优先级队列priority_queue
优先级队列
之前我们在数据结构学过堆,在STL容器适配器里面学习了queue,本次深入探讨一下他们的亲戚——优先级队列。
priority_queue
- 优先级队列
- 前言
- 一、基本使用
-
- 1.直接使用priority_queue
- 2.利用全局函数构造堆
- 二、模拟实现
- 总结
前言
1.优先级队列是一种容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准(严格是说在判断的时候会用"<",而不是"<=",弱排序是因为,一旦"<“成立便认为存在”<“关系,返回ture,而忽略了”=“关系和”>"区别,把它们归结为false。),因此它的第一个元素总是他所包含的元素中最大的;
2.类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先级队列中位于顶部的元素);
3.优先级队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器暨将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类。queue提供了一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素,元素从特定容器的“尾部”弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部;
4.底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类,容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器,并支持:empty()、size()、front()、push_back()、pop_back();
5.标准容器类vector和deque满足这些要求,默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector;
6.需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构,容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用算法函数make_heap、push_heap、pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
一、基本使用
优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中的元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用priority_queue。注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆(升序排序)。
1.直接使用priority_queue
void main()
{
vector<int> iv{
5, 8, 3, 2, 1, 4, 9, 7 };
priority_queue<int> pq;//直接使用priority_queue
for (int i = 0; i < iv.size(); ++i)
{
pq.push(iv[i]);//入堆
}
cout << "pq size = " << pq.size() << endl;
cout << "pq top = " << pq.top() << endl;//取堆顶
pq.pop();
cout << "pq top = " << pq.top() << endl;
for (const auto&e : iv)
{
cout << e << " ";//vector里面的数据顺序没变
}
cout << endl;
}
2.利用全局函数构造堆
make_heap
void main()
{
vector<int> iv{
5, 8, 3, 2, 1, 4, 9, 7 };
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
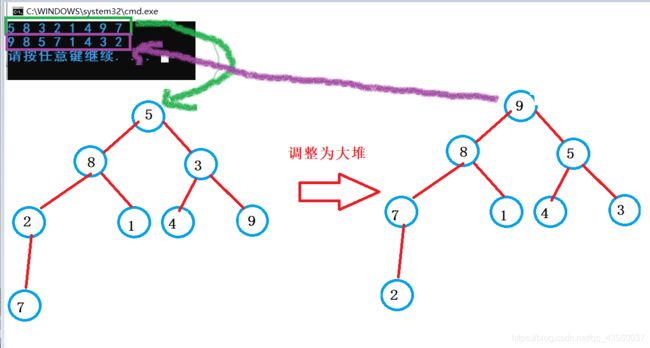
make_heap(iv.begin(), iv.end());//构造大堆
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
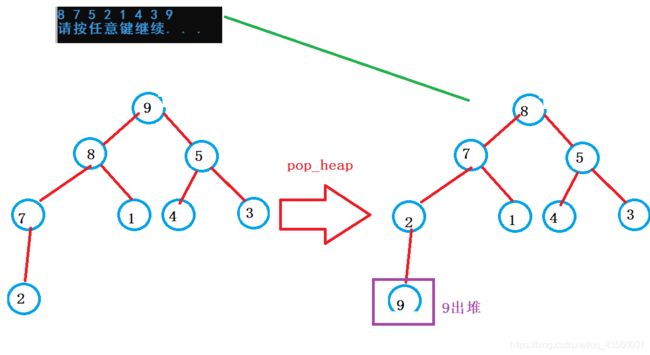
pop_heap(iv.begin(), iv.end());//删除堆顶元素
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
auto it = iv.end();//迭代器
for (int i = 0; i < iv.size(); ++i)
{
pop_heap(iv.begin(), it);
--it;
}
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
void main()
{
vector<int> iv{
5, 8, 3, 2, 1, 4, 9, 7 };
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
make_heap(iv.begin(), iv.end());//构造大堆
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
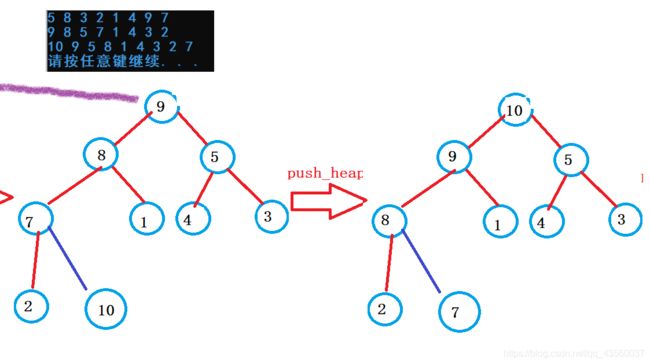
iv.push_back(10);
push_heap(iv.begin(), iv.end());//调整为大堆
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
sort_heap(iv.begin(), iv.end());
