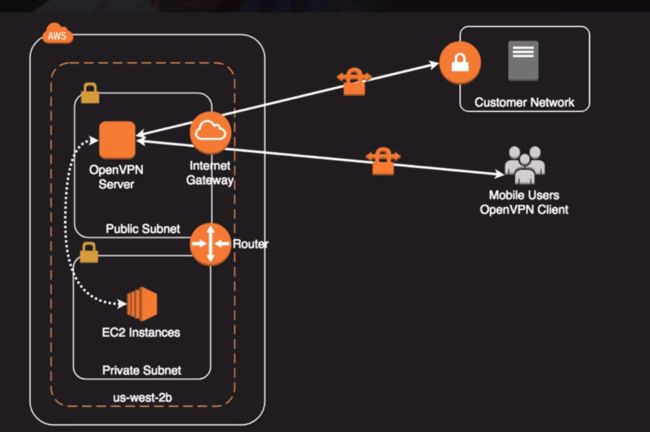
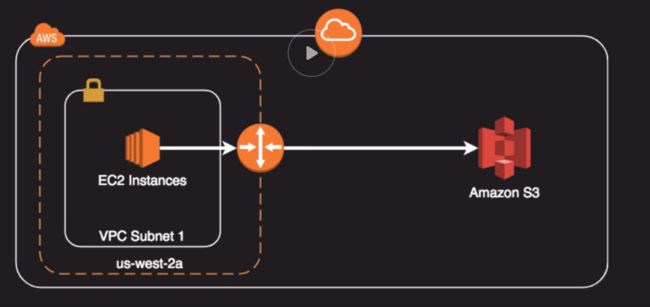
Data Persistance
a. Persistent Data Store: Glacier, RDS
b. Transient Data Store: SQS, SNS
c. Ephemeral Data Store: EC2 Instance Store, MemcachedIOPS vs Throughput
a. IOPS: measure of how fast we can read and write to a device
b. Throughput: measure of how much data can be moved at a timeConsistency Models
a. ACID: Atomic (all or nothing); Consistent (must be valid), Isolated (can't mess with one another), Durable (Completed transaction must stick around)
b. BASE: Basic Availability (values availability even if stale), soft-state (might not be instantly consistent across stores), eventual consistency (will achieve consistency at some point)S3
a. an Object Store
b. Maximum object size is 5TB; largest object in a single PUT is 5 TB
c. multi-part uploads is recommended if larger than 100MB
d. Consistency: read-after-write consistency for PUTs of new objects; HEAD or GET requests of the key before an object exists will result in eventual consistency; s3 offers eventual consistency for overwrite PUTs and DELETEs; updates to a single key are atomic.
e. S3 Security: user-based (IAM policies) -> resource based (bucket policy)-> resource based (object ACL); optional MFA before delete or changing the version state
f. versioning: new version each write, enable "roll-back" and "un-delete" capabilities; old versions count as billable size until they are permanently deleted; integrated with Lifecycle Management (optimize storage cost; adhere to data retention policies; keep s3 volumes well-maintained)
g. Cross-Region Replication: security, compliance, latency
h. Analytics: Data Lake Concept (Athena, Redshift Spectrum, QuickSight); IoT Streaming Data Repo (Kinesis Firehose); Machine Learning and AI Storage (Rekognition, Lex, MXNet); Storage Class Analysis (S3 Management Analytics)
i. S3 Encription at Rest (SSE-S3 (AES-256); SSE-C (AES-256 your own); SSE-KMS; Client-Side (your own local encryption)
j. Transfer Acceleration: Speed up data uploads using Cloud Front in reverse
k. Requester Pays: the requester rather than the bucket owner pays for requests and data transfer
l. Tags: assign tags to objects for use in costing, billing, security, etc.
