信息收集之:主动信息收集——服务扫描
信息收集之:主动信息收集——服务扫描
- 3 服务扫描
-
- 3.1 Banner 捕获
-
- 3.1.1 使用 nc 捕获连接时的 Banner 信息
- 3.1.2 使用 python 脚本捕获 Banner 信息
- 3.1.3 dmitry
- 3.1.4 NMAP
- 3.1.5 amap (了解)
- 3.2 服务识别
-
- 3.2.1 NMAP
- 3.2.2 amap(了解)
- 3.3 操作系统识别
-
- 3.3.1 SCAPY 判定
- 3.3.2 NAMP
- 3.3.3 xprobe2(了解)
- 3.3.4 被动操作系统识别
- 3.4 SNMP 分析
-
- 3.4.1 snmp-check
- 3.4.2 onesixtyone
- 3.5 SMB 扫描
-
- 3.5.1 SNMP
- 3.5.2 nbtscan
- 3.5.3 enum4linux
- 3.6 SMTP 扫描
- 3.7 防火墙识别
-
- 3.7.1 端口识别
- 3.7.2 通过 python 脚本探测
- 3.8 负载均衡识别
-
- 3.8.1 lbd
- 3.9 WAF 识别
-
- 3.9.1 wafw00f
郑重声明:
本笔记编写目的只用于安全知识提升,并与更多人共享安全知识,切勿使用笔记中的技术进行违法活动,利用笔记中的技术造成的后果与作者本人无关。倡导维护网络安全人人有责,共同维护网络文明和谐。
3 服务扫描
在进行渗透测试的时候很多网络服务是漏洞频发的高危对象,对网络上的特定服务进行扫描,往往能让我们少走弯路,增加渗透成功的几率。因此很多渗透测试人员在确定了开放端口后,通常会对相应端口上所运行服务的信息进行更深入的挖掘,通常称为服务查点。
识别服务以及操作系统版本的方法
- Banner 捕获
- 服务识别
- 操作系统识别
- SNMP 分析(通过系统内部信息来进行信息的探测和搜索,所以准确性也会比较高)
- 防火墙识别(识别边界防火墙的类型以及过滤机制,从而绕过和躲避它)
3.1 Banner 捕获
主要获取内容:
- 软件开发商
- 软件名称
- 服务类型
- 版本号(直接发现已知的漏洞和弱点)
3.1.1 使用 nc 捕获连接时的 Banner 信息
nc -nv 192.168.100.129 22
3.1.2 使用 python 脚本捕获 Banner 信息
import socket
bangrab = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
bangrab.connect(('192.168.100.129', 22))
print(bangrab.recv(4096))
bangrab.close()
# 若不允许抓取 Banner,recv函数无返回将挂起
# 输出:b'SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1\n'
# ---------------- 脚本升级 -----------------------
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
import select
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("./ban_grab.py [Target IP] [First Port] [Last Port]")
print("Example: ./ban_grab.py 10.0.0.5 1 100")
print("Example will grab banners for TCP ports 1 through 100 on 10.0.0.5")
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
start = int(sys.argv[2])
end = int(sys.argv[3])
for port in range(start, end):
try:
bangrab = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
bangrab.connect((ip, port))
ready = select.select([bangrab], [], [], 1)
if ready[0]:
print("TCP Port " + str(port) + " - " + bangrab.recv(4096).decode('utf-8'))
bangrab.close()
except:
pass
3.1.3 dmitry
dmitry -pb 192.168.31.251 # -b 表示 banner 捕获,没有显示的就是被管理员隐藏了
3.1.4 NMAP
nmap -sT -p20-30 --script=banner.nse 192.168.31.251
# nmap中集成的 script 脚本/usr/share/nmap/scripts/
3.1.5 amap (了解)
amap -B 172.16.36.135 21
amap -B 172.16.36.135 1-65535
amap -B 172.16.36.135 1-65535 | grep on
3.2 服务识别
- Banner信息抓取能力有限,因为管理员可能会隐藏或者修改Banner信息,以此来提升系统的安全性
- NMAP 通过响应特征(signature)分析识别服务,发送系列复杂的探测,相对全面且可靠。
3.2.1 NMAP
nmap -sV -p 80 192.168.31.251
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.8 ((Ubuntu) DAV/2)