for (const auto&e : iv)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
如果想要构建小堆(降序排序):
就需要使用仿函数greater(仿函数的本质就是个对象,重载了符号“()”)
#include 
如果priority_queue的内容是自定义类型,则必须对比较符号“<,>”进行重载。
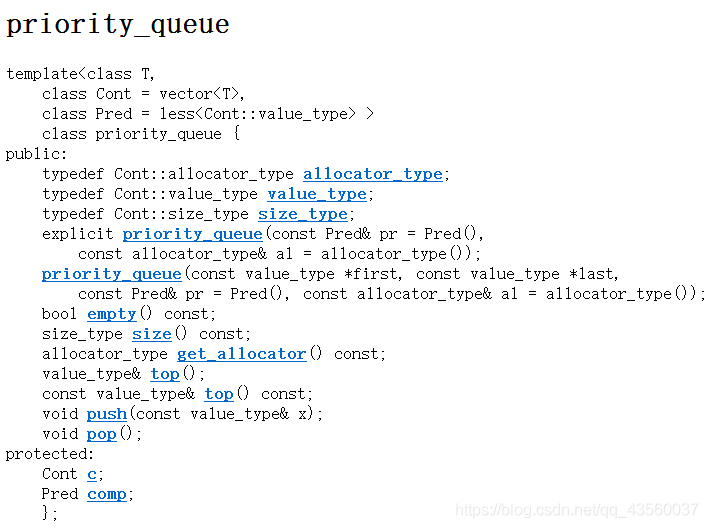
二、模拟实现
有3个模板参数,第一个是数据类型,第二个是要适配的容器,第三个相当于一个谓词(仿函数)。
第一种模拟方法(使用全局函数):
namespace LJL
{
template<class T, class Cont = vector<T>, class Pred = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
//萃取
typedef T value_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
public:
explicit priority_queue(const Pred &pr = Pred()):sz(0)//构造
{
}
priority_queue(const value_type *first, const value_type *last,
const Pred &pr = Pred()) :c(first, last)
{
make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(),pr);//pr参数为仿函数,不传则默认为大堆
sz = c.size();
}
void push(const value_type &x)
{
c.push_back(x);
push_heap(c.begin(), c.end());//调整为大堆push_heap()需要引入queue头文件
sz++;
}
void pop()
{
pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end());
sz--;
}
/*void Show()const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < c.size(); ++i)
{
cout << c[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}*/
public:
value_type &top()
{
return c.front();}
size_type size()const
{
return sz;}
bool empty()const
{
return sz == 0;}
private:
Cont c;
Pred comp;
size_t sz;
};
}
第二种模拟方法:
namespace LJL
{
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>,class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
priority_queue()
{
}
priority_queue(const T *first, const T *last,
const Compare &pr = Compare()) :c(first, last), comp(pr)
{
int curpos = c.size() / 2 - 1;//最后一个分支的位置
//调整
while (curpos >= 0)
{
_adjustdown(curpos);//向下调整
curpos--;
}
}
void Show()const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < c.size(); ++i)
{
cout << c[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
public:
bool empty()const
{
return c.size() == 0;}
size_t size()const
{
return c.size();}
T &top()
{
return c.front();
}
void push(const T &x)
{
c.push_back(x);
_adjustup(c.size()-1);//从末尾的位置向根调整
}
void pop()
{
std::swap(*c.begin(),*(--c.end()));//首尾交换
c.pop_back();//删除堆尾
_adjustdown(0);
}
protected:
void _adjustdown(int start)
{
int n = c.size();
int i = start;
int j = 2 * i + 1;//左子树
while (j < n)
{
//less c[j]
if (j + 1 < n && comp(c[j] , c[j + 1]))//左右子树比较出的较大的那个
{
j++;
}
if (comp(c[i] , c[j]))//交换
{
T tmp = c[i];
c[i] = c[j];
c[j] = tmp;
i = j;
j = 2 * i + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void _adjustup(int start)
{
int j = start;
int i = (j - 1)/2;
while (i >= 0)
{
if (comp(c[i] , c[j]))
{
T tmp = c[i];
c[i] = c[j];
c[j] = tmp;
j = i;
i = (j - 1) / 2;
}
else
break;
}
}
private:
Container c;
Compare comp;
};
}