更多内容请点击 我的博客 查看,欢迎来访。
用来做什么?
个人在写博客时,发现上传的图片如果很大,web访问第一次加载该图片就特别的慢。
可以考虑使用缩略图,浏览时显示缩略图,如果要看高清图,需点击图片放大查看。
但更希望找到一种能无损压缩图片的方法,由于博客使用的截图大部分是png,就开始在网上查找了。
使用 Pillow 压缩图片(效果不好)
测试支持png、jpg等
import os
import shutil
from PIL import Image # 处理图片
from PIL import ImageDraw # 图片水印使用
from PIL import ImageFont # 图片文字水印
# 图片压缩,添加水印功能
class CompressWatermarkImage(object):
def __init__(self):
self.suffix = ['.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg']
self.size = 80 * 1024 # 设置小于80kb的图片不压缩
def compress(self, src_image, dst_image):
# 图片压缩:src_image、dst_image为绝对路径
if os.path.isfile(src_image) and os.path.splitext(src_image)[1] in self.suffix and os.path.getsize(src_image) > self.size: # 指定文件后缀
try:
# 打开原图片缩小后保存,可以用if src_file.endswith(".jpg")或者split,splitext等函数等针对特定文件压缩
s_img = Image.open(src_image)
w, h = s_img.size
# 设置压缩尺寸和选项,注意尺寸要用括号
d_img = s_img.resize((int(w / 2), int(h / 2)), Image.ANTIALIAS)
# 可以用src_image原路径保存,即覆盖源文件。或者更改后缀保存,save()后面可以加压缩编码选项JPEG之类的
d_img.save(dst_image, quality=95)
print(f"压缩到{dst_image}成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"压缩到{dst_image}失败", e)
def watermark(self, src_image, dst_image):
# 添加水印:src_image、dst_image为绝对路径
# 打开图片
img = Image.open(src_image)
# 图片大小:宽,高
width, height = img.size
# 水印字体大小,可以根据图片高度的1/10之一当做水印文字的大小
font_size = int(height / 10)
# 设置所使用的字体
font = ImageFont.truetype(r"C:\Windows\Fonts\STXINWEI.ttf", font_size)
# 画图
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text(xy=(0, height - font_size * 2), text="http://blog.starmeow.cn", fill=(18, 183, 222, 300), font=font) # 设置文字位置/内容/颜色/字体
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) # 绘图
# 另存图片
img.save(dst_image)
def upload_processing(self, src_image):
# 上传图片是就进行压缩和添加水印操作
path_file, suffix = os.path.splitext(src_image) # 路径\文件名;.png
dst_image = path_file + '_cw_img_bak' + suffix
shutil.copy(src_image, dst_image)
# 添加水印后再压缩
self.watermark(src_image, src_image) # 添加水印直接覆盖自己
# 压缩图片
self.compress(src_image, src_image) # 压缩时直接覆盖源文件保存
# !!!批处理时才能使用
def walk_path(self, src_root_path, dst_root_path):
# 遍历指定目录,压缩和添加水印
if not os.path.exists(dst_root_path):
os.makedirs(dst_root_path) # 创建备份目录
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(src_root_path):
rel_path = str(root).replace(src_root_path, '').lstrip('\\').lstrip('/') # 获取基于src_root_path的相对路径,去除前面\\(Windows),取出/(Linux)
# print(rel_path)
for file in files:
# 拼接基于dst_root_path新的路径
dst_path = os.path.join(dst_root_path, rel_path)
if not os.path.exists(dst_path):
os.makedirs(dst_path) # 如果不存在目标文件夹,则创建
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, file) # 目标文件
if os.path.exists(dst_file):
