MS-SQL
变量
一个@为局部变量,两个@@为全局变量
@@error 最后一句SQL语句的错误编号 错误码
@@identity最后一次插入的标示值符
insert into biao(lie) output inserted.id values(zhi)
select @@identity
@@language
@@version
@@transcount当前事务数
@@severname本地服务器名字
@@rowcount受上句SQL语句影响的行数
@@max_connections可以创建同时连接的最大数目
先定义,后使用。ADO.Net中给变量起别名加@ 任何一个名字会被认为是一个列或者存储过程
定义:declare @变量 类型 declare @name nvarchar(4)
赋值:set @变量 =值
select @变量=值, @变量=值
比如
declare @name='张三'
declare @sid =1
select @name= stuName from student where stu_id=@sid 将张三换成查出的name值。
流程控制
在sql执行特定的脚本。循环判断,if else
if(条件表达式) --没有{},用begin end代替。
begin语句end
else
begin语句end
例如
DECLARE @num int SET @num =2; IF(@num=2) begin select '是二' end else begin select '不是二' end
while(条件表达式) begin 语句 continue break end
1-100和
--定义两个变量,总和与指针赋初值0 和1
DECLARE @sum int declare @index int select @sum=0,@index=1 while(@index!>100) begin set @sum=@index+ @sum set @index=@index+1 end SELECT @sum
1-100的素数
只能被1和本身整除的数字 2 3 5 7 11 13 17
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 2; i <100; i++) { int j; for ( j = 2; j < i; j++) { if (i%j == 0) { break; } } if (j == i) { Console.Write( i+","); } } Console.ReadKey(); } }
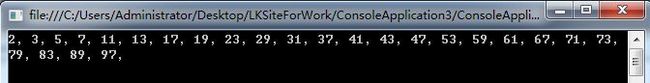
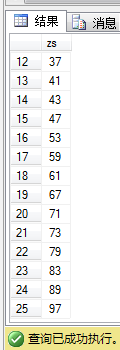
SQL:列出实现1-100所有的质数
CREATE table zhishu( zs int ) SELECT * from zhishu DECLARE @i int DECLARE @j int SET @i = 2 WHILE(@i<100) begin set @j =2 while(@j<@i) BEGIN IF(@i%@j=0) begin break end set @j=@j+1 end IF(@i=@j) BEGIN insert INTO zhishu(zs)VALUES(@i) end set @i=@i+1 end
求:1-100所有偶数的和
DECLARE @su int declare @inde int select @su=0,@inde=1 while(@inde!>100) begin IF(@inde%2=0) BEGIN set @su=@inde+ @su end set @inde=@inde+1 end SELECT @su
case函数
放在select之后,对字段处理显示数据变化。给一般用户看这些数据,需要改值,比如 f代表女,m代表男。
2种:
简单case函数,相当c#switch case。
case 字段
when 值1 then 显示1
when 值2 then 显示2
else 显示
end
select id ,name,
case sex when 'f' then '女' when ‘m’ then ‘男’ else ‘不知’ end as[性别],--需要为此列取个别名,上个sex字段名不能用了。
from biao
搜索case函数相当c#if else if
case
when 字段表达式 then 显示1
when sex=‘f’ then 显示2
else 显示
end
SELECT name, CASE WHEN (age>=20 and age<=30 and cashM>=2000 and cashM<=10000) then '1' WHEN (age>=30 and age<=80 and cashM>=3000 and cashM<=10000) then '2' END AS "年龄工资" from cash
trancate 删除
公共表表达式 修改视图
表联合
:union列数目没变化,可以将结果集合并,没有改变结果的结构。多个select。行数增加而已。
表连接
数据源的操作,from后面的事情
改变列的数目,3列和9列的表合并成12列的表称为连接
交叉连接:cross两个表的笛卡尔积。生成辅助表,用于数据优化,需要1234纯数字连续据表
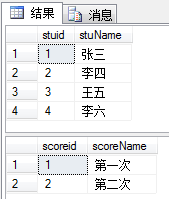
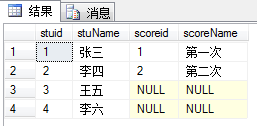