3.2.2 amap(了解)
amap 192.168.1.134 80
amap 172.16.36.135 20-30
amap 172.16.36.135 20-30 –q
# 最详细扫描
amap 172.16.36.135 20-30 -qb
3.3 操作系统识别
- 目的:判断目标主机是 Windows 主机还是 Linux 主机
- 原理:通过TTL(Time To Live)存活时间判定操作系统类型
- TTL <= 64: Linux / Unix 主机
- 64 < TTL <= 128: Windows 主机
- TTL = 255: 某些 UNIX 主机
3.3.1 SCAPY 判定
#!/usr/bin/python
from scapy.all import *
import logging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage --/ttl_os.py [IP Address]")
print("Example --/ttl_os.py 192.168.0.1")
print("Example will preform ttl analysis to attempt to determine whether the system is windows or linux/unix")
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
ans = sr1(IP(dst=str(ip)) / ICMP(), timeout=1, verbose=0)
if ans is None:
print("NO response was returned")
elif int(ans[IP].ttl) <= 64:
print("Host is Linux/Unix")
else:
print("Host is Windows")
3.3.2 NAMP
#-O:参数,识别操作系统
nmap -O 192.168.31.251
3.3.3 xprobe2(了解)
xprobe2 1.1.1.1 #结果有误差,不推荐
3.3.4 被动操作系统识别
- IDS
- 抓包分析
- 被动扫描
- p0f:结合ARP地址欺骗识别全网OS
3.4 SNMP 分析
SNMP:“简单网络管理协议”,用于网络管理的协议。SNMP用于网络设备的管理。SNMP 提供了“读”,“写”,“Trap” 操作。由于SNMP经常被错误配置,因此可以通过获取 community string 后,获取大量目标主机的信息。
MIB Tree :SNMP Management Information Base (MIB)树形的网络设备管理功能数据库
Windows 当前系统所有账号:1.3.6.1.4.1.77.1.2.25
NMAP 扫描确定目标主机运行 SNMP 服务:
nmap -sU -p161 192.168.1.108
使用 snmpwalk 进行 SNMP 信息收集:
# 查看目标主机所有 MIB 信息
snmpwalk -c public -v 2c 192.168.31.95
# 查看当前系统所有账号信息
snmpwalk -c public -v 2c 192.168.31.95 1.3.6.1.4.1.77.1.2.25
3.4.1 snmp-check
snmpcheck是一款SNMP信息收集工具
# 图形化界面命令:
snmpcheck
# CLI 界面命令:
snmp-check
snmp-check -c public 192.168.31.95
snmp-check -c public -v 2c -w 192.168.31.95
3.4.2 onesixtyone
onesixtyone 192.168.31.95 public
onesixtyone -c /usr/share/doc/onesixtyone/dict.txt -i hosts.txt -o host_snmp.log -w 10
3.5 SMB 扫描
SMB(全称是Server Message Block)是一个协议名,它能被用于Web连接和客户端与服务器之间的信息沟通。
- 它是微软历史上出现安全问题最多的协议。
- 用于文件共享。实现复杂,默认开放
- SMB常用的端口有两个 139 和 445,较新的操作系统会使用445端口。
SMB1:存在空会话无身份认证访问漏洞,基于此可以收集到以下信息
- 密码策略
- 用户名
- 组名
- 机器名
- 用户、组SID
3.5.1 SNMP
# NMAP 扫描发现运行 SMB 服务主机:
nmap -v -p139,445 192.168.31.1-254 --open
# 获取目标主机的更多信息
nmap -p139,445 --script=smb-os-discovery.nse 192.168.31.253
# 查询目标主机是否存在可利用的漏洞
nmap -v -p139,445 --script=smb-vuln-*.nse --script-args=unsafe=1 192.168.31.253
3.5.2 nbtscan
- 可以扫早期的 Windows 系统
- 可以进行跨网段扫描
nbtscan -r 192.168.1.0/24 # -r:用本地端口137扫描
3.5.3 enum4linux
枚举 windows 信息,可以进行跨网段的扫描,不支持大范围的网路扫描,扫描返回的信息详细
enum4linux -a 192.168.60.10
3.6 SMTP 扫描
- SMTP 扫描最主要的作用是发现目标 STMP 服务器上的邮件账号。
- 通过主动对目标的SMTP(邮件服务器)发动扫描。
- 再配合如 NMAP 工具枚举出邮箱账号,主要的用途是社会工程学,发钓鱼邮箱
# 探测并验证目标主机
nc -nv 192.168.31.251 25