m. Events: trigger notification to SNS, SQS or Lambda when certain events happen in your bucket
n. Static Web Hosting
o. BitTorrent: Use the BitTorrent protocol to retrieve any publicly available object by automatically generating
a .torrent fileGlacier
a. Cheap, slow to respond, seldom accessed
b. Used by AWS Storage Gateway Virtual Tape Library
c. Integrated with S3 via Lifecycle Management
d. Faster retrieval speed options if you pay more (still archive option)
e. Glacier Vault: IAM manages acces; Glacier Vault Lock manages policies (e.g. no deletes or MFA, immutable); Archive (File, zip, tar, etc. Max size 40TB, Immutable)
f. Glacier Vault Lock: you can initiate it and then decide whether to abort or complete it within 24 hoursEBS ("virtual hard drives" can only be used with EC2 and Tied to a single AZ, variety of optimized choices for IOPS, Throughput and Cost, Snapshots are great)
a. Compared with Instance (Instance - temporary; ideal for caches, buffers, work areas; dta goes away when EC2 is stopped or terminated)
b. Amazon EBS Snapshots (Cost-effective and easy backup strategy, share data sets with other users or accounts, migrate a system to a new AZ or region, converted unencrypted volume to an encrypted volume; incremental snapshot)
c. Schedule snapshots from volumes or instance every X hours by creating Snapshot Lifecycle Policy; retention rules to remove stale snapshotsEFS
a. Implementation of NFS file share
b. Elastic storage capacity, and pay for only what you use (in contrast to EBS)
c. Multi-AZ metadata and data storage
d. Configure mount-points in one or many AZs
e. can be mounted from on-premises systems (security concern though)
f. alternatively, use Amazon DataSync
g. 3x more expensive than EBS and 20x more expensive than S3-
Amazon Storage Gateway
a. VM that run on-premises with VMWare or Hyper V or via a specially configured Dell hardware appliance
b. Provides local storage resources backed by S3 and Glacier
c. Often used in disaster recovery preparedness to sync to AWS
d. Useful in cloud migrations
e. modes
Amazon WorkDocs
a. Secure, fully managed file collaboration service
b. Can integrate with AD for SSO
c. Web, mobile and native clients (no Linux client)
d. HIPAA, PCI DSS and ISO compliance requirements
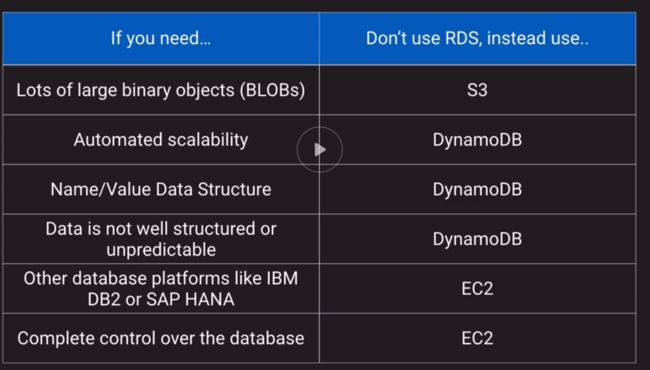
e. Available SDK for creating complementary appsDatabase on EC2
