笔记是学习了小马哥在慕课网的课程的《Spring Boot 2.0深度实践之核心技术篇》的内容结合自己的需要和理解做的笔记。
前言
在这看这篇笔记之前,个人建议去看一下上一篇,因为这里很多用到的扩展方法都是基于Environment生命周期来的。所以如果有迷惑的地方可以先了解一下Environment生命周期,再回来思考一下,就能有一定的理解了。
扩展外部化配置属性源
配置方式概览
- 基于
SpringApplicationRunListener#environmentPrepared - 基于
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent扩展外部化配置属性源 - 基于
EnvironmentPostProcessor扩展外部化配置属性源 - 基于
ApplicationContextInitializer扩展外部化配置属性源 - 基于
SpringApplicationRunListener#contextPrepared扩展外部化配置属性源 - 基于
SpringApplicationRunListener#contextLoaded扩展外部化配置属性源
这篇笔记我们先介绍前3个配置方式。
前置工作
1.创建一个SpringBoot项目,目录如下:
2.pom.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
3.application.properties
#Springboot默认配置读取
test=0
4.引导类
/**
* @ClassName ExternalizedBootstrap
* @Description 引导类
* @Author Neal
* @Date 2019/1/18 11:11
* @Version 1.0
*/
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "neal.externalized") //扫描指定包下的类
public class ExternalizedBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context =
new SpringApplicationBuilder(ExternalizedBootstrap.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE) // 非 Web 应用
.run(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = context.getEnvironment();
System.err.println("测试扩展外部化配置结果: " + environment.getProperty("test"));
//打印所有资源配置对象
environment.getPropertySources().forEach(propertySource -> {
System.err.printf("PropertySource[名称:%s] : %s\n",propertySource.getName(),propertySource);
System.out.println();
});
// 关闭上下文
context.close();
}
}
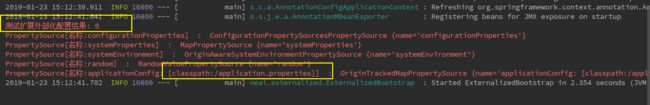
5.没进行外部化配置时,启动查看。
我们可以看到SpringBoot的几个内置的资源对象,并且 我们在application.properties中定义的test=1外部化值已经取到了。
下面让我们扩展外部化,使其更新test的值。
基于 SpringApplicationRunListener#environmentPrepared
实现基础
在之前我们介绍也自己写过 SpringApplicationRunListener相关的demo 这里就不做重复,我们看到主要就是使用environmentPrepared 方法来进行外部化的资源配置。在上一篇Springboot--扩展外部化配置(一)中,我们提到在SpringBoot启动时会在prepareEnvironment方法中调用SpringApplicationRunListener实现类的 environmentPrepared方法。部分源码如下:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//创建 ConfigurableEnvironment 对象
//如果是 Servlet容器则返回 StandardServletEnvironment 对象
//如果是 其他的类型 则返回 StandardEnvironment 对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置environment
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//监听 environmentPrepared 事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
所以我们可以利用environmentPrepared方法来进行外部化配置。
具体实现
1.实现SpringApplicationRunListener接口并重写environmentPrepared 方法。
ExternalizePropertyListener.java
/**
* 扩展 {@link PropertySource}
*/
public class ExternalizePropertyListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener,Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
public ExternalizePropertyListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
}
@Override
public void starting() {
}
/**
* 扩展外部化资源
* @param environment
*/
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//获取项目跟路径
String classpath = ExternalizePropertyListener.class.getResource("/").getPath();
//获取PropertySource组合对象
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
//获取自定义的外部化配置资源
File file = new File(classpath +"config/externalizepropertylistener.properties");
/**
* 获取Property对象
*/
InputStreamReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
//声明一个properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 加载字符流成为 Properties 对象
properties.load(reader);
//声明Spring内置PropertiesPropertySource对象
PropertiesPropertySource propertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource("from---ExternalizePropertyListener",properties);
//将配置资源放到其他配置资源的首位
propertySources.addFirst(propertySource);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
}
//加载顺序在EventPublishingRunListener之前
// 这么做是为了之后的外部化配置展示
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -1;
}
}
这里有个重点就是 我们设置的getOrder() 方法返回值是-1,因为Springboot默认的实现EventPublishingRunListener的顺序是0。所以我们需要在他之前加载处理。
2.配置自定义的外部化资源,我们这里的文件的存放位置\resources\config\externalizepropertylistener.properties
#ExternalizePropertyListener 对应的配置
test=1
设置一个KEY-VALUE值。
3.将自定义的ExternalizePropertyListener 加入到 resources\META-INF\spring.factories
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyListener
启动容器,查看结果
我们可以看到 我们自定义的外部资源内容已经在项目中加载,并且打印出的结果是0,表示已经覆盖了之前的默认配置(application.properties)时打印的值。
基于 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 扩展外部化配置属性源
实现基础
这个方式的实现基础就是监听事件ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent ,这也是我们在之前笔记中提到的,具体不做太多的解释,结论就是我们在使用SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类EventPublishingRunListener#environmentPrepared时,在这里发布了 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent `事件,因此我们可以通过这个点,去监听该事件并进行外部化扩展。
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));
}
具体实现
1.监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 的实现类ExternalizePropertyEventListener.java
/**
* 扩展外部化配置
*/
public class ExternalizePropertyEventListener implements ApplicationListener {
/**
* 监听到内容时触发的方法
* @param event
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
//获取项目跟路径
String classpath = ExternalizePropertyEventListener.class.getResource("/").getPath();
//获取PropertySource组合对象
