cls)),之后为hyp
保存hyp到yaml文件
"""
print_mutation(hyp.copy(), results, yaml_file, opt.bucket)
# Plot results
plot_evolution(yaml_file)
print('Hyperparameter evolution complete. Best results saved as: %s\nCommand to train a new model with these '
'hyperparameters: $ python train.py --hyp %s' % (yaml_file, yaml_file))
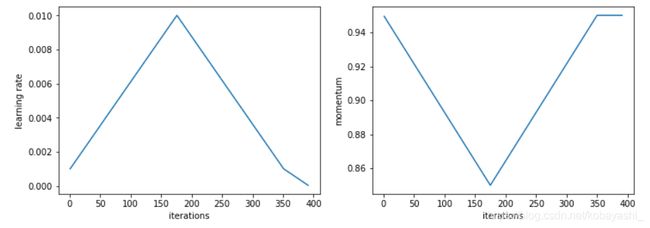
问题: 训练策略
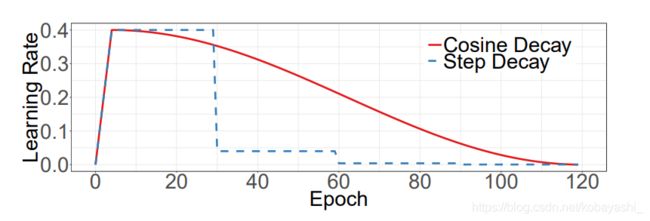
# Scheduler https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.html#OneCycleLR
lf = lambda x: ((1 + math.cos(x * math.pi / epochs)) / 2) * (1 - hyp['lrf']) + hyp['lrf'] # cosine
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf)
# plot_lr_scheduler(optimizer, scheduler, epochs)
根据代码给的连接,查到了OneCycleLR.3
可以将学习率和动量分为3个部分,学习率先上升,接着下降,然后继续下降;动量先下降,然后上升,然后不变.
1.当模型刚开始训练的时候,模型见到的数据都新的,这意味着模型能够很快地根据数据进行修正.这个时候如果学习过大,很容易导致模型对该数据过拟合,后面要通过很多轮才能拉回来,所以需要warmup.
2.在 Cycle 中期,高学习率将作为正则化的角色,并使 NN 不会过拟合。它们将阻止模型落在损失函数的陡峭区域,而是找到更平坦的最小值。
3.然后训练的最后一部分,学习率下降直到消失,将允许我们得到更平滑的部分内的局部最小值。
不过,学习率函数定义的是Cosine Learning Rate Decay,余弦方式进行学习率衰减,OneCycleLR可能是以后的版本会用到.
问题: nbs是什么
nbs = 64 #名义batch_size
accumulate = max(round(nbs / total_batch_size), 1) # accumulate loss before optimizing,累积loss,即保证无论batch_size多大,都是使用batch_size=64来更新
hyp['weight_decay'] *= total_batch_size * accumulate / nbs # scale weight_decay
这个做法是保证每次都是每64个batch才进行梯度更新,nbs:nomial batch size,名义批次大小.
