LinearSystem.py
from .Matrix import Matrix
from .Vector import Vector
class LinearSystem:
def __init__(self, A, b):
assert A.row_num() == len(b), "row number of A must be equal to the length of b"
self._m = A.row_num()
self._n = A.col_num()
assert self._m == self._n # TODO: no this restriction,现在是方阵以后消除这个限制
self.Ab = [Vector(A.row_vector(i).underlying_list() + [b[i]])
for i in range(self._m)]
# 私有
def _max_row(self, index, n):
"""
寻找第iindex 行到底n 行最大的主元
:param index: 第index行第index列
:param n: 方程个数
:return:
"""
# ret 表示具体是哪一行
best, ret = self.Ab[index][index], index
for i in range(index + 1, n):
# 往下进行运算, 找到比大的就更新值
if self.Ab[i][index] > best:
best, ret = self.Ab[i][index], i
return ret
def _forward(self):
n = self._m
for i in range(n):
# Ab[i][i]为主元, Ab[i][i]有可能为零,减小误差我都去找一下最大的,颠倒顺序方程的接不变
max_row = self._max_row(i, n)
self.Ab[i], self.Ab[max_row] = self.Ab[max_row], self.Ab[i]
# 将主元归为一
self.Ab[i] = self.Ab[i] / self.Ab[i][i] # TODO: self.Ab[i][i] == 0?
for j in range(i + 1, n):
self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][i] * self.Ab[i]
def _backward(self):
n = self._m
# 终止于第0行 左闭右开
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
# Ab[i][i]为主元
for j in range(i - 1, -1, -1):
self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][i] * self.Ab[i]
# 1、先声明 高斯消元法
def gauss_jordan_elimination(self):
self._forward()
# self._backward()
def fancy_print(self):
for i in range(self._m):
print(" ".join(str(self.Ab[i][j]) for j in range(self._n)), end=" ")
print("|", self.Ab[i][-1])
- 测试
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
from playLA.Vector import Vector
from playLA.LinearSystem import LinearSystem
if __name__ == "__main__":
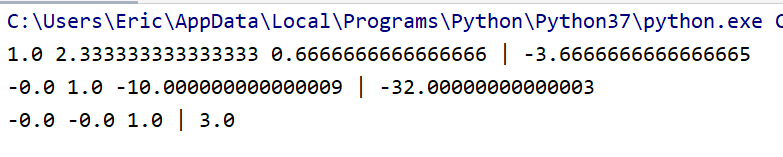
A = Matrix([[1, 2, 4], [3, 7, 2], [2, 3, 3]])
b = Vector([7, -11, 1])
ls = LinearSystem(A, b)
ls.gauss_jordan_elimination()
ls.fancy_print()
print()
# #
# A2 = Matrix([[1, -3, 5], [2, -1, -3], [3, 1, 4]])
# b2 = Vector([-9, 19, -13])
# ls2 = LinearSystem(A2, b2)
# ls2.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls2.fancy_print()
# print()
# #
# A3 = Matrix([[1, 2, -2], [2, -3, 1], [3, -1, 3]])
# b3 = Vector([6, -10, -16])
# ls3 = LinearSystem(A3, b3)
# ls3.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls3.fancy_print()
# print()
#
# A4 = Matrix([[3, 1, -2], [5, -3, 10], [7, 4, 16]])
# b4 = Vector([4, 32, 13])
# ls4 = LinearSystem(A4, b4)
# ls4.