风格迁移0-08:stylegan-源码无死角解读(4)-G_synthesis,G_mapping详解
以下链接是个人关于stylegan所有见解,如有错误欢迎大家指出,我会第一时间纠正,如有兴趣可以加微信:a944284742相互讨论技术。若是帮助到了你什么,一定要记得点赞奥!因为这是对我最大的鼓励。
风格迁移0-08:stylegan-目录-史上最全:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43013761/article/details/100895333
前言
该小节,我会为大家讲解G_mapping,G_synthesis网络,分别为下图红框中的两个部分:
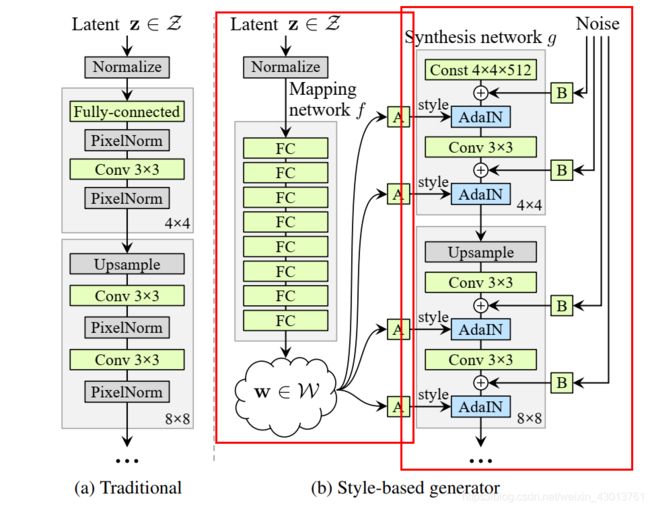
再源码中,先构建的是G_synthesis网络,即右边红框的网络,但是为了方便大家的理解,我决定先讲解G_mapping网络,即左边的网络。那么下面就开始吧,注意下面的两个网络都再源码的training/networks_stylegan.py文件中。
G_mapping注释
下面是对G_mapping函数的注释
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Mapping network used in the StyleGAN paper,
# 该函数,再我们的架构中只要注意到dlatent_broadcast参数为18即可,latents_in其通过映射之后,
# 得到论文W,W再进行广播,得到18个512维的style,即输出为[?,18,512]
def G_mapping(
latents_in, # First input: Latent vectors (Z) [minibatch, latent_size].
labels_in, # Second input: Conditioning labels [minibatch, label_size].
latent_size = 512, # Latent vector (Z) dimensionality.
label_size = 0, # Label dimensionality, 0 if no labels.
dlatent_size = 512, # Disentangled latent (W) dimensionality.
dlatent_broadcast = None, # Output disentangled latent (W) as [minibatch, dlatent_size] or [minibatch, dlatent_broadcast, dlatent_size].
mapping_layers = 8, # Number of mapping layers.
mapping_fmaps = 512, # Number of activations in the mapping layers.
mapping_lrmul = 0.01, # Learning rate multiplier for the mapping layers.
mapping_nonlinearity = 'lrelu', # Activation function: 'relu', 'lrelu'.
use_wscale = True, # Enable equalized learning rate?
normalize_latents = True, # Normalize latent vectors (Z) before feeding them to the mapping layers?
dtype = 'float32', # Data type to use for activations and outputs.
**_kwargs): # Ignore unrecognized keyword args.
act, gain = {
'relu': (tf.nn.relu, np.sqrt(2)), 'lrelu': (leaky_relu, np.sqrt(2))}[mapping_nonlinearity]
# Inputs.
latents_in.set_shape([None, latent_size])
labels_in.set_shape([None, label_size])
latents_in = tf.cast(latents_in, dtype)
labels_in = tf.cast(labels_in, dtype)
x = latents_in
# Embed labels and concatenate them with latents.
if label_size:
with tf.variable_scope('LabelConcat'):
w = tf.get_variable('weight', shape=[label_size, latent_size], initializer=tf.initializers.random_normal())
y = tf.matmul(labels_in, tf.cast(w, dtype))
x = tf.concat([x, y], axis=1)
