本文由colodoo(纸伞)整理
QQ 425343603
Java学习交流群(717726984)
环境搭建
import com.zhisan.spring.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainXml {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// XML方式
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.login();
}
}
resource/spring.xml
package com.zhisan.spring.service;
public class UserService {
public void login() {
System.out.println("login");
}
}
4.0.0
com.zhisan
spring-study
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.10.RELEASE
阅读
我们先省略掉XML部分的处理逻辑,我们把他分为处理前,处理后,处理中;而AbstractApplicationContext这个抽象类,就基本包含了大部分的处理中的操作逻辑,我们先从这个类入手,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造方法中打个断点,开始阅读!
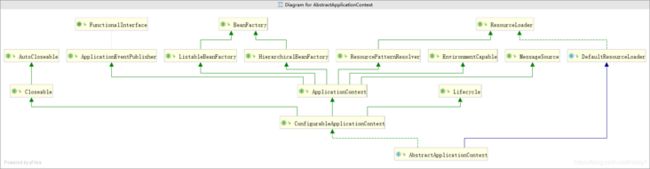
我们先看看这个类的抽象类org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext的UML关系图。
抽象应用容器构造方法(AbstractApplicationContext)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#AbstractApplicationContext(org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext)
/**
* Create a new AbstractApplicationContext with the given parent context.
* @param parent the parent context
*/
public AbstractApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
this();
setParent(parent);
}设置了一些简单的参数,没有实际bean操作逻辑。
刷新(refresh)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
没错,这次又来到了这个方法,我在源码解析:Spring Boot启动流程(一)文章中有对这部分简单的注释,我直接照搬过来。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// 准备刷新
// tip:一些设置参数,可不细看
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部 bean 工厂
// 获取刷新 bean 工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备 bean 工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对 bean 工厂进行后处理。
// tip:这部分涉及Web服务器的启动,如servlet
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// 调用在上下文中注册为 bean 的工厂处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截 bean 创建的 bean 处理器。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// 初始化此上下文的消息源。
initMessageSource();
// 为此上下文初始化事件多播器。
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化特定上下文子类中的其他特殊 bean。
onRefresh();
// 检查侦听器 bean 并注册它们。
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例。
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后一步:发布相应的事件。
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}这次我们对每个方法都进行深入的解析。
首先synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)锁住“刷新”和“销毁”的同步监视器。
然后进入刷新前的准备阶段。
准备刷新(prepareRefresh)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#prepareRefresh
/**
* 准备此上下文以进行刷新、设置其启动日期和活动标志以及执行属性源的任何初始化。
*/
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// 记录启动时间
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 设置关闭状态为false
this.closed.set(false);
// 切换容器的状态为激活
this.active.set(true);
// 判断当前是否启用了调试日志记录
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
// 当前是否启用了跟踪日志记录
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// 在上下文环境中初始化任何占位符属性源
// tip:没有实际作用,交给子类去实现。
initPropertySources();
// 验证所有标记为必需的属性都是可解析的:
// 参见 ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 这部分getEnvironment我省略了,主要看校验的逻辑。
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// 存储预刷新应用程序侦听器
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// 将本地应用程序侦听器重置为预刷新状态.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// 允许收集早期的 ApplicationEvents,
// 一旦多播器可用就发布...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}上面过了一个大概的流程,基本上大部分都是环境准备步骤,以上可以拆分的几个点如下:
- validateRequiredProperties 校验必须属性
验证必需的属性(validateRequiredProperties)
org.springframework.core.env.AbstractPropertyResolver#validateRequiredProperties
@Override
public void validateRequiredProperties() {
// 缺失必须属性异常
MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();
for (String key : this.requiredProperties) {
if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {
ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
// 任何一个必须属性为空都会抛出异常
if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {
throw ex;
}
}继续往下阅读,基本环境准备就绪了,我们接下来就要创建一个bean工厂了。
获得Bean工厂(obtainFreshBeanFactory)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory
/**
* Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factor.
* @return the fresh BeanFactory instance
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #getBeanFactory()
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 刷新bean工厂
refreshBeanFactory();
// 获得bean工厂
return getBeanFactory();
}其中包含refreshBeanFactory这个方法,它用于创建和初始化bean工厂,以及bean定义的初始化。
刷新 Bean 工厂(refreshBeanFactory)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
/**
* 此实现执行此上下文的底层 bean 工厂的实际刷新,关闭先前的 bean 工厂(如果有)并为上下文生命周期的下一个阶段初始化一个新的 bean 工厂。
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 是否存在bean工厂
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 销毁bean工厂
destroyBeans();
// 关闭bean工厂
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建新的bean工厂(初始化工厂)
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 设置ID
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 自定义 Bean 工厂(可以忽略)
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 加载bean定义(这里是注册bean定义的入口,可以深入研究)
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
// 设置bean工厂当前对象
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}这部分有几个比较重要的几个方法要单独抽取出来解释:
- createBeanFactory(用于初始化bean工厂)
loadBeanDefinitions(加载bean定义)
- initBeanDefinitionReader(初始化bean定义阅读器)此处可以忽略
- loadBeanDefinitions(加载bean定义)
总结
因为obtainFreshBeanFactory这个方法做了不少事情,所以我们做一个小小的总结。
- 创建bean工厂(beanFactory)
- 读取资源(这里是spring.xml文件)
- 加载bean定义(beanDefinitions)
以及几个用于注册bean定义的源码入口可以深入的去阅读。
- BeanDefinitionReaderUtils
- DefaultListableBeanFactory
最后返回一个beanFactory用于后面所有操作的bean工厂,也是这个方法的目的。
准备Bean工厂(prepareBeanFactory)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#prepareBeanFactory
/**
* 配置工厂的标准上下文特征,例如上下文的 ClassLoader 和后处理器。
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}一些默认参数的设置,不细究。
后置处理bean工厂(postProcessBeanFactory)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#postProcessBeanFactory
这部分是预留的,用于扩展。
总结
上篇主要包含了如下几个内容。
- 环境准备
- 初始化bean工厂
- 读取资源(可以为xml或者注解方式)
- 加载bean定义
上篇到此,下篇会讲关于实例化和初始化相关入口。