App.module.ts 的源代码:
export class AppModule {
constructor(private config: DebugConfig,
private actions$: Actions,
private cartService: ActiveCartService){
// console.log('Jerry config: ', this.config);
this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(CartActions.LOAD_CART),
map((action: CartActions.LoadCart) => action.payload),
tap((data) => console.log('Jerry cart: ' , data))).subscribe();
this.cartService.getLoading().subscribe((data) => console.log('Jerry cart loading? ', data));
}
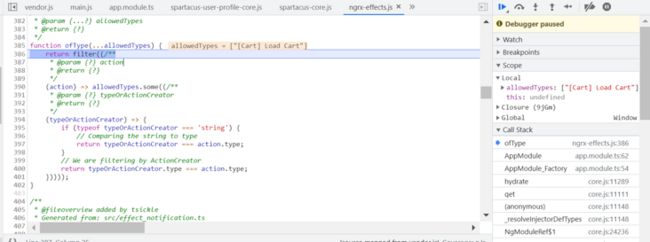
}数组的 some 方法:检查数组元素是否满足 predicate 函数指定的条件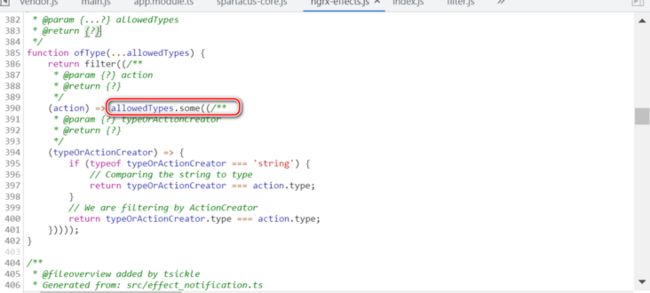
然后执行 map 操作,返回一个 OperatorFunction,作为 pipe 的输入条件之一: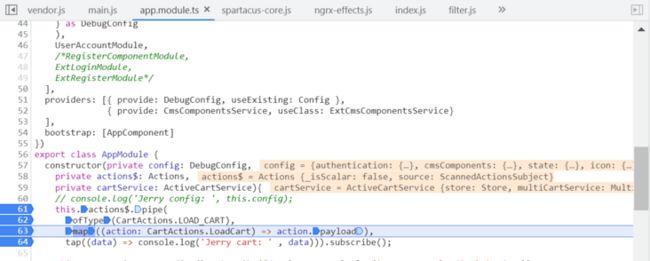
quantity 的值来自 activeCartService 维护的 active cart 的 deliveryItemsQuantity 字段。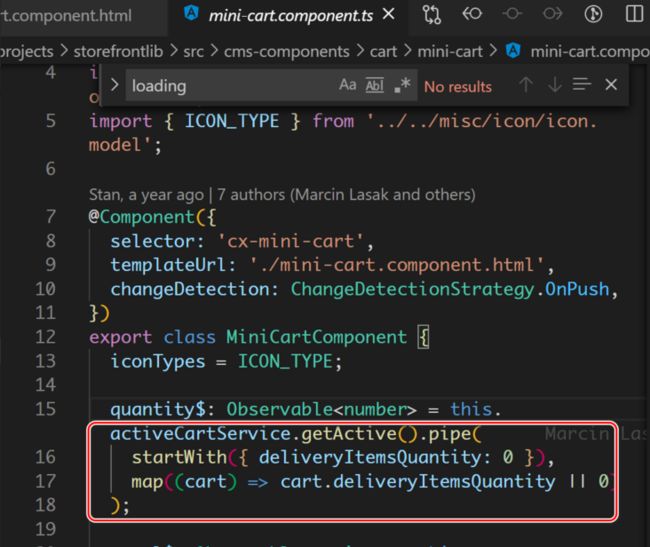