gradient accumulation
问题: yolov5用的loss是怎么样的
general.py
首先要清楚anchor的设置4。
1.yolov5的anchor根据形状规则选择,而不是iou阈值;
2.bbox使用3个grid来预测,一个目标grid+2个最近grid。
根据[4]做了如下标注:
def build_targets(p, targets, model):
# Build targets for compute_loss(), input targets(image,class,x,y,w,h)
det = model.module.model[-1] if is_parallel(model) else model.model[-1] # Detect() module
na, nt = det.na, targets.shape[0] # number of anchors, targets
tcls, tbox, indices, anch = [], [], [], []
gain = torch.ones(7, device=targets.device) # normalized to gridspace gain
ai = torch.arange(na, device=targets.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt) # same as .repeat_interleave(nt)
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[:, :, None]), 2) # append anchor indices,<将anchor重复3次?>
g = 0.5 # bias
#附近4个点
off = torch.tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1], # j,k,l,m
# [1, 1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [-1, -1], # jk,jm,lk,lm
], device=targets.device).float() * g # offsets
for i in range(det.nl):#分配网络预测的框,3个预测框
anchors = det.anchors[i]
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain;增益,用于将特征图转换到原图,这里是赋4个值
# Match targets to anchors
t = targets * gain
if nt:
# Matches
'''1.先计算anchor和wh的比值得到r;
2.和阈值比较,小于阈值(4)的保留,然后过滤t=t[j]。如果r过高,说明anchor和wh匹配程度不高应该舍弃,不强制进行回归;
'''
r = t[:, :, 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratio
j = torch.max(r, 1. / r).max(2)[0] < model.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare
# j = wh_iou(anchors, t[:, 4:6]) > model.hyp['iou_t'] # iou(3,n)=wh_iou(anchors(3,2), gwh(n,2))
t = t[j] # filter
# Offsets
'''1.计算目标中心点最近的2个网格,将这两个网格也加入预测,正样本个数x3
'''
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse
j, k = ((gxy % 1. < g) & (gxy > 1.)).T
l, m = ((gxi % 1. < g) & (gxi > 1.)).T
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j]
else:
t = targets[0]
offsets = 0
# Define
b, c = t[:, :2].long().T # image, class
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gwh = t[:, 4:6] # grid wh
gij = (gxy - offsets).long()
gi, gj = gij.T # grid xy indices
# Append
a = t[:, 6].long() # anchor indices
indices.append((b, a, gj, gi)) # image, anchor, grid indices
tbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # box
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
tcls.append(c) # class
return tcls, tbox, indices, anch
损失函数组成:
1.分类损失,置信度损失用的是BCELoss;
2.bbox回归使用CIOU损失
def compute_loss(p, targets, model): # predictions, targets, model
device = targets.device
lcls, lbox, lobj = torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device)
tcls, tbox, indices, anchors = build_targets(p, targets, model) # targets
h = model.hyp # hyperparameters
# Define criteria
BCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.Tensor([h['cls_pw']])).to(device)
BCEobj = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.Tensor([h['obj_pw']])).to(device)
# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3
cp, cn = smooth_BCE(eps=0.0) #标签平滑,eps=0意味着不使用
# Focal loss
g = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gamma,使用focal loss,如果hyp.yaml中fl_gamma>0则使用focal loss
if g > 0:
BCEcls, BCEobj = FocalLoss(BCEcls, g), FocalLoss(BCEobj, g)
# Losses
nt = 0 # number of targets
np = len(p) # number of outputs
balance = [4.0, 1.0, 0.4] if np == 3 else [4.0, 1.0, 0.4, 0.1] # P3-5 or P3-6
for i, pi in enumerate(p): # layer index, layer predictions
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # image, anchor, gridy, gridx
tobj = torch.zeros_like(pi[..., 0], device=device) # target obj
n = b.shape[0] # number of targets
if n:
nt += n # cumulative targets
ps = pi[b, a, gj, gi] # prediction subset corresponding to targets
# Regression
pxy = ps[:, :2].sigmoid() * 2. - 0.5
pwh = (ps[:, 2:4].sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anchors[i]
pbox = torch.cat((pxy, pwh), 1).to(device) # predicted box
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, CIoU=True) # iou(prediction, target) ],CIOU损失
lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou loss
# Objectness
tobj[b, a, gj, gi] = (1.0 - model.gr) + model.gr * iou.detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype) # iou ratio
# Classification
if model.nc > 1: # cls loss (only if multiple classes)
t = torch.full_like(ps[:, 5:], cn, device=device) # targets
t[range(n), tcls[i]] = cp
lcls += BCEcls(ps[:, 5:], t) # BCE
# Append targets to text file
# with open('targets.txt', 'a') as file:
# [file.write('%11.5g ' * 4 % tuple(x) + '\n') for x in torch.cat((txy[i], twh[i]), 1)]
lobj += BCEobj(pi[..., 4], tobj) * balance[i] # obj loss
s = 3 / np # output count scaling
lbox *= h['box'] * s
lobj *= h['obj'] * s * (1.4 if np == 4 else 1.)