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls4.fancy_print()
# print()
# #
# A5 = Matrix([[6, -3, 2], [5, 1, 12], [8, 5, 1]])
# b5 = Vector([31, 36, 11])
# ls5 = LinearSystem(A5, b5)
# ls5.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls5.fancy_print()
# print()
# #
# A6 = Matrix([[1, 1, 1], [1, -1, -1], [2, 1, 5]])
# b6 = Vector([3, -1, 8])
# ls6 = LinearSystem(A6, b6)
# ls6.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls6.fancy_print()
# print()
更一般形式的高斯消元法
from .Matrix import Matrix
from .Vector import Vector
from ._globals import is_zero
class LinearSystem:
def __init__(self, A, b):
assert A.row_num() == len(b), "row number of A must be equal to the length of b"
self._m = A.row_num()
self._n = A.col_num()
# assert self._m == self._n # TODO: no this restriction
self.Ab = [Vector(A.row_vector(i).underlying_list() + [b[i]])
for i in range(self._m)]
self.pivots = []
def _max_row(self, index_i, index_j, n):
best, ret = abs(self.Ab[index_i][index_j]), index_i
for i in range(index_i + 1, n):
if abs(self.Ab[i][index_j]) > best:
best, ret = abs(self.Ab[i][index_j]), i
return ret
def _forward(self):
i, k = 0, 0
while i < self._m and k < self._n:
# 看Ab[i][k]位置是否可以是主元
max_row = self._max_row(i, k, self._m)
self.Ab[i], self.Ab[max_row] = self.Ab[max_row], self.Ab[i]
if is_zero(self.Ab[i][k]):
k += 1
else:
# 将主元归为一
self.Ab[i] = self.Ab[i] / self.Ab[i][k]
for j in range(i + 1, self._m):
self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][k] * self.Ab[i]
self.pivots.append(k)
i += 1
def _backward(self):
n = len(self.pivots)
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
k = self.pivots[i]
# Ab[i][k]为主元
for j in range(i - 1, -1, -1):
self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][k] * self.Ab[i]
def gauss_jordan_elimination(self):
"""如果有解,返回True;如果没有解,返回False"""
self._forward()
self._backward()
for i in range(len(self.pivots), self._m):
if not is_zero(self.Ab[i][-1]):
return False
return True
def fancy_print(self):
for i in range(self._m):
print(" ".join(str(self.Ab[i][j]) for j in range(self._n)), end=" ")
print("|", self.Ab[i][-1])
测试
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
from playLA.Vector import Vector
from playLA.LinearSystem import LinearSystem
if __name__ == "__main__":
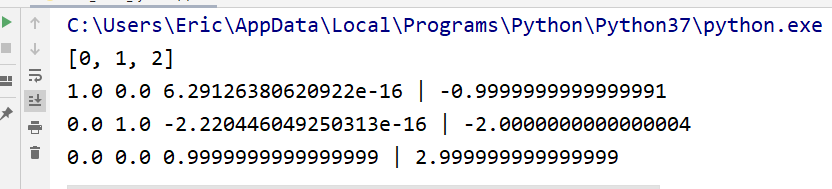
A = Matrix([[1, 2, 4], [3, 7, 2], [2, 3, 3]])
b = Vector([7, -11, 1])
ls = LinearSystem(A, b)
ls.gauss_jordan_elimination()
print(ls.pivots)
ls.fancy_print()
print()
