Class 内部中有个方法缓存 cache_t,用散列表来缓存调用过的方法,可以提高访问方法的速度。
一、cache_t结构
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets;//数组
mask_t _mask;//
mask_t _occupied;
public:
struct bucket_t *buckets();
mask_t mask();
mask_t occupied();
void incrementOccupied();
void setBucketsAndMask(struct bucket_t *newBuckets, mask_t newMask);
void initializeToEmpty();
mask_t capacity();
bool isConstantEmptyCache();
bool canBeFreed();
static size_t bytesForCapacity(uint32_t cap);
static struct bucket_t * endMarker(struct bucket_t *b, uint32_t cap);
void expand();
void reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity);
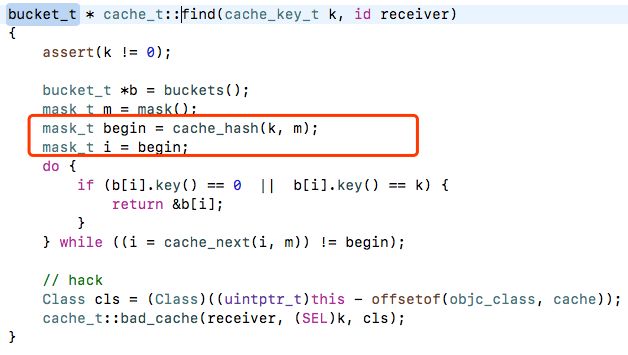
struct bucket_t * find(cache_key_t key, id receiver);
static void bad_cache(id receiver, SEL sel, Class isa) __attribute__((noreturn));
};
1.struct bucket_t *_buckets:数组
struct bucket_t {
private:
cache_key_t _key;//@selector()
IMP _imp;//函数地址
public:
inline cache_key_t key() const { return _key; }
inline IMP imp() const { return (IMP)_imp; }
inline void setKey(cache_key_t newKey) { _key = newKey; }
inline void setImp(IMP newImp) { _imp = newImp; }
void set(cache_key_t newKey, IMP newImp);
};
1)cache_key_t _key:@selector(),方法名字
2)IMP _imp:函数地址
2.mask_t _mask:总槽位-1
3.mask_t _occupied:实际使用槽位
二、如何映射?
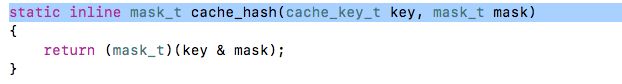
1)发现了映射关系是 key & mask = index。
2)key 是什么?@selector(方法名)
3)mask 是什么?总槽位-1
4)key & mask = index: index 一定是<=_ mask
**Hash表的原理其实是:f(key) = index。通过一个函数 直接找到 index。
结构示意图:
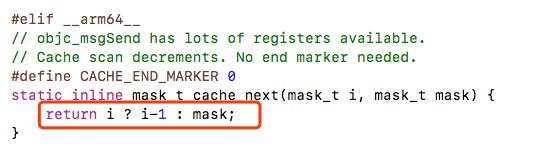
Hash 表会有碰撞的问题(@selector(test) & _mask 和 @selector(test1) & _mask 值相同),看看苹果是如何解决的:
发现当发生碰撞的时候,索引会-1,查找下一个。
三、验证方法缓存
#ifndef MyClass_h
#define MyClass_h
typedef uint32_t mask_t;
typedef uintptr_t cache_key_t;
typedef unsigned long uintptr_t;
struct bucket_t {
char *_key;//@selector()
IMP _imp;//函数地址
};
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets;//数组
mask_t _mask;//数组count - 1
mask_t _occupied;//实际使用槽位
};
struct gl_objc_class{
Class isa;
Class superclass;
struct cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
uintptr_t bits;
};
#endif /* MyClass_h */
没有模拟碰撞
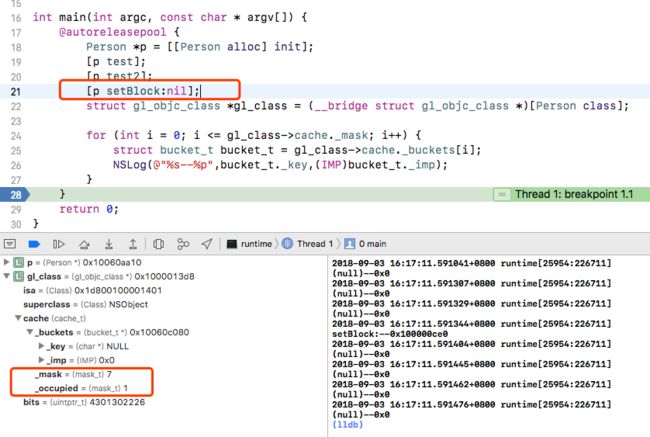
现在默认的_mask 是 3 ,说明槽位是 4 个,实际占用槽位是3个。然后我们再多调用一个方法:
发现_occupied数量等于_mask时,再次加入一个缓存方法时,槽位的总量会变大,槽位会变为原来的2倍,源码中有写到:
void cache_t::expand()
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity();
uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) {
// mask overflow - can't grow further
// fixme this wastes one bit of mask
newCapacity = oldCapacity;
}
reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity);
}
同时发现,扩容的时候将Hash 表里的内容进行了清空。
再看一个现象,Kid 是继承自 Person 的类
当子类没有方法时候,会调用父类的方法,并且将父类的方法缓存到了本类的cache 里。
总结:
1、每个Class 里会有一个cache 方法缓存。
2、cache 本质是一个 Hash表。
3、hash 函数式 f(@selector()) = index, @selector() & _mask。
4、槽位如果不够,_mask 会变换,变为原来的2倍,并且扩展槽位的时候,会清空数组里原有的缓存内容。
5、子类没有实现方法会调用父类的方法,会将父类方法加入到子类自己的cache 里。