a. Run any database with full control and ultimate flexibility
b. Must manage everything like backups, redundancy, patching, scale
c. Good option if you require a database not yet supported by RDS, such as IBM DB2 or SAP HANA
d. Good option if it is not feasible to migrate to AWS-managed database-
RDS (managed database option for MySQL, Maria, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle and MySQL-compatible Aurora)
a. Best for structured, relational data store needs
b. Aims to be drop-in replacement for existing on-prem instances of same databases
c. Automated backups and patching in customer-defined maintenance windows
d. Push-button scaling, replication and redundancy
e. RDS anti-patterns
f. multi-AZ RDS
g. Read-replicas service regional (non-transactional database does not support replication)
h. Sync Replication (multi-az, between master and standby) vs Async Replication (read-replica, second/min delay)
i. One AZ fails, standy-by in another AZ assumes role of master, read replicas keep on keeping on
j. Whole region failed, read replica promoted to Stand-Alone (single-AZ), single AZ reconfigured to Multi-AZ -
Dynamo DB
a. Managed, multi-AZ noSQL data store with cross-region replication option
b. defaults to eventual consistency reads but can request strongly consistent read via SDK parameter
c. Priced on throughput, rather than compute
d. Provision read and write capacity in anticipation of need
e. Auto scale capacity adjust per configured min/max levels
f. On-Demand capacity for flexible capacity at a small premium cost
g. Achieve ACID compliance with DynamoDB transactions
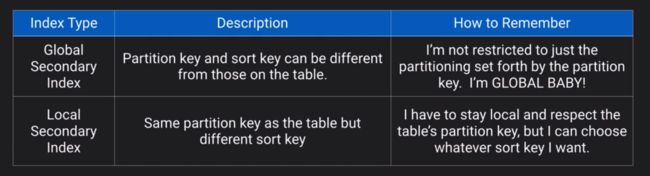
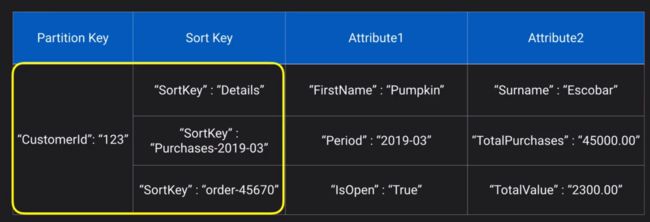
h. Partition key: A simple primary key which must be unique, to create an internal hash mapping
i. A composite primary key: a partition key + sort key, can have occurrences of the same partition key so long as the sort key is different
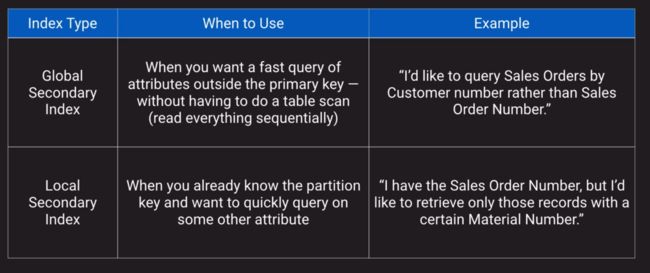
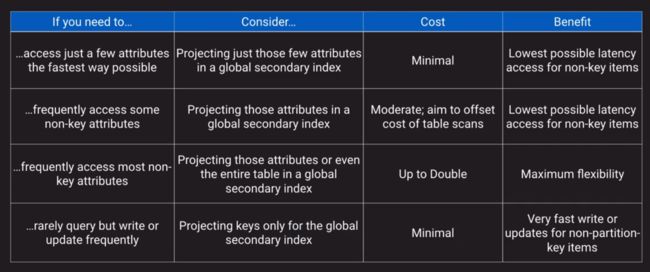
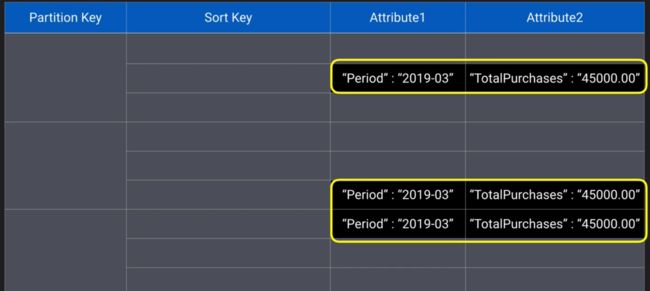
j. Secondary indexes (there is a limit to the number of indexes and attributes per index; it takes up storage space as well)
k. Attribute Projections (like view in traditional database, not more than 20 attributes across all indexes)
l.
m.
m. Sparse Indexes
n. Replicas via Secondary Indexes
-
Redshift
-
Data Lake
d.
