App启动涉及三个进程和六个大类:
三个进程:
Launcher进程:整个App启动流程的起点,负责接收用户点击屏幕事件,它其实就是一个Activity,里面实现了点击事件,长按事件,触摸等事件,可以这么理解,把Launcher想象成一个总的Activity,屏幕上各种App的Icon就是这个Activity的button,当点击Icon时,会从Launcher跳转到其他页面;
SystemServer进程:这个进程在整个的Android进程中是非常重要的一个,地位和Zygote等同,它是属于Application Framework层的,Android中的所有服务,例如AMS, WindowsManager, PackageManagerService等等都是由这个SystemServer fork出来的。所以它的地位可见一斑。
App进程:你要启动的App所运行的进程;
六个大类:
ActivityManagerService:(AMS)AMS是Android中最核心的服务之一,主要负责系统中四大组件的启动、切换、调度及应用进程的管理和调度等工作,其职责与操作系统中的进程管理和调度模块相类似,因此它在Android中非常重要,它本身也是一个Binder的实现类。
Instrumentation:监控应用程序和系统的交互;
ActivityThread:应用的入口类,通过调用main方法,开启消息循环队列。ActivityThread所在的线程被称为主线程;
ApplicationThread:ApplicationThread提供Binder通讯接口,AMS则通过代理调用此App进程的本地方法
ActivityManagerProxy:AMS服务在当前进程的代理类,负责与AMS通信。
ApplicationThreadProxy:ApplicationThread在AMS服务中的代理类,负责与ApplicationThread通信。
可以说,启动的流程就是通过这六个大类在这三个进程之间不断通信的过程;
我先简单的梳理一下app的启动的步骤:
(1)启动的起点发生在Launcher活动中,启动一个app说简单点就是启动一个Activity,那么我们说过所有组件的启动,切换,调度都由AMS来负责的,所以第一步就是Launcher响应了用户的点击事件,然后通知AMS
(2)AMS得到Launcher的通知,就需要响应这个通知,主要就是新建一个Task去准备启动Activity,并且告诉Launcher你可以休息了(Paused);
(3)Launcher得到AMS让自己“休息”的消息,那么就直接挂起,并告诉AMS我已经Paused了;
(4)AMS知道了Launcher已经挂起之后,就可以放心的为新的Activity准备启动工作了,首先,APP肯定需要一个新的进程去进行运行,所以需要创建一个新进程,这个过程是需要Zygote参与的,AMS通过Socket去和Zygote协商,如果需要创建进程,那么就会fork自身,创建一个线程,新的进程会导入ActivityThread类,这就是每一个应用程序都有一个ActivityThread与之对应的原因;
(5)进程创建好了,通过调用上述的ActivityThread的main方法,这是应用程序的入口,在这里开启消息循环队列,这也是主线程默认绑定Looper的原因;
(6)这时候,App还没有启动完,要永远记住,四大组建的启动都需要AMS去启动,将上述的应用进程信息注册到AMS中,AMS再在堆栈顶部取得要启动的Activity,通过一系列链式调用去完成App启动;
详细的调用流程:
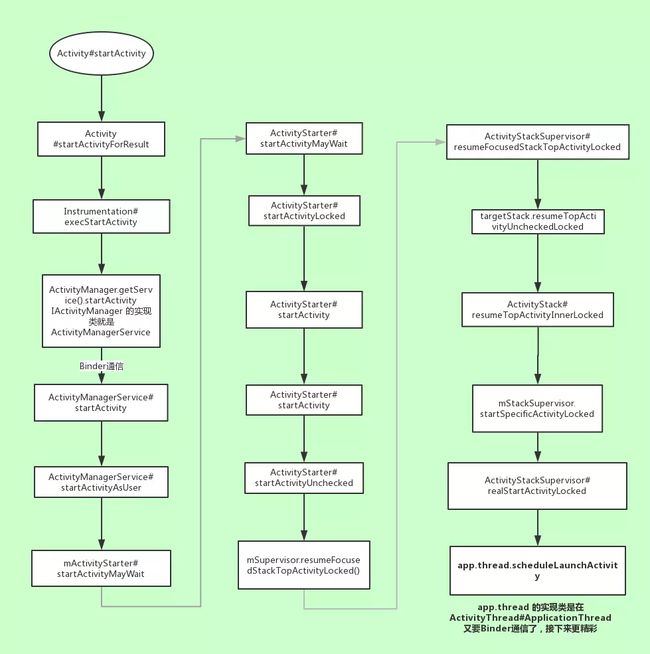
1. startActivity 我们去启动一个新页面
LaunchActivity 也没多干什么事,LaunchActivity 会解析我们点击图标对应的 app 的配置文件,获取期中信息构建 intent ,然后再调用 startActivity
// 桌面点击app图标
public void onClick(View v) {
...
Object tag = v . getTag ();
if (taginstanceof ShortcutInfo) {
onClickAppShortcut(v);
}
}
protected void onClickAppShortcut(final View v) {
...
