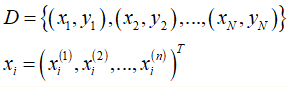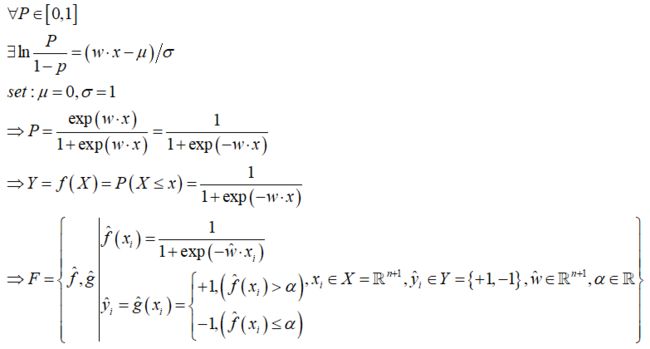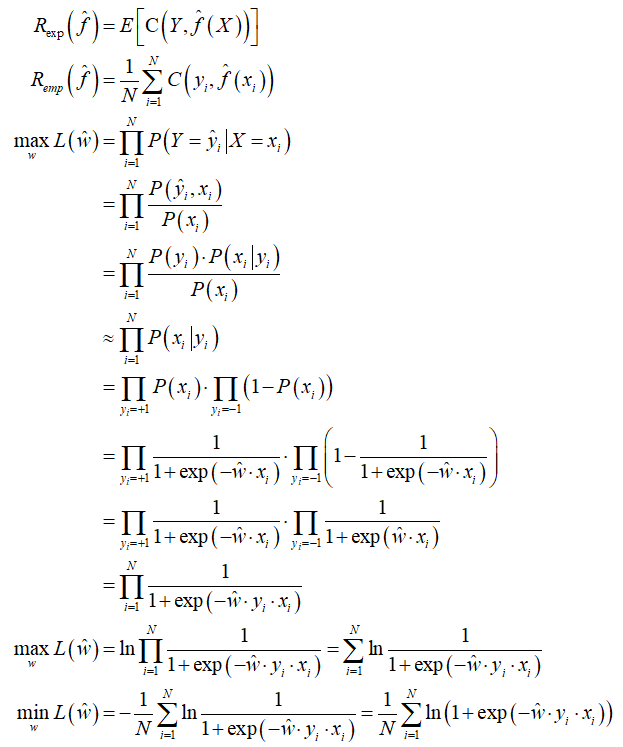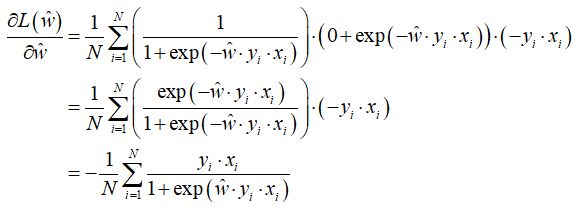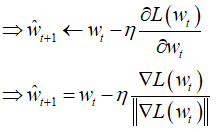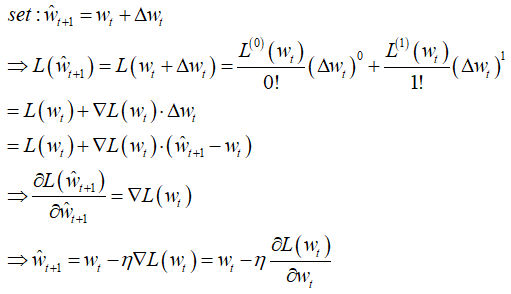返回主页
Logistic Regression 是统计学习的经典分类算法,是一种 对数线性模型。
1、数据集与特征空间
2、假设空间
Logistic Regression 的假设函数由 对数几率(log odds) 假设推导而来。
3、目标函数及其推导
从极大似然估计的角度推出 Logistic Regression 的目标函数。
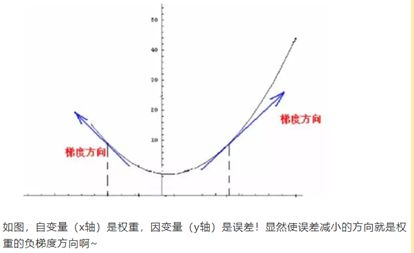
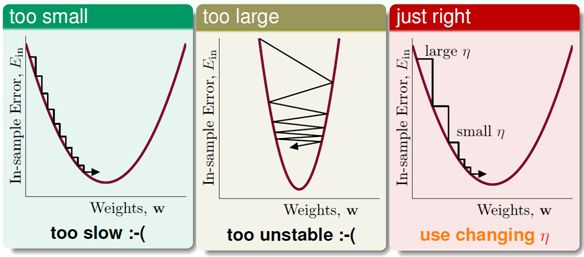
4、优化算法(梯度下降)
梯度下降由泰勒一阶展开推导而来,同理,可以由二阶展开推出牛顿法以及拟牛顿法,此处不予赘述
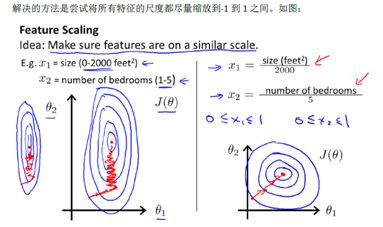
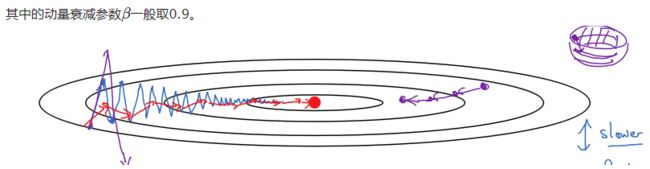
在实际应用中,使用逻辑斯回归建议进行如下处理:
1、特征标准化(z-scale),使所有特征的尺度缩放到 [-1,+1] 之间,避免出现锯齿效应,影响收敛速度。
2、考虑加入动量(Momentum),抑制震荡,加快收敛速度。
手写算法并与 Sklearn 进行对比
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class LogitRegModel(object):
def __init__(self, max_iter=5000, eta=0.01, alpha=0.5, beta=0.9):
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.eta = eta
self.alpha = alpha
self.beta = beta
def z_scale(self, x_train):
'''z标准化,在动用距离度量的算法中,必须先进行标准化以消除数据量纲的影响'''
mu = np.mean(x_train, axis=0)
std = np.std(x_train, axis=0)
return mu, std
def data_transform(self, mu, std, x_train, x_test):
'''
数据变换
1、执行标准化操作
2、插入截距项
'''
x_train_scale = (x_train - mu) / std
x_test_scale = (x_test - mu) / std
intercept_train = np.ones(x_train_scale.shape[0]).reshape(-1, 1)
intercept_test = np.ones(x_test_scale.shape[0]).reshape(-1, 1)
x_train_scale = np.concatenate([intercept_train, x_train_scale], axis=1)
x_test_scale = np.concatenate([intercept_test, x_test_scale], axis=1)
return x_train_scale, x_test_scale
def get_loss(self, x_train_scale, y_train, w):
'''计算损失函数值'''
loss = np.mean(np.log(1.0 + np.exp(-x_train_scale.dot(w) * y_train)))
return loss
def get_derivative(self, x_train_scale, y_train, w, dv):
'''计算梯度(含动量, beta = 0 则为原始梯度下降)'''
fenzi = -y_train * x_train_scale
fenmu = 1.0 + np.exp(x_train_scale.dot(w) * y_train)
dw = np.mean(fenzi / fenmu, axis=0)
dw = dw.reshape(-1, 1)
dv = self.beta * dv + (1 - self.beta) * dw
return dv
def fit(self, x_train_scale, y_train):
'''模型训练'''
# 参数初始化
w = np.zeros(x_train_scale.shape[1]) + 0.001
w = w.reshape(-1, 1)
dv = np.zeros_like(w)
# 损失值保存列表
loss_res = []
# 迭代
for epoch in range(self.max_iter):