a. Query raw data without extensive pre-processing
b. Lessen time from data collection to data value
c. Identify correlations between disparate data sets
Neptune
a. Fully-managed graph database
b. Supports open graph APIs for both Gremlin and SPARQL-
Elasticache
a. Fully managed implementation of two popular in-memory data stores - Redis and Memcached
b. Push-button scalability for memory, writes and reads
c. In Memory key/value store - not persistent in the traditional sense
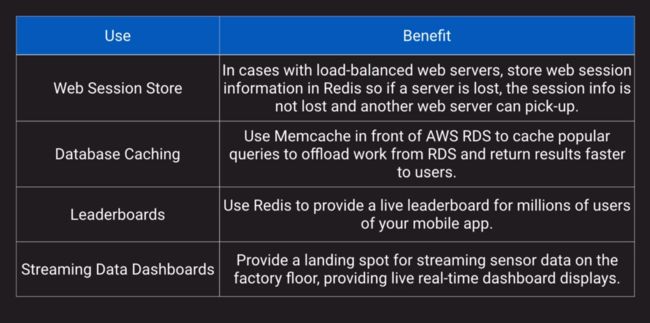
d. Use cases
e. Memcached vs Redis
Amazon Athena: SQL Engine overliad on S3 base on Presto; Query raw data objects as they sit in an S3 bucket; Use or convert your data to Parquet format if possible for a big performance jump; Similar in concept to Redshift but Athena does not need to perform joins with other data sources while Redshit Spectrum want to join S3 data with exsiting RedShift tables or create union products
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
a. Based on blockchain concepts
b. Provides an immutable and transparent journal as a service without having to setup and maintain an entire blockchain framework
c. Centralized design allows for higher performance and scalability
d. Append-only concept where each record contributes to the integrity of the chainAmazon Managed Blockchain
a. Fully managed blockchain framework supporting open source frameworks of Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum
b. Distributed consensus-based concept consisting of a network, members, nodes and potentially applications
c. Uses the Amazon QLDB ordering service to maintain complete history of all transactionsAmazon Timestream Database
a. Fully managed database service specifically built for storing and analyzing time-series data
b. Alternatively to DynamoDB or RedShift and includes some built-in analytics like interpoloation and smoothing
c. Use cases: industrial machinery; sensor networks and equipment telemetry-
DocumentDB (MongaDB compatibility)
-
Elastic Search
-
Database Options
-
Storage options
Pro Tips:
a. Use archiving and backup as the pilot for AWS business case
b. Make use of the S3 endpoints within your VPC
c. Learn how to properly secure your S3 bucket
d. Encrypt, Encrypt, Encrypt
e. Consider Aurora for your production MySQL/Maria or PostgreSQL needs
f. Consider NoSQL if you don't need relational database features
g. Database on EC2 cost less on the surface than RDS, but remember to factor in management (backup, patching, OS-level hardening)
h. There can be a performance hit when RDS backups run if you have only a single AZ instance-
Questions
a.
b.
c. AWS Glue -> Crawler -> Specify data store -> Create an IAM role to access the data->Add Database to store the output -> Run the crawler -> One table will be added -> Athena-> Query against the table->quicksight to visualize the data -
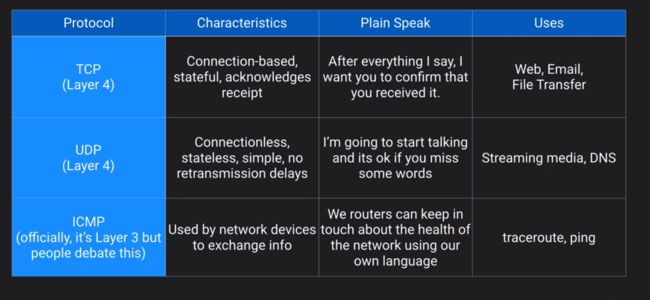
Network Protocols
-
Ephemeral Ports
-
Reserve IP Addresses
The Physical to Logical assignment of AZ's is done at the account level. AZ with the same name may refer to different physical AZ in a different account.
