Android优化————布局优化
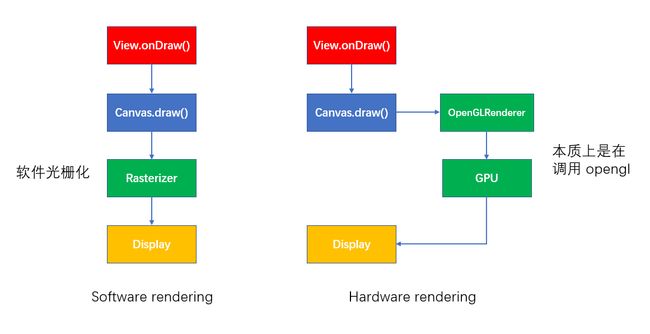
绘画原理
Android的绘制主要是借助cpu和gpu结合刷新机制共同完成的
绘制过程使用skia库(2D),硬件本质是采用openGL库进行绘制
16ms内渲染一次,否则会掉帧
布局加载原理
Android中的布局加载入口为setContentView(),分析如下:
@Override
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getDelegate().setContentView(layoutResID);
}
//AppCompatDelegate.java
public abstract void setContentView(@LayoutRes int resId);
查看抽象接口实现
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
//获取content跟布局
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
//移除所有布局
contentParent.removeAllViews();
//加载新布局
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
//接口状态通知
mOriginalWindowCallback.onContentChanged();
}
进入inflate方法:
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root) {
return inflate(resource, root, root != null);
}
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
final Resources res = getContext().getResources();
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "INFLATING from resource: \"" + res.getResourceName(resource) + "\" ("
+ Integer.toHexString(resource) + ")");
}
final XmlResourceParser parser = res.getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
getLayout方法返回一个XmlResourceParser对象:
public XmlResourceParser getLayout(@LayoutRes int id) throws NotFoundException {
return loadXmlResourceParser(id, "layout");
}
@NonNull
XmlResourceParser loadXmlResourceParser(@AnyRes int id, @NonNull String type)
throws NotFoundException {
final TypedValue value = obtainTempTypedValue();
try {
final ResourcesImpl impl = mResourcesImpl;
impl.getValue(id, value, true);
if (value.type == TypedValue.TYPE_STRING) {
return impl.loadXmlResourceParser(value.string.toString(), id,
value.assetCookie, type);
}
throw new NotFoundException("Resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id)
+ " type #0x" + Integer.toHexString(value.type) + " is not valid");
} finally {
releaseTempTypedValue(value);
}
}
进入loadXmlResourceParser:
@NonNull
XmlResourceParser loadXmlResourceParser(@NonNull String file, @AnyRes int id, int assetCookie,
@NonNull String type)
throws NotFoundException {
if (id != 0) {
try {
synchronized (mCachedXmlBlocks) {
final int[] cachedXmlBlockCookies = mCachedXmlBlockCookies;
final String[] cachedXmlBlockFiles = mCachedXmlBlockFiles;
final XmlBlock[] cachedXmlBlocks = mCachedXmlBlocks;
// First see if this block is in our cache.
final int num = cachedXmlBlockFiles.length;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (cachedXmlBlockCookies[i] == assetCookie && cachedXmlBlockFiles[i] != null
&& cachedXmlBlockFiles[i].equals(file)) {
return cachedXmlBlocks[i].newParser();
}
}
// Not in the cache, create a new block and put it at
// the next slot in the cache.
final XmlBlock block = mAssets.openXmlBlockAsset(assetCookie, file);
if (block != null) {
final int pos = (mLastCachedXmlBlockIndex + 1) % num;
mLastCachedXmlBlockIndex = pos;
final XmlBlock oldBlock = cachedXmlBlocks[pos];
if (oldBlock != null) {
oldBlock.close();
}
cachedXmlBlockCookies[pos] = assetCookie;
cachedXmlBlockFiles[pos] = file;
cachedXmlBlocks[pos] = block;
return block.newParser();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
final NotFoundException rnf = new NotFoundException("File " + file
+ " from xml type " + type + " resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id));
rnf.initCause(e);
throw rnf;
}
}
throw new NotFoundException("File " + file + " from xml type " + type + " resource ID #0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(id));
}
加载指定布局文件的xml,生成XMLBlock:
/*package*/ final XmlBlock openXmlBlockAsset(int cookie, String fileName)
throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (!mOpen) {
throw new RuntimeException("Assetmanager has been closed");
}
long xmlBlock = openXmlAssetNative(cookie, fileName);
if (xmlBlock != 0) {
XmlBlock res = new XmlBlock(this, xmlBlock);
incRefsLocked(res.hashCode());
return res;
}
}
throw new FileNotFoundException("Asset XML file: " + fileName);
}
private native final long openXmlAssetNative(int cookie, String fileName);
最终指向了native方法
获取到XMLResourceParser后,进行渲染:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final Context inflaterContext = mContext;
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context) mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = inflaterContext;
View result = root;
try {
// Look for the root node.
