24、深入浅出MFC学习笔记,Document-View再学习(1)
1、由于CDocument派生自CObject,所以它就有了CObject所支持的性质,如RTTI,动态创建,文件读写(Serialization)。又由于它也派生自CCmdTarget,所以它可以接收来自菜单或工具栏的WM_COMMAND消息。[1,P341]
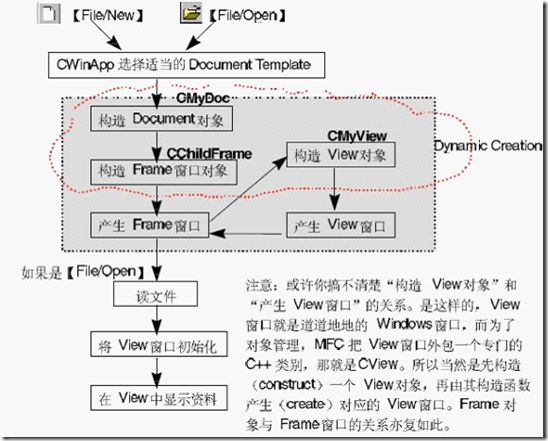
2、Document/View/Frame的产生
对于单文档,派生类型的变量为:
CDocument* m_pOnlyDoc;
如果是多文档,则为:
CPtrList m_docList;
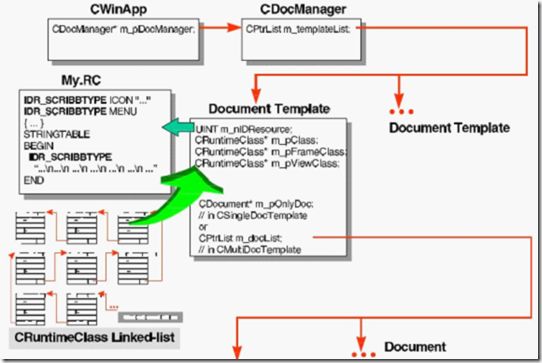
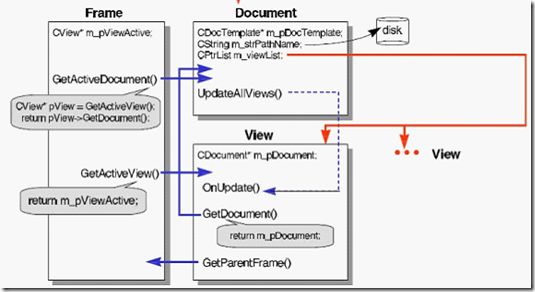
3、CDocTemplate,CDocument,CView,CFrameWnd之间的关系
可以看到,是CWinApp来管理Document Template。[1,P342]
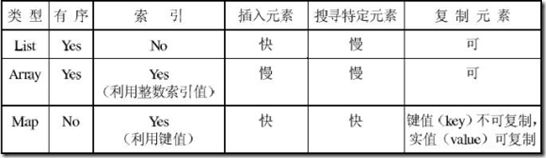
4、MFC Collection Classes的选用
1)MFC Collection Classes分为三种类型:
Array 数组
List 双向链表
Map 对象成对出现
收集的对象中,有两种特别需要说明,一是Ob,一是Ptr:
■Ob表示衍生自CObject的任何对象。MFC提供CObList、CObArray两种类别。
■Ptr表示对象指针。MFC提供CPtrList、CPtrArray两种类别。
当我们考虑使用MFC collection classes 时,除了考虑上述三种类型的特性,还要考虑以下几点:
■是否使用C++ template(对于type-safe 极有帮助)。
■储存于collection class 之中的元素是否要做文件读写动作(Serialize)。
■储存于collection class 之中的元素是否要有转储(dump)和错误诊断能力。
说明:dump为指内存转储文件时一个进程或系统在某一给定的时间的快照。[4]
关于collection classes性质,如是否可文件读写(Serializable),可转储(dump),及是否是类型安全的,[1,P350]整理了一份详细的表格。
2)Template-Based Classes
MFC的collection classes 里头有一些是template-based,对于类型检验的功夫做得比较好。这些类别区分为:
■ 简单型- CArray、CList、CMap。它们都衍生自CObject,所以它们都具备了文件读写、执行时期型别鉴识、动态生成等性质。
■ 类型指针型- CTypedPtrArray、CTypedPtrList、CTypedPtrMap。这些类别要求你在参数中指定基础类别,而基础类别必须是MFC 之中的non-templatepointer collections,例如CObList 或CPtrArray。新类别将继承基础类别的所有性质。
3)使用方法
Template-Based Classes 的使用方法(注意:需包含afxtempl.h)
简单型template-based classes 使用时需要指定参数:
■ CArray<TYPE, ARG_TYPE>
■ CList<TYPE, ARG_TYPE>
■ CMap<KEY, ARG_KEY, VALUE, ARG_VALUE>
其中TYPE 用来指定你希望收集的对象的类型,它们可以是:
■ C++ 基础型别,如int、char、long、float 等等。
■ C++ 结构或类别。
ARG_TYPE 则用来指定函数的参数类型。如:
需要一个int 阵列,数组成员函数(例如Add)的参数是int:
CArray<int, int> m_intArray;
m_intArray.Add(15);
再如,我们需要一个由CPoint 组成的数组,数组成员函数(例如Add)的参数是CPoint:
CArray<CPoint, CPoint> m_pointArray;
CPoint point(18, 64);
m_pointArray.Add(point);
「类型指针」型的template-based classes 使用时亦需指定参数:
■ CTypedPtrArray<BASE_CLASS, TYPE>
■ CTypedPtrList<BASE_CLASS, TYPE>
■ CTypedPtrMap<BASE_CLASS, KEY, VALUE>
其中TYPE 用来指定你希望收集的对象的类型,它们可以是:
■ C++ 基础型别,如int、char、long、float 等等。
■ C++ 结构或类别。
BASE_CLASS 则用来指定基础类别,它可以是任何用来收集指针的non-template collection classes,例如CObList或CObArray或CPtrList或CPtrArray等。