# [-1, -2, 3]
#
# A2 = Matrix([[1, -3, 5], [2, -1, -3], [3, 1, 4]])
# b2 = Vector([-9, 19, -13])
# ls2 = LinearSystem(A2, b2)
# ls2.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls2.fancy_print()
# print()
# # [2, -3, -4]
#
# A3 = Matrix([[1, 2, -2], [2, -3, 1], [3, -1, 3]])
# b3 = Vector([6, -10, -16])
# ls3 = LinearSystem(A3, b3)
# ls3.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls3.fancy_print()
# print()
# # [-2, 1, -3]
#
# A4 = Matrix([[3, 1, -2], [5, -3, 10], [7, 4, 16]])
# b4 = Vector([4, 32, 13])
# ls4 = LinearSystem(A4, b4)
# ls4.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls4.fancy_print()
# print()
# # [3, -4, 0.5]
#
# A5 = Matrix([[6, -3, 2], [5, 1, 12], [8, 5, 1]])
# b5 = Vector([31, 36, 11])
# ls5 = LinearSystem(A5, b5)
# ls5.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls5.fancy_print()
# print()
# # [3, -3, 2]
#
# A6 = Matrix([[1, 1, 1], [1, -1, -1], [2, 1, 5]])
# b6 = Vector([3, -1, 8])
# ls6 = LinearSystem(A6, b6)
# ls6.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls6.fancy_print()
# print()
# # [1, 1, 1]
#
# A7 = Matrix([[1, -1, 2, 0, 3],
# [-1, 1, 0, 2, -5],
# [1, -1, 4, 2, 4],
# [-2, 2, -5, -1, -3]])
# b7 = Vector([1, 5, 13, -1])
# ls7 = LinearSystem(A7, b7)
# ls7.gauss_jordan_elimination()
# ls7.fancy_print()
# print()
#
# A8 = Matrix([[2, 2],
# [2, 1],
# [1, 2]])
# b8 = Vector([3, 2.5, 7])
# ls8 = LinearSystem(A8, b8)
# if not ls8.gauss_jordan_elimination():
# print("No Solution!")
# ls8.fancy_print()
# print()
#
# A9 = Matrix([[2, 0, 1],
# [-1, -1, -2],
# [-3, 0, 1]])
# b9 = Vector([1, 0, 0])
# ls9 = LinearSystem(A9, b9)
# if not ls9.gauss_jordan_elimination():
# print("No Solution!")
# ls9.fancy_print()
# print()
实现矩阵的求逆运算
在LinearSystem.py中添加inv(A)函数
def inv(A):
if A.row_num() != A.col_num():
return None
n = A.row_num()
ls = LinearSystem(A, Matrix.identity(n))
if not ls.gauss_jordan_elimination():
return None
invA = [[row[i] for i in range(n, 2*n)] for row in ls.Ab]
return Matrix(invA)
测试
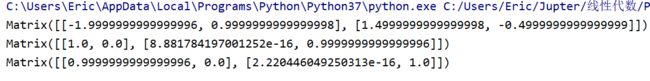
A = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
invA = inv(A)
print(invA)
print(A.dot(invA))
print(invA.dot(A))
LU分解
from .Matrix import Matrix
from .Vector import Vector
from ._globals import is_zero
def lu(matrix):
assert matrix.row_num() == matrix.col_num(), "matrix must be a square matrix"
n = matrix.row_num()
A = [matrix.row_vector(i) for i in range(n)]
L = [[1.0 if i == j else 0.0 for i in range(n)] for j in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
# 看A[i][i]位置是否可以是主元
if is_zero(A[i][i]):
return None, None
else:
for j in range(i + 1, n):
p = A[j][i] / A[i][i] # p 是某一行减去另一行的k倍的那个k
