css水平垂直居中总结
在网页布局中,垂直居中对齐总是一个绕不过的话题,而且这两种对齐方式由于浏览器渲染方式的不同,也存在很多不同的场景,本文试图将这些场景一一列举并给出解决方案,也是对这个知识点的一点回顾和总结。
1.水平居中
水平居中这个问题首先要搞清楚存在两个条件才能够称之为水平居中,即父元素必须是块级盒子容器,父元素宽度必须已经被设定好,在这两个前提下我们来看水平居中问题。
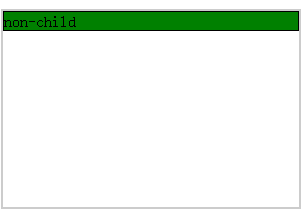
场景1:子元素是块级元素且宽度没有设定
在这种情况下,实际上也不存在水平居中一说,因为子元素是块级元素没有设定宽度,那么它会充满整个父级元素的宽度,即在水平位置上宽度和父元素一致
html代码
<div class="wrap"> <div class="non-child"> non-child </div> </div>
css代码:
.wrap{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .non-child{ border: 1px solid #000; background: green; }
结果:
场景2:子元素是行内元素,子元素宽度是由其内容撑开的
这种情况下解决方案是给父元素设定text-align:center;
html代码:
<div class="wrap center"> <span class="span">1111</span> </div>
css代码
.wrap{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .span{ background: red; } .center{ text-align: center; }
结果:

场景3
子元素是块级元素且宽度已经设定
这种情形存在多种解法,下面一一来列举
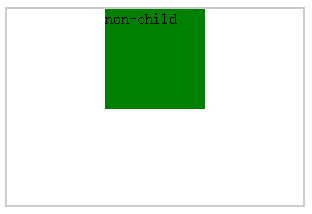
解法1:给子元素添加margin:0 auto;
HTML代码
<div class="wrap"> <div class="child auto"> non-child </div> </div>
css代码:
.child{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: green; box-sizing: border-box; } .auto{ margin:0 auto; } .wrap{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果
解法2:通过计算指定父元素的padding-left或padding-right
HTML代码
<div class="wrap padding"> <div class="child "> non-child </div> </div>
css代码:
.child{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: green; box-sizing: border-box; } .padding{ padding-left: 100px; } .wrap{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果同上,这里计算父元素padding-left或padding-right的方法为(父元素宽度-子元素宽度)/2,注意这里为了计算方便给父元素和子元素都设定了box-sizing:border-box,这样设定的宽度就是包含border+padding+content整个宽度来计算的,如果不设定box-sizing:border-box,浏览器默认是认为content-box,所以设定的宽度仅包含content的宽度,在这种情况下,计算父容器的padding-left或padding-right的方式就是[(父容器content宽度+左右border宽度)-(子容器content宽+水平padding宽+左右border宽)]/2,可以看到较为麻烦,所以这里建议让父元素和子元素都采取border-box.
解法3:计算得到子元素的margin-left或margin-right
html代码
<div class="wrap"> <div class="child margin"> non-child </div> </div>
css代码
.child{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: green; box-sizing: border-box; } .margin{ margin-left:100px; } .wrap{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果同上,这里计算子元素margin-left或margin-right的方法同上。
解法4:
通过子元素相对父元素绝对定位
html代码
<div class="relative"> <div class="child absolute"> non-child </div> </div>
css代码
.relative{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; position: relative; } .absolute{ position: absolute; left:50%; margin-left:-50px; } .child{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: green; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果同上,这里还要设定子元素margin-top为-50是需要消除父元素50%造成的偏移
解法5:利用flex-box
HTML代码
<div class="flex"> <div class="child "> non-child </div> </div>
css代码
.flex{ width: 300px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; display:flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content:center; } .child{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: green; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果同上
2.垂直居中
和水平居中一样,这里要讲垂直居中,首先设定两个条件即父元素是盒子容器且高度已经设定
场景1:子元素是行内元素,高度是由其内容撑开的
这种情况下,需要通过设定父元素的line-height为其高度来使得子元素垂直居中
html代码
<div class="wrap line-height"> <span class="span">111111</span> </div>
css代码
.wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .span{ background: red; } .line-height{ line-height: 300px; }
结果

场景2:子元素是块级元素但是子元素高度没有设定,在这种情况下实际上是不知道子元素的高度的,无法通过计算得到padding或margin来调整,但是还是存在一些解法。
解法1:通过给父元素设定display:table-cell;vertical-align:middle来解决
html代码
<div class="wrap table-cell"> <div class="non-height ">11111</div> </div>
css代码
.table-cell{ display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle; } .non-height{ background: green; } .wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; }
结果

解法2:flexbox
html代码
<div class="wrap flex"> <div class="non-height ">1111</div> </div>
css代码
.wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .non-height{ background: green; } .flex{ display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; }
结果同上
场景3:子元素是块级元素且高度已经设定
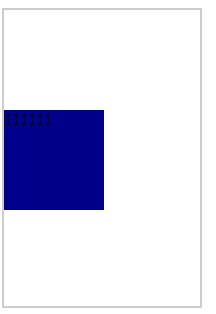
解法1:
计算子元素的margin-top或margin-bottom,计算方法为父(元素高度-子元素高度)/2
html代码
<div class="wrap "> <div class="div1 margin">111111</div> </div>
css代码
.wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .div1{ width:100px ; height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; background: darkblue; } .margin{ margin-top: 100px; }
结果
解法2:计算父元素的padding-top或padding-bottom,计算方法为(父元素高度-子元素高度)/2
html代码
<div class="wrap padding"> <div class="div1 ">111111</div> </div>
css代码
.wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .padding{ padding-top: 100px; } .div1{ width:100px ; height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; background: darkblue; }
结果同上
解法3:利用绝对定位,让子元素相对于父元素绝对定位
html代码
<div class="wrap relative"> <div class="div1 absolute">111111</div> </div>
css代码
.relative{ position: relative; } .absolute{ position: absolute; top:50%; margin-top: -50px; } .wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .div1{ width:100px ; height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; background: darkblue; }
结果同上
解法4:利用flexbox
html代码
<div class="wrap flex"> <div class="div1 ">111111</div> </div>
css代码
.flex{ display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; } .wrap{ width:200px ; height: 300px; border: 2px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } .div1{ width:100px ; height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; background: darkblue; }
结果同上