# 当第一次备份后,后面再运行时,以另一名称保存,即不影响初始文件命名方式
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, 'last_' + file)
src_file = os.path.join(root, file) # 源文件
# 即将src_file复制到dst_file
# print(src_file, ' --> ', dst_file)
shutil.copy(src_file, dst_file)
# 添加水印
self.watermark(src_file, src_file) # 添加水印直接覆盖自己
# 压缩图片
self.compress(src_file, src_file) # 压缩时直接覆盖源文件保存
使用方式
ci = CompressWatermarkImage()
# 指定目录,遍历将图片压缩及添加水印
ci.walk_path(r'**media\blog\images', r'**media\blog\images压缩加水印前备份')
# 指定图片添加水印
ci.watermark(r'**cover\04\BLOG_20200403_120041_66.png', r'**cover\04\newBLOG_20200402_220015_39.png')
TinyPNG实现图片高质量压缩(网络影响)
介绍
使用脚本批量压缩,每个月的免费额度为500张图片;
一张图片重复上传不会消耗额度;
pypi安装:https://pypi.org/project/tinify/
官网地址:https://tinypng.com/
API Key获取
在TinyPng网站的Developer API页面上注册一个账号,并获取API key
输入用户名、邮箱,收到的邮件内容如下:
进去之后就可以看到API Key了
如果没复制好Key的内容,访问 https://tinypng.com/dashboard/api 重新获取即可
安装Python库tinify
pip install tinify
Python代码实现
import tinify
# 使用TinyPNG压缩图片
def tinify(src_image, dst_image):
tinify.key = "tVyt6R7Z**************nqqFPwkb"
old_size = round(os.path.getsize(src_image) / 1024, 2)
# 上传压缩过程
tinify.from_file(src_image).to_file(dst_image)
new_size = round(os.path.getsize(dst_image) / 1024, 2)
print('{}压缩后:{}kb -> {}kb'.format(dst_image, old_size, new_size))
使用pngquant压缩图片(推荐)
官网: https://pngquant.org/
只支持png图片
命令行
- Binary for macOS (v2.12.5)
- Binary for Windows
- Package for Debian Important: don't use version 1.0 from Debian oldstable! Only install 2.0+ from "stretch".
- Various Linux packages, RPM spec
- Latest source code (to build on other platforms)
选项(以Win为例)
-
--force / -f:覆盖现有的输出文件,即多次执行名字相同进行覆盖 -
--skip-if-larger:只有当转换后的文件比原始文件小时才保存它们 -
--output file / -o file要使用的目标文件路径,而不是--ext设置的,不设置则默认输出当源文件相同路径下 -
--ext new.png:设置输出图片的后缀名,默认使用-fs8.png做后缀(防止与源文件重名),假如设置-ext=.png则需要带上--force参数,否则会提示输出文件与输入文件重名无法覆盖 -
--quality min-max:min 和 max 是从 0-100 的数值,用于设置压缩后图片的品质,品质越高压缩率越低;如果转换后的图片比最低品质还低,就不保存,并返回错误码99 -
--speed N:转换速度与品质的比例。1(最佳品质),11(速度最快且粗糙),默认是3 -
--nofs:禁用 Floyd–Steinberg dithering (即基于错误扩散的抖动算法)效果 -
--posterize N:按位数减少调色板的精度。当图像在低深度屏幕上显示时使用(例如,16位显示或压缩的纹理在ARBB44格式); -
--strip:不要复制可选的 PNG 块。在MAC(使用Cocoa reader)时,元数据总是被删除。 -
--verbose / -v:打印状态消息
Windows操作压缩
下载工具Binary for Windows解压后会出现 pngquant.exe 文件
# 压缩后覆盖原文件保存
\pngquant>pngquant.exe --force --skip-if-larger --output 1.png --quality 50-80 --verbose 1.png
# 压缩后不覆盖,而是生成1.new.png
\pngquant>pngquant.exe --force --skip-if-larger --output 1.new.png --quality 50-80 --verbose 1.png
Debian操作压缩
安装pngquant
# apt-get install pngquant -y
# pngquant --force --skip-if-larger --output 1.new.png --quality 50-80 --verbose 1.png
这个和Win下操作一样
Python代码实现
import os
