matlab学习:高阶绘图
1.各种绘图
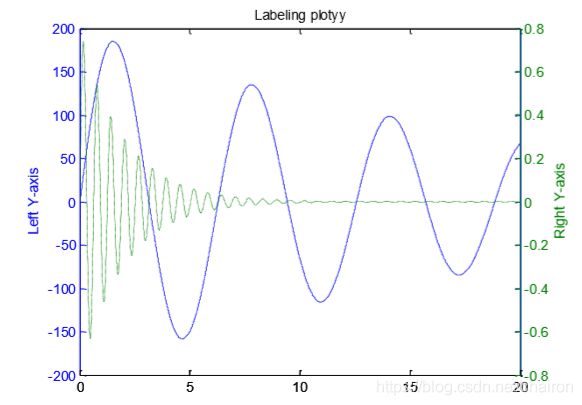
1.plotyy()
x = 0:0.01:20;
y1 = 200*exp(-0.05*x).*sin(x);
y2 = 0.8*exp(-0.5*x).*sin(10*x);
[AX,H1,H2] = plotyy(x,y1,x,y2); %h1为y1的handle,h2为y2的handle
set(get(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Left Y-axis')
set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Right Y-axis')
title('Labeling plotyy');
set(H1,'LineStyle','--');
set(H2,'LineStyle',':');
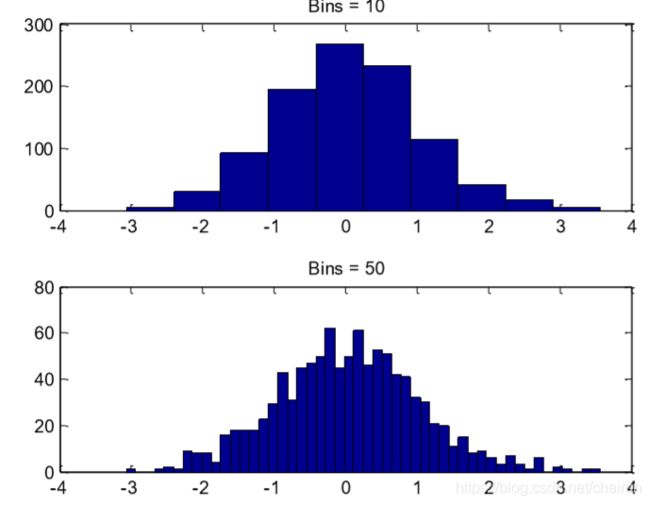
2.Histogram直方图
%historgram 看整体的情况
y = randn(1,1000);
subplot(2,1,1);
hist(y,10); %产生10个bins
title('Bins = 10');
subplot(2,1,2);
hist(y,50);
title('Bins = 50');
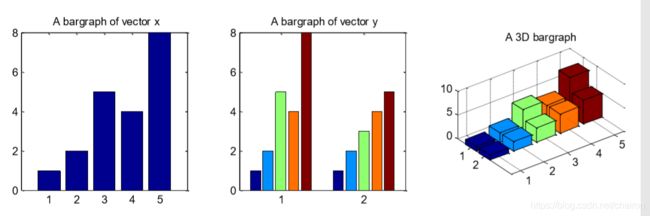
3.Bar Charts
%Bar Charts 适合看单个情况
x = [1 2 5 4 8];
y = [x;1:5];
subplot(1,3,1);
bar(x); %2D的一维数组
title('A bargraph of vector x');
subplot(1,3,2);
bar(y);%2D的二维矩阵
title('A bargraph of vector y');
subplot(1,3,3);
bar3(y); %绘制成三维图像
title('A 3D bargraph');
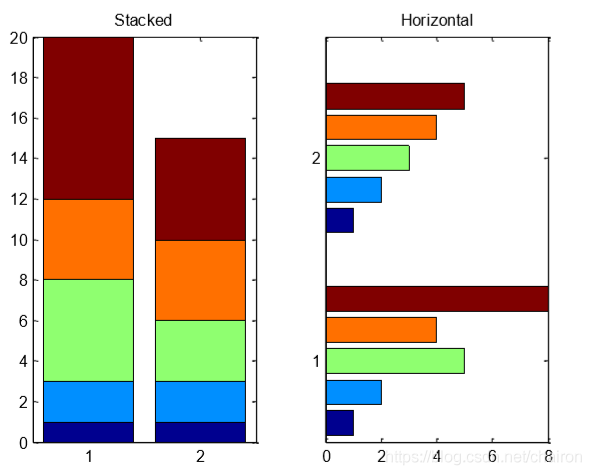