MutablePropertySources propertySources = event.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
//获取自定义的外部化配置资源
File file = new File(classpath +"config/externalizepropertyeventlistener.properties");
/**
* 获取Property对象
*/
InputStreamReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
//声明一个properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 加载字符流成为 Properties 对象
properties.load(reader);
//声明Spring内置PropertiesPropertySource对象
PropertiesPropertySource propertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource("from---ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent",properties);
//将配置资源放到其他配置资源的首位
propertySources.addFirst(propertySource);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.外部化资源配置 config/externalizepropertyeventlistener.properties
#ExternalizePropertyEventListener 对应的配置
test=2
3.将自定义的ExternalizePropertyEventListener加入到 resources\META-INF\spring.factories
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyListener
#ApplicationListener
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyEventListener
启动容器,查看结果
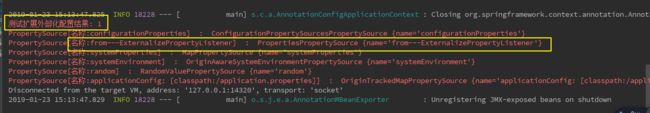
我们可以看到黄色框和绿色框都加载了,为什么值是2而不是1呢,换句话说为什么除了ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource之外,在首位的是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 而不是ExternalizePropertyListener 呢,这个原因就是我们之前在ExternalizePropertyListener 设置的加载顺序的原因,因为 ExternalizePropertyListener 在 EventPublishingRunListener之前执行,所以还没等发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件,ExternalizePropertyListener 的资源类已经放入了上下文中并且暂时放在首位,但是当EventPublishingRunListener执行并且发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件后,我们自定义的事件监听(ExternalizePropertyEventListener)才会触发,所以ExternalizePropertyEventListener配置的资源会放在 ExternalizePropertyListener 资源之前。因此我们的值是2 不是1。
基于 EnvironmentPostProcessor 扩展外部化配置属性源
实现基础
我们也许好奇,到底application.properties或者application.yml是被哪个实现类何时加载的。我们来看这个每一个类org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener 这个类的主要作用就是通过从众所周知的文件位置加载属性来配置上下文环境。 默认情况下,属性将从“application.properties”和/或“application.yml”文件加载。具体的细节大家可以看这个类的源码,我们现在直接讲述到底是何时去调用EnvironmentPostProcessor 接口中的方法。
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener#onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//发布事件时,判断是否是 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
//加载获取所有实接口的类不包括自己
List postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
//将自己加到postProcessors
postProcessors.add(this);
//排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
//遍历执行postProcessEnvironment
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(),
event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
我们可以看到这个方法名,就是在EnvironmentPreparedEvent事件发布时进行监听,但是我们刚刚也了解了另一种方式,监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent ,其实监听的内容是一样的,只是执行顺序不同。我们通过debugger的方式了解到 onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent的监听方法是在ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 之间执行的。所以在实现的时候我们要注意 这个调用顺序,防止因为顺序而影响配置结果。
具体实现
1.实现EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的类 ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor.java
/**
* EnvironmentPostProcessor 方式实现外部化配置
*/
public class ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor,Ordered {
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
//获取PropertySource组合对象
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
//获取项目跟路径
String classpath = ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor.class.getResource("/").getPath();
//获取自定义的外部化配置资源
File file = new File(classpath +"config/environmentpostprocessor.properties");
/**
* 获取Property对象
*/
InputStreamReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
//声明一个properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 加载字符流成为 Properties 对象
properties.load(reader);
//声明Spring内置PropertiesPropertySource对象
PropertiesPropertySource propertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource("from---ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor",properties);
//将配置资源放到其他配置资源的首位
propertySources.addFirst(propertySource);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
//设置执行顺序在 ConfigFileApplicationListener之后
//也就是 加载application.properties 之前
return ConfigFileApplicationListener.DEFAULT_ORDER - 1;
}
}
2.外部化资源配置 config/environmentpostprocessor.properties
#EnvironmentPostProcessor 对应的配置
test=3
3.将自定义的ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor加入到 resources\META-INF\spring.factories
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyListener
#ApplicationListener
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyEventListener
#EnvironmentPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
neal.externalized.listener.ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor
启动容器,查看结果
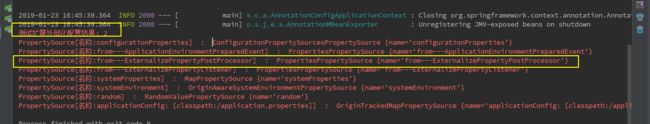
我们可以看到,最后的结果是2而不是3,这就是我们之前讲的 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent执行在ExternalizePropertyPostProcessor之后,要想实现赋值为3的结果,我们只需要将 ExternalizePropertyEventListener注释掉,在运行容器。
小结
我们可以看到扩展顽不化资源有很多方式,但是我们最主要的就是要知道这些配置方法的执行顺序,才能保证我们的扩展可以正确的执行。下一篇我把之后的几种方式介绍完。