遍历问题
2020.11.02
No.94 二叉树的中序遍历
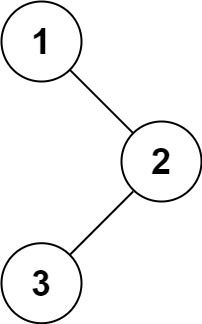
给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,3,2]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=94 lang=javascript
*
* [94] 二叉树的中序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let r = [];
// 递归函数
const recurse = root => {
// 递归终止条件
if(!root) return;
// 先遍历左子树
recurse(root.left);
// 遇到终止条件,此时的val是符合终止条件的值
r.push(root.val);
// 再遍历右子树
recurse(root.right);
};
recurse(root);
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=94 lang=javascript
*
* [94] 二叉树的中序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = [];
const stk = [];
while (root || stk.length) {
while (root) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.push(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=94 lang=javascript
*
* [94] 二叉树的中序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = [];
let predecessor = null;
while (root) {
if (root.left) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right && predecessor.right !== root) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (!predecessor.right) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
res.push(root.val);
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.push(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=94 lang=javascript
*
* [94] 二叉树的中序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (root) {
return [...inorderTraversal(root.left), root.val, ...inorderTraversal(root.right)]
} else {
return []
}
}有四种解法:1、利用递归来实现遍历,对于递归的终止条件要处理好,相当于是隐式的栈应用;2、利用栈来显式的执行,可以控制迭代和停止;3、Morris遍历算法:其本质是利用树种大量的null空间,利用线索树来实现链路的线索,该算法的核心是:当前节点记为cur,a、如果cur无左子节点,cur右移 cur = cur.right;b、如果有左子节点,找到cur左子树的最右节点,记为mostright,b1、如果mostright的right为null,让其指向cur,并且cur左移 cur = cur.left;b2、如果mostright的right指向cur,让其指为null,cur右移 cur = cur.right;4、利用js的...的iterable属性,可最简化写法
2020.11.03
No.102 二叉树的层序遍历
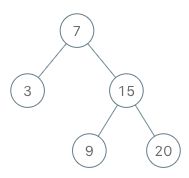
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例:
二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=102 lang=javascript
*
* [102] 二叉树的层序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
const r = [];
// 构造hash表
let obj = {};
// 递归循环 增加一个层级判断n
const recurse = (curr, n) => {
if(!curr) return;
if(!obj[n]) {
obj[n] = [curr.val]
} else {
obj[n].push(curr.val)
}
n++;
recurse(curr.left, n);
recurse(curr.right, n)
}
recurse(root, 0);
for(let key in obj) {
r.push(obj[key]);
}
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=102 lang=javascript
*
* [102] 二叉树的层序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const items = []; // 存放所有节点
const queue = [root, null]; // null 简化操作
let levelNodes = []; // 存放每一层的节点
while (queue.length > 0) {
const t = queue.shift();
if (t) {
levelNodes.push(t.val)
if (t.left) {
queue.push(t.left);
}
if (t.right) {
queue.push(t.right);
}
} else { // 一层已经遍历完了
items.push(levelNodes);
levelNodes = [];
if (queue.length > 0) {
queue.push(null)
}
}
}
return items;
};本题有两种思路:1、DFS:关键点在增加一个层级维度的判断,可以使用hash表或者队列等来实现;2、BFS:利用队列来优化循环的层数,从而实现广度优先搜索
2020.11.04
No.103 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层次遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回锯齿形层次遍历如下:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=103 lang=javascript
*
* [103] 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {
const r = [];
// 构造hash表
let obj = {};
const recurse = ( node, n ) => {
if(!node) return;
if( !obj[n] ) {
obj[n] = [node.val];
} else {
obj[n].push(node.val)
};
n++;
recurse(node.left, n);
recurse(node.right, n);
};
recurse(root, 0);
for(let key in obj) {
// 偶数层从左向右,奇数层从右向左
if( key % 2 == 0 ) {
r.push(obj[key]);
} else {
r.push(obj[key].reverse());
}
}
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=103 lang=javascript
*
* [103] 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var zigzagLevelOrder = function (root) {
let r = []
let queen = []
if (root) {
queen.push([root, 0])
}
while (queen.length) {
let [node, depth] = queen.shift()
node.left && queen.push([node.left, depth + 1])
node.right && queen.push([node.right, depth + 1])
if (!r[depth]) {
r[depth] = []
}
if (depth % 2 === 1) {
r[depth].unshift(node.val)
} else {
r[depth].push(node.val)
}
}
return r
};两种解法:1、DFS:只需将102层次遍历后的hash表中的key按奇偶要求进行输出即可;2、BFS:构造队列,同样对层次奇偶进行要求输出即可
2020.11.05
No.105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
注意:
你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=105 lang=javascript
*
* [105] 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
// 递归终止条件
if(inorder.length == 0) return null;
// 根节点一定是前序遍历数组的第一个,在中序遍历数组中获取其位置,可以分离左子树和右子树
const root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]),
idx = inorder.indexOf(preorder[0]);
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1,idx+1), inorder.slice(0,idx));
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(idx+1), inorder.slice(idx+1));
return root;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=105 lang=javascript
*
* [105] 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
pre = i = 0
build = function(stop) {
console.log(stop);
if (inorder[i] != stop) {
var root = new TreeNode(preorder[pre++])
root.left = build(root.val)
i++
root.right = build(stop)
return root
}
return null
}
return build()
};递归构建,有两种方法:1、利用slice切割根节点,递归,这样比较消耗性能,可以用map以及指针等优化处理;2、省去空间的消耗,这里利用一个停止位点进行每次迭代的输出,是generator函数的延展实现
2020.11.06
