在Spring Bean实例过程中,如何使用反射和递归处理的Bean属性填充?
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!
《Spring 手撸专栏》目录
- 第 1 章:开篇介绍,我要带你撸 Spring 啦!
- 第 2 章:小试牛刀,实现一个简单的Bean容器
- 第 3 章:初显身手,运用设计模式,实现 Bean 的定义、注册、获取
- 第 4 章:崭露头角,基于Cglib实现含构造函数的类实例化策略
- 第 5 章:一鸣惊人,为Bean对象注入属性和依赖Bean的功能实现
- 第 6 章:待归档…
一、前言
超卖、掉单、幂等,你的程序总是不抗揍!
想想,运营已经对外宣传了七八天的活动,满心欢喜的等着最后一天页面上线对外了,突然出现了一堆异常、资损、闪退,而用户流量稍纵即逝,最后想死的心都有!
就编程开发来讲,丢三落四、乱码七糟,可能这就是大部分初级程序员日常开发的真实写照,在即使有测试人员验证的情况下,也会出现带Bug上线的现象,只不过是当时没有发现而已!因为是人写代码,就一定会有错误,即使是老码农
就程序Bug来讲,会包括产品PRD流程上的Bug、运营配置活动时候的Bug、研发开发时功能实现的Bug、测试验证时漏掉流程的Bug、上线过程中运维服务相关配置的Bug,而这些其实都可以通过制定的流程规范和一定的研发经验积累,慢慢尽可能减少。
而另外一类是沟通留下的Bug,通常情况下业务提需求、产品定方案、研发做实现,最终还要有UI、测试、运营、架构等等各个环节的人员参与到一个项目的承接、开发到上线运行,而在这一群人需要保持一个统一的信息传播其实是很难的。比如在项目开发中期,运营给产品说了一个新增的需求,产品觉得功能也不大,随即找到对应的前端研发加个逻辑,但没想到可能也影响到了后端的开发和测试的用例。最后功能虽然是上线了,可并不在整个产研测的需求覆盖度范围里,也就隐形的埋下了一个坑。
所以,如果你想让你的程序很抗揍,接的住农夫三拳,那么你要做的就不只是一个单纯的搬砖码农!
二、目标
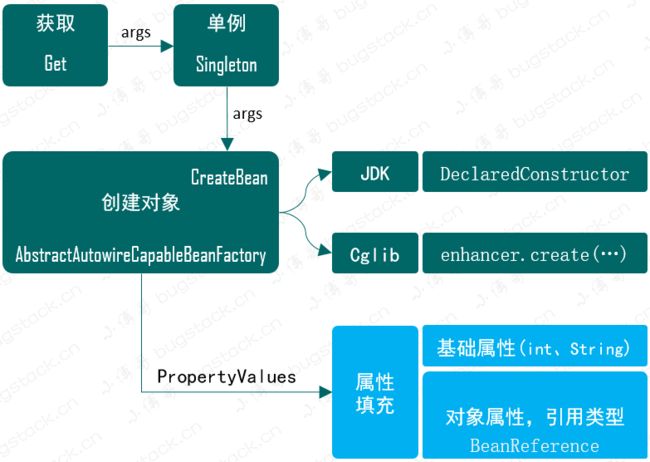
首先我们回顾下这几章节都完成了什么,包括:实现一个容器、定义和注册Bean、实例化Bean,按照是否包含构造函数实现不同的实例化策略,那么在创建对象实例化这我们还缺少什么?其实还缺少一个关于类中是否有属性的问题,如果有类中包含属性那么在实例化的时候就需要把属性信息填充上,这样才是一个完整的对象创建。
对于属性的填充不只是 int、Long、String,还包括还没有实例化的对象属性,都需要在 Bean 创建时进行填充操作。不过这里我们暂时不会考虑 Bean 的循环依赖,否则会把整个功能实现撑大,这样新人学习时就把握不住了,待后续陆续先把核心功能实现后,再逐步完善
三、设计
鉴于属性填充是在 Bean 使用 newInstance 或者 Cglib 创建后,开始补全属性信息,那么就可以在类 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的 createBean 方法中添加补全属性方法。这部分大家在实习的过程中也可以对照Spring源码学习,这里的实现也是Spring的简化版,后续对照学习会更加易于理解
- 属性填充要在类实例化创建之后,也就是需要在
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的 createBean 方法中添加applyPropertyValues操作。 - 由于我们需要在创建Bean时候填充属性操作,那么就需要在 bean 定义 BeanDefinition 类中,添加 PropertyValues 信息。
- 另外是填充属性信息还包括了 Bean 的对象类型,也就是需要再定义一个 BeanReference,里面其实就是一个简单的 Bean 名称,在具体的实例化操作时进行递归创建和填充,与 Spring 源码实现一样。Spring 源码中 BeanReference 是一个接口
四、实现
1. 工程结构
small-spring-step-04
└── src
├── main
│ └── java
│ └── cn.bugstack.springframework.beans
│ ├── factory
│ │ ├── factory
│ │ │ ├── BeanDefinition.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanReference.java
│ │ │ └── SingletonBeanRegistry.java
│ │ ├── support
│ │ │ ├── AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── AbstractBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanDefinitionRegistry.java
│ │ │ ├── CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ │ ├── DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