import platform
def pngquant(src_image, dst_image):
if os.path.isfile(src_image) and os.path.splitext(src_image)[1] == '.png': # 指定文件后缀
cmd = 'pngquant --force --skip-if-larger --output {} --quality 50-80 --verbose {}'.format(dst_image, src_image)
# Linux和Windows通用
rt = os.system(cmd)
# print(rt)
if rt == 0:
print(f"压缩到{dst_image}成功")
elif rt == 1:
print(f"压缩到{dst_image}失败,命令错误")
elif rr == 2:
print(f"压缩到{dst_image}失败,参数错误")
else:
print('其它错误')
return rt
# Windows上使用方法
pngquant(r'C:\Users\LR\Desktop\pngquant\1.png', dst_image=r'C:\Users\LR\Desktop\pngquant\2.png')
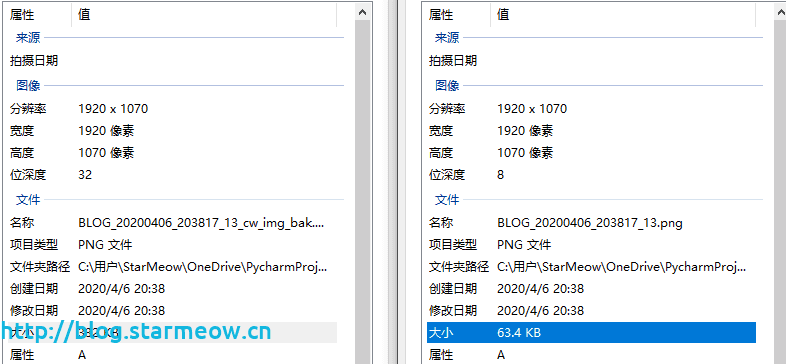
压缩对比
可以节省约70%的空间。
综合应用指定图片打水印且压缩
- 实现了3种压缩图片的方法,如果是png图片,推荐使用pngquant工具
- 实现了1中加水印的方法
- 指定图片的绝对路径,先对该图片进行备份,然后加水印,最后压缩,pngquant压缩比还是比较可观的。
# 图片压缩,添加水印功能
class CompressWatermarkImage(object):
def __init__(self):
self.suffix = ['.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg']
self.size = 80 * 1024 # 设置小于80kb的图片不压缩
# 使用 Pillow 压缩图片(效果不好)
def pillow_compress(self, src_image, dst_image):
# 图片压缩:src_image、dst_image为绝对路径
if os.path.splitext(src_image)[1] in self.suffix and os.path.getsize(src_image) > self.size: # 指定文件后缀
try:
# 打开原图片缩小后保存,可以用if src_file.endswith(".jpg")或者split,splitext等函数等针对特定文件压缩
s_img = Image.open(src_image)
w, h = s_img.size
# 设置压缩尺寸和选项,注意尺寸要用括号
d_img = s_img.resize((int(w / 2), int(h / 2)), Image.ANTIALIAS)
# 可以用src_image原路径保存,即覆盖源文件。或者更改后缀保存,save()后面可以加压缩编码选项JPEG之类的
d_img.save(dst_image, quality=95)
print(f"运行pillow_compress压缩到{dst_image}成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"运行pillow_compress压缩到{dst_image}失败", e)
# 使用TinyPNG压缩图片
def tinify_compress(self, src_image, dst_image):
tinify.key = "tVyt6R7*******************qqFPwkb"
tinify.from_file(src_image).to_file(dst_image)
print(f'运行tinify_compress压缩到{dst_image}完成')
# 使用pngquant压缩图片,只能压缩png图片
def pngquant_compress(self, src_image, dst_image):
if os.path.splitext(src_image)[1] == '.png': # 指定文件后缀
if platform.system() == 'Linux':
# 如果是Debian
if os.system('which pngquant') != 0:
os.system('apt-get install pngquant -y') # 如果是Debian以root用户登录执行命令
# 其他系统没做判断了
pngquant = '/usr/bin/pngquant'
elif platform.system() == 'Windows':
pngquant = r'C:\Apps\pngquant\pngquant.exe'
else:
# 获取不管在Windows还是Linux上都添加环境变量,直接运行 pngquant 命令即可。
pngquant = 'pngquant'
cmd = '{} --force --skip-if-larger --output {} --quality 20-50 --verbose {}'.format(pngquant, dst_image, src_image)
rt = os.system(cmd)
# print(rt)
if rt == 0:
print(f"运行pngquant_compress压缩到{dst_image}成功")
elif rt == 1:
print(f"运行pngquant_compress压缩到{dst_image}失败,命令错误")
elif rt == 2:
print(f"运行pngquant_compress压缩到{dst_image}失败,参数错误")
else:
print('运行pngquant_compress其它错误')