No.106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意:
你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=106 lang=javascript
*
* [106] 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @param {number[]} postorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
if( inorder.length == 0 ) return null;
const root = new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.length - 1]),
idx = inorder.indexOf(postorder[postorder.length-1]);
root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0,idx), postorder.slice(0, idx));
root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(idx+1),postorder.slice(idx,postorder.length-1));
return root;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=106 lang=javascript
*
* [106] 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @param {number[]} postorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
let p = i = postorder.length - 1;
let build = (stop) => {
if(inorder[i] != stop) {
let root = new TreeNode(postorder[p--])
root.right = build(root.val)
i--
root.left = build(stop)
return root
}
return null
}
return build()
};105题目变形,只需对后序倒序取根就可以分开左右子树
2020.11.09
No.107 二叉树的层次遍历-ii
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其自底向上的层次遍历为:
[
[15,7],
[9,20],
[3]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=107 lang=javascript
*
* [107] 二叉树的层次遍历 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrderBottom = function(root) {
const r = [];
// 构造hash表
let obj = {};
const recurse = ( node, n ) => {
if(!node) return;
if(!obj[n]) {
obj[n] = [node.val]
} else {
obj[n].push(node.val)
};
n++;
recurse(node.left,n);
recurse(node.right,n)
};
recurse(root, 0);
for( let key in obj) {
r.push(obj[key])
};
return r.reverse();
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=107 lang=javascript
*
* [107] 二叉树的层次遍历 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrderBottom = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const items = []; // 存放所有节点
const queue = [root, null]; // null 简化操作
let levelNodes = []; // 存放每一层的节点
while (queue.length > 0) {
const t = queue.shift();
if (t) {
levelNodes.push(t.val)
if (t.left) {
queue.push(t.left);
}
if (t.right) {
queue.push(t.right);
}
} else { // 一层已经遍历完了
items.push(levelNodes);
levelNodes = [];
if (queue.length > 0) {
queue.push(null)
}
}
}
return items.reverse();
};思路和102题一样,只需要将结果反转即可
2020.11.10
No.144 二叉树的前序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=144 lang=javascript
*
* [144] 二叉树的前序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
const r = [];
const recurse = node => {
if(!node) return;
r.push(node.val);
node.left && recurse(node.left);
node.right && recurse(node.right)
};
recurse(root);
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=144 lang=javascript
*
* [144] 二叉树的前序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const r = [],
stack = [root];
while( stack.length > 0 ) {
const node = stack.pop()
r.push(node.val);
// 构造栈,入栈需要先进入右节点,再进入左节点,出栈时才能先左后右
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
}
return r;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=144 lang=javascript
*
* [144] 二叉树的前序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = [];
let predecessor = null;
while (root) {
if (root.left) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right && predecessor.right !== root) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (!predecessor.right) {
predecessor.right = root;
res.push(root.val);
root = root.left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.push(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=144 lang=javascript
*
* [144] 二叉树的前序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (root) {
return [ root.val, ...preorderTraversal(root.left), ...preorderTraversal(root.right) ]
} else {
return []
}
};同94的中序遍历的四种方案:1、递归;2、栈优化;3、Morris算法;4、js的...迭代
2020.11.11
No.145 二叉树的后序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [3,2,1]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=145 lang=javascript
*
* [145] 二叉树的后序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
const r = [];
const recurse = node => {
if(!node) return;
node.left && recurse(node.left);
node.right && recurse(node.right);
r.push(node.val);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=145 lang=javascript
*
* [145] 二叉树的后序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const r = [],
stack = [root];
while( stack.length > 0 ) {
let node = stack.pop();
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
r.unshift(node.val);
}
return r;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=145 lang=javascript
*
* [145] 二叉树的后序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = [];
let predecessor = null;
while (root) {
if (root.right) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.right;
while (predecessor.left && predecessor.left !== root) {
predecessor = predecessor.left;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (!predecessor.left) {
predecessor.left = root;
res.unshift(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
predecessor.left = null;
root = root.left;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.unshift(root.val);
root = root.left;
}
}
return res;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=145 lang=javascript
*
* [145] 二叉树的后序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (root) {