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("Creating root view: "
+ name);
System.out.println("**************************");
}
//如果是merge标签,查看是否是当前布局的父节点,不是的话抛出异常
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("使用XmlPull解析布局,如果是merge标签,merge节点不是当前布局的父节点,则抛出异常,进入CreateViewFromTag:
private View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
return createViewFromTag(parent, name, context, attrs, false);
}
View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
boolean ignoreThemeAttr) {
......
try {
View view;
if (mFactory2 != null) {
view = mFactory2.onCreateView(parent, name, context, attrs);
} else if (mFactory != null) {
view = mFactory.onCreateView(name, context, attrs);
} else {
view = null;
}
if (view == null && mPrivateFactory != null) {
view = mPrivateFactory.onCreateView(parent, name, context, attrs);
}
if (view == null) {
final Object lastContext = mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = context;
try {
if (-1 == name.indexOf('.')) {
view = onCreateView(parent, name, attrs);
} else {
view = createView(name, null, attrs);
}
} finally {
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
}
}
...
}
}
使用mFactory2、mFactory、mPrivateFactory创建view,最终时调用createView方法,内部采用反射创建节点,过多的反射会造成性能问题,可以进行优化。
获取界面布局耗时
- 手动埋点,打印时间
- AOP打印setContView的时间
- 重写LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2方法,打印每一个控件的耗时时间
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 使用LayoutInflaterCompat.Factory2全局监控Activity界面每一个控件的加载耗时,
// 也可以做全局的自定义控件替换处理,比如:将TextView全局替换为自定义的TextView。
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(getLayoutInflater(), new LayoutInflater.Factory2() {
@Override
public View onCreateView(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
if (TextUtils.equals(name, "TextView")) {
// 生成自定义TextView
}
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 1
View view = getDelegate().createView(parent, name, context, attrs);
LogHelper.i(name + " cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
return view;
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
});
//也可以直接调用这个方法
// LayoutInflater.from(this).setFactory2(new LayoutInflater.Factory2() {
// @Override
// public View onCreateView(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//
// if (TextUtils.equals(name, "TextView")) {
// // 生成自定义TextView
// }
// long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
// // 1
// View view = getDelegate().createView(parent, name, context, attrs);
// AppLog.E(name + " cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
// return view;
// }
//
// @Override
// public View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
// return null;
// }
// });
// 2、setFactory2方法需在super.onCreate方法前调用,否则无效
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(getLayoutId());
unBinder = ButterKnife.bind(this);
mActivity = this;
ActivityCollector.getInstance().addActivity(this);
onViewCreated();
initToolbar();
initEventAndData();
}
优化工具
Lint
Android Studio自带工具,可以进行代码校验,发现代码结构/质量问题
Layout Inspector
Android Studio推荐布局检测工具,可以查看整个布局的层级,进而优化处理
GPU过度绘制
手机中打开开发者选项-开启GPU过度绘制
布局优化的必要性
- 减少页面卡顿,提高流畅度
- 减少线上bug产出
总体原则
- 避免层间嵌套
- 减少绘制时间,三个方法的执行时间
优化方法
-
使用include标签重用公共布局
-
使用merge减少视图层级
当使用的是merge时,连续两个布局相似会合并,减少层级。
-
使用viewStub延迟加载,减少资源浪费
-
简单布局使用LinearLayout,复杂布局使用RelativeLayout或者ConstraintLayout减少层级嵌套。
-
善用控件属性
- TextView实现图片+文字显示
- 使用LinearLayout自带的分割线
-
使用space控件
-
尽量少使用wrap_content,增加计算成本,绘制过久
主要布局比较
| 名称 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| RelativeLayout | 减少层级嵌套 | onDraw执行两次,耗时 |
| LinearLayout | 不使用weight,onDraw执行一次 | 布局时容易层级嵌套 |
| FrameLayout | ||
| ConstraintLayout | 减少层级 + 比例布局 | 耗时 |
总结:性能好的布局,FrameLayout和LinearLayout
功能复杂,需要层级嵌套使用RelativeLayout或者ConstraintLayout。
优先考虑层级问题,在考虑单个布局性能问题