-
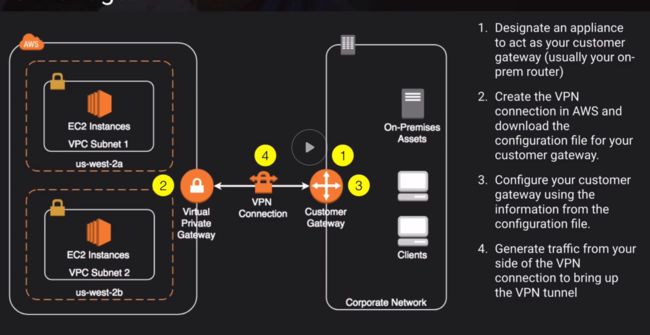
AWS Managed VPN
-
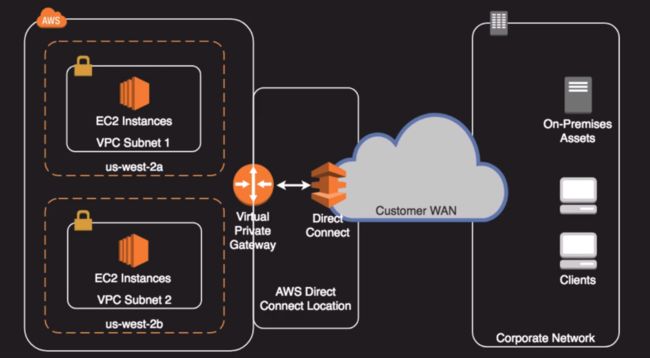
Direct Connect
-
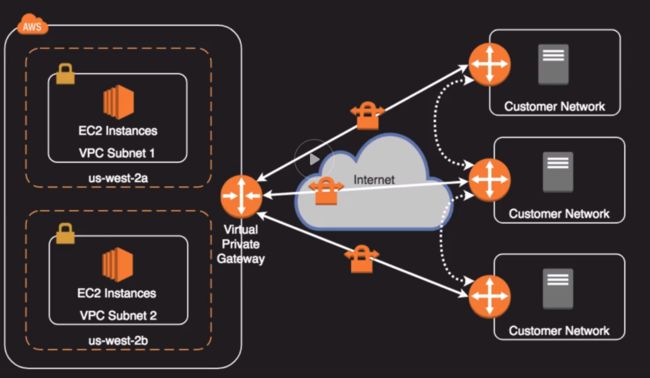
Direct Connect + VPN
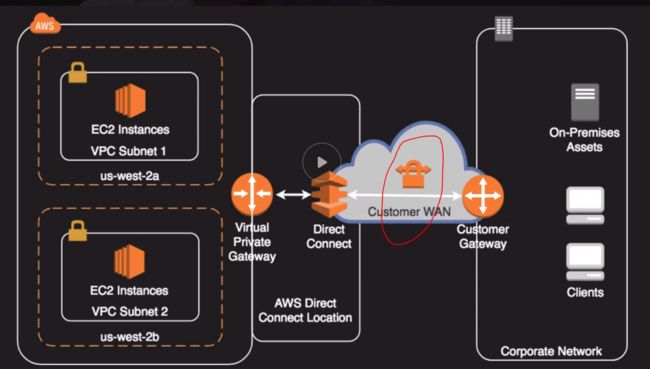 Direct Connect + VPN Architecture
Direct Connect + VPN Architecture -
VPN CloudHub (MPLS)
-
Software VPN (unmanaged VPN)
-
Transit VPC
-
VPC to VPC Connectivity
a. VPC Peering
b. AWS PrivateLink
Internet Gateways: horizontally scaled, redundant and highly available component that allows communication between your VPC and the Internet; No availablility risk or bandwidth constraints; If your subnet is associated with a route to the Internet, then it is a public subnet; Support IPv4and IPV5.