// Start activities
startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(v);
}
private void startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(View v) {
ItemInfo item =(ItemInfo) v . getTag ();
Intent intent;
// 通过 PackageManagerService 解析AndroidManifest.xml
if (iteminstanceof PromiseAppInfo) {
PromiseAppInfo promiseAppInfo =(PromiseAppInfo) item;
intent = promiseAppInfo.getMarketIntent();
}else {
intent = item.getIntent();
}
...
boolean success = startActivitySafely (v, intent, item);
...
}
public boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, ItemInfo item) {
...
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
...
startActivity(intent, optsBundle);
...
}
这样 app 冷启动和 Activity 启动 Activity 就联系起来了,app 冷启动相比多了一步获取目标 app 信息构建 intent 过程,然后都会走 Activity.startActivity()
2. Activity.startActivity()
Activity.startActivity() 调的是 startActivityForResult(), startActivityForResult() 方法会使用 mInstrumentation.execStartActivity()
//
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode,
@Nullable Bundle options) {
...
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
...
}
3. mInstrumentation.execStartActivity
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity 里面会调 ActivityManager.startActivity ,ActivityManager 知道了吧,是 Activity 与 ActivityManagerService 的远程 AIDL 通讯类,并把反向 AIDL 通讯对象 ApplicationThread 传给远程 ActivityManagerService , 方便 ActivityManagerService 回调,这样看 Activity 把创建 Activity 的任务交给了 远程 ActivityManagerService
//
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
...
try {
...
// 这个 whoThread 就是 ApplicationThread 反向 AIDL 通讯对象
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
...
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
return null;
}
4. ActivityManagerService.startActivity
//
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
ActivityManagerService 的 startActivity 里面多次调用了其他方法:
startActivity()
-> ActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait()
-> ActivityStarter.startActivityLocked()
-> ActivityStarter.startActivity()
-> ActivityStarter.startActivityUnchecked()
-> ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked()
-> ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked()
-> ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked()
-> ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked()
上边的方法一个调用一个;一直到在 startSpecificActivityLocked 这个方法里才能看到核心内容,这个方法中会判断目标进程是否存在,存在则通知进程启动 Activity,否则就先将进程创建出来
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
...
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
...
// 如果进程已存在,则通知进程启动组件
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
...
}
// 否则先将进程创建出来
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
...
}
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
...
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, entryPointArgs);
...
}
5. ActivityManagerService.realStartActivityLocked 创建新 Activity
我们先来看 realStartActivityLocked 这个方法,这个方法会通过 ApplicationThread 回调 UI 进程创建一个 Activity 出来,app.thread 就是我们之前传递过去的 ApplicationThread AIDL 反向回调
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
//...code
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent (r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global and
// override configs.
mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,
r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
//...code
}
6. Process.start 创建目标进程
在 4 中,我们看到 ActivityManagerService 会判断目标进程存不存在,不存在就 fork 一个新的进程出来,Process.start 就是创建进程的代码
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
return zygoteProcess.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
}
zygoteProcess.start
-> startViaZygote()
-> zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote)
-> Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
Zygote进程完成了进程创建的操作后就会执行ActivityThread的main()方法
系统在 fork 一个新的进程后,会在新的进程里面启动 Ui 线程,也就是 ActivtyThread 对象,而 ActivtyThread.main() 方法才是一个 app 进程真正的开始‘
public static void main(String[] args){
...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//初始化Looper
...
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
//实例化一个ActivityThread
thread.attach(false);
//这个方法最后就是为了发送出创建Application的消息
...
Looper.loop();
//主线程进入无限循环状态,等待接收消息
}
mian 方法中,先把 UI 线程的 looper 消息队列准备好,然后 new 一个 UI 线程对象,然后初始化 UI 线程的参数,最后把 UI 线程的 looper 消息队列跑起来,UI 线程进入等待任务阶段
这里面我们需要详细看看 thread.attach(false) UI 线程初始化参数方法干了什么
public void attach(boolean system){
...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
//获得IActivityManager实例,下面会看看它是个啥
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
//看见没?关键啊。mAppThread这个参数下面也会说一下
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
...
}
可以看到我们把 AIDL 反向回调通讯注册到了 ActivityManagerService 里面,然后那必然操作又切回到了系统的 ActivityManagerService 进程里,接着 ActivityManagerService 里面的代码走到了 attachApplicationLocked 这个位置
attachApplicationLocked 方法很重要,期中执行了2个操作,先创建 application 对象,再创建 Activity 对象,这2个方法可是串行执行的,都是 AIDL 远程操作
//
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
....
// 创建 application 对象
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
...
// 然后再创建 Activity 对象
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
...
}
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
final String processName = app.processName;
...
if (realStartActivityLocked(activity, app,
top == activity /* andResume */, true /* checkConfig */)) {
...
}
...
}
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
...
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global
// and override configs.
mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,
r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
...
