浅析java类加载源码及测试
时间:20180225
类加载ClassLoader的源码中最重要的是ClassLoader方法、loadClass方法、findClass方法及defineClass方法,至于其他的方法不做解释。
// -- Class --
//通过name(二进制字节码)加载类,并按双亲委派的算法去执行
//findLoadedClass在已经加载的类中去寻找
//任何加载器都有父加载器
//如果某个加载器的父加载器为空(NULL),则父加载器为启动加载器(Bootstrap ClassLoader,虚拟机默认的加载器)
//如果要自己实现加载器,需要重载findClass()方法
//没有找到类时throws ClassNotFoundException异常
protected Class loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
//1. 检查当前类是否已经被加载
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
//2.如果当前类没有被加载过
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
//3.并且当前加载器的父加载器不为空,即不为启动加载器
if (parent != null) {
//4.1 循环委托给自己的父加载器(Ext或者App)
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
//4.2 循环委托给自己的父加载器(Bootstrap )
//返回通过BootStrap类加载器加载得到的类
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
//返回通过BootStrap类加载器加载得到的类
private Class findBootstrapClassOrNull(String name)
{
if (!checkName(name)) return null;
return findBootstrapClass(name);
}
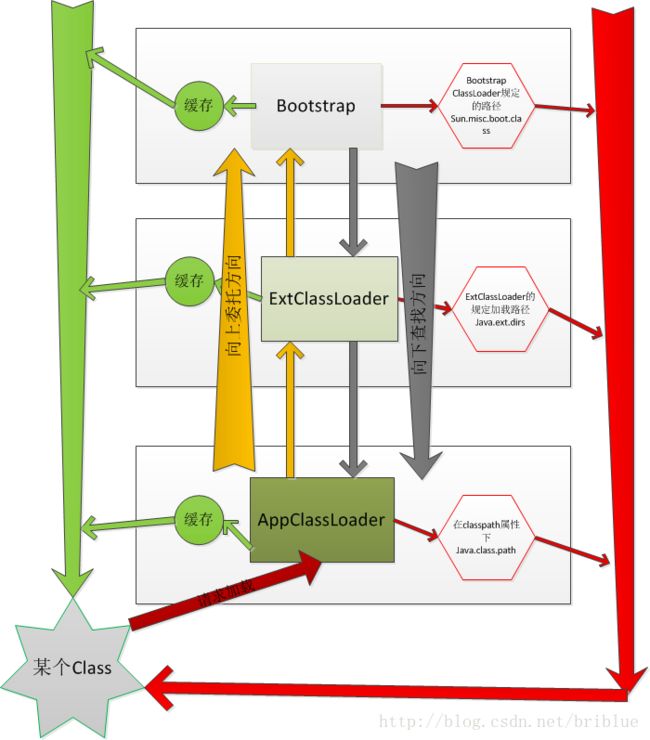
代码解释:按照包含关系(非继承关系)
- 自定义加载器--->父加载器(自定义启动器or应用加载器App ClassLoader)--->父加载器(Ext ClassLoader)--->父加载器(启动加载器Bootstrap ClassLoader)。
- 代码中利用递归不停查找类的加载器的父加载器。直到最终找到的父加载器为NULL也就是为启动加载器时。
- Bootstrap ClassLoader加载器中调用findBootstrapClassOrNull()方法首先查找缓存,如果没有找到的话,就去找自己规定的路径下,也就是sun.mic.boot.class下面的路径,找到就返回,没有找到,就让子加载器自己去找(递归实现)。
- ExtClassLoader查找不成功,App ClassLoader就自己去查找。找到就返回。如果没有找到就让子加载器去找。如果子加载器(自定义加载器没有找到)?就会抛出异常(hrows ClassNotFoundException异常)。
- 上面代码及解释中。说明了双亲委派的加载流程。我们可以发现委派是从下向上。然后具体查找过程却是自上而下。如图解中。
图解双亲委派模型
/**
* Finds the class with the specified binary name.
* This method should be overridden by class loader implementations that
* follow the delegation model for loading classes, and will be invoked by
* the {@link #loadClass loadClass} method after checking the
* parent class loader for the requested class. The default implementation
* throws a ClassNotFoundException.
*
* @param name
* The binary name of the class
*
* @return The resulting Class object
*
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* If the class could not be found
*
* @since 1.2
*/
protected Class findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
/**
* Converts an array of bytes into an instance of class Class,
* with an optional ProtectionDomain. If the domain is
* null, then a default domain will be assigned to the class as
* specified in the documentation for {@link #defineClass(String, byte[],
* int, int)}. Before the class can be used it must be resolved.
*
* The first class defined in a package determines the exact set of
* certificates that all subsequent classes defined in that package must
* contain. The set of certificates for a class is obtained from the
* {@link java.security.CodeSource CodeSource} within the
* ProtectionDomain of the class. Any classes added to that
* package must contain the same set of certificates or a
* SecurityException will be thrown. Note that if
* name is null, this check is not performed.