lcls *= h['cls'] * s
bs = tobj.shape[0] # batch size
loss = lbox + lobj + lcls
return loss * bs, torch.cat((lbox, lobj, lcls, loss)).detach()
问题:check_anchor函数
# Anchors
if not opt.noautoanchor:
check_anchors(dataset, model=model, thr=hyp['anchor_t'], imgsz=imgsz)
check_anchor根据网络的输出与数据集里面的anchor计算best possible recall,bpr,如果召回率低于0.98,用kmean来修改anchor。因为提供的anchor是COCO上聚类的,在使用自己的数据集的时候可以使用这个功能。
def check_anchors(dataset, model, thr=4.0, imgsz=640):
# Check anchor fit to data, recompute if necessary
print('\nAnalyzing anchors... ', end='')
m = model.module.model[-1] if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.model[-1] # Detect()
shapes = imgsz * dataset.shapes / dataset.shapes.max(1, keepdims=True)
scale = np.random.uniform(0.9, 1.1, size=(shapes.shape[0], 1)) # augment scale
wh = torch.tensor(np.concatenate([l[:, 3:5] * s for s, l in zip(shapes * scale, dataset.labels)])).float() # wh
def metric(k): # compute metric
r = wh[:, None] / k[None]
x = torch.min(r, 1. / r).min(2)[0] # ratio metric
best = x.max(1)[0] # best_x
aat = (x > 1. / thr).float().sum(1).mean() # anchors above threshold
bpr = (best > 1. / thr).float().mean() # best possible recall
return bpr, aat
bpr, aat = metric(m.anchor_grid.clone().cpu().view(-1, 2))
print('anchors/target = %.2f, Best Possible Recall (BPR) = %.4f' % (aat, bpr), end='')
if bpr < 0.98: # threshold to recompute
print('. Attempting to generate improved anchors, please wait...' % bpr)
na = m.anchor_grid.numel() // 2 # number of anchors
new_anchors = kmean_anchors(dataset, n=na, img_size=imgsz, thr=thr, gen=1000, verbose=False)
new_bpr = metric(new_anchors.reshape(-1, 2))[0]
if new_bpr > bpr: # replace anchors
new_anchors = torch.tensor(new_anchors, device=m.anchors.device).type_as(m.anchors)
m.anchor_grid[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchor_grid) # for inference
m.anchors[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchors) / m.stride.to(m.anchors.device).view(-1, 1, 1) # loss
check_anchor_order(m)
print('New anchors saved to model. Update model *.yaml to use these anchors in the future.')
else:
print('Original anchors better than new anchors. Proceeding with original anchors.')
print('') # newline
问题:使用超参数进化算法5
YOLOv5可以使用遗传算法(GA)对超参数进行进化,包括数据增强的设置。
1.超参数初始化
好的先验能够带来好的结果。
yolov5/data/hyp.scratch.yaml
2.定义适应度
yolov5/utils/general.py
def fitness(x):
# Returns fitness (for use with results.txt or evolve.txt)
w = [0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.9] # weights for [P, R, [email protected], [email protected]:0.95]
return (x[:, :4] * w).sum(1)
3.进化
命令如下
# Single-GPU
python train.py --epochs 10 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache --evolve
# Multi-GPU
for i in 0 1 2 3; do
nohup python train.py --epochs 10 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache --evolve --device $i &
done
这会使用300轮来进化超参数。
不过在使用这个的时候遇到了如下错误:
