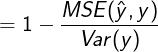衡量线性回归法的指标MSE、RMSE、MAE、R Squared(最佳)
线性回归算法的评测

均方误差MSE(Mean Squared Error)

均方根误差RMSE(Root Mean Squared Error)

平均绝对误差MAE(Mean Absolute Error)
### 05 衡量回归算法的标准
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
### 波士顿房产数据
boston = datasets.load_boston()
print(boston.DESCR)
boston.feature_names
输出结果:array(['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD',
'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT'], dtype=')
x = boston.data[:,5]#只使用房间数量这个特征
x.shape
输出结果:(506,)
y = boston.target
y.shape
输出结果:(506,)
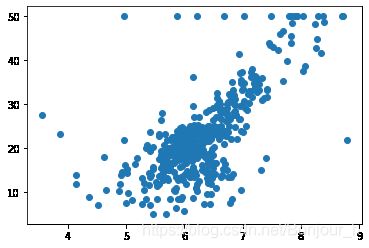
plt.scatter(x,y)
plt.show()
np.max(y)
x = x[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
plt.scatter(x,y)
plt.show()
### 使用简单线性回归法
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,seed = 666)
x_train.shape
输出结果:(392,)
x_test.shape
输出结果:(98,)
from playML.SimpleLinearRegression import SimpleLinearRegression
reg = SimpleLinearRegression()
reg.fit(x_train,y_train)
reg.a_
输出结果:7.8608543562689555
reg.b_
输出结果:-27.459342806705543
plt.scatter(x_train,y_train)
plt.plot(x_train,reg.predict(x_train),color="r")
plt.show()
y_predict = reg.predict(x_test)
### MSE
mse_test = np.sum((y_predict - y_test) ** 2)/len(y_test)
mse_test
输出结果:24.156602134387438
### RMSE
from math import sqrt
rmse_test = sqrt(mse_test)
rmse_test
输出结果:4.914936635846635
### MAE
mae_test = np.sum(np.absolute(y_predict - y_test)) / len(y_test)
mae_test
输出结果:3.5430974409463873
### scikit-learn中的MSE和MAE
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
mean_squared_error(y_test,y_predict)
输出结果:24.156602134387438
mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_predict)
输出结果:3.5430974409463873
import numpy as np
from .metrics import r2_score
class SimpleLinearRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Simple Linear Regression模型"""
self.a_ = None
self.b_ = None
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集x_train, y_train训练Simple Linear Regression模型"""
assert x_train.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert len(x_train) == len(y_train), \
"the size of x_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
x_mean = np.mean(x_train)
y_mean = np.mean(y_train)
self.a_ = (x_train - x_mean).dot(y_train - y_mean) / (x_train - x_mean).dot(x_train - x_mean)
self.b_ = y_mean - self.a_ * x_mean
return self
def predict(self, x_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集x_predict,返回表示x_predict的结果向量"""
assert x_predict.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert self.a_ is not None and self.b_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
return np.array([self._predict(x) for x in x_predict])
def _predict(self, x_single):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
return self.a_ * x_single + self.b_
def score(self, x_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 x_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(x_test)
return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "SimpleLinearRegression()"
import numpy as np
def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None):
"""将数据 X 和 y 按照test_ratio分割成X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test"""
assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0], \
"the size of X must be equal to the size of y"
assert 0.0 <= test_ratio <= 1.0, \
"test_ration must be valid"
if seed:
np.random.seed(seed)
shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X))
test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio)
test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size]
train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:]
X_train = X[train_indexes]
y_train = y[train_indexes]
X_test = X[test_indexes]
y_test = y[test_indexes]
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
R Squared


分子表示使用我们的模型预测产生的错误
分母表示使用 y = y ˉ y=\bar{y} y=yˉ预测产生的错误
- R 2 < = 1 R^{2} <= 1 R2<=1
- R 2 R^{2} R2越大越好。当我们的预测模型不犯任何错误时, R 2 R^{2} R2得到最大值1
- 当我们的模型等于基准模型时, R 2 R^{2} R2为0
- 如果 R 2 R^{2} R2< 0,说明我们学习到的模型还不如基准模型。此时,很可能我们的数据不存在任何线性关系。
### R Square
1 - mean_squared_error(y_test,y_predict) / np.var(y_test)
输出结果:0.6129316803937322
from playML.metrics import r2_score
r2_score(y_test,y_predict)
输出结果:0.6129316803937322
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
r2_score(y_test,y_predict)
输出结果:0.6129316803937324
reg.score(x_test,y_test)
输出结果:0.6129316803937322