* You should always pass in the binary name of the
* class you are defining as well as the bytes. This ensures that the
* class you are defining is indeed the class you think it is.
*
*
The specified name cannot begin with "java.", since
* all classes in the "java.* packages can only be defined by the
* bootstrap class loader. If name is not null, it
* must be equal to the binary name of the class
* specified by the byte array "b", otherwise a {@link
* NoClassDefFoundError NoClassDefFoundError} will be thrown.
*
* @param name
* The expected binary name of the class, or
* null if not known
*
* @param b
* The bytes that make up the class data. The bytes in positions
* off through off+len-1 should have the format
* of a valid class file as defined by
* The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification.
*
* @param off
* The start offset in b of the class data
*
* @param len
* The length of the class data
*
* @param protectionDomain
* The ProtectionDomain of the class
*
* @return The Class object created from the data,
* and optional ProtectionDomain.
*
* @throws ClassFormatError
* If the data did not contain a valid class
*
* @throws NoClassDefFoundError
* If name is not equal to the binary
* name of the class specified by b
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* If either off or len is negative, or if
* off+len is greater than b.length.
*
* @throws SecurityException
* If an attempt is made to add this class to a package that
* contains classes that were signed by a different set of
* certificates than this class, or if name begins with
* "java.".
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)
throws ClassFormatError
{
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class c = defineClass1(name, b, off, len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
三、举例
-
例子1
package com.test.jvm;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
private String name;//加载器名称
private String path;//加载器名称
//构造函数
public MyClassLoader(String name , String path) {
super();//让系统类加载器为该类父加载器
this.name = name;
this.path = path;
}
//构造函数,制定父加载器
public MyClassLoader(ClassLoader parent, String name, String path) {
super(parent);//显示的指定父加载器
this.name=name;
this.path=path;
}
/**
* 加载我们定义的类,通过我们定义的ClassLoader
*/
@Override
protected Class findClass(String name)throws ClassNotFoundException{
byte[] data = null;
Class C = null;
try {
data = readClassFileToByteArray(name);
C = this.defineClass(name, data, 0, data.length);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return C;
}
//如果不重写 ToString 结果是 Demo :com.test.jvm.MyClassLoader@55f96302
//为name(全限定名\类名)对应类数据所在的地址,toString的作用是将地址转换为类名
//即加上下面三行代码后返回结果变为:Demo :TanShen
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
/**
*获取硬盘.class文件中的字节码数据,将数据存储与数组中
*.class文件由.java文件经过cmd执行javc生成
*1.处理传入的name(com.test.jvm.Demo或者Demo)
* @param name
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private byte[] readClassFileToByteArray(String name) throws Exception {
name = name.replaceAll("\\.","/");
String filePath = this.path + name + ".class";
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStream is = null;
byte[] returnData = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
is = new FileInputStream(file);
int tmp = 0;
while((tmp = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(tmp);
}
returnData = os.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
is.close();
os.close();
}
return returnData;
}
}
package com.test.jvm;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//new一个自定义的类加载器;并在N:/tmp/ 目录下放入Demo.java文件
MyClassLoader loader = new MyClassLoader("TanShen","N:/tmp/");
System.out.println("当前加载器: "+loader);