如我们需要一个衍生自CObList 的类别,用来管理一个串行,而串列组成份子为CStroke*:
CTypedPtrList<CObList,CStroke*> m_strokeList;
CStroke* pStrokeItem = new CStroke(20);
m_strokeList.AddTail(pStrokeItem);
5、API
SetCapture
The SetCapture function sets the mouse capture to the specified window belonging
to the current thread. Once a window has captured the mouse, all mouse input is directed
to that window, regardless of whether the cursor is within the borders of that window. Only one window at a time can capture the mouse.
If the mouse cursor is over a window created by another thread, the system will
direct mouse input to the specified window only if a mouse button is down.
6、存储和恢复对象的过程在MFC之称为serialization。负责这件任务的就是MFC CObject类中的一个名为Serialize的虚函数,文件的读和写都通过它。
intel采用little-endian字节排列方式,每一个字组的前后字节系颠倒放置。如0004,在内存中为0400。
示例读写
void CStroke::Serialize(CArchive& ar)
{
if (ar.IsStoring())
{
ar << (WORD)m_nPenWidth;
m_pointArray.Serialize(ar);
}
else
{
WORD w;
ar >> w;
m_nPenWidth = w;
m_pointArray.Serialize(ar);
}
}
7、注册
示例注册
 REGEDIT
REGEDIT
REGEDIT
; This .REG file may be used by your SETUP program.
; If a SETUP program
is
not available, the entries below will be
; registered
in
your InitInstance automatically with a call to
; CWinApp::RegisterShellFileTypes and COleObjectFactory::UpdateRegistryAll.
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.SCB
=
Scribble.Document
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Scribble.Document\shell\open\command
=
SCRIBBLE.EXE
%
1
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Scribble.Document\shell\open\ddeexec
=
[open(
"
%1
"
)]
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Scribble.Document\shell\open\ddeexec\application
=
SCRIBBLE
; note: the application
is
optional
; (it defaults to the app name
in
"
command
"
)
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Scribble.Document
=
Scribb Document
参考
[1] 深入浅出MFC
[2] MFC Technical Notes
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/h6h0eact%28VS.80%29.aspx
[3] http://www.cnblogs.com/mydomain/archive/2011/02/26/1966034.html
[4] http://www.cnblogs.com/awpatp/archive/2010/03/07/1680185.html