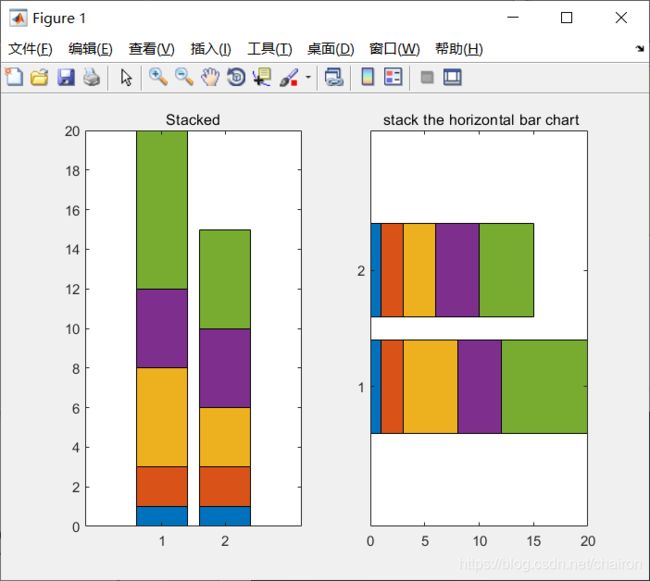
4.Stacked and Horizontal Bar Charts
饼图的堆叠和水平化
- barh():水平化,坐标轴旋转90度,x轴变y轴,y变x轴
- stack():堆叠
%%
%barh():水平化,坐标轴旋转90度,x轴变y轴,y变x轴
x = [1 2 5 4 8];
y = [x;1:5];
subplot(1,2,1);
bar(y,'stacked'); %叠在一起
title('Stacked');
subplot(1,2,2);
barh(y,'stacked'); % stack the horizontal bar chart
title('Horizontal');
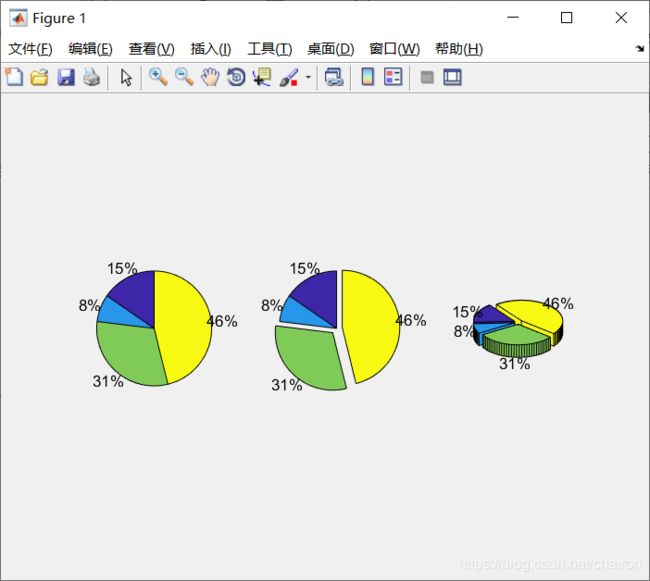
5.Pie Charts
%Pie Charts
a = [10 5 20 30];
subplot(1,3,1);
pie(a);
subplot(1,3,2);
pie(a, [0,0,1,1]); %取1对应部分分离,取0对应部分合在一起
subplot(1,3,3);
pie3(a, [1,1,1,1]);
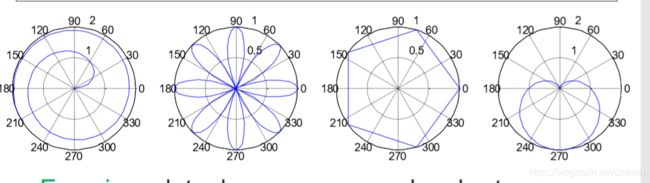
7.Polar Chart 极坐标图
polar(theta, r);%theta:旋转角度;r:半径
%Polar Chart
x = 1:100;
theta = x/10;
r = log10(x);
subplot(1,4,1);
polar(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi);
r = cos(4*theta);
subplot(1,4,2);
polar(theta, r);%theta:旋转角度;r:半径
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi, 6);%0~2pi,分为6个点,即五段
r = ones(1,length(theta));
subplot(1,4,3);
