摘要:本文通过实际案例,说明如何按日期来对订单数据进行水平分库和分表,实现数据的分布式查询和操作。
本文分享自华为云社区《数据库分库分表Java实战经验总结 丨【绽放吧!数据库】》,作者: jackwangcumt。
我们知道,当前的应用都离不开数据库,随着数据库中的数据越来越多,单表突破性能上限记录时,如MySQL单表上线估计在近千万条内,当记录数继续增长时,从性能考虑,则需要进行拆分处理。而拆分分为横向拆分和纵向拆分。一般来说,采用横向拆分较多,这样的表结构是一致的,只是不同的数据存储在不同的数据库表中。其中横向拆分也分为分库和分表。
1 示例数据库准备
为了说清楚如何用Java语言和相关框架实现业务表的分库和分表处理。这里首先用MySQL数据库中创建两个独立的数据库实例,名字为mydb和mydb2,此可演示分库操作。另外在每个数据库实例中,创建12个业务表,按年月进行数据拆分。具体的创建表脚本如下:
CREATE TABLE `t_bill_2021_1` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单id',
`user_id` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户id',
`address_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '地址id',
`status` char(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '订单状态',
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
CREATE TABLE `t_bill_2021_2` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单id',
`user_id` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户id',
`address_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '地址id',
`status` char(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '订单状态',
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
-- 省略....
CREATE TABLE `t_bill_2021_12` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单id',
`user_id` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户id',
`address_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '地址id',
`status` char(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '订单状态',
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;成功执行脚本后,在MySQL管理工具中可以看到如下的示例界面: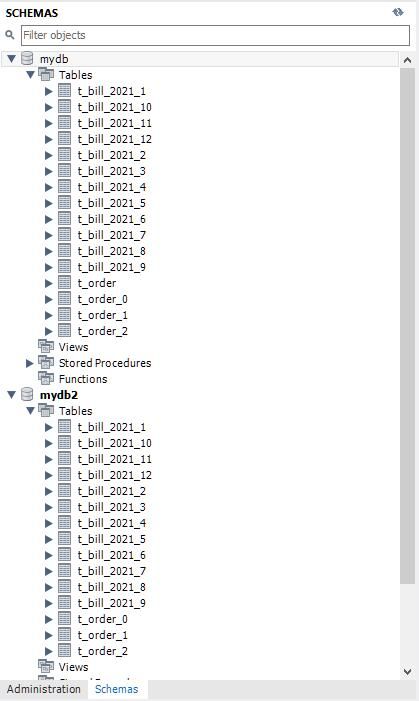
2 分库分表实现
在Java语言下的框架中,有众多的开源框架,其中关于分库分表的框架,可以选择Apache ShardingSphere,其官网介绍说:ShardingSphere 是一套开源的分布式数据库解决方案组成的生态圈,它由 JDBC、Proxy 和 Sidecar(规划中)这 3 款既能够独立部署,又支持混合部署配合使用的产品组成。 它们均提供标准化的数据水平扩展、分布式事务和分布式治理等功能,可适用于如 Java 同构、异构语言、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。Apache ShardingSphere 5.x 版本开始致力于可插拔架构。 目前,数据分片、读写分离、数据加密、影子库压测等功能,以及 MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQLServer、Oracle 等 SQL 与协议的支持,均通过插件的方式织入项目。官网地址为: https://shardingsphere.apache... 。
下面的示例采用Spring Boot框架来实现,相关的库通过Maven进行管理。首先给出pom.xml配置文件的定义:
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.5.3
com.example
wyd
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
wyd
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
3.1.1
4.0.0-RC2
5.0.0-beta
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
2.0.1
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
${mybatis-plus.version}
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
joda-time
joda-time
2.9.8
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter
${sharding-sphere.version}
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-namespace
${sharding-sphere.version}
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.postgresql
postgresql
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
其次,给出一个实体类,它对应于上述创建的数据库表t_bill,其定义如下:
package com.example.wyd.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@TableName("t_bill")
public class Bill {
private Long orderId;
private Integer userId;
private Long addressId;
private String status;
private Date createTime;
public void setOrderId(Long orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public void setUserId(Integer userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public void setAddressId(Long addressId) {
this.addressId = addressId;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
}映射类BillMapper定义如下:
package com.example.wyd.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Bill;
public interface BillMapper extends BaseMapper {
} 服务类接口定义如下:
package com.example.wyd.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Bill;
public interface BillService extends IService {
} 服务类接口的实现类定义如下:
package com.example.wyd.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Bill;
import com.example.wyd.mapper.BillMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BillServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements BillService {
} 这里我们采用了MybatisPlus框架,它可以很方便的进行数据库相关操作,而无需过多写SQL来实现具体业务逻辑。通过上述定义,通过继承接口的方式,并提供实体类的定义,MybatisPlus框架会通过反射机制来根据数据库设置来生成SQL语句,其中包含增删改查接口,具体的实现我们并未具体定义。