return [ ...postorderTraversal(root.left), ...postorderTraversal(root.right), root.val]
} else {
return []
}
};同144前序遍历,有四种解法:1、递归;2、栈;3、Morris算法;4、...展开符
2020.11.12
No.1008 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
返回与给定前序遍历 preorder 相匹配的二叉搜索树(binary search tree)的根结点。
(回想一下,二叉搜索树是二叉树的一种,其每个节点都满足以下规则,对于 node.left 的任何后代,值总 < node.val,而 node.right 的任何后代,值总 > node.val。此外,前序遍历首先显示节点 node 的值,然后遍历 node.left,接着遍历 node.right。)
题目保证,对于给定的测试用例,总能找到满足要求的二叉搜索树。
示例:
输入:[8,5,1,7,10,12]
输出:[8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
提示:
1 <= preorder.length <= 100
1 <= preorder[i] <= 10^8
preorder 中的值互不相同
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-search-tree-from-preorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=1008 lang=javascript
*
* [1008] 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var bstFromPreorder = function(preorder) {
if(preorder.length == 0) return null;
const root = preorder.shift();
let node = new TreeNode(root);
node.left = bstFromPreorder(preorder.filter(item => item <= root));
node.right = bstFromPreorder(preorder.filter(item => item > root))
return node;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=1008 lang=javascript
*
* [1008] 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var bstFromPreorder = function(preorder) {
if(preorder.length == 0) return null;
let root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]),
stack = [root],
curr,
child;
for( let i = 1; i < preorder.length; i++ ) {
child = new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
curr = stack[0];
while( stack.length != 0 && stack[0].val < child.val ) {
curr = stack.shift();
}
curr.val > child.val ? curr.left = child : curr.right = child;
stack.unshift(child);
}
return root;
};两种解法:1、递归,对于根的左右要求进行分离;2、使用栈优化方案1中的递归
总结:
- 和问题常见的做法主要是利用map、hash、栈型等数据结构来进行优化处理,其次是利用左右指针的归约来进行循环的次数;
- 对于子问题常见的解法是利用动态规划及回溯剪枝来处理优化
二叉搜索树问题
2020.11.13
No.95 不同的二叉搜索树-ii
给定一个整数 n,生成所有由 1 ... n 为节点所组成的 二叉搜索树 。
示例:
输入:3
输出:
[
[1,null,3,2],
[3,2,null,1],
[3,1,null,null,2],
[2,1,3],
[1,null,2,null,3]
]
解释:
以上的输出对应以下 5 种不同结构的二叉搜索树:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
提示:
0 <= n <= 8
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=95 lang=javascript
*
* [95] 不同的二叉搜索树 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {TreeNode[]}
*/
var generateTrees = function(n) {
// 结果个数符合卡特兰数字
if( n == 0 ) return [];
// 递归构建树
const buildTree = ( start, end ) => {
let r = [];
// 递归终止条件
if( start > end ) return [null];
for( let i = start; i <= end; i++ ) {
// 以i为中心分成左右两边
let left = buildTree( start, i-1 ),
right = buildTree( i+1, end );
for( const leftNode of left ) {
for( const rightNode of right ) {
let node = new TreeNode(i);
node.left = leftNode;
node.right = rightNode;
r.push(node)
}
}
}
return r;
}
return buildTree(1, n);
};主要是递归解决:按根节点分离左右子节点,然后递归生成树,再拼接到根节点上
2020.11.16
No.96 不同的二叉搜索树
给定一个整数 n,求以 1 ... n 为节点组成的二叉搜索树有多少种?
示例:
输入: 3
输出: 5
解释:
给定 n = 3, 一共有 5 种不同结构的二叉搜索树:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=96 lang=javascript
*
* [96] 不同的二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var numTrees = function(n) {
// 结果符合卡特兰数 ( 1 / n+1 ) * C(2n,n) => ( 1 / n+1 )*( 2n! / n! * n! )
const fac = m => {
let f = 1;
while( m > 0 ) {
f*=m;
m--;
}
return f;
};
return ( 1 / ( n + 1 ) ) * fac(2*n) / ( fac(n) * fac (n) )
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=96 lang=javascript
*
* [96] 不同的二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var numTrees = function(n) {
if(n===1||n===0) return 1;
var res=0;
for(var i=1;i<=n;i++){
res += numTrees(i-1) * numTrees(n-i);
}
return res;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=96 lang=javascript
*
* [96] 不同的二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var numTrees = function(n) {
var dp= new Array(n+1).fill(0);
dp[0]=1;
dp[1]=1;
for(var i=2;i<=n;i++){
for(var j=1;j<=i;j++){
dp[i] += dp[j-1]*dp[(i-j)];
}
}
return dp[n];
};有三种解法:1、数学方法:结果符合卡特兰数,使用卡特兰数的通项公式解决,(1/n+1)*C2nn;2、递归;3、动态规划
2020.11.17
No.98 验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
输入:
2
/ \
1 3
输出: true
示例 2:
输入:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
输出: false
解释: 输入为: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]。
根节点的值为 5 ,但是其右子节点值为 4 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=98 lang=javascript
*
* [98] 验证二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidBST = function(root) {
// 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = root => {
const r = [];
const recurse = root => {
if(!root) return;
recurse(root.left);
r.push(root.val);
recurse(root.right);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
}
// 判断是否升序
const isAsec = arr => {
for(let p1=0,p2=1;p2=arr[p2]) return false;
}
return true;
}
return isAsec(inorderTraversal(root));
}; 方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=98 lang=javascript
*
* [98] 验证二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidBST = function(root) {
// 递归
const helper = (root, lower, upper) => {
if (root === null) {
return true;
}
if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};有两种解法:1、利用中序遍历为升序的特点,构造中序遍历,判断是否升序;2、递归
2020.11.18
No.99 恢复二叉搜索树
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的两个节点被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树。
进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现。你能想出一个只使用常数空间的解决方案吗?