polar(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi);
r = 1-sin(theta);
subplot(1,4,4);
polar(theta , r);
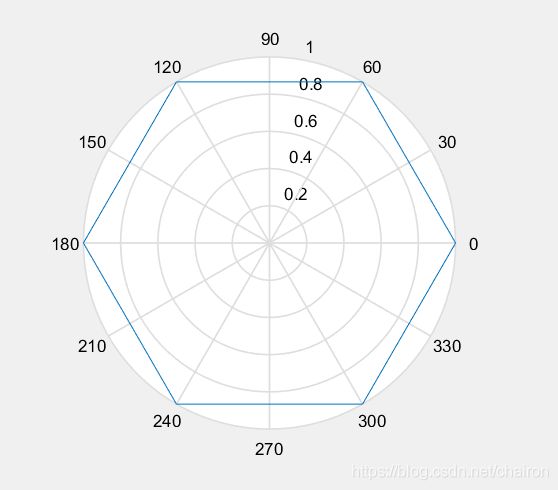
- 作业:绘制六边形
%作业 六边形
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi, 7);
r = ones(1,length(theta));
polar(theta,r);
7.Stairs and Stem Charts
%Stairs and Stem Charts
x = linspace(0, 4*pi, 40);
y = sin(x);
subplot(1,2,1);
stairs(y);
subplot(1,2,2);
stem(y);
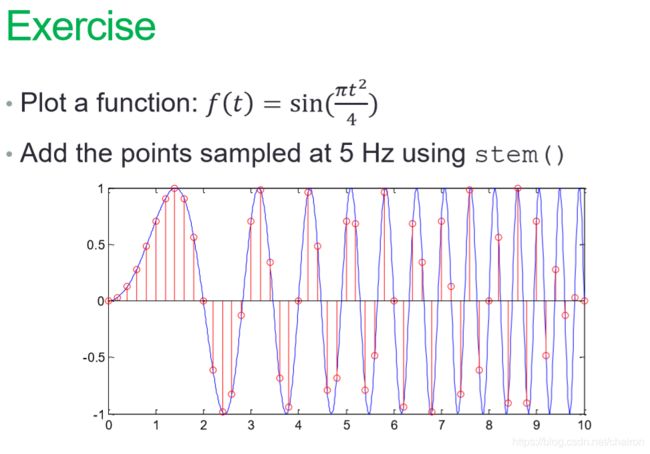
%作业
x =linspace(0,10);
y=sin(pi*(x.^2)/4);
hold on
plot(x,y,'b');
stem(x,y,'r');
hold off
2.绘制几何图片
1.fill():填充
% fill :stop sigin
%t =(1:2:15)'*pi/8;
t=linspace(0,2*pi,9);
x = sin(t);
y = cos(t);
fill(x,y,'r');
axis square off;
text(0,0,'STOP','Color', 'w', 'FontSize', 80, ...
'FontWeight','bold', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
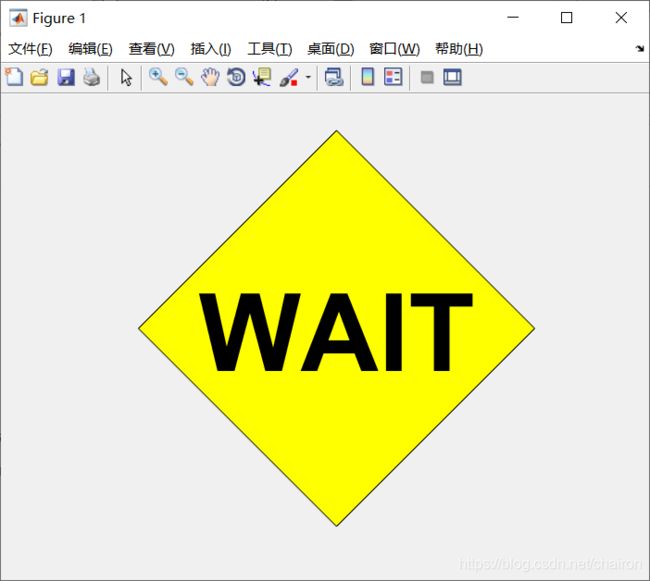
- 小练习:
%作业
t =linspace(0,2*pi,5);
x = sin(t);
y = cos(t);
fill(x,y,'y');
axis square off;
text(0,0,'WAIT','Color', 'k', 'FontSize', 70, ...