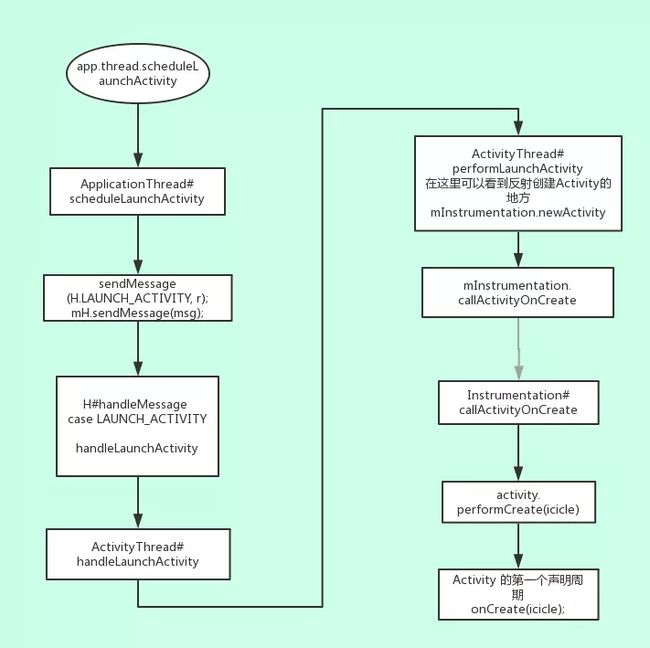
7. UI 线程接受消息,new application 对象
可以看见 attachApplicationLocked 又通过 ApplicationThread 回调,让 UI 进程干活了,注意这个 ApplicationThread 所在的进程就不是我们发起 startActivity 的 LaunchActivity 所在的进程了,而是我们刚刚 fork 出来的目标进程了
接着我们来看看 UI 进程的 bindApplication 方法
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial) {
...
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj) {
sendMessage(what, obj, 0, 0, false);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}
ApplicationThread 发送了一个 H.BIND_APPLICATION 的消息,该消息会由 ActivityThread 一个名叫 H 的 handle内部类接收
//
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
switch (msg.what) {
...
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
...
}
}
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
...
final InstrumentationInfo ii;
...
// 创建 mInstrumentation 实例
if (ii != null) {
final ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo();
ii.copyTo(instrApp);
instrApp.initForUser(UserHandle.myUserId());
final LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo,
appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true, false);
final ContextImpl instrContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, pi);
try {
final ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
...
} else {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
}
...
Application app;
...
// 创建 Application 实例
try {
...
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
...
try {
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
} finally {
...
}
...
}
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
...
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {// 传入为 null 所以不走
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
...
return app;
}
static public Application newApplication(Class clazz, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = (Application)clazz.newInstance();
app.attach(context);
return app;
}
该 handle 会创建一个 mInstrumentation 实例,然后创建出上下文对象,application 对象,application 绑定上下文,mInstrumentation 对象会执行 application.onCreate() 初始化
8. UI 线程接受消息,new activity 对象
在6里面,ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked() 里面连着干了2件事,先创建 application ,完事再创建 activity 对象,在7里面我们创建完了 application 对象,下面就该创建 activity 对象了
//
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List pendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
...
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity() 方法里发送一个 H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY 创建 activity 对象的消息
然后 ActivityThread 的 handle 接受消息,由 Instrumentation new activity 对象,activity 对象初始化参数,最后由 Instrumentation 执行 activity.onCreate() 初始化方法
//
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List pendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
...
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
switch (msg.what) {
...
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY");
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
...
}
}
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) {
...
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
...
}
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
...
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
try {
// 返回之前创建过的 application 对象
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
...
if (activity != null) {
...
// attach 到 window 上
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback);
...
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
...
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
return activity;
}
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
public Activity newActivity(Class clazz, Context context,
IBinder token, Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
Object lastNonConfigurationInstance) throws InstantiationException,
IllegalAccessException {
Activity activity = (Activity)clazz.newInstance();
ActivityThread aThread = null;
activity.attach(context, aThread, this, token, 0 /* ident */, application, intent,
info, title, parent, id,
(Activity.NonConfigurationInstances)lastNonConfigurationInstance,
new Configuration(), null /* referrer */, null /* voiceInteractor */,
null /* window */, null /* activityConfigCallback */);
return activity;
}
到这 activity 的创建流程算是完事了,之后走 activity 的生命周期函数,再由 window 渲染界面显示,但是这里我们还要看看 activity.attach方法,看看 activity 初始化了什么参数,方面之后我们继续说 window
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow (this, window);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode);
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
mMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token;
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
mReferrer = referrer;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mTitle = title;
mParent = parent;
mEmbeddedID = id;
mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances;
if (voiceInteractor != null) {
if (lastNonConfigurationInstances != null) {
mVoiceInteractor = lastNonConfigurationInstances.voiceInteractor;
} else {
mVoiceInteractor = new VoiceInteractor (voiceInteractor, this, this,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager) context . getSystemService (Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo . FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
}
创建了 PhoneWindow 窗口,给窗口对象注册监听,通过窗口Window创建,初始参数赋值,把和 WindowManagerService 远程通讯的 WindowManagerImpl AIDL 对象绑定给 PhoneWindow
参考文章:
startActivity启动流程的源码学习
Android App启动流程详解
app 启动流程
App启动流程