USE lianxi; --删除表格 drop table dbo.num15; DROP table num25; CREATE table t_stu( stuid int ,stuName nvarchar(4) ) CREATE table t_score( scoreid int ,scoreName nvarchar(4) ) INSERT into t_stu VALUES(1,'张三'),(2,'李四'); INSERT into t_stu VALUES(3,'王五'),(4,'李六'); INSERT into t_score VALUES(1,'第一次'),(2,'第二次') --删除前几行数据 DELETE top (4) from t_stu; SELECT *FROM t_stu; SELECT* FROM t_score;
交叉连接最为基本。
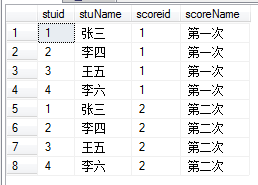
SELECT * FROM t_stu as t1 CROSS JOIN t_score as t2;
内连接:on条件,就是主外键相同时,找到对应的信息。此种方法有交叉连接的基础再on主外键,记住。
SELECT * FROM t_stu as t1 INNER JOIN t_score as t2 on t1.stuid=t2.scoreid;
外连接:outer join一般省略,用左连接和右连接 全连接
SELECT * FROM t_stu as t1 LEFT join t_score as t2 on t1.stuid=t2.scoreid;
SELECT * FROM t_stu as t1 RIGHT join t_score as t2 on t1.stuid=t2.scoreid;
SELECT * FROM t_stu as t1 full join t_score as t2 on t1.stuid=t2.scoreid;
表表达式
派生表(临时表),公共表表达式(临时),视图(持久存在)可能浪费资源哦
3种,派生表(临时表)将查询的数据作为from后的数据源,和子查询有点类似。但是子查询是一个或多个值,用in,而派生表是一张表。
查询是必须用括号括起来。不能是游标,必须是结果集。所以不能只含有order by。可以top oderby
比如有张学生表和课程表,要求查询15年山东的学生,同时显示课程。
就会 select *
from student as t1 inner jion course as t2 on t1.id=t2.stu_courid
where datediff(year,studate,getdate())=0 and stuaddr like'%山东%'
我们可以先把学生表和课程表连接,求出学生课程表。
作为派生表数据源,select * from (派生表)as 表别名 where datediff(year,studate,getdate())=0 and stuaddr like'%山东%'
公共表表达式
CTE(Common Table Expression)。
http://www.cnblogs.com/CareySon/archive/2011/12/12/2284740.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/aierong/archive/2008/07/31/1257250.html
视图
为了使T-SQL代码更加简洁和可读,在一个查询中引用另外的结果集都是通过视图而不是子查询来进行分解的.但是,视图是作为系统对象存在数据库中,那对于结果集仅仅需要在存储过程或是用户自定义函数中使用一次的时候,使用视图就显得有些奢侈。
事务
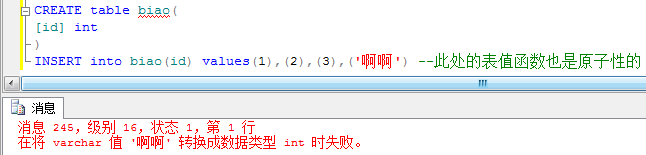
和values()()表值函数类似,原子性的操作,作为一个整体(由多个sql语句组成)执行。每句sql语句就是一个事务。防止一些更改,删除,插入等动作造成错误。
开启事务:begin transaction
控制事务是否整体执行。commit rollback commit rollback和begin之间的所有代码为整体。
事务提交:commit transaction 让这个事务起效,就是执行事务
事务回滚:rollback transaction 不让这个事务起效。
表值函数的原子性执行
事务的原子性执行。
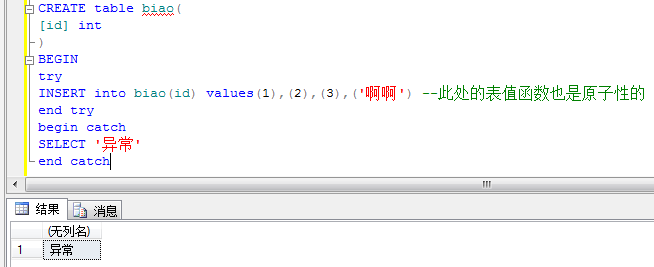
CREATE table biao( [id] int ) begin transaction declare @myerror int; set @myerror=0;--一定赋初值,否则为null +-*/都为null insert into biao(id) values('奥奥') set @myerror=@myerror+@@error; insert into biao(id) values(2) set @myerror=@myerror+@@error; if(@myerror>0) begin rollback end else begin commit end SELECT *FROM biao
此时的第一句insert语句就报出错误,第二句就没有检测。
虽然有一行收到影响,但是select的时候,还是没有执行,被回滚了。但是消息中是报出错误信息
两次的结果相同,都没有执行,区别在错误信息的爆出。
事务的细节:只有commit后才会对数据库的数据造成影响,但是错误还是照常编译报错
对待这些错误信息,会返回到c#中作为异常来出现。需要在数据库本身先判断有异常否,再执行,不要讲这个异常返回到c#程序中。
所以在数据库中的事务中用到异常代码块来判断,有异常回滚,正常commit
异常代码块
所以出现错误就rollback回滚,不出现错误就执行commit。就需要数据库中的异常代码块begin try ***end try begin catch**end catch