# Normalize latents.
if normalize_latents:
x = pixel_norm(x)
# Mapping layers.
for layer_idx in range(mapping_layers):
with tf.variable_scope('Dense%d' % layer_idx):
fmaps = dlatent_size if layer_idx == mapping_layers - 1 else mapping_fmaps
x = dense(x, fmaps=fmaps, gain=gain, use_wscale=use_wscale, lrmul=mapping_lrmul)
x = apply_bias(x, lrmul=mapping_lrmul)
x = act(x)
# Broadcast.
if dlatent_broadcast is not None:
with tf.variable_scope('Broadcast'):
x = tf.tile(x[:, np.newaxis], [1, dlatent_broadcast, 1])
# Output为[?, 18, 512]
assert x.dtype == tf.as_dtype(dtype)
return tf.identity(x, name='dlatents_out')
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Synthesis network used in the StyleGAN paper.
大家不要奇怪,为什么注释得这么粗糙,因为太过于简单了,所以就没有注释了,其主要就是经过八个全连接操作,然后通过dlatent_broadcast进行广播,得到[?, 18, 512]的矩阵。这里的[?, 18, 512]对应则上图中左框的部分,本人感觉这里没有进行反射变换A的操作。也就是只完成了下面部分(蓝框部分):
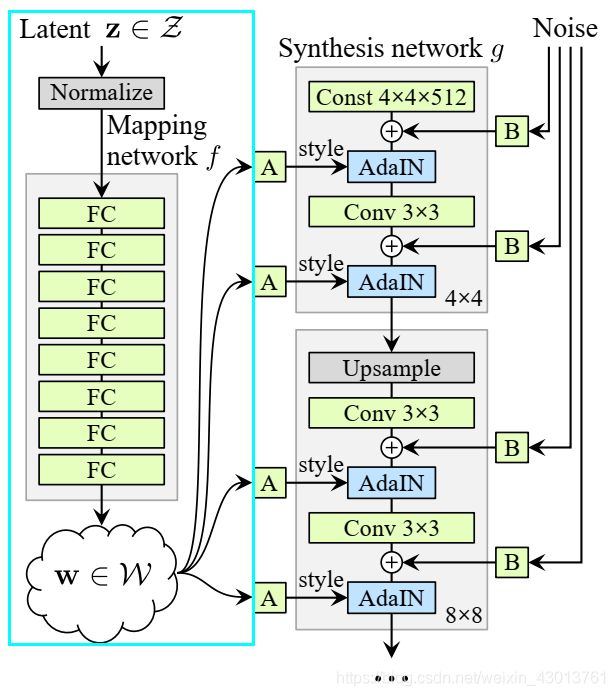
这样我们就得到了[?, 18, 512]的输出,后面与G_synthesis网络搭配使用。
G_synthesis注释
现在我们来看看G_synthesis网络,即下图中框出的网络:
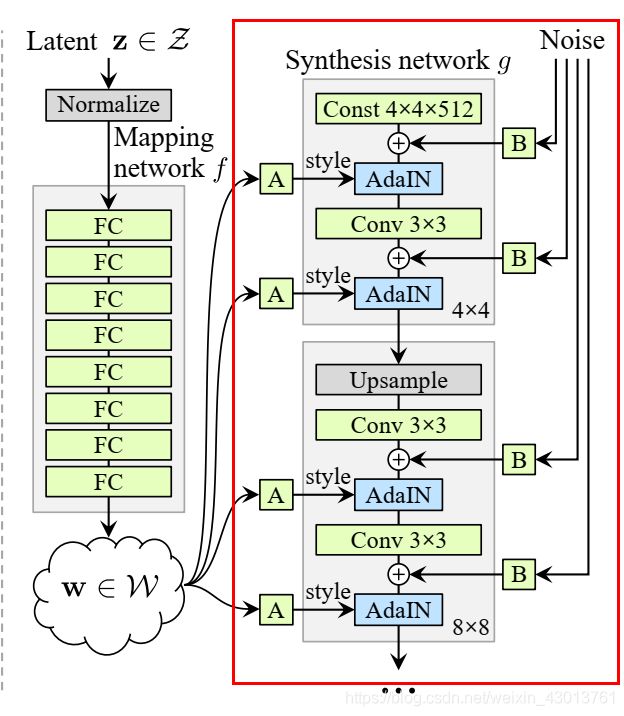
下面是G_synthesis函数源码的注释(请大家找到G_synthesis函数看起):
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pixelwise feature vector normalization.