输入:root = [1,3,null,null,2]
输出:[3,1,null,null,2]
解释:3 不能是 1 左孩子,因为 3 > 1 。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
示例 2:
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
输出:[2,1,4,null,null,3]
解释:2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3 。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
提示:
树上节点的数目在范围 [2, 1000] 内
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/recover-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=99 lang=javascript
*
* [99] 恢复二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var recoverTree = function(root) {
// 1 将错位的二叉搜索树中序遍历,确定错误位点
// 1.1 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = root => {
const r = [];
const recurse = root => {
if(!root) return;
recurse(root.left);
r.push(root.val);
recurse(root.right);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
}
// 1.2 获取替换位置
const replaceIdx = arr => {
const _arr = arr.slice().sort((a,b)=>a-b);
let r = [];
for(let i=0;i {
if(root) {
if(root.val == x || root.val == y) {
root.val = root.val == x ? y : x;
if(--count == 0) return;
}
swapRoot(root.left, count, x, y);
swapRoot(root.right, count, x, y);
}
}
const [x,y] = replaceIdx(inorderTraversal(root)).slice(0,2);
swapRoot(root,2,x,y);
}; 方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=99 lang=javascript
*
* [99] 恢复二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var recoverTree = function(root) {
const swap = (x, y) => {
const temp = x.val;
x.val = y.val;
y.val = temp;
}
const stack = [];
let x = null, y = null, pred = null;
while (stack.length || root !== null) {
while (root !== null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (pred !== null && root.val < pred.val) {
y = root;
if (x === null) {
x = pred;
}
else break;
}
pred = root;
root = root.right;
}
swap(x, y);
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=99 lang=javascript
*
* [99] 恢复二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var recoverTree = function(root) {
const swap = (x, y) => {
const temp = x.val;
x.val = y.val;
y.val = temp;
}
let x = null, y = null, pred = null, predecessor = null;
while (root !== null) {
if (root.left !== null) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right !== null && predecessor.right !== root)
predecessor = predecessor.right;
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (predecessor.right === null) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
if (pred !== null && root.val < pred.val) {
y = root;
if (x === null) {
x = pred;
}
}
pred = root;
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
if (pred !== null && root.val < pred.val) {
y = root;
if (x === null) {
x = pred;
}
}
pred = root;
root = root.right;
}
}
swap(x, y);
};整体思路同98题的第一种方案,都是利用中序遍历为升序来获取错误位点,本题hard主要在于对空间复杂度的优化,有三种方案:1、利用数组去查找错误位点;2、利用一个pred的位置,只要获取到不相同就可以停止,不需要完全遍历完数组,相当于隐式的数组;3、Morris算法,可以将空间复杂度降为常数级别
2020.11.19
No.173 二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。
调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // 返回 3
iterator.next(); // 返回 7
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 9
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 15
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 20
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 false
提示:
next() 和 hasNext() 操作的时间复杂度是 O(1),并使用 O(h) 内存,其中 h 是树的高度。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 中至少存在一个下一个最小的数。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=173 lang=javascript
*
* [173] 二叉搜索树迭代器
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
var BSTIterator = function(root) {
// 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = root => {
const r = [];
const recurse = root => {
if(!root) return;
recurse(root.left);
r.push(root.val);
recurse(root.right);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
};
/**
* 其实返回一个对象就行了,这里用到了js的原型链机制
* {
arr: arr,
i: 0,
next: function() {
let hasNext = this.hasNext(),
next = hasNext ? this.arr[this.i++] : undefined;
return next;
},
hasNext: function() {
return this.i < this.arr.length;
}
* }
*/
// 挂到this上
this.arr = inorderTraversal(root);
this.i = 0;
};
/**
* @return the next smallest number
* @return {number}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function() {
let hasNext = this.hasNext(),
next = hasNext ? this.arr[this.i++] : undefined;
return next;
};
/**
* @return whether we have a next smallest number
* @return {boolean}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function() {
return this.i < this.arr.length;
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new BSTIterator(root)
* var param_1 = obj.next()
* var param_2 = obj.hasNext()
