之前写的几种数据结构--数组.栈.队列等都算静态数据结构,就算是实现了动态扩容其底层也是通过静态数组来完成的.本篇链表才是真正的动态数据结构,也是最简单的动态数据结构
属性:
①:相邻元素之间通过指针连接。
②:最后一个元素的后继指针为NULL。
③:链表的空间能够按需分配。
④:没有内存空间的浪费。
结构:
- 链表数据存储在内部
节点(Node)中 - Node中包含了该节点的数据和它的下一个节点
class Node{
E e;
Node next;
}
代码实现:
添加插入数据:
public class LinkList {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e,Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e,null);
}
public Node(){
this(null,null);
}
}
private int size;
private Node head;
public LinkList(){
head = null;
size = 0;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public Boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index,E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
if (index==0) {
addFirst(e);
}else {
Node prve = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prve = prve.next;
}
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = prve.next;
// prve.next = node;
// 该行代码等效于上面3行
prve.next = new Node(e,prve.next);
size++;
}
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
// 第一种写法
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = head;
// head = node;
// 第二种
head = new Node(e,head);
size++;
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
-
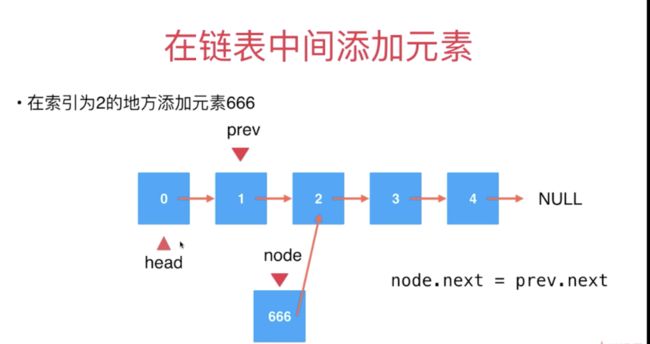
addFirst函数--添加一个新的头结点,这样原来的头结点就往后移一位--也就是新节点的的next等于之前的头结点 - 实现代码中
add函数稍微需要理解一下,下面放张图来帮助理解:
使用虚拟头节点:
从上面的代码中可以看到头结点是一个比较特殊的节点,于其他节点不同由于它是第一个节点所以没有其他节点来指向它,这样就造成了对于头结点需要一些逻辑判断上的操作
而通过虚拟头结点我们可以规避的这些,其主要实现就是创建一个结点它不需要存储数据,唯一目的就是通过它来指向结点--这个被指向的结点就是实际的头结点:
private Node dummyHead;
public LinkList() {
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0,e);
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node prve = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) {
prve = prve.next;
}
prve.next = new Node(e, prve.next);
size++;
}
链表的set和get方法
public E get(int index){
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
}
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
public E getLast(){
return get(size-1);
}
public Boolean contain(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.e==e) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
public void set(int index,E e){
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.e = e;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// Node cur = dummyHead.next;
// while(cur != null){
// res.append(cur + "->");
// cur = cur.next;
// }
for(Node cur = dummyHead.next ; cur != null ; cur = cur.next)
res.append(cur + "->");
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
测试以及结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
[0]
[1, 0]
[2, 1, 0]
[3, 2, 1, 0]
[4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
[4, 3, 666, 2, 1, 0]
Process finished with exit code 0
删除元素:
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置删除元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E remove(int index){
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node pre= dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pre= pre.next;
}
Node delNode= pre.next;
pre.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next= null;
size--;
return delNode.e;
}
时间复杂度分析:
- 添加操作:O(n)
addFirst() O(1)
addLast() O(n)
add(index,e) O(n/2)=O(n) - 删除操作:O(n)
removeFirst() O(1)
removeLast() O(n)
remove(index) O(n/2)=O(n) - 查找操作:O(n)
get(index) O(n)
contain(e) O(n)
从上面时间复杂度分析可以看出链表的增、删、改(这里没有)、查的时间复杂度都是O(n),相对于数组结构并没有什么优势,但细心的同学可以看出,当对链表头进行操作时它的时间复杂度为O(1)--相当的高效。聪明的同学就应该想到了,栈这种数据结构非常就适合使用链表来实现,下一篇就通过链表来实现栈这个数据结构。