def pixel_norm(x, epsilon=1e-8):
with tf.variable_scope('PixelNorm'):
epsilon = tf.constant(epsilon, dtype=x.dtype, name='epsilon')
return x * tf.rsqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(x), axis=1, keepdims=True) + epsilon)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Instance normalization.
def instance_norm(x, epsilon=1e-8):
assert len(x.shape) == 4 # NCHW
with tf.variable_scope('InstanceNorm'):
orig_dtype = x.dtype
x = tf.cast(x, tf.float32)
# 每个减去所有总像素的均值
x -= tf.reduce_mean(x, axis=[2,3], keepdims=True)
# 创建一个常量epsilon
epsilon = tf.constant(epsilon, dtype=x.dtype, name='epsilon')
x *= tf.rsqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(x), axis=[2,3], keepdims=True) + epsilon)
x = tf.cast(x, orig_dtype)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Style modulation.
def style_mod(x, dlatent, **kwargs):
# 第一次该函数被调用时为x[?,512,4,4],dlatent(?,5112)
with tf.variable_scope('StyleMod'):
# dlatent通过dense全链接得到W,再转化论文中style,[?,1024],后面变成[?,2,512,1,1]
style = apply_bias(dense(dlatent, fmaps=x.shape[1]*2, gain=1, **kwargs))
# [?,2,512,1,1],注意每个分辨率都对应着两个
style = tf.reshape(style, [-1, 2, x.shape[1]] + [1] * (len(x.shape) - 2))
# x[?,512,4,4] * ([?,1,512,1,1]+1) + [?,1,512,1,1],这里的style[:,0]时论文中的Ys,i style[:,1]为论文中的Yb,j
return x * (style[:,0] + 1) + style[:,1]
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Synthesis network used in the StyleGAN paper.
def G_synthesis(
dlatents_in, # Input: Disentangled latents (W) [minibatch, num_layers, dlatent_size].
dlatent_size = 512, # Disentangled latent (W) dimensionality.
num_channels = 3, # Number of output color channels.
resolution = 1024, # Output resolution.
fmap_base = 8192, # Overall multiplier for the number of feature maps.
fmap_decay = 1.0, # log2 feature map reduction when doubling the resolution.
fmap_max = 512, # Maximum number of feature maps in any layer.
use_styles = True, # Enable style inputs?
const_input_layer = True, # First layer is a learned constant?
use_noise = True, # Enable noise inputs?
randomize_noise = True, # True = randomize noise inputs every time (non-deterministic), False = read noise inputs from variables.
nonlinearity = 'lrelu', # Activation function: 'relu', 'lrelu'
use_wscale = True, # Enable equalized learning rate?
use_pixel_norm = False, # Enable pixelwise feature vector normalization?
use_instance_norm = True, # Enable instance normalization?
dtype = 'float32', # Data type to use for activations and outputs.
fused_scale = 'auto', # True = fused convolution + scaling, False = separate ops, 'auto' = decide automatically.
blur_filter = [1,2,1], # Low-pass filter to apply when resampling activations. None = no filtering.
structure = 'auto', # 'fixed' = no progressive growing, 'linear' = human-readable, 'recursive' = efficient, 'auto' = select automatically.
is_template_graph = False, # True = template graph constructed by the Network class, False = actual evaluation.
force_clean_graph = False, # True = construct a clean graph that looks nice in TensorBoard, False = default behavior.