*/方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=173 lang=javascript
*
* [173] 二叉搜索树迭代器
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
var BSTIterator = function(root) {
let gen = function* () {
let stack = [];
let node = root;
while (node || stack.length) {
while (node) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
yield node.val;
node = node.right;
}
}
this.gen = gen();
this.cursor = this.gen.next();
};
/**
* @return the next smallest number
* @return {number}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function() {
let value = this.cursor.value;
this.cursor = this.gen.next();
return value;
};
/**
* @return whether we have a next smallest number
* @return {boolean}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function() {
return !this.cursor.done;
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new BSTIterator(root)
* var param_1 = obj.next()
* var param_2 = obj.hasNext()
*/整体思路就是先获取中序遍历,中序遍历可以有不同的优化,然后实现迭代器,这里有两种方案:1、利用js的原型链机制;2、利用js的es6已经实现的生成器
2020.11.20
No.230 二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数。
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
3
/ \
1 4
\
2
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
/
1
输出: 3
进阶:
如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化 kthSmallest 函数?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=230 lang=javascript
*
* [230] 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var kthSmallest = function(root, k) {
// 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = root => {
const r = [];
const recurse = root => {
// 这里对r的长度进行判断剪枝优化
if(!root || r.length >= k) return;
recurse(root.left);
r.push(root.val);
recurse(root.right);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
};
return inorderTraversal(root)[k-1]
};利用中序遍历获取第k-1个元素即可,求中序遍历的方法见94题,有四种方案,由于会频繁修改树,因而这里可以根据获取数组长度等进行优化
2020.11.23
No.235 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]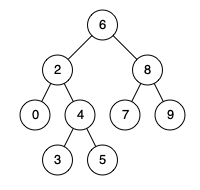
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=235 lang=javascript
*
* [235] 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 获取路径,返回一个数组链表
const bstPath = ( root, val ) => {
const r = [];
// 递归
const recurse = node => {
if(!node) return;
const v = node.val;
r.unshift(v);
if( val > v) {
recurse(node.right);
} else if ( val < v ) {
recurse(node.left);
} else {
return;
}
};
recurse(root);
return r;
};
// 根据路径数组,返回两数组最近公共祖先
const lowestCommonValue = ( arr1, arr2 ) => {
let s,l;
if( arr1.length <= arr2.length ) {
s = arr1;
l = arr2;
} else {
s = arr2;
l = arr1;
}
for(let i=0; i方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=235 lang=javascript
*
* [235] 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
const lowestCommonAncestor = (root, p, q) => {
if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}
return root;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=235 lang=javascript
*
* [235] 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
const lowestCommonAncestor = (root, p, q) => {
while (root) {
if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) {
root = root.left;
} else if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) {
root = root.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
return root;
};有三种解法:1、构造路径链表结构,获取数组链表的最近公共节点;2、递归;3、迭代
2020.11.24
No.501 二叉搜索树中的众数
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
例如:
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],
1
\
2
/
2
返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=501 lang=javascript
*
* [501] 二叉搜索树中的众数
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findMode = function(root) {
// 构造hash表
const obj = {};
const recurse = node => {
if(!node) return;
if(obj[node.val]) {
obj[node.val]++;
} else {
obj[node.val] = 1;
}
node.left && recurse(node.left);
node.right && recurse(node.right);
}
recurse(root);
// 获取value的最大值
let max = Math.max(...Object.values(obj));
// 对hash表遍历,获取对应最大值的key
const r = [];
for(let key in obj) {
if(obj[key] == max) r.push(key);
}
return r;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=501 lang=javascript
*
* [501] 二叉搜索树中的众数
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findMode = function(root) {
let base = 0, count = 0, maxCount = 0;
let answer = [];
const update = (x) => {
if (x === base) {
++count;
} else {
count = 1;
base = x;
}
if (count === maxCount) {
answer.push(base);
}
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
answer = [base];
}
}
const dfs = (o) => {
if (!o) {
return;
}
dfs(o.left);
update(o.val);
dfs(o.right);
}
dfs(root);
return answer;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=501 lang=javascript
