Vue 相关学习笔记 (基础篇)
Vue 是什么?
欢迎访问我的小站
- Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 view) 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架
- vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合
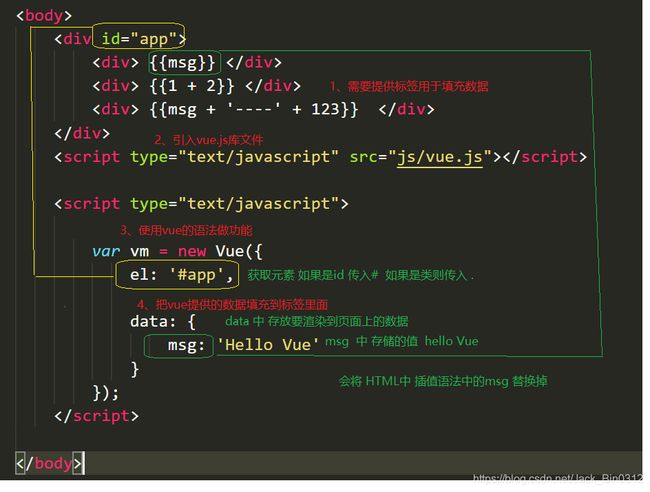
使用Vue将helloworld 渲染到页面上
<body>
<div id="app">
<div> {
{msg}} div>
<div> {
{1+2}} div>
<div> {
{msg + "----" + 123}} div>
div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//3、使用Vue的语法做功能
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app', //获取元素 如果是id传入‘#’ 如果是类传入‘.’
//4、把Vue提供的数据填充到标签中
data: {
//data中存放要渲染到页面上的数据
msg: 'Hello vue' // msg中存储值hello vue
}
});
script>
body>
指令
- 本质就是自定义属性
- Vue中指定都是以 v- 开头
v-cloak
-
防止页面加载时出现闪烁问题
<style type="text/css"> /* 1、通过属性选择器 选择到 带有属性 v-cloak的标签 让他隐藏 */ [v-cloak]{ /* 元素隐藏 */ display: none; } style> <body> <div id="app"> <div v-cloak >{ {msg}}div> div> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js">script> <script type="text/javascript"> var vm = new Vue({ // el 指定元素 id 是 app 的元素 el: '#app', // data 里面存储的是数据 data: { msg: 'Hello Vue' } }); script> body> html>
v-text
- v-text指令用于将数据填充到标签中,作用于插值表达式类似,但是没有闪动问题
- 如果数据中有HTML标签会将html标签一并输出
- 注意:此处为单向绑定,数据对象上的值改变,插值会发生变化;但是当插值发生变化并不会影响数据对象的值
<div id="app">
<p v-text="msg">p>
<p>
{
{msg}}
p>
div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'Hello Vue.js'
}
});
script>
v-html
-
用法和v-text 相似 但是他可以将HTML片段填充到标签中
-
可能有安全问题, 一般只在可信任内容上使用
v-html,永不用在用户提交的内容上 -
它与v-text区别在于v-text输出的是纯文本,浏览器不会对其再进行html解析,但v-html会将其当html标签解析后输出。
<div id="app"> <p v-html="html">p> <p>{ {message}}p> <p v-text="text">p> div> <script> let app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data: { message: "通过双括号绑定", html: "html标签在渲染的时候被解析", text: "html标签在渲染的时候被源码输出", } }); script>
v-pre
- 显示原始信息跳过编译过程
- 跳过这个元素和它的子元素的编译过程。
- 一些静态的内容不需要编译加这个指令可以加快渲染
<span v-pre>{
{ this will not be compiled }}span>
<span v-pre>{
{msg}}span>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'Hello Vue.js'
}
});
script>
v-once
- 执行一次性的插值【当数据改变时,插值处的内容不会继续更新】
<span v-once>{
{ msg}}span>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'Hello Vue.js'
}
});
script>
双向数据绑定
- 当数据发生变化的时候,视图也就发生变化
- 当视图发生变化的时候,数据也会跟着同步变化
v-model
- v-model是一个指令,可以实现数据的双向绑定,限制在
、