所以,事务和begin try end try begin catch end catch 来结合保证原子性操作和对异常信息的处理。
储存过程
存在数据库当中已经编译好的sql语句,提高信息安全性(防止sql注入),减少网络流量
sql是一个脚本语言,先编译后执行。
c#中sql语句需要在dbms中先编译后执行。效率低。而且存在传输问题。
将一个sql语句变成储存过程 -- 视图 内联表值函数 公用表表达式 都需要as来个sql语句引导
create procedure usp_ming alter 修改表结构 视图
as sql语句
as begin 多条sql语句 end go
用的时候直接[exec] usp_ming
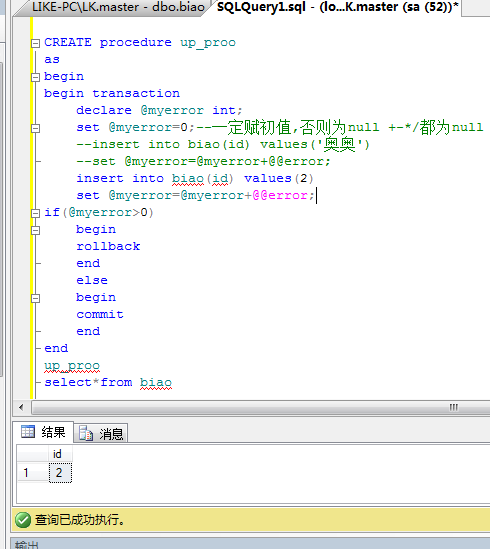
事务和存储过程结合。
存储过程可以包含事务,事务包含异常代码块。
上面都是用户定义的存储过程up_。当然有系统存储过程sp_,xp_
系统存储过程sp_** 查阅sql联机丛书
sp_renamedb更改数据库的名字
sp_database
sp_helpdb
http://www.cnblogs.com/hantianwei/archive/2012/07/23/2605274.html 系统存储过程 大全
有参存储过程:
sp_renamedb [ @dbname = ] 'old_name' , [ @newname = ] 'new_name' --有参存储过程
create procedure up_ming
@变量 类型
as
begin
sql语句
end
分页的存储过程
因为这条语句比较长。最好传输少。用预编译的存储过程效率更高。
1,要生成连续的编号。row_number() over order by(字段) as ming
分页:每页显示几行,现在看第几页 每页5行,看第3页
sql2000,
-CREATE table biao( [id] int ) insert into biao(id) values (2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9),(10), (11),(12),(13),(14),(15),(16),(17),(18),(19),(20), (21),(22),(23),(24),(25),(26),(27) --每页5行,看第3页 每页m行(固定),第n页 select top 5 * from biao where [id] not in (SELECT top ((3-1)*5) id FROM biao) --子查询 --n-1*m
同样我们可以对连续的id用between and
select * from biao where [id] between (5*(3-1)+1) AND (5*3)
记过和上面一样。
但是对一些没有连续id的数据,我们怎么办,我们需要添加一个连续的列。用到的函数row_number() over (order by 字段):根据一个表的字段的顺序来添加一列
create table luanbiao( num int ) insert into luanbiao VALUES(100),(1002),(1300),(1500),(10),(180),(1400), (1080),(170),(108),(192),(210),(5100),(6100),(18700),(17500),(187700), (19700),(1087780),(10270),(10370),(1037530),(10373370),(1373700) select * from luanbiao select *from (select row_number() OVER (ORDER by num)as xuhao, * from luanbiao)as table_zi --列名起名字,表也要起名字。 row_number() over(order by 字段) where table_zi.xuhao between ((3-1)*5+1)and 3*5 --((n-1)*m+1)and n*m
如果没有给加序列号的表起别名,是要出错的。因为 where的字段。 2个select。
1 not in 2 row_number() over order by(zi) as lieming 3 里面select 的表起个as biaoming 4 2个select 5最好携程存储过程。6 where between
7 做尾页 下一页需要总页数。ceiling(7/3.0)记得有个数必须是浮点数。 @Count= count(*)from biao @PageCount=@Count*1.0/@PageSize
7行 每页3行 3页 7/3=2 6行 每页3行 2页
CREATE proc usp_fenye @PageIndex int, --逗号 @PageSize int, @PageCount int output as DECLARE @Count int; SELECT @Count=count(*)FROM Photos; SELECT @PageCount=ceiling(@Count*1.0/@PageSize); SELECT *FROM (SELECT row_number() OVER (order BY Photos.P_Id) as xuhao,* FROM Photos)as biao WHERE xuhao BETWEEN (@PageIndex-1)*@PageSize+1AND @PageIndex*@PageSize; declare @N INT EXEC usp_fenye 2,3,@N output print @N