# 计算梯度
dv = self.get_derivative(x_train_scale, y_train, w, dv)
# 梯度下降
w = w - self.eta * dv
# 更新损失值
loss = self.get_loss(x_train_scale, y_train, w)
loss_res.append(loss)
return w, loss_res
def predict(self, x_test_scale, w):
'''模型预测'''
y_pred_probs = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x_test_scale.dot(w)))
y_pred = np.where(y_pred_probs > self.alpha, 1, -1)
return y_pred_probs, y_pred
def get_score(self, y_true, y_pred):
'''模型评估'''
score = sum(y_true == y_pred) / len(y_true)
return score
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 构造二分类数据集
N = 200; n = 4
x1 = np.random.uniform(low=1, high=5, size=[N, n]) + np.random.randn(N, n)
y1 = np.tile(-1, N)
x2 = np.random.uniform(low=5, high=10, size=[N, n]) + np.random.randn(N, n)
y2 = np.tile(1, N)
x = np.concatenate([x1, x2], axis=0)
y = np.concatenate([y1, y2]).reshape(-1, 1)
x, y = shuffle(x, y, random_state=0)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2)
# 手写模型
model = LogitRegModel(max_iter=5000, eta=0.01, alpha=0.5, beta=0.9)
mu, std = model.z_scale(x_train)
x_train_scale, x_test_scale = model.data_transform(mu, std, x_train, x_test)
w, loss_res = model.fit(x_train_scale, y_train)
print(f"LogitRegModel 参数:\n{w}")
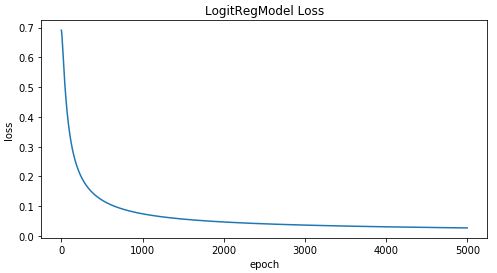
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
ax.plot(loss_res)
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("loss")
plt.title("LogitRegModel Loss")
plt.show()
y_pred_probs, y_pred = model.predict(x_test_scale, w)
score = model.get_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"LogitRegModel 预测准确率:{score}")
# sklean
scale = StandardScaler(with_mean=True, with_std=True)
scale.fit(x_train)
x_train_scale = scale.transform(x_train)
x_test_scale = scale.transform(x_test)
clf = LogisticRegression(fit_intercept=True, solver="lbfgs", max_iter=5000, multi_class="ovr")
clf.fit(x_train_scale, y_train)
clf.coef_
clf.intercept_
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test_scale).reshape(-1, 1)
score = sum(y_test == y_pred) / len(y_test)
print(f"Sklearn 预测准确率:{score}")
LogitRegModel 参数:
[[0.18014117]
[1.63708775]
[1.64705508]
[1.5463744 ]
[1.61056801]]
LogitRegModel 预测准确率:[0.975]
array([[1.83258875, 1.93575921, 1.69735311, 1.87150825]])
array([0.39294385])
Sklearn 预测准确率:[0.975]
返回主页