-
React中一个常见模式是为一个组件返回多个元素。Fragments可以让你聚合一个子元素列表,并且不在DOM中增加额外节点。
class Columns extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
Hello
World
);
}
}
注意:①key 是唯一可以传递给 Fragment 的属性。② 在 React 中,<> 是
-
Strict Mode严格模式
StrictMode是一个用以标记出应用中潜在问题的工具。与Fragment类似,StrictMode不会渲染任何真实的UI。它为其后代元素触发额外的检查和警告。
import { StrictMode, Component } from 'react'
class Child extends Component {
// 以下三个函数在 React v16.3 已不被推荐,未来的版本会废弃。
componentWillMount() {
console.log('componentWillMount')
}
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate')
}
componentWillReceiveProps() {
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps')
}
render() {
return (
)
}
}
export default class StrictModeExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
)
}
}
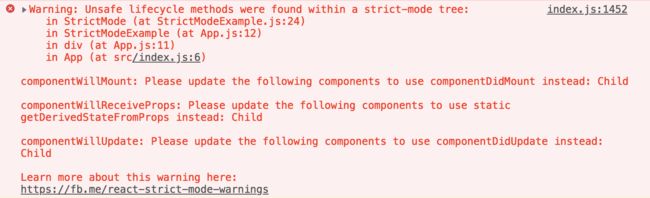
由于在StrictMode内使用了三个即将废弃的API,打开控制台 ,可看到如下错误提醒:
注释:严格模式检查只在开发模式下运行,不会与生产模式冲突。
-
createRef (v16.3)
(1) 老版本ref使用方式
① 字符串形式:
② 回调函数形式:(this.input = input)} />
(2) 字符串形式缺点
① 需要内部追踪ref的this取值,会使React稍稍变慢。
② 有时候this与你想象的并不一致。
import React from 'react'
class Children extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
//
console.log('children ref', this.refs.titleRef)
}
render() {
return (
{this.props.renderTitle()}
)
}
}
class Parent extends React.Component {
// 放入子组件渲染
renderTitle = () => (
{this.props.title}
)
componentDidMount() {
// undefined
console.log('parent ref:', this.refs.titleRef)
}
render() {
return (
(3) createRef语法
import React from 'react'
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.inputRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return ;
}
componentDidMount() {
this.inputRef.current.focus();
}
}
export default MyComponent
- 调用
setState更新状态时,若之后的状态依赖于之前的状态,推荐使用传入函数形式。
语法:setState((prevState, props) => stateChange, [callback])
例如,假设我们想通过props.step在状态中增加一个值:
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return {counter: prevState.counter + props.step};
});
- 错误边界
(1) 错误边界用于捕获其子组件树JavaScript异常,记录错误并展示一个回退的UI的React组件,避免整个组件树异常导致页面空白。
(2) 错误边界在渲染期间、生命周期方法内、以及整个组件树构造函数内捕获错误。
(3) 组件如果定义了static getDerivedStateFromError()或componentDidCatch()中的任意一个或两个生命周期方法 。当其子组件抛出错误时,可使用static getDerivedStateFromError()更新state,可使用componentDidCatch()记录错误信息。
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
// You can also log the error to an error reporting service
logErrorToMyService(error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return Something went wrong.
;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
而后你可以像一个普通的组件一样使用:
注释:getDerivedStateFromError和componentDidCatch方法使用一个即可捕获子组件树错误。
-
Portal
(1)Portals提供了一种很好的将子节点渲染到父组件以外的DOM节点的方式。
(2) 通过Portals进行事件冒泡
尽管portal可以被放置在DOM树的任何地方,但在其他方面其行为和普通的React子节点行为一致。一个从portal内部会触发的事件会一直冒泡至包含React树 的祖先。
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Modal extends React.Component {
render() {
return this.props.clicks % 2 === 1
? this.props.children
: ReactDOM.createPortal(
this.props.children,
document.getElementById('modal'),
);
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
);
}
}
class Parent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {clicks: 0};
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState(prevState => ({
clicks: prevState.clicks + 1