Use case: provide route table target for Internet-bound traffic; perform NAT for instances with public IP addresses (not for instances with prviate IP's only)Egress-Only Internet Gateway (only for IPv6)
a. IPv6 addresses are globally unique and are therefore public by default
b. Provides outbound Interenet access for IPv6 addressed instances
c. Prevents inbound access to those IPv6 instances
d. Must create a custom route for ::/0 to the Egress-Only Internet Gateway
e. Use Egress-only Internet Gateway instead of NAT for IPv6NAT Instance: EC2 instance from a special AWS-provided AMI; translate traffic from many private IP instance to a single public IP and back; doesn't allow public internet initiated connection into private instances; not supported for IPv6 (use Egress-Only Gateway instead); NAT instance must live on a public subnet with route to Internet Gateway; Private instances in private subnet must have route to the NAT instance, usually the default route destination of 0.0.0.0/0
NAT Gateway: fully managed NAT service; must be created in a public subnet; uses an Elstatic IP for public IP for the life of the Gateway; Private instances in private subnet must have route to the NAT instance, usually the default route destination of 0.0.0.0/0; Created in specified AZ with redundancy in that zone; For multi-AZ redundancy, create NAT Gateways in each AZ with routes for private subnets to use the local Gateway; Up to 5Gbps bandwidth that can scale up to 45 Gbps; Cannot use a NAT Gateway to access VPC peering, VPN or Direct Connect, so be sure to include specific routes to those in your route table
-
NAT Gateway vs NAT Instance
-
VPC Routing
a. Routing tables: VPC have an implicit router and main routing table; you can modify the main routing table or create new tables; each route table contains a local route for the CIDR block; most specific route for an adress wins