**_kwargs): # Ignore unrecognized keyword args.
# 根据图片分辨率,求得其图片是2的resolution_log2次方,在这里输入图片为1024,即为2的10次方。即resolution_log2=10
resolution_log2 = int(np.log2(resolution))
assert resolution == 2**resolution_log2 and resolution >= 4
# 可以看到默认值fmap_base为8192, 8192/512=18,这里主要是根据stage参数,求得有多少个f,可以说是全连接fc的数目,或者W通过反正变化成A的数目
def nf(stage): return min(int(fmap_base / (2.0 ** (stage * fmap_decay))), fmap_max)
# 应该是一个滤波模糊操作
def blur(x): return blur2d(x, blur_filter) if blur_filter else x
if is_template_graph: force_clean_graph = True
if force_clean_graph: randomize_noise = False
if structure == 'auto': structure = 'linear' if force_clean_graph else 'recursive'
# 激活函数
act, gain = {
'relu': (tf.nn.relu, np.sqrt(2)), 'lrelu': (leaky_relu, np.sqrt(2))}[nonlinearity]
# 前面知道resolution_log2为10,根据论文我们可以知道,其为styles为8层
num_layers = resolution_log2 * 2 - 2
# 如果use_styles不为真,则所有的styles都是相同的一个
num_styles = num_layers if use_styles else 1
images_out = None
# Primary inputs.
# 这里的输入就是styles或者说W,用于控制图片合成的风格(None, 18, 512)
dlatents_in.set_shape([None, num_styles, dlatent_size])
dlatents_in = tf.cast(dlatents_in, dtype)
lod_in = tf.cast(tf.get_variable('lod', initializer=np.float32(0), trainable=False), dtype)
# Noise inputs.
# 从论文我们可以知道每一个噪音对应一个style,并且噪音是随机初始化的,范围为[-1,1]之间
noise_inputs = []
if use_noise:
for layer_idx in range(num_layers):
res = layer_idx // 2 + 2
shape = [1, use_noise, 2**res, 2**res]
noise_inputs.append(tf.get_variable('noise%d' % layer_idx, shape=shape, initializer=tf.initializers.random_normal(), trainable=False))
# Things to do at the end of each layer.
# 该函数主要整合style以及噪声
def layer_epilogue(x, layer_idx):
if use_noise:
# 把噪声加入图片
x = apply_noise(x, noise_inputs[layer_idx], randomize_noise=randomize_noise )
# 加上一个偏置b
x = apply_bias(x)
# 一个激活函数,rule或者prule
x = act(x)
# 是否把像素进行正则化,使其范围到[-1,1]
if use_pixel_norm:
x = pixel_norm(x)
# 实例归一化,对HW进行归一化,保证图片之间的独立性,同时加快生成的收敛
if use_instance_norm:
x = instance_norm(x)
# 如果使用了style,则让dlatents_in经过反射A,加入到AdaIN,实现对风格的调整
if use_styles:
x = style_mod(x, dlatents_in[:, layer_idx], use_wscale=use_wscale)
return x
# Early layers.
with tf.variable_scope('4x4'):
# 这里是论文style net的第一层,
if const_input_layer:
with tf.variable_scope('Const'):
# nf(1),是为了求出第一层,对应的全链接层为1层,所以x为[1,512,4,4]
x = tf.get_variable('const', shape=[1, nf(1), 4, 4], initializer=tf.initializers.ones())
# 通过layer_epilogue加入了style以及噪音
x = layer_epilogue(tf.tile(tf.cast(x, dtype), [tf.shape(dlatents_in)[0], 1, 1, 1]), 0)
else:
with tf.variable_scope('Dense'):
x = dense(dlatents_in[:, 0], fmaps=nf(1)*16, gain=gain/4, use_wscale=use_wscale) # tweak gain to match the official implementation of Progressing GAN
x = layer_epilogue(tf.reshape(x, [-1, nf(1), 4, 4]), 0)
with tf.variable_scope('Conv'):
# 经过一个卷积之后再接一个layer_epilogue
x = layer_epilogue(conv2d(x, fmaps=nf(1), kernel=3, gain=gain, use_wscale=use_wscale), 1)