}));
}
render() {
return (
Number of clicks: {this.state.clicks}
);
}
}
export default Parent
注释:当组件由portal渲染方式切换为普通渲染方式,会导致该组件被卸载之后重新渲染。组件放大功能如果通过portal方式实现,放大前的状态(滚动位置、焦点位置等)无法保持。
-
fiber介绍
fiber是React 16中新的和解引擎。它的主要目的是使虚拟DOM能够进行增量渲染。
(1) 同步更新过程的局限
当React决定要加载或者更新组件树时,会做很多事,比如调用各个组件的生命周期函数,计算和比对Virtual DOM,最后更新DOM树,这整个过程是同步进行的。浏览器那个唯一的主线程都在专心运行更新操作,无暇去做任何其他的事情。
(2)React Fiber的方式
破解JavaScript中同步操作时间过长的方法其实很简单——分片。
React Fiber把更新过程碎片化,执行过程如下面的图所示,每执行完一段更新过程,就把控制权交还给React负责任务协调的模块,看看有没有其他紧急任务要做,如果没有就继续去更新,如果有紧急任务,那就去做紧急任务。
维护每一个分片的数据结构,就是Fiber。
(3)React Fiber更新过程的两个阶段
在React Fiber中,一次更新过程会分成多个分片完成,所以完全有可能一个更新任务还没有完成,就被另一个更高优先级的更新过程打断,这时候,优先级高的更新任务会优先处理完,而低优先级更新任务所做的工作则会完全作废,然后等待机会重头再来。
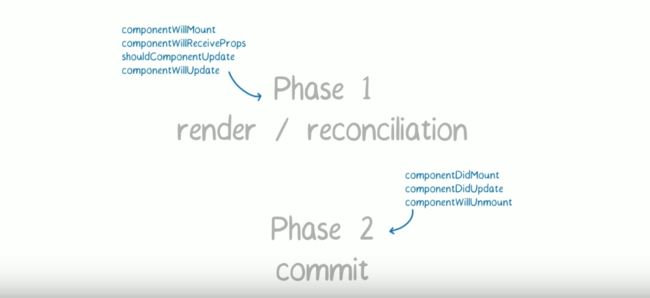
React Fiber一个更新过程被分为两个阶段(Phase):第一个阶段Reconciliation Phase和第二阶段Commit Phase。
在第一阶段Reconciliation Phase,React Fiber会找出需要更新哪些DOM,这个阶段是可以被打断的;但是到了第二阶段Commit Phase,那就一鼓作气把DOM更新完,绝不会被打断。
(4)React Fiber对现有代码的影响
因为第一阶段的过程会被打断而且“重头再来”,就会造成第一阶段中的生命周期函数在一次加载和更新过程中可能会被多次调用!
第一个阶段的四个生命周期函数中,componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillMount和componentWillUpdate这三个函数可能包含副作用,所以当使用React Fiber的时候一定要重点看这三个函数的实现。
注释:大家应该都清楚进程(Process)和线程(Thread)的概念,在计算机科学中还有一个概念叫做Fiber,英文含义就是“纤维”,意指比Thread更细的线,也就是比线程(Thread)控制得更精密的并发处理机制。 - 声明周期变化
从v16.3开始,原来的三个生命周期componentWillMount、componentWillUpdate、componentWillReceiveProps将被废弃,取而代之的是两个全新的生命周期:
①static getDerivedStateFromProps
②getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -
getDerivedStateFromProps用法
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState)
组件实例化后和接受新属性时将会调用getDerivedStateFromProps。它应该返回一个对象来更新状态,或者返回null来表明新属性不需要更新任何状态。
如果父组件导致了组件的重新渲染,即使属性没有更新,这一方法也会被调用。
如果你只想处理变化,你可能想去比较新旧值。调用this.setState()通常不会触发getDerivedStateFromProps()。 -
getStapshotBeforeUpdate
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()在最新的渲染输出提交给DOM前将会立即调用。它让你的组件能在当前的值可能要改变前获得它们。这一生命周期返回的任何值将会 作为参数被传递给componentDidUpdate()。
class ScrollingList extends React.Component {
listRef = React.createRef();
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
// Are we adding new items to the list?
// Capture the current height of the list so we can adjust scroll later.
if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {
return this.listRef.current.scrollHeight;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
// If we have a snapshot value, we've just added new items.
// Adjust scroll so these new items don't push the old ones out of view.
if (snapshot !== null) {
this.listRef.current.scrollTop +=
this.listRef.current.scrollHeight - snapshot;
}
}
render() {
return (
{/* ...contents... */}
);
}
}
在上面的例子中,为了支持异步渲染,在getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 中读取scrollHeight而不是componentWillUpdate,这点很重要。由于异步渲染,在“渲染”时期(如componentWillUpdate和render)和“提交”时期(如getSnapshotBeforeUpdate和componentDidUpdate)间可能会存在延迟。如果一个用户在这期间做了像改变浏览器尺寸的事,从componentWillUpdate中读出的scrollHeight值将是滞后的。
-
Context用法
import React from 'react'
const ThemeContext = React.createContext();
const ThemedButton = (props) => (
{ context => {props.text} }
)
const Toolbar = () => (
)
export default Toolbar
注释:在 Context.Consumer 中,children必须为函数。
参考资料
React中文文档
深入React v16新特性(一)
深入React v16新特性(二)