b. BGP: propagates info about network to allow for dynamic routing; required for direct connect and optional for VPN; alternative of not using BGP with AWS VPC is static routes; AWS supports BGP community tagging as a way to control traffic scope and route preference; required TCP port 179 + ephemeral ports; autonomous system number (ASN) = unique endpoint identifier; weighting is local to the router and higher weight is preferred path for outbound traffic
-
Route 53 Routing (Register domain names, check the health of your domain resources, route internet traffic for your domain)
a. Route 53 Routing Policies
b. Route 53 is a global service
-
ELB Routing
e.
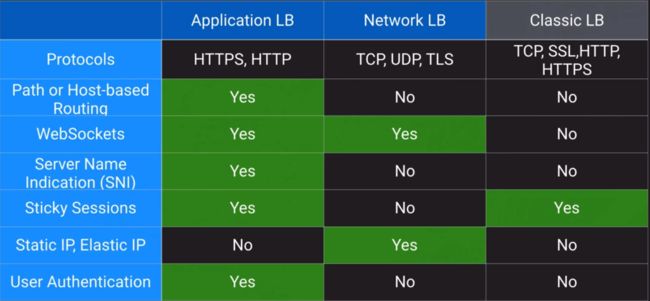
a. Distribute inbound connections to one or many backend endpoints
b. Three different options: Application Load Balancer (Layer 7); Network Load Balancer (Layer 4); Classic Load Balancer (Layer 4 or Layer 7)
c. Can be used for public/private workloads
d. Consume IP addresses within a VPC subnet for scaling
f.
g. Network Load Balancer Routing: Port Number/ TCP connections to backend are persisted for the duration of the connection
h. Application Load Balancer Routing: Host-base routing/Path-based outing/Http header-based routing/Http method-based routing/Query string parameter based routing/Source IP address CIDR-based routing
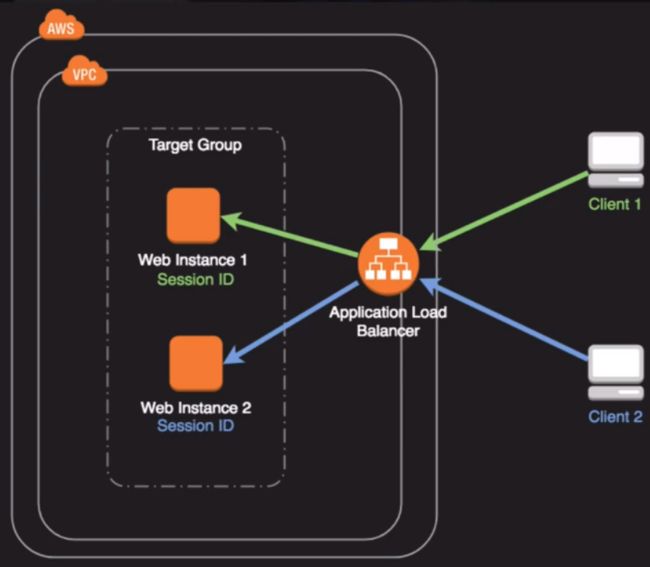
i. Stick Sessions (important feature for web application)
Enhanced Networking
a. Generally used for High Performance Computing use-cases
b. Uses single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) to deliver higher performance than traditional virtualised network interfaces
c. Might have to install drvier if other than Amazon Linux HVM AMI
d. Intel 82599 VF Interface (10 Gbps) vs Elastic Network Adapter (25 Gbps)-
Placement Groups