'FontWeight','bold', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
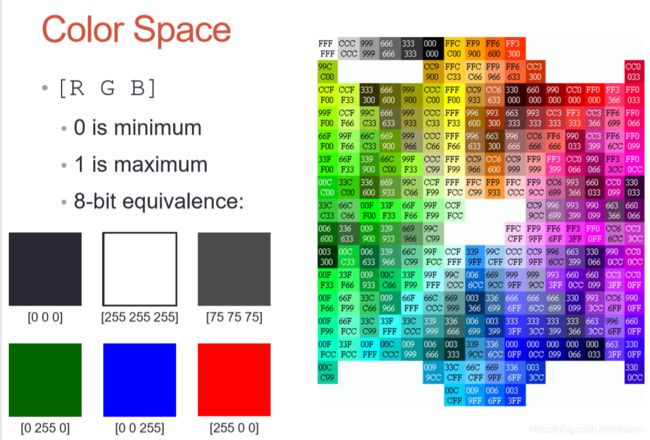
3.Color Space
4. 把矩阵转为图像
- Visualizing Data as An Image: imagesc()
1.Display values of a matrix as an “image”
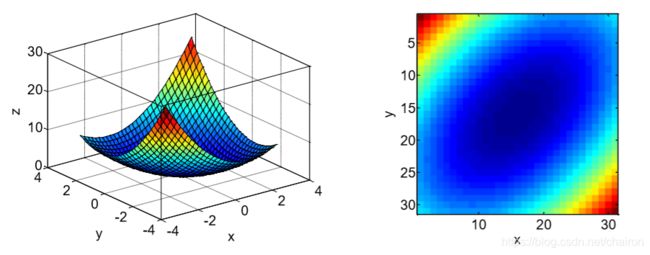
- 使用imagesc()函数可以将三维图转换为二维俯视图,通过点的颜色指示高度.
[x, y] = meshgrid(-3:.2:3,-3:.2:3);
z = x.^2 + x.*y + y.^2;
surf( x, y, z);
box on;
set(gca,'FontSize', 16);
zlabel('z');
xlim([-4 4]);
xlabel('x');
ylim([-4 4]);
ylabel('y');
figure
imagesc(z); %把z以色彩图像显示
axis square;
xlabel('x'); ylabel('y');
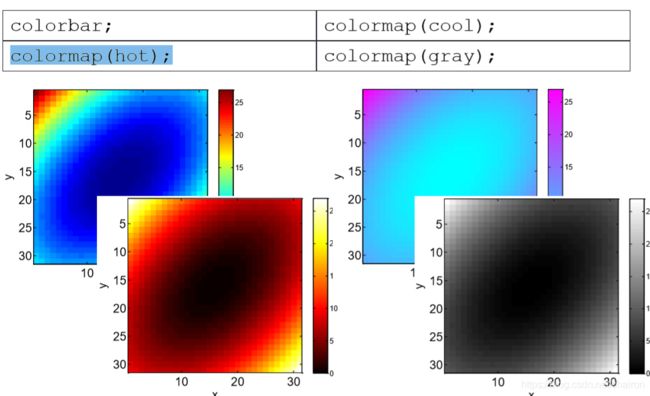
colorbar;%相当于legend
colormap(hot);%色系图
a = colormap(prism)
2.Color Bar and Scheme
| 函数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| colorbar | 显示图中颜色的图例,相当于legend |
| colormap(hot) | 显示色系图,偏红色,为内置色系 |
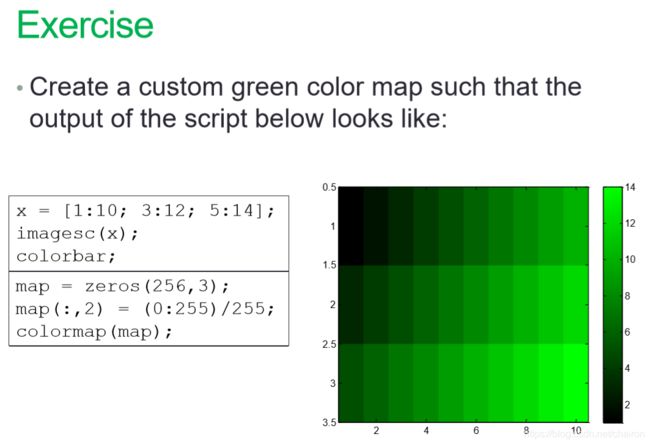
3.Built-in Colormaps
x = [1:10; 3:12; 5:14];
imagesc(x); %转化为图像
colorbar;
map = zeros(256,3); %色彩空间全部置为0
map(:,2) = (0:255)/255;%第二列,即G列取值映射为0`1 渐变
colormap(map);%转化为map
5.3D Plots
1. 3D绘图函数功能
| 函数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| plot3 | 3D曲线 |
| surf | 3D曲线的表面图,3D的曲面,会填充 |
| surfc | 在surf图下方产生投影 |
| surface | 创建一个surface对象 |