│ │ │ ├── InstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ │ └── SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ └── BeanFactory.java
│ ├── BeansException.java
│ ├── PropertyValue.java
│ └── PropertyValues.java
└── test
└── java
└── cn.bugstack.springframework.test
├── bean
│ ├── UserDao.java
│ └── UserService.java
└── ApiTest.java
工程源码:公众号「bugstack虫洞栈」,回复:Spring 专栏,获取完整源码
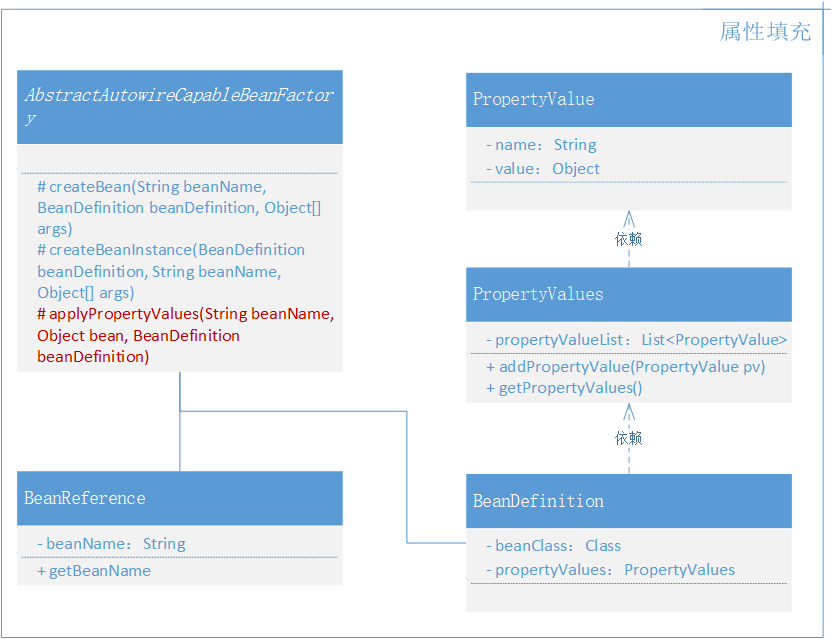
Spring Bean 容器类关系,如图 5-2
- 本章节中需要新增加3个类,
BeanReference(类引用)、PropertyValue(属性值)、PropertyValues(属性集合),分别用于类和其他类型属性填充操作。 - 另外改动的类主要是
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,在 createBean 中补全属性填充部分。
2. 定义属性
cn.bugstack.springframework.beans.PropertyValue
public class PropertyValue {
private final String name;
private final Object value;
public PropertyValue(String name, Object value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
// ...get/set
}
cn.bugstack.springframework.beans.PropertyValues
public class PropertyValues {
private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList = new ArrayList<>();
public void addPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) {
this.propertyValueList.add(pv);
}
public PropertyValue[] getPropertyValues() {
return this.propertyValueList.toArray(new PropertyValue[0]);
}
public PropertyValue getPropertyValue(String propertyName) {
for (PropertyValue pv : this.propertyValueList) {
if (pv.getName().equals(propertyName)) {
return pv;
}
}
return null;
}
}
- 这两个类的作用就是创建出一个用于传递类中属性信息的类,因为属性可能会有很多,所以还需要定义一个集合包装下。
3. Bean定义补全
cn.bugstack.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition
public class BeanDefinition {
private Class beanClass;
private PropertyValues propertyValues;
public BeanDefinition(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.propertyValues = new PropertyValues();
}
public BeanDefinition(Class beanClass, PropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.propertyValues = propertyValues != null ? propertyValues : new PropertyValues();
}
// ...get/set
}
- 在 Bean 注册的过程中是需要传递 Bean 的信息,在几个前面章节的测试中都有所体现
new BeanDefinition(UserService.class, propertyValues); - 所以为了把属性一定交给 Bean 定义,所以这里填充了 PropertyValues 属性,同时把两个构造函数做了一些简单的优化,避免后面 for 循环时还得判断属性填充是否为空。
4. Bean 属性填充
cn.bugstack.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory {
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy();