CloudFront: Distributed connect delivery service for simple static asset caching up to 4k live and on-demand video streaming; integrated with Amazon Certificate Manager and supports SNI (server name indication): allow clients to choose which server it will connect if there are multiple servers share the same IP address
-
Slow connection between VPC (note that internet gateway does not have a bandwidth limit)
-
Distribute web application traffic (session sticky, application layer)
-
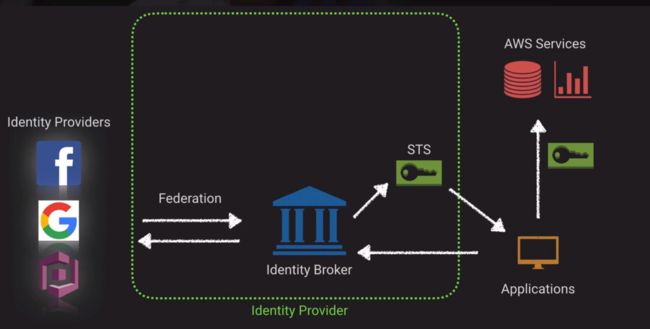
Three popular authentication/authorization methods
AWS Tools for Account Management
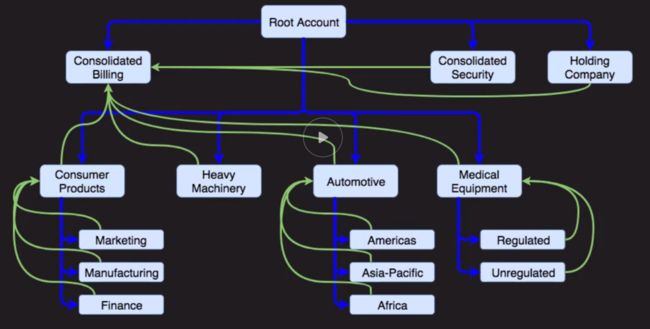
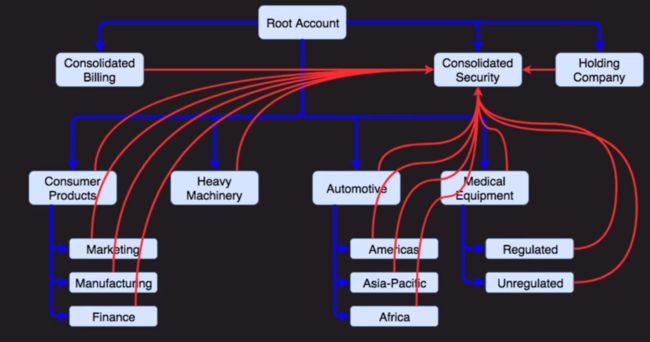
a. AWS Organisations
b. Service Control Policies (sub-account inherited parent account's policies)
c. Tagging
d. Resource Groups
e. Consolidated Billing-
Account Structure
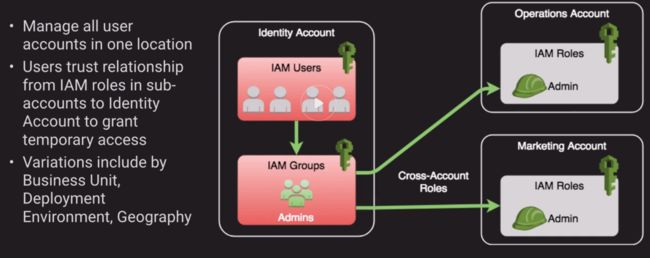
a. Identity Account Structure
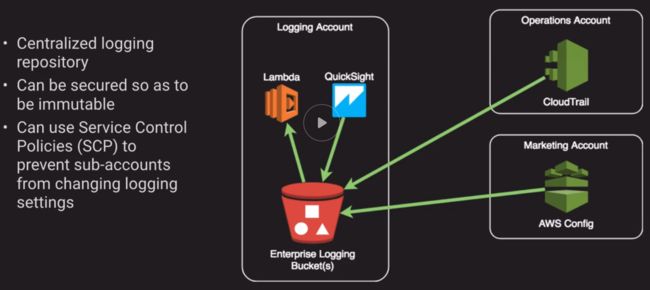
b. Loggin Account Structure
c. Publishing Account Structure
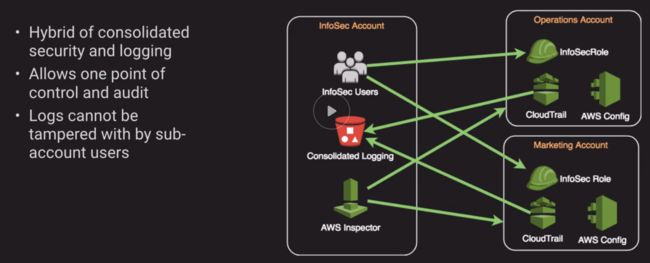
d. Information Security Account Structure
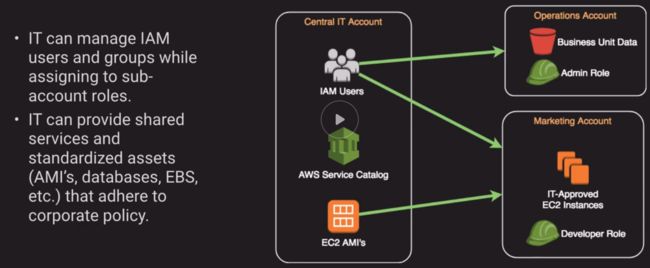
e. Central IT Account Structure
f. Example:
-
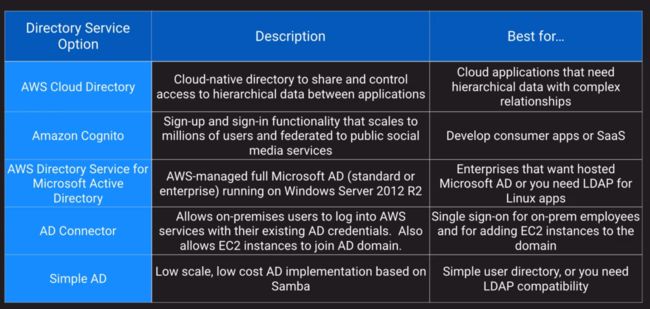
AWS Directory Services
-
AD Connector vs Simple AD
-
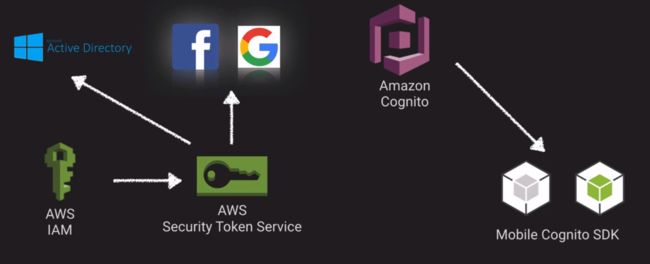
Credential and Access Management
-
Token vending machine concept
-
AWS Secrets Manager
Encryption
a. Encryption at Rest: data is encrypted where it is stored such as on EBS, on S3, in an RDS database, or in an SQS queue waiting to be processed
b. Encryption in Transit: data is encrypted as it flows through a network or process, such as SSL/TLS for HTTPS, or with IPSec for VPN connectionsKey management service (KMS)
a. Key storage, management and auditing
b. Tightly integrated into Many AWS service-
DDoS
-
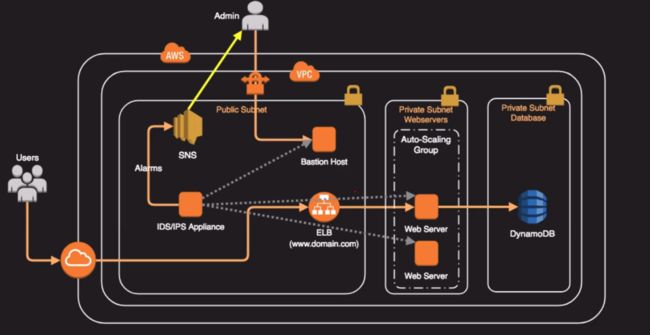
Intruder Detection and Prevention
-
Cloud Watch vs Cloud Trail