| mesh | 绘制一个矩阵的点连成的3D曲面,不会填充 |
| meshc | 在mesh下方产生投影 |
| contour | 绘制等高线 |
| contourf | 绘制等高线,并且填充 |
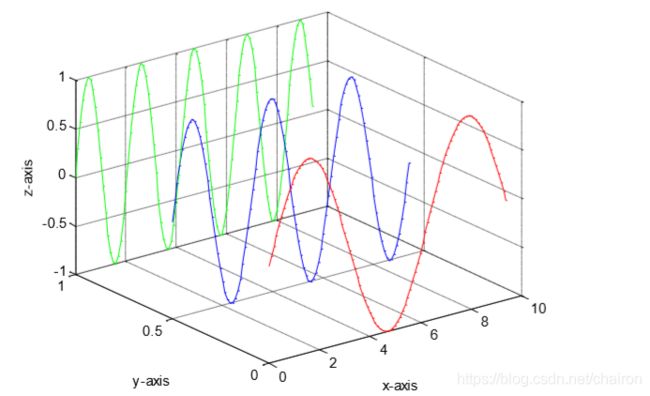
2. plot3()
- 我们对一个二维网格矩阵应用函数z = f ( x , y ) 才能得到三维图形,因此在得到三维数据之前我们应当使用meshgrid()函数生成二维网格矩阵.
- meshgrid()函数将输入的两个向量进行相应的行扩充和列扩充以得到两个增广矩阵,对该矩阵可应用二元函数。
x=0:0.1:3*pi;
z1=sin(x);
z2=sin(2.*x);
z3=sin(3.*x);
y1=zeros(size(x));
y3=ones(size(x));
y2=y3./2;
plot3(x,y1,z1,'r',x,y2,z2,'b',x,y3,z3,'g');
grid on;
xlabel('x-axis');
ylabel('y-axis');
zlabel('z-axis');
3.More 3D Line Plots
t = 0:pi/50:10*pi;
plot3(sin(t),cos(t),t) %?三维曲线
grid on;
axis square;
turns = 40*pi;
t = linspace(0,turns,4000);
x = cos(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
y = sin(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
z = t./turns;
plot3(x,y,z);
grid on;
4. 3D Surface Plots
- [X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(x,y,z) 返回由向量 x、y 和 z 定义的三维网格坐标。
- X、Y 和 Z 表示的网格的大小为 length(y)×length(x)×length(z)。
- 使用 meshgrid 去创建给定范围的X和Y矩阵
- X 变化时,Y不变;Y变化时,X不变。
- Surface Plots:
% [X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(x,y,z) 返回由向量 x、y 和 z 定义的三维网格坐标。
%X、Y 和 Z 表示的网格的大小为 length(y)×length(x)×length(z)。
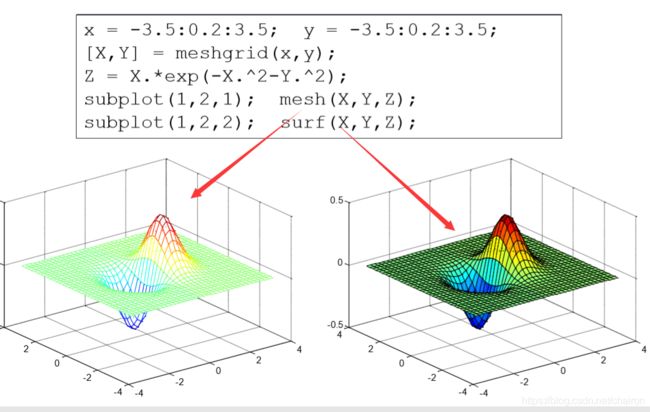