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
Object bean = null;
try {
bean = createBeanInstance(beanDefinition, beanName, args);
// 给 Bean 填充属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Instantiation of bean failed", e);
}
addSingleton(beanName, bean);
return bean;
}
protected Object createBeanInstance(BeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName, Object[] args) {
Constructor constructorToUse = null;
Class<?> beanClass = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor ctor : declaredConstructors) {
if (null != args && ctor.getParameterTypes().length == args.length) {
constructorToUse = ctor;
break;
}
}
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(beanDefinition, beanName, constructorToUse, args);
}
/**
* Bean 属性填充
*/
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
try {
PropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
String name = propertyValue.getName();
Object value = propertyValue.getValue();
if (value instanceof BeanReference) {
// A 依赖 B,获取 B 的实例化
BeanReference beanReference = (BeanReference) value;
value = getBean(beanReference.getBeanName());
}
// 属性填充
BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, name, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Error setting property values:" + beanName);
}
}
public InstantiationStrategy getInstantiationStrategy() {
return instantiationStrategy;
}
public void setInstantiationStrategy(InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy) {
this.instantiationStrategy = instantiationStrategy;
}
}
- 这个类的内容稍微有点长,主要包括三个方法:createBean、createBeanInstance、applyPropertyValues,这里我们主要关注 createBean 的方法中调用的 applyPropertyValues 方法。
- 在 applyPropertyValues 中,通过获取
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues()循环进行属性填充操作,如果遇到的是 BeanReference,那么就需要递归获取 Bean 实例,调用 getBean 方法。 - 当把依赖的 Bean 对象创建完成后,会递归回现在属性填充中。这里需要注意我们并没有去处理循环依赖的问题,这部分内容较大,后续补充。BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, name, value) 是 hutool-all 工具类中的方法,你也可以自己实现
五、测试
1. 事先准备
cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.UserDao
public class UserDao {
private static Map<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
hashMap.put("10001", "小傅哥");
hashMap.put("10002", "八杯水");
hashMap.put("10003", "阿毛");
}
public String queryUserName(String uId) {
return hashMap.get(uId);
}
}
cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.UserService
public class UserService {
private String uId;
private UserDao userDao;
public void queryUserInfo() {
System.out.println("查询用户信息:" + userDao.queryUserName(uId));
}
// ...get/set
}
- Dao、Service,是我们平常开发经常使用的场景。在 UserService 中注入 UserDao,这样就能体现出Bean属性的依赖了。
2. 测试用例
@Test
public void test_BeanFactory() {
// 1.初始化 BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 2. UserDao 注册
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("userDao", new BeanDefinition(UserDao.class));
// 3. UserService 设置属性[uId、userDao]
PropertyValues propertyValues = new PropertyValues();
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("uId", "10001"));
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("userDao",new BeanReference("userDao")));
// 4. UserService 注入bean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(UserService.class, propertyValues);
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("userService", beanDefinition);
// 5. UserService 获取bean
UserService userService = (UserService) beanFactory.getBean("userService");
userService.queryUserInfo();
}
- 与直接获取 Bean 对象不同,这次我们还需要先把 userDao 注入到 Bean 容器中。
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("userDao", new BeanDefinition(UserDao.class)); - 接下来就是属性填充的操作了,一种是普通属性
new PropertyValue("uId", "10001"),另外一种是对象属性new PropertyValue("userDao",new BeanReference("userDao")) - 接下来的操作就简单了,只不过是正常获取 userService 对象,调用方法即可。
3. 测试结果
查询用户信息:小傅哥
Process finished with exit code 0
-
从测试结果看我们的属性填充已经起作用了,因为只有属性填充后,才能调用到Dao方法,如:
userDao.queryUserName(uId) -
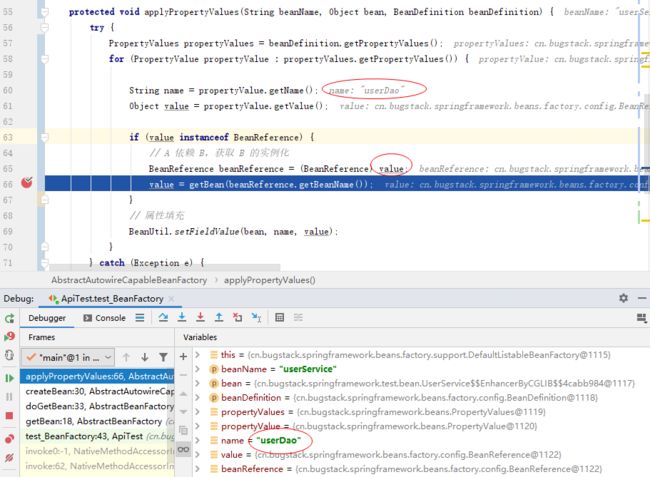
那么我们在看看Debug调试的情况下,有没有进入到实现的 Bean 属性填充中,如下:
- 好,就是截图这里,我们看到已经开始进行属性填充操作了,当发现属性是 BeanReference 时,则需要获取创建 Bean 实例。
六、总结
- 在本章节中我们把 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 类中的创建对象功能又做了扩充,依赖于是否有构造函数的实例化策略完成后,开始补充 Bean 属性信息。当遇到 Bean 属性为 Bean 对象时,需要递归处理。最后在属性填充时需要用到反射操作,也可以使用一些工具类处理。
- 每一个章节的功能点我们都在循序渐进的实现,这样可以让新人更好的接受关于 Spring 中的设计思路。尤其是在一些已经开发好的类上,怎么扩充新的功能时候的设计更为重要。学习编程有的时候学习思路设计要比仅仅是做简单实现,更能提升编程思维。
- 到这一章节关于 Bean 的创建操作就开发完成了,接下来需要整个框架的基础上完成资源属性的加载,就是我们需要去动 Xml 配置了,让我们这小框架越来越像 Spring。另外在框架实现的过程中所有的类名都会参考 Spring 源码,以及相应的设计实现步骤也是与 Spring 源码中对应,只不过会简化一些流程,但你可以拿相同的类名,去搜到每一个功能在 Spring 源码中的实现。
七、系列推荐
- 《Spring 手撸专栏》第 1 章:开篇介绍,我要带你撸 Spring 啦!
- 小傅哥,一个有“副业”的码农!
- 你说,怎么把Bean塞到Spring容器?
- 大学毕业要写多少行代码,才能不用花钱培训就找到一份开发工作?
- 数学,离一个程序员有多近?