A[j] = A[j] - p * A[i]
L[j][i] = p
return Matrix(L), Matrix([A[i].underlying_list() for i in range(n)])
测试
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
from playLA.LU import lu
if __name__ == "__main__":
A1 = Matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [3, -3, 5]])
L1, U1 = lu(A1)
print(L1)
print(U1)
print(L1.dot(U1))
print()
A2 = Matrix([[1, 4, 5, 3], [5, 22, 27, 11], [6, 19, 27, 31], [5, 28, 35, -8]])
L2, U2 = lu(A2)
print(L2)
print(U2)
print(L2.dot(U2))
print()
A3 = Matrix([[1, 2, 3], [3, 7, 14], [4, 13, 38]])
L3, U3 = lu(A3)
print(L3)
print(U3)
print(L3.dot(U3))
print()
秩
在LinearSystem.py中添加irank(A)函数
def rank(A):
ls = LinearSystem(A)
ls.gauss_jordan_elimination()
zero = Vector.zero(A.col_num())
return sum([row != zero for row in ls.Ab])
测试
A6 = Matrix([[1, 1, 1], [1, -1, -1], [2, 1, 5]])
A7 = Matrix([[1, -1, 2, 0, 3],
[-1, 1, 0, 2, -5],
[1, -1, 4, 2, 4],
[-2, 2, -5, -1, -3]])
A8 = Matrix([[2, 2],
[2, 1],
[1, 2]])
print("rank A8 = {}".format(rank(A8)))
print("rank A7 = {}".format(rank(A7)))
print("rank A6 = {}".format(rank(A6)))
施密特过程
GramSchmidtProcess.py
from .Vector import Vector
from .Matrix import Matrix
from .LinearSystem import rank
def gram_schmidt_process(basis):
matrix = Matrix(basis)
assert rank(matrix) == len(basis)
res = [basis[0]]
for i in range(1, len(basis)):
p = basis[i]
for r in res:
p = p - basis[i].dot(r) / r.dot(r) * r
res.append(p)
return res;
测试
from playLA.Vector import Vector
from playLA.GramSchmidtProcess import gram_schmidt_process
from itertools import product
if __name__ == "__main__":
basis1 = [Vector([2, 1]), Vector([1, 1])]
res1 = gram_schmidt_process(basis1)
for row in res1:
print(row)
res1 = [row / row.norm() for row in res1]
for row in res1:
print(row)
print(res1[0].dot(res1[1]))
print()
basis2 = [Vector([2, 3]), Vector([4, 5])]
res2 = gram_schmidt_process(basis2)
res2 = [row / row.norm() for row in res2]
for row in res2:
print(row)
print(res2[0].dot(res2[1]))
print()
basis3 = [Vector([1, 0, 1]), Vector([3, 1, 1]), Vector([-1, -1, -1])]
res3 = gram_schmidt_process(basis3)
res3 = [row / row.norm() for row in res3]
for row in res3:
print(row)
print(sum(res3[i].dot(res3[j]) for i, j in product(range(3), repeat=2) if i != j))
print()
basis4 = [Vector([1, 1, 5, 2]), Vector([-3, 3, 4, -2]), Vector([-1, -2, 2, 5])]
res4 = gram_schmidt_process(basis4)
res4 = [row / row.norm() for row in res4]
for row in res4:
print(row)
print(sum(res4[i].dot(res4[j]) for i, j in product(range(3), repeat=2) if i != j))
print()
basis5 = [Vector([1, 2, 3, 4]), Vector([2, 1, 1, 0]), Vector([3, 0, -1, 3])]
res5 = gram_schmidt_process(basis5)
res5 = [row / row.norm() for row in res5]