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,2,1);
mesh(X,Y,Z); %3维的点连起来
subplot(1,2,2);
surf(X,Y,Z);%3维的面,填充
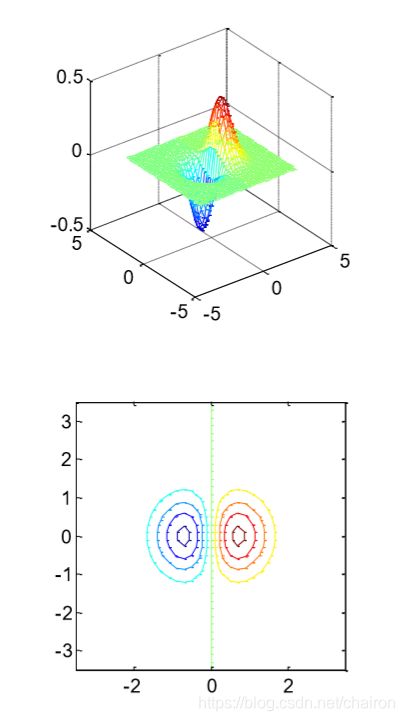
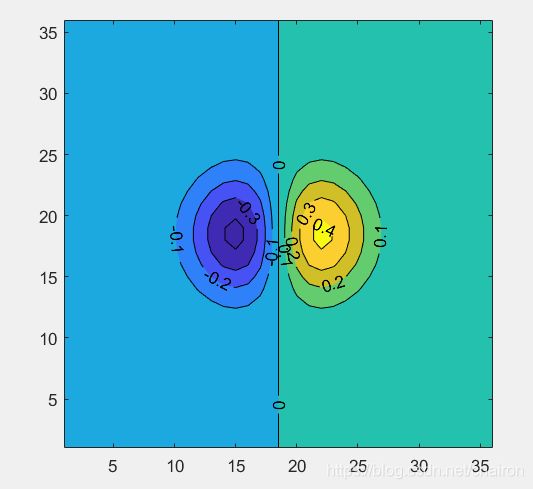
5. contour():3D图像在二维平面上的等高线
%counter 绘制矩阵的等高线
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(2,1,1);
mesh(X,Y,Z); %其中 Z 解释为有关 x-y 平面的高度。Z 必须至少是 2×2 矩阵,该矩阵包含至少两个不同值。
%x 值对应于 Z 的列索引,y 值对应于 Z 的行索引。自动选择等高线层级。
axis square;
subplot(2,1,2);
contour(X,Y,Z);
axis square;
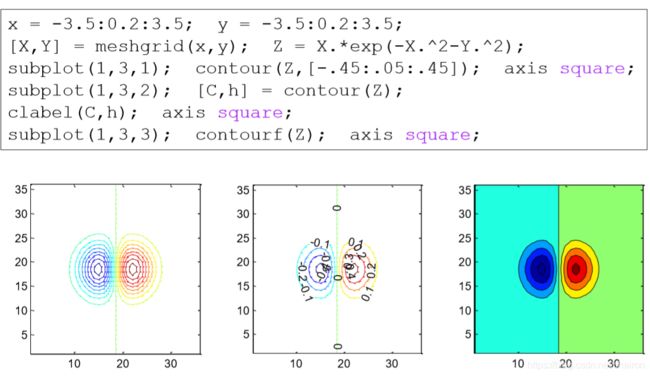
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
%subplot(1,3,1);
%contour(Z,[-.45:.05:.45]);
%要在 k 层级绘制等高线,请使用 contour(Z,[k k])。指定向量 v 可将 LevelListMode 属性设置为 manual。
%axis square;
%subplot(1,3,2);
%[C,h] = contour(Z);
%[C,h] = contour(...) 返回等高线矩阵 C(包含定义等高线的数据)和 Contour 对象 h。
%Contour 对象的 ContourMatrix 属性也包含等高线矩阵。
[C,h] = contourf(Z);
clabel(C,h); %clabel 函数使用等高线矩阵标记等高线。
%axis square;
%subplot(1,3,3);
%contourf(Z);%填充的二维等高线图
axis square;
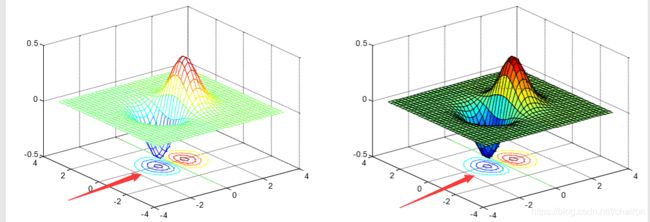
6.meshc() and surfc()
在相应的图像下方产生投影
%meshc() and surfc():在图像下方产生投影
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,2,1);
meshc(X,Y,Z);
subplot(1,2,2);
surfc(X,Y,Z);
7.View Angle: view()