return rt
# 调用压缩图片的方法
def compress(self, src_image, dst_image):
if os.path.isfile(src_image):
old_size = round(os.path.getsize(src_image) / 1024, 2)
if os.path.splitext(src_image)[1] == '.png':
self.pngquant_compress(src_image, dst_image)
else:
try:
self.tinify_compress(src_image, dst_image)
except Exception:
self.pillow_compress(src_image, dst_image)
new_size = round(os.path.getsize(dst_image) / 1024, 2)
print('压缩:{}kb -> {}kb,节省空间:{}%'.format(old_size, new_size, round((old_size - new_size) / old_size * 100, 2)))
else:
print('不是文件,不执行压缩')
# 添加图片水印
def watermark(self, src_image, dst_image):
# 添加水印:src_image、dst_image为绝对路径
# 打开图片
img = Image.open(src_image)
# 图片大小:宽,高
width, height = img.size
# 水印字体大小,可以根据图片高度的1/15之一当做水印文字的大小
font_size = int(height / 15)
# 设置所使用的字体
# font = ImageFont.truetype(r"C:\Windows\Fonts\STXINWEI.ttf", font_size)
# 使用自定义的ttf文件
font = ImageFont.truetype(os.path.join(settings.MEDIA_ROOT, 'blog/fonts/Ubuntu-Medium.ttf'), font_size)
# 画图
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text(xy=(0, height - font_size * 2), text="http://blog.starmeow.cn", fill=(18, 183, 222, 300), font=font) # 设置文字位置/内容/颜色/字体
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) # 绘图
# 另存图片
img.save(dst_image)
def upload_processing(self, src_image):
"""
上传图片是就进行压缩和添加水印操作;
备份文件->加水印->压缩
:param src_image: 操作图片的绝对路径
:return:
"""
path_file, suffix = os.path.splitext(src_image) # 路径\文件名;.png
dst_image = path_file + '_cw_img_bak' + suffix
shutil.copy(src_image, dst_image)
print('添加水印中···')
self.watermark(src_image, src_image) # 添加水印直接覆盖自己
print('压缩图片中···')
self.compress(src_image, src_image) # 压缩时直接覆盖源文件保存
# !!!批处理时才能使用
def walk_path(self, src_root_path, dst_root_path):
# 遍历指定目录,压缩和添加水印
if not os.path.exists(dst_root_path):
os.makedirs(dst_root_path) # 创建备份目录
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(src_root_path):
rel_path = str(root).replace(src_root_path, '').lstrip('\\').lstrip('/') # 获取基于src_root_path的相对路径,去除前面\\(Windows),取出/(Linux)
# print(rel_path)
for file in files:
# 拼接基于dst_root_path新的路径
dst_path = os.path.join(dst_root_path, rel_path)
if not os.path.exists(dst_path):
os.makedirs(dst_path) # 如果不存在目标文件夹,则创建
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, file) # 目标文件
if os.path.exists(dst_file):
# 当第一次备份后,后面再运行时,以另一名称保存,即不影响初始文件命名方式
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, 'last_' + file)
src_file = os.path.join(root, file) # 源文件
# 即将src_file复制到dst_file
# print(src_file, ' --> ', dst_file)
shutil.copy(src_file, dst_file)
# 添加水印
self.watermark(src_file, src_file) # 添加水印直接覆盖自己
# 压缩图片
self.compress(src_file, src_file) # 压缩时直接覆盖源文件保存