HELO 'hostname'
VRFY '用户名'
AUTH
密码
# 扫描用户账户
# --script=smtp-enum-users.nse 指定用枚举的方式发现用户
# --script-args=smtp-enum-users.methods={VRFY} 指定用什么方式去枚举用户,这里用 VRFY
nmap smtp.163.com -p25 --script=smtp-enum-users.nse --script-args=smtp-enum-users.methods={VRFY}
# 使用 smtp-user-enum 工具进行邮箱用户名枚举
smtp-user-enum -M VRFY -U users.txt -t 10.0.0.1
# 开放中继扫描,容易使邮件服务器变成肉鸡,可以被黑客拿来作跳板机。
nmap smtp.163.com -p25 --script=smtp-open-relay.nse
3.7 防火墙识别
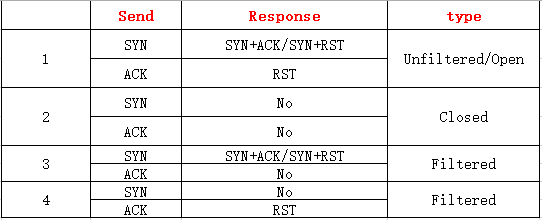
3.7.1 端口识别
通过检查回包,识别端口是否经过防火墙过滤(存在误差)。
- 原理:在检测防火墙是否对一个端口过滤还是关闭,可通过发送两个类型的数据包来判断,第一个是 Syn 包,第二个是 Ack 包。分别根据这两个包的返回来进行确认。正常的请求过程是发 Syn ,回 Syn /Ack ,发 Ack ,回 Fin/Ack 。两个发两个回,所以可以通过两回来确认。这里分为四种情况。
3.7.2 通过 python 脚本探测
#!/usr/bin/python
from scapy.all import *
import logging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage - ./FW_detect.py [Target.IP] [Target Port]")
print("Example - ./FW_detect.py 1.1.1.1 443")
print("Example will determine if filtering exists on port 443 of Host 1.1.1.1")
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
port = int(sys.argv[2])
ACK_response = sr1(IP(dst=ip) / TCP(dport=port, flags="A"), timeout=1, verbose=0)
SYN_response = sr1(IP(dst=ip) / TCP(dport=port, flags="S"), timeout=1, verbose=0)
if (int(SYN_response[TCP].flags) == 18 or int(SYN_response[TCP].flags) == 6) and int(ACK_response[TCP].flags) == 4:
print("Port is unfiltered or open")
elif SYN_response is None and int(ACK_response[TCP].flags) == 4:
print("Stateful filtering in place")
elif (int(SYN_response[TCP].flags) == 18 or int(SYN_response[TCP].flags) == 6) and ACK_response[TCP].flags is None:
print("Stateful filtering in place")
elif (ACK_response is None) and (SYN_response is None):
print("Port is closed")
else:
print("Unable to determine if the port is filtered")
3.8 负载均衡识别
- 广域网负载均衡:
他的原理就是DNS,即使用 DNS 轮询来进行负载均衡,同一个域名会被解析成多个 A 记录解析到多个 IP 地址上。 - 服务器负载均衡:
基于 WEB 的服务,经常使用的是 Nginx、Apache 这种应用层的负载均衡。 - 使用负载均衡设备实现。
- 目的:
在扫描探测的阶段,我们也有必要发现一下目标域名被解析到多少个服务器,这些服务器有可能因为管理员的配置不善,不同的服务器之间他们的安全防护是不一样的,配置也不一样,有的 IP 可能就会存在问题。这时候我们去识别目标系统使用的是什么负载均衡,以及这个负载均衡,他是不是本身存在有漏洞。
3.8.1 lbd
# usage: /usr/bin/lbd domain [port] {https}
lbd www.qq.com
# 基本上大站要么是广域网的、要么是服务器的负载均衡,即使扫描到同一个域名只解析到一个ip地址,这个地址对应的设备也基本是负载均衡设备,而不是他真实的服务器
# 这些负载均衡设备将用户的请求转发到真正的后端服务器上,通过这种方式把后端服务器隐藏起来,让工具者没有办法发现
# 另外在负载均衡设备上有可能会存在一些安全过滤防护机制,你的攻击的流量先发给这些设备,这些设备会过滤掉,清洗一下再发给后端服务器。
3.9 WAF 识别
Web应用防护系统(也称为:网站应用级入侵防御系统。英文:Web Application Firewall,简称:WAF)。
Web应用防火墙是通过执行一系列针对HTTP/HTTPS的安全策略来专门为Web应用提供保护的一款产品。
3.9.1 wafw00f
# 查看当前所支持的 WAF 品牌
wafw00f -l
# 查看当前
wafw00f https://www.qq.com