- view()视角,包括观察的角度,和俯视/仰视
- light():光线
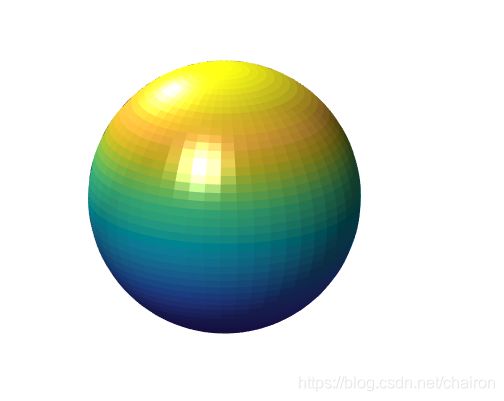
%View Angle: view()视角,包括观察的角度,和俯视/仰视
sphere(50);
shading flat;
light('Position',[1 3 2]); %光线位置
light('Position',[-3 -1 3]);
material shiny;
axis vis3d off;
set(gcf,'Color',[1 1 1]);
view(-45,20);%观察角度
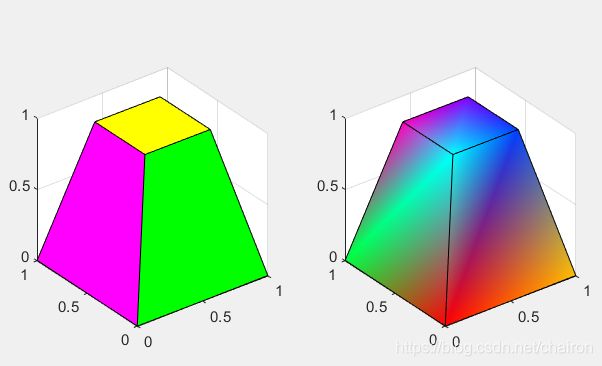
8.patch()
- 创建一个或多个填充多边形
- patch(‘Faces’,F,‘Vertices’,V) 创建一个或多个多边形,其中 V 指定顶点的值,F 定义要连接的顶点。
- patch(X,Y,Z,C) 使用 X、Y 和 Z 在三维坐标中创建多边形。C 确定多边形的颜色。通过指定 FaceColor 属性来设置颜色。
- 要在三维视图中查看这些多边形,请使用 view(3) 命令。
%patch() : A graphical object containing polygons 创建一个或多个填充多边形
v = [0 0 0; 1 0 0 ; 1 1 0; 0 1 0; 0.25 0.25 1; ...
0.75 0.25 1; 0.75 0.75 1; 0.25 0.75 1];
f = [1 2 3 4; 5 6 7 8; 1 2 6 5; 2 3 7 6; 3 4 8 7; 4 1 5 8];
subplot(1,2,1);
patch('Vertices', v, 'Faces', f, ...
'FaceVertexCData', hsv(6), 'FaceColor', 'flat'); %patch('Faces',F,'Vertices',V) 创建一个或多个多边形,其中 V 指定顶点的值,F 定义要连接的顶点。
view(3); %patch(X,Y,Z,C) 使用 X、Y 和 Z 在三维坐标中创建多边形。要在三维视图中查看这些多边形,请使用 view(3) 命令。C 确定多边形的颜色。
axis square tight; %通过指定 FaceColor 属性来设置颜色。
grid on;
subplot(1,2,2);
patch('Vertices', v, 'Faces', f, ...
'FaceVertexCData', hsv(8), 'FaceColor', 'interp');
view(3);
axis square tight;
grid on;