*
* [501] 二叉搜索树中的众数
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findMode = function(root) {
let base = 0, count = 0, maxCount = 0;
let answer = [];
const update = (x) => {
if (x === base) {
++count;
} else {
count = 1;
base = x;
}
if (count === maxCount) {
answer.push(base);
}
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
answer = [base];
}
}
let cur = root, pre = null;
while (cur !== null) {
if (cur.left === null) {
update(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
continue;
}
pre = cur.left;
while (pre.right !== null && pre.right !== cur) {
pre = pre.right;
}
if (pre.right === null) {
pre.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
} else {
pre.right = null;
update(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return answer;
};有三种方案:1、最简单也是最好想的,利用hash表构造判断众数;2、方案1会额外利用hash表的空间,利用中序遍历可以使用几个指针来进行判断输出,空间复杂度为O(n);3、进一步优化方案2,利用Morris算法优化中序遍历时的空间损耗,空间复杂度为O(1)
2020.11.25
No.530 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:
输入:
1
\
3
/
2
输出:
1
解释:
最小绝对差为 1,其中 2 和 1 的差的绝对值为 1(或者 2 和 3)。
提示:
树中至少有 2 个节点。
本题与 783 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes/ 相同
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=530 lang=javascript
*
* [530] 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
// 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = root => {
const r = [];
const recurse = root => {
if(!root) return;
recurse(root.left);
r.push(root.val);
recurse(root.right);
}
recurse(root);
return r;
};
const arr = inorderTraversal(root);
let min = Infinity;
for(let p1=0, p2=1; p2 < arr.length; p1++, p2++) {
if( min > arr[p2]-arr[p1] ) min = arr[p2]-arr[p1]
};
return min;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=530 lang=javascript
*
* [530] 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let ans = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, pre = -1;
const dfs = (root) => {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
if (pre == -1) {
pre = root.val;
} else {
ans = Math.min(ans, root.val - pre);
pre = root.val;
}
dfs(root.right);
}
dfs(root);
return ans;
};还是利用中序遍历进行扩展,有两种方案:1、中序遍历后升序数组进行最小差值输出;2、优化额外的数组空间,利用几个指针,在中序遍历中进行判断输出
2020.11.26
No.669 修剪二叉搜索树
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树不应该改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构(即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在唯一的答案。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
输出:[1,null,2]
示例 2: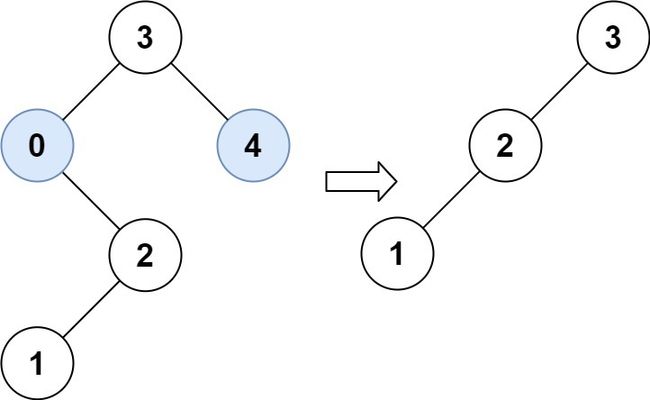
输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
输出:[3,2,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1], low = 1, high = 2
输出:[1]
示例 4:
输入:root = [1,null,2], low = 1, high = 3
输出:[1,null,2]
示例 5:
输入:root = [1,null,2], low = 2, high = 4
输出:[2]
提示:
树中节点数在范围 [1, 104] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 104
树中每个节点的值都是唯一的
题目数据保证输入是一棵有效的二叉搜索树
0 <= low <= high <= 104
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=669 lang=javascript
*
* [669] 修剪二叉搜索树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} low
* @param {number} high
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
// 递归终止条件
if(!root) return root;
if( root.val >= low && root.val <= high ) {
// 满足要求,继续递归
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
} else {
// 比最小值小,放弃左侧树,root值为右侧值
if(root.val < low) return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
// 比最大值大,放弃右侧树,root值为左侧值
if(root.val > high) return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
}
return root;
};正常递归思路,需要根据区间判断是否继续向下递归,当不满足条件时修改需要递归的root的值
总结:
- 二叉搜索树问题常见的做法仍然是递归去处理,这里最常利用的就是二叉搜索树的中序遍历为升序数组进行相关扩展;
- 对于递归时产生的空间优化问题,可以通过指针等来优化栈空间等的使用,也可结合之前遍历问题中的时间优化问题,提高效率
- 树的问题中有时也会涉及数学相关的问题,可直接根据数学问题来解,如卡特兰数等
特殊二叉树问题
2020.11.27
No.101 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
进阶:
你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=101 lang=javascript
*
* [101] 对称二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
// 中序遍历+层数
const inorderLevelTraversal = function(root) {
const r = [];
const recurse = ( node, n ) => {
if(!node) return;
n++;
recurse(node.left, n);
r.push([node.val,n])
recurse(node.right, n);
};
recurse(root, 0);
return r;
};
const r = inorderLevelTraversal(root);
console.log('r', r);
// 判断中序遍历数组是否对称
let p1 = 0,
p2 = r.length - 1;
while( p1 < p2 ) {
if( r[p1][0] != r[p2][0] || r[p1][1] != r[p2][1] ) return false;
p1++;
p2--;
};
return true;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=101 lang=javascript
*
* [101] 对称二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
const isSymmetric = (root) => {
const check = (left, right) => {
if (left == null && right == null) { // 两个子树都为null,是对称的