System.out.println("loader父加载器: "+loader.getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父加载器: "+loader.getParent().getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父父加载器: "+loader.getParent().getParent().getParent());
Class c = loader.loadClass("Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
Demo.java中代码(别忘记cmd中执行 javac Demo,进行编译生产Demo.class)
public class Demo{
public Demo(){
System.out.println("Demo :" + this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
以上执行结果:
当前加载器: TanShen
loader父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f
loader父父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@55f96302
loader父父父加载器: null
Demo :TanShen
-
例子2
MyClassLoader.java无变化
在eclipse下新建一个Demo.java 如下:
package com.test.jvm;
public class Demo {
public Demo() {
//调用本类的 类加载器
System.out.println("A Demo : " + this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
package com.test.jvm;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//new一个自定义的类加载器
MyClassLoader loader = new MyClassLoader("TanShen","N:/tmp/");
System.out.println("当前加载器: "+loader);
System.out.println("loader父加载器: "+loader.getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父加载器: "+loader.getParent().getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父父加载器: "+loader.getParent().getParent().getParent());
Class c = loader.loadClass("com.test.jvm.Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
本地Demo.java中代码,并将Demo.java放入N:\tmp\com\test\jvm路径下(别忘记cmd中执行 javac Demo)
package com.test.jvm;
public class Demo{
public Demo(){
//调用本类的 类加载器
System.out.println("Demo :" + this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
eclipse目录
eclipse执行结果:
当前加载器: TanShen
loader父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f
loader父父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@55f96302
loader父父父加载器: null
A Demo : sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f
-
例子3
其他不变仅仅TestDemo进行改变
package com.test.jvm;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//new一个自定义的类加载器
MyClassLoader tanShenloader = new MyClassLoader("TanShen","N:/tmp/");
MyClassLoader wuKongloader = new MyClassLoader(tanShenloader,"WuKong","N:/tmp/");
System.out.println("当前加载器: "+wuKongloader);
System.out.println("loader父加载器: "+wuKongloader.getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父加载器: "+wuKongloader.getParent().getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父父加载器: "+wuKongloader.getParent().getParent().getParent());
System.out.println("loader父父父加载器: "+wuKongloader.getParent().getParent().getParent().getParent());
Class c = wuKongloader.loadClass("com.test.jvm.Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
结果:
当前加载器: WuKong
loader父加载器: TanShen
loader父父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f
loader父父父加载器: sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@55f96302
loader父父父加载器: null
A Demo : sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f
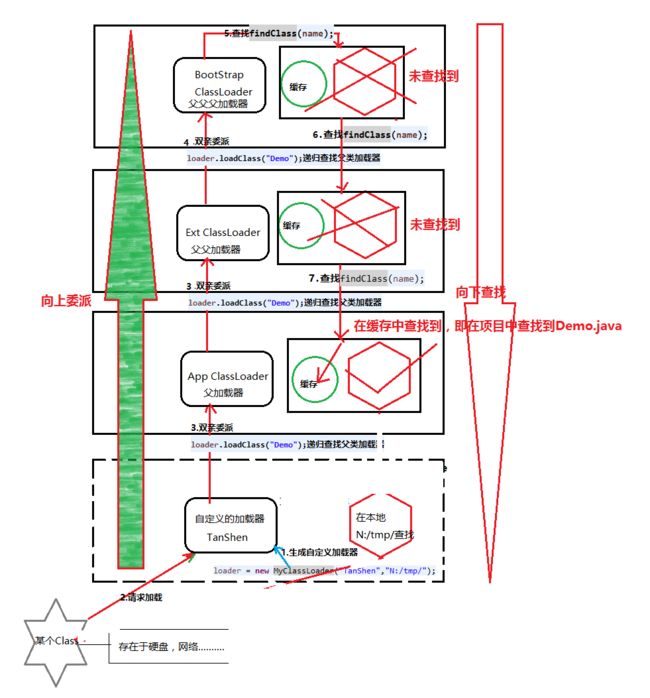
案例分析:
当前自定义的加载器为WuKong,并指定其父加载器为:TanShen(也为自定义加载器),根据双亲委派模型,会继续寻找TanShen父加载器AppClassLoader;继而ExtClassLoader,最总 null==BootStrapClassLoader;
最后是
A Demo : sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e25154f去执行加载类,为什么?因为向下查找类的过程,AppClassLoader在缓存中找到了类Demo(就是java工程目录下的文件)。
-
例子4
其他不变仅仅TestDemo进行改变
package com.test.jvm;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//new一个自定义的类加载器
MyClassLoader wuKongloader = new MyClassLoader(null,"WuKong","N:/tmp/");
System.out.println("当前加载器: "+wuKongloader);
System.out.println("loader父加载器: "+wuKongloader.getParent());
Class c = wuKongloader.loadClass("com.test.jvm.Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
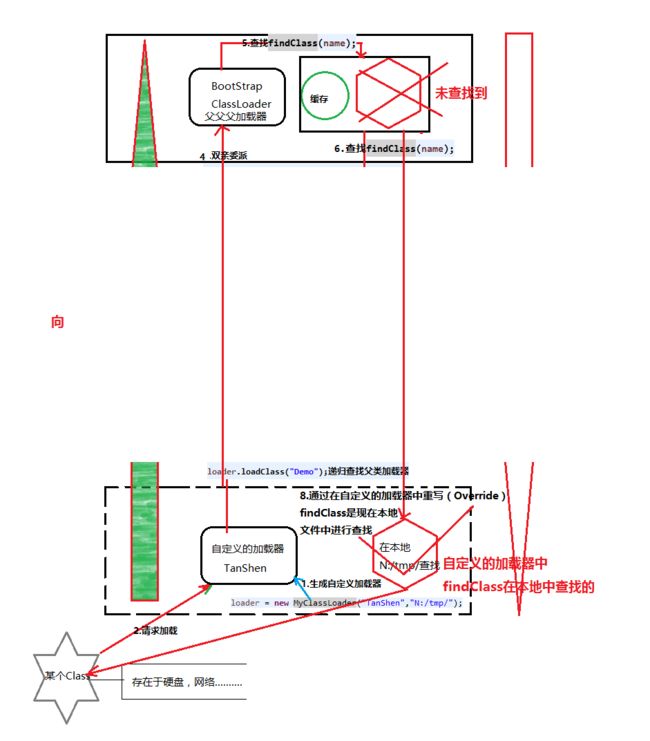
结果
当前加载器: WuKong
loader父加载器: null
Demo :WuKong
图解分析
参考
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av17748750/
http://blog.csdn.net/briblue/article/details/54973413
搜索“探索JVM底层奥秘ClassLoader源码分析与案例讲解“