Namespace(adam=False, batch_size=16, bucket='', cache_images=True, cfg='./models/yolov5s.yaml', data='./data/coco128.yaml', device='', epochs=3, evolve=True, global_rank=-1, hyp='data/hyp.scratch.yaml', image_weights=False, img_size=[640, 640], local_rank=-1, logdir='runs/', multi_scale=False, name='', noautoanchor=False, nosave=False, notest=False, rect=False, resume=False, single_cls=False, sync_bn=False, total_batch_size=16, weights='', workers=8, world_size=1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "train.py", line 525, in
hyp[k] = max(hyp[k], v[1]) # lower limit
KeyError: 'anchors'
我们需要注释掉 ‘anchors’: (2, 2.0, 10.0),
meta = {
'lr0': (1, 1e-5, 1e-1), # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
'lrf': (1, 0.01, 1.0), # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
'momentum': (0.3, 0.6, 0.98), # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
'weight_decay': (1, 0.0, 0.001), # optimizer weight decay
'warmup_epochs': (1, 0.0, 5.0), # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
'warmup_momentum': (1, 0.0, 0.95), # warmup initial momentum
'warmup_bias_lr': (1, 0.0, 0.2), # warmup initial bias lr
'box': (1, 0.02, 0.2), # box loss gain
'cls': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # cls loss gain
'cls_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # cls BCELoss positive_weight
'obj': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
'obj_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # obj BCELoss positive_weight
'iou_t': (0, 0.1, 0.7), # IoU training threshold
'anchor_t': (1, 2.0, 8.0), # anchor-multiple threshold
# 'anchors': (2, 2.0, 10.0), # anchors per output grid (0 to ignore)#如果使用进化算法需要注释这一行
'fl_gamma': (0, 0.0, 2.0), # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
'hsv_h': (1, 0.0, 0.1), # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_s': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_v': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
'degrees': (1, 0.0, 45.0), # image rotation (+/- deg)
'translate': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image translation (+/- fraction)
'scale': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image scale (+/- gain)
'shear': (1, 0.0, 10.0), # image shear (+/- deg)
'perspective': (0, 0.0, 0.001), # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
'flipud': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip up-down (probability)
'fliplr': (0, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip left-right (probability)
'mosaic': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
'mixup': (1, 0.0, 1.0)} # image mixup (probability)
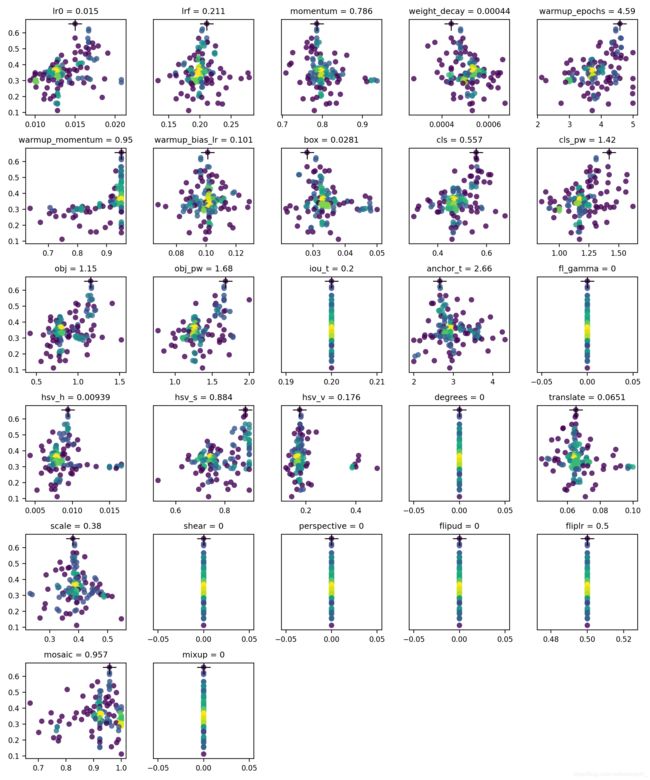
跑了100次,每次10个epoch。得到结果如下,x轴代表超参数的值,y轴代表fitness。
yolov5/evolve.png
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.01534.pdf ,PANet ↩︎
https://blog.csdn.net/Q1u1NG/article/details/107463417 ↩︎
文章:https://sgugger.github.io/the-1cycle-policy.html?utm_source=ld246.com,论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.07120.pdf, pytorch:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.html#OneCycleLR ↩︎
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/183838757 ↩︎
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/607 ↩︎