for row in res5:
print(row)
print(sum(res5[i].dot(res5[j]) for i, j in product(range(3), repeat=2) if i != j))
print()
QR分解
GramSchmidtProcess.py添加
def qr(A):
assert A.row_num() == A.col_num(), "A must be square"
basis = [A.col_vector(i) for i in range(A.col_num())];
P = gram_schmidt_process(basis)
Q = Matrix([v / v.norm() for v in P]).T()
R = Q.T().dot(A)
return Q, R
测试
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
from playLA.GramSchmidtProcess import qr
if __name__ == "__main__":
A1 = Matrix([[1, 1, 2],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]])
Q1, R1 = qr(A1)
print(Q1)
print(R1)
print(Q1.dot(R1))
print()
A2 = Matrix([[2, -1, -1],
[2, 0, 2],
[2, -1, 3]])
Q2, R2 = qr(A2)
print(Q2)
print(R2)
print(Q2.dot(R2))
numpy
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import eig
if __name__ == "__main__":
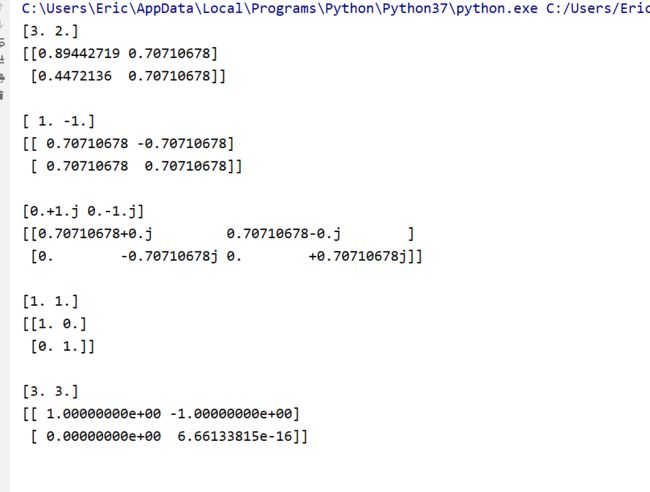
A1 = np.array([[4, -2],
[1, 1]]);
eigenvalues1, eigenvectors1 = eig(A1);
print(eigenvalues1)
print(eigenvectors1)
print()
# 关于y=x翻转
A2 = np.array([[0, 1],
[1, 0]]);
eigenvalues2, eigenvectors2 = eig(A2);
print(eigenvalues2)
print(eigenvectors2)
print()
# 旋转90度
A3 = np.array([[0, -1],
[1, 0]]);
eigenvalues3, eigenvectors3 = eig(A3);
print(eigenvalues3)
print(eigenvectors3)
print()
# 单位矩阵
A4 = np.array([[1, 0],
[0, 1]]);
eigenvalues4, eigenvectors4 = eig(A4);
print(eigenvalues4)
print(eigenvectors4)
print()
# 几何重数为1
A5 = np.array([[3, 1],
[0, 3]]);
eigenvalues5, eigenvectors5 = eig(A5);
print(eigenvalues5)
print(eigenvectors5)
print()
自己实现特征值和特征向量
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import eig, inv
from playLA.LinearSystem import rank
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
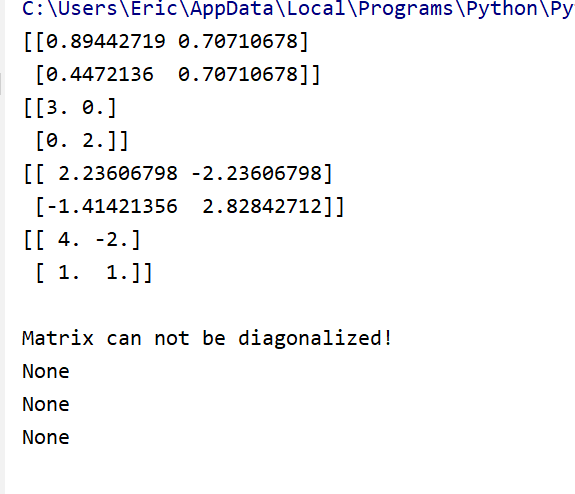
def diagonalize(A):
assert A.ndim == 2
assert A.shape[0] == A.shape[1]
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = eig(A)
P = eigenvectors
if rank(Matrix(P.tolist())) != A.shape[0]:
print("Matrix can not be diagonalized!")
return None, None, None
D = np.diag(eigenvalues)
Pinv = inv(P)
return P, D, Pinv
if __name__ == "__main__":
A1 = np.array([[4, -2],
[1, 1]])
P1, D1, Pinv1 = diagonalize(A1)
print(P1)
print(D1)
print(Pinv1)
print(P1.dot(D1).dot(Pinv1))
print()
A2 = np.array([[3, 1],
[0, 3]])
P2, D2, Pinv2 = diagonalize(A2)
print(P2)
print(D2)
print(Pinv2)
print()
SVD分解
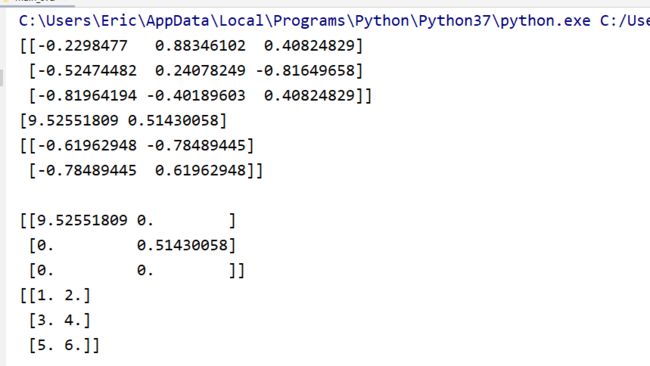
import numpy as np
from scipy.linalg import svd
if __name__ == "__main__":
A = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
U, s, VT = svd(A)
print(U)
print(s)
print(VT)
print()
Sigma = np.zeros(A.shape)
for i in range(len(s)):
Sigma[i][i] = s[i]
print(Sigma)
print(U.dot(Sigma).dot(VT))