下面定义一个自定义的分库算法,具体实现如下:
package com.example.wyd;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingValue;
import java.util.Collection;
//自定义数据库分片算法
public class DBShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection availableTargetNames, PreciseShardingValue shardingValue) {
//真实数据库节点
availableTargetNames.stream().forEach((item) -> {
System.out.println("actual db:" + item);
});
//逻辑表以及分片的字段名
System.out.println("logicTable:"+shardingValue.getLogicTableName()+";shardingColumn:"+ shardingValue.getColumnName());
//分片数据字段值
System.out.println("shardingColumn value:"+ shardingValue.getValue().toString());
//获取字段值
long orderId = shardingValue.getValue();
//分片索引计算 0 , 1
long db_index = orderId & (2 - 1);
for (String each : availableTargetNames) {
if (each.equals("ds"+db_index)) {
//匹配的话,返回数据库名
return each;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
} 下面给出数据的分表逻辑,这个定义稍显复杂一点,就是根据业务数据的日期字段值,根据月份落入对应的物理数据表中。实现示例代码如下:
package com.example.wyd;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingValue;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
//表按日期自定义分片
public class TableShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection availableTargetNames, PreciseShardingValue shardingValue) {
//真实数据库节点
availableTargetNames.stream().forEach((item) -> {
System.out.println("actual db:" + item);
});
//逻辑表以及分片的字段名
System.out.println("logicTable:"+shardingValue.getLogicTableName()+";shardingColumn:"+ shardingValue.getColumnName());
//分片数据字段值
System.out.println("shardingColumn value:"+ shardingValue.getValue().toString());
//获取表名前缀
String tb_name = shardingValue.getLogicTableName() + "_";
//根据日期分表
Date date = shardingValue.getValue();
String year = String.format("%tY", date);
String mon =String.valueOf(Integer.parseInt(String.format("%tm", date)));
//String dat = String.format("%td", date); //也可以安装年月日来分表
// 选择表
tb_name = tb_name + year + "_" + mon;
//实际的表名
System.out.println("tb_name:" + tb_name);
for (String each : availableTargetNames) {
//System.out.println("availableTableName:" + each);
if (each.equals(tb_name)) {
//返回物理表名
return each;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
} 数据的分库分表可以在Spring Boot的属性配置文件中进行设(application.properties):
server.port=8080
#########################################################################################################
# 配置ds0 和ds1两个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = ds0,ds1
#ds0 配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type = com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.jdbc-url = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username = uname
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password = pwd
#ds1 配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type = com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.jdbc-url = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb2characterEncoding=utf8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username = uname
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password = pwd
#########################################################################################################
# 默认的分库策略:id取模
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column = id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression = ds$->{id % 2}
#########################################################################################################
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_bill_$->{2021..2021}_$->{1..12}
#数据库分片字段
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=order_id
#自定义数据库分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.example.wyd.DBShardingAlgorithm
#表分片字段
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=create_time
#自定义表分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.table-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.example.wyd.TableShardingAlgorithm
#########################################################################################################
# 使用SNOWFLAKE算法生成主键
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.key-generator.column = order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.key-generator.type = SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_bill.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