return true;
}
if (left && right) { // 两个子树都存在,则需要:root值相同,且他们的子树也满足镜像
return left.val == right.val && check(left.left, right.right) && check(left.right, right.left);
}
return false; // 一个子树存在一个不存在,肯定不对称
};
if (root == null) { // 如果传入的root就是null,对称
return true;
}
return check(root.left, root.right); // 否则,判断它的左右子树是否满足对称
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=101 lang=javascript
*
* [101] 对称二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
const isSymmetric = (root) => {
if (root == null) return true;
const queue = [];
queue.push(root.left, root.right); // 起初入列两个子树
while (queue.length) { // 队列清空就结束,没有节点可入列了
const levelSize = queue.length; // 当前层的节点个数
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i += 2) { // 当前层的节点成对出列
const left = queue.shift();
const right = queue.shift(); // 出列一对节点
if ((left && right == null) || (left == null && right)) { // 有一个存在有一个不存在
return false;
}
if (left && right) { // 两个都存在
if (left.val != right.val) { // 节点值不同,不对称
return false;
}
queue.push(left.left, right.right); // 推入下一层的一对节点
queue.push(left.right, right.left); // 推入下一层的一对节点
}
}
}
return true; // bfs结束,始终没有返回false,则返回真
};有三种解法:1、参考中序遍历思路,判断中序遍历后的数组是否对称,这里需要加入层数来避免有一个节点为null无法判断的情形;2、DFS递归,直接递归判断;3、BFS迭代,维护一个队列进行判断
2020.11.30
No.110 平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
示例 2: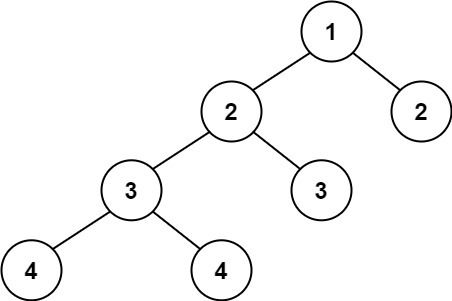
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:true
提示:
树中的节点数在范围 [0, 5000] 内
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=110 lang=javascript
*
* [110] 平衡二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isBalanced = function(root) {
// 获取树的高度
const getTreeHeight = tree => {
if(!tree) return true;
return 1 + Math.max(getTreeHeight(tree.left),getTreeHeight(tree.right))
};
// 差值比较后返回结果
if(!root) return true;
const lh = getTreeHeight(root.left),
rh = getTreeHeight(root.right);
// 如果结果有大于1的直接false
if(Math.abs(lh-rh) > 1 ) {
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=110 lang=javascript
*
* [110] 平衡二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isBalanced = function(root) {
// 判断是否平衡
const balanced = function (node) {
if (!node) return 0
const left = balanced(node.left)
const right = balanced(node.right)
if (left === -1 || right === -1 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) {
return -1
}
return Math.max(left, right) + 1
}
return balanced(root) !== -1;
};有两种方案:1、自顶向下:获取左子树和右子树高度比较,如果不符合直接返回false,否则向下递归;2、自底向上:类似后序遍历方案,先判断左子树,再判断右子树,再判断根节点,有不符合就返回false,否则向上递归
2020.12.01
No.226 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
备注:
这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=226 lang=javascript
*
* [226] 翻转二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var invertTree = function(root) {
let temp = null;
const recurse = node => {
if(!node) return;
temp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = temp;
recurse(node.left);
recurse(node.right);
};
recurse(root);
return root;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=226 lang=javascript
*
* [226] 翻转二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var invertTree = function(root) {
if (!root) return root;
const queue = [root]; // 维护一个队列,初始推入第一层的root
while (queue.length) {
const cur = queue.shift(); // 出列的节点
[cur.left, cur.right] = [cur.right, cur.left]; // 交换左右子树
cur.left && queue.push(cur.left);
cur.right && queue.push(cur.right);
}
return root;
};面试考树最常考的题,两种方案:1、递归;2、迭代
2020.12.02
No.617 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例 1:
输入:
Tree 1 Tree 2 1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
输出:
合并后的树:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=617 lang=javascript
*
* [617] 合并二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} t1
* @param {TreeNode} t2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(t1, t2) {
// 以t1为基准
if(!t1) return t2;
if(!t2) return t1;
t1.val = t2.val + t1.val;
t1.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
t1.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return t1;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=617 lang=javascript
*
* [617] 合并二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} t1
* @param {TreeNode} t2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(t1, t2) {
// 以t1为基准
if(!t1) return t2;
if(!t2) return t1;
t1.val = t2.val + t1.val;
// 构造栈空间迭代
const stack = [[t1, t2]];
while (stack.length) {
const [p, q] = stack.shift();
if (p.left && q.left) {
p.left.val += q.left.val
stack.push([p.left, q.left]);
} else if (!p.left) p.left = q.left;
else if (!q.left) q.left = p.left;
if (p.right && q.right) {