# Building blocks for remaining layers.
# 指定一个分辨率对应的层数,然后进行构建,
def block(res, x): # res = 3..resolution_log2
with tf.variable_scope('%dx%d' % (2**res, 2**res)):
with tf.variable_scope('Conv0_up'):
x = layer_epilogue(blur(upscale2d_conv2d(x, fmaps=nf(res-1), kernel=3, gain=gain, use_wscale=use_wscale, fused_scale=fused_scale)), res*2-4)
with tf.variable_scope('Conv1'):
x = layer_epilogue(conv2d(x, fmaps=nf(res-1), kernel=3, gain=gain, use_wscale=use_wscale), res*2-3)
return x
# 进行输出,把像素转化为RGB
def torgb(res, x): # res = 2..resolution_log2
lod = resolution_log2 - res
with tf.variable_scope('ToRGB_lod%d' % lod):
return apply_bias(conv2d(x, fmaps=num_channels, kernel=1, gain=1, use_wscale=use_wscale))
# Fixed structure: simple and efficient, but does not support progressive growing.
# 简单高效,只再最后一层输出图像,并且不能增长,也即使分辨率固定没有上采样
if structure == 'fixed':
for res in range(3, resolution_log2 + 1):
x = block(res, x)
images_out = torgb(resolution_log2, x)
# Linear structure: simple but inefficient.
# 线性结构,每个stage都会输出RGB图像,并且分辨率随着层次增加,源码使用的模式为该模式
if structure == 'linear':
images_out = torgb(2, x)
for res in range(3, resolution_log2 + 1):
lod = resolution_log2 - res
x = block(res, x)
img = torgb(res, x)
images_out = upscale2d(images_out)
with tf.variable_scope('Grow_lod%d' % lod):
images_out = tflib.lerp_clip(img, images_out, lod_in - lod)
# Recursive structure: complex but efficient.
# 这个没有看懂,不过我运行的也没有调用
if structure == 'recursive':
def cset(cur_lambda, new_cond, new_lambda):
return lambda: tf.cond(new_cond, new_lambda, cur_lambda)
def grow(x, res, lod):
y = block(res, x)
img = lambda: upscale2d(torgb(res, y), 2**lod)
img = cset(img, (lod_in > lod), lambda: upscale2d(tflib.lerp(torgb(res, y), upscale2d(torgb(res - 1, x)), lod_in - lod), 2**lod))
if lod > 0: img = cset(img, (lod_in < lod), lambda: grow(y, res + 1, lod - 1))
return img()
images_out = grow(x, 3, resolution_log2 - 3)
assert images_out.dtype == tf.as_dtype(dtype)
return tf.identity(images_out, name='images_out')
其实,我感觉自己的注释已经很详细了,但是我觉得还是有必要说一下总体的流程:
其网络首先是定义了第一层,即:
with tf.variable_scope('4x4'):
......
......
然后根据structure参数,对网络结构进行选择,我们的网络使用的是structure == ‘linear’。要注意函数:
def layer_epilogue(x, layer_idx):
其主要工作完成了红框中的如下部分:

大家可能对反射变换A不是很理解,其实反射变换A就是一个全连接层,这样就能通过网络迭代,学习到自己层相关的权重参数,其实现是再style_mod函数中的:
# dlatent通过dense全链接得到W,再转化论文中style,[?,1024],后面变成[?,2,512,1,1]
style = apply_bias(dense(dlatent, fmaps=x.shape[1]*2, gain=1, **kwargs))
具体实现为dense函数:
# Fully-connected layer.
def dense(x, fmaps, **kwargs):
if len(x.shape) > 2:
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, np.prod([d.value for d in x.shape[1:]])])
w = get_weight([x.shape[1].value, fmaps], **kwargs)
w = tf.cast(w, x.dtype)
return tf.matmul(x, w)
相信到这里,大家应该算是比较了解整体的架构了,如果有细节地方不是很了解的,可以加我微信,进行详细的讨论沟通。