#########################################################################################################
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true最后,我们给出一个定义的Controller类型,来测试分库分表的查询和保存操作是否正确。HomeController类定义如下:
package com.example.wyd.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Bill;
import com.example.wyd.service.BillService;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class HomeController {
@Autowired
private BillService billService;
//http://localhost:8080/api/query?start=2021-02-07%2000:00:00&end=2021-03-07%2000:00:00
@RequestMapping("/query")
public List queryList(@RequestParam("start") String start, @RequestParam("end") String end) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
Date date = sdf.parse(start);
Date date2 = sdf.parse(end);
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.ge("create_time",date)
.and(qw-> qw.le("create_time", date2)).last("limit 1,10");
List billIPage = billService.list(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(billIPage.size());
billIPage.forEach(System.out::println);
return billIPage;
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//http://localhost:8080/api/save?userid=999&addressId=999&status=M&date=2021-03-07%2000:00:00
@RequestMapping("/save")
public String Save(@RequestParam("userid") int userId, @RequestParam("addressId") long AddressId,
@RequestParam("status") String status
,@RequestParam("date") String strDate) {
String ret ="0";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
Date date = sdf.parse(strDate);
Bill bill = new Bill();
bill.setUserId(userId);
bill.setAddressId(AddressId);
bill.setStatus(status);
bill.setCreateTime(date);
boolean isOk = billService.save(bill);
if (isOk){
ret ="1";
}
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ret;
}
} 至此,我们可以用测试类初始化一些数据,并做一些初步的数据操作测试:
package com.example.wyd;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Bill;
import com.example.wyd.dao.Order;
import com.example.wyd.service.BillService;
import com.example.wyd.service.OrderService;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class OrderServiceImplTest extends WydApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BillService billService;
@Test
public void testBillSave(){
for (int i = 0 ; i< 120 ; i++){
Bill bill = new Bill();
bill.setUserId(i);
bill.setAddressId((long)i);
bill.setStatus("K");
bill.setCreateTime((new Date(new DateTime(2021,(i % 11)+1,7,00, 00,00,000).getMillis())));
billService.save(bill);
}
}
@Test
public void testGetByOrderId(){
long id = 626038622575374337L; //根据数据修改,无数据会报错
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("order_id", id);
Bill bill = billService.getOne(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(bill.toString());
}
@Test
public void testGetByDate(){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
Date date = sdf.parse("2021-02-07 00:00:00");
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("create_time",date);
List billIPage = billService.list(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(billIPage.size());
System.out.println(billIPage.toString());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testGetByDate2(){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
Date date = sdf.parse("2021-02-07 00:00:00");
Date date2 = sdf.parse("2021-03-07 00:00:00");
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.ge("create_time",date)
.and(qw-> qw.le("create_time", date2));
List billIPage = billService.list(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(billIPage.size());
billIPage.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
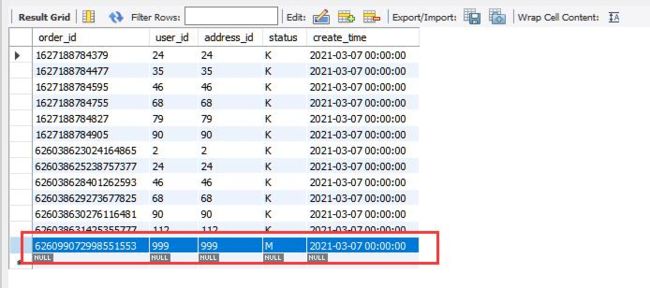
} 执行上述测试,通过后会生成测试数据。
3 验证
打开浏览器,输入网址进行查询测试:http://localhost:8080/api/que...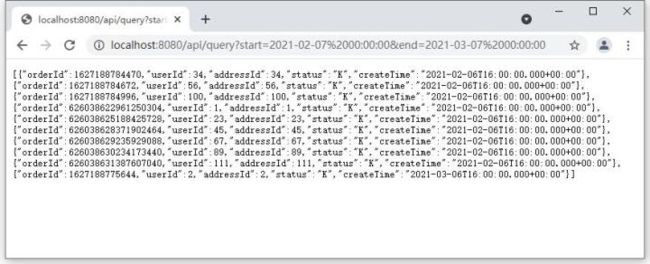
输入如下网址进行数据新增测试:http://localhost:8080/api/sav...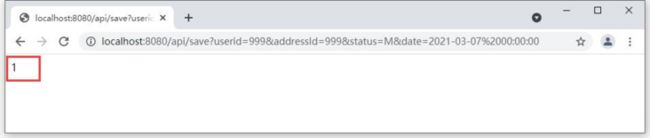
通过跟踪分析,此数据落入如下的表中,SQL语句如下:
SELECT * FROM mydb2.t_bill_2021_3 LIMIT 0, 1000这里还需要注意,ShardingSphere 还支持分布式事务,感兴趣的可以阅读官网相关资料进行学习。