二叉树的遍历是指按照某种顺序访问二叉树中的每个结点,使得每个结点都只被访问一次。
通过一次完整的遍历,可使二叉树中的结点由原来的非线性序列变为某种意义的线性序列。根据根节点访问的顺序不同,遍历的顺序分为前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历。
二叉树的遍历方法与算法实现
img
先序遍历
如果二叉树为空,则遍历的结果为空,否则:
访问根节点
先序遍历左子树
-
先序遍历右子树
简言之:根 -> 左 -> 右
图示:A B D E F G C
中序遍历
如果二叉树为空,则遍历的结果为空,否则:
中序遍历根节点的左子树
访问根节点
-
中序遍历根节点的右子树
简言之:左 -> 根 -> 右
图示:D E B G F A C
后序遍历
若二叉树为空,遍历结果为空,否则:
后序遍历根节点的左子树
后续遍历根节点的右子树
-
访问根节点
简言之:左 -> 右 -> 根
图示:E D G F B C A
Java 代码实现二叉树的遍历
package test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
public class Tree {
private Node root;
private List list = new ArrayList<>();
public Tree() {
init();
}
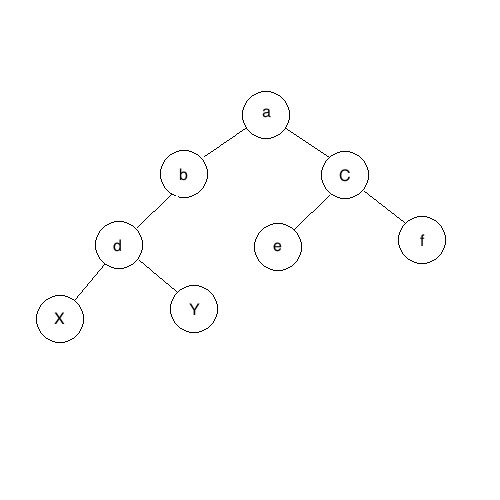
private void init() {
Node x = new Node("X", null, null);
Node y = new Node("Y", null, null);
Node d = new Node("d", x, y);
Node e = new Node("e", null, null);
Node f = new Node("f", null, null);
Node c = new Node("c", e, f);
Node b = new Node("b", d, null);
Node a = new Node("a", b, c);
root = a;
}
// 定义节点类
private class Node {
private String data;
private Node lChild;// 左子树
private Node rChild;// 右子树
public Node(String data, Node lChild, Node rChild) {
this.data = data;
this.lChild = lChild;
this.rChild = rChild;
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(Node node) {
list.add(node);// 将根节点存入list
// 如果左子树不为空,继续在找,在递归调用方法的时候一直会将子树的根存入list,这就做到了先遍历根节点
if (node.lChild != null) {
preOrder(node.lChild);
}
// 无论走到哪一层,只要当节点左子树为空,那么就可以在右子树遍历,保证根左右的遍历
if (node.rChild != null) {
preOrder(node.rChild);
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void inOrder(Node node) {
if (node.lChild != null) {
preOrder(node.lChild);
}
list.add(node);
if (node.rChild != null) {
preOrder(node.rChild);
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder(Node node) {
if (node.lChild != null) {
preOrder(node.lChild);
}
if (node.rChild != null) {
preOrder(node.rChild);
}
list.add(node);
}
/**
* 返回当前树的深度 一棵树只有一个结点,它的深度为1 如果根节点只有左子树而没有右子树,那么树的深度是其左子树的深度加1
* 如果根节点只有右子树而没有左子树,那么树的深度是其右子树的深度加1 如果既有左子树也有右子树,那么深度是其左/右子树的深度的较大值再加1
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
public int getTreeDepth(Node node) {
if (node.lChild == null && node.rChild == null) {
return 1;
}
int left = 0, right = 0;
if (node.lChild != null) {
left = getTreeDepth(node.lChild);
}
if (node.rChild != null) {
left = getTreeDepth(node.rChild);
}
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
public List getResult() {
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree tree = new Tree();
System.out.println("根节点:" + tree.root);
// tree.preOrder(tree.root);
// tree.inOrder(tree.root);
tree.postOrder(tree.root);
for (Node node : tree.getResult()) {
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("树的深度:" + tree.getTreeDepth(tree.root));
}
}
以上代码绘制的二叉树为
运行结果
先序遍历
根节点:test.Tree$Node@33909752
a b d X Y c e f
树的深度:3
------------------------------------------------------------
中序遍历
根节点:test.Tree$Node@33909752
b d X Y a c e f
树的深度:3
------------------------------------------------------------
后序遍历
根节点:test.Tree$Node@33909752
b d X Y c e f a
树的深度:3