p.right.val += q.right.val;
stack.push([p.right, q.right]);
} else if (!p.right) p.right = q.right;
else if (!q.right) q.right = p.right;
}
return t1;
};同226,树的基本操作,面试树常考,有两种方案:1、递归;2、迭代
2020.12.03
No.654 最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组。一个以此数组构建的最大二叉树定义如下:
二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素。
左子树是通过数组中最大值左边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
右子树是通过数组中最大值右边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
通过给定的数组构建最大二叉树,并且输出这个树的根节点。
示例 :
输入:[3,2,1,6,0,5]
输出:返回下面这棵树的根节点:
6
/ \
3 5
\ /
2 0
\
1
提示:
给定的数组的大小在 [1, 1000] 之间。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=654 lang=javascript
*
* [654] 最大二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function(nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return null;
const root = new TreeNode(Math.max(...nums));
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(0,nums.indexOf(Math.max(...nums))));
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(nums.indexOf(Math.max(...nums))+1));
return root;
};典型的递归问题,以最大值作为分割点
2020.12.04
No.655 输出二叉树
在一个 m*n 的二维字符串数组中输出二叉树,并遵守以下规则:
行数 m 应当等于给定二叉树的高度。
列数 n 应当总是奇数。
根节点的值(以字符串格式给出)应当放在可放置的第一行正中间。根节点所在的行与列会将剩余空间划分为两部分(左下部分和右下部分)。你应该将左子树输出在左下部分,右子树输出在右下部分。左下和右下部分应当有相同的大小。即使一个子树为空而另一个非空,你不需要为空的子树输出任何东西,但仍需要为另一个子树留出足够的空间。然而,如果两个子树都为空则不需要为它们留出任何空间。
每个未使用的空间应包含一个空的字符串""。
使用相同的规则输出子树。
示例 1:
输入:
1
/
2
输出:
[["", "1", ""],
["2", "", ""]]
示例 2:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
\
4
输出:
[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],
["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],
["", "", "4", "", "", "", ""]]
示例 3:
输入:
1
/ \
2 5
/
3
/
4
输出:
[["", "", "", "", "", "", "", "1", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["", "", "", "2", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "5", "", "", ""]
["", "3", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["4", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]]
注意: 二叉树的高度在范围 [1, 10] 中。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/print-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=655 lang=javascript
*
* [655] 输出二叉树
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var printTree = function(root) {
// 获取树的高度
const treeHeight = root => {
if(!root) return 0;
return treeHeight(root.left) > treeHeight(root.right) ? ( treeHeight(root.left) + 1 ): (treeHeight(root.right) + 1);
};
// 填充输出值
const printValue = (r, root, n, left, right ) => {
if(root) {
let mid = Math.floor( ( left + right ) / 2 );
r[n][mid] = root.val + '';
printValue(r, root.left, n+1, left, mid);
printValue(r, root.right, n+1, mid+1, right)}
};
const m = treeHeight(root),
n = Math.pow(2,m) - 1;
console.log(m)
const r = new Array(m);
for(let i=0;i二分法递归,先生成二维数组,再在对应位置填充值
2020.12.06
No.998 最大二叉树-ii
最大树定义:一个树,其中每个节点的值都大于其子树中的任何其他值。
给出最大树的根节点 root。
就像之前的问题那样,给定的树是从表 A(root = Construct(A))递归地使用下述 Construct(A) 例程构造的:
如果 A 为空,返回 null
否则,令 A[i] 作为 A 的最大元素。创建一个值为 A[i] 的根节点 root
root 的左子树将被构建为 Construct([A[0], A[1], ..., A[i-1]])
root 的右子树将被构建为 Construct([A[i+1], A[i+2], ..., A[A.length - 1]])
返回 root
请注意,我们没有直接给定 A,只有一个根节点 root = Construct(A).
假设 B 是 A 的副本,并附加值 val。保证 B 中的值是不同的。
返回 Construct(B)。
输入:root = [4,1,3,null,null,2], val = 5
输出:[5,4,null,1,3,null,null,2]
解释:A = [1,4,2,3], B = [1,4,2,3,5]
示例 2: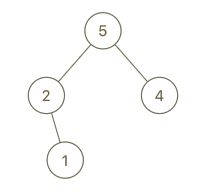
输入:root = [5,2,4,null,1], val = 3
输出:[5,2,4,null,1,null,3]
解释:A = [2,1,5,4], B = [2,1,5,4,3]
示例 3:
输入:root = [5,2,3,null,1], val = 4
输出:[5,2,4,null,1,3]
解释:A = [2,1,5,3], B = [2,1,5,3,4]
提示:
1 <= B.length <= 100
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=998 lang=javascript
*
* [998] 最大二叉树 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var insertIntoMaxTree = function(root, val) {
// 中序遍历
const inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let r = [];
// 递归函数
const recurse = root => {
// 递归终止条件
if(!root) return;
// 先遍历左子树
recurse(root.left);
// 遇到终止条件,此时的val是符合终止条件的值
r.push(root.val);
// 再遍历右子树
recurse(root.right);
};
recurse(root);
return r;
};
// 数组的最大二叉树
const constructMaximumBinaryTree = function(nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return null;
const root = new TreeNode(Math.max(...nums));
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(0,nums.indexOf(Math.max(...nums))));
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(nums.indexOf(Math.max(...nums))+1));
return root;
};
const A = inorderTraversal(root);
A.push(val);
return constructMaximumBinaryTree(A);
};94题和655题的综合,先求出中序遍历数组,在数组后添加val值,对新数组进行求最大树
总结:
- 特殊二叉树主要是树的不同形态的处理,常见的主要是递归和迭代,面试中常常要求都写出来;
- 根据不同要求获取树,算是树的基本考察,面试过程中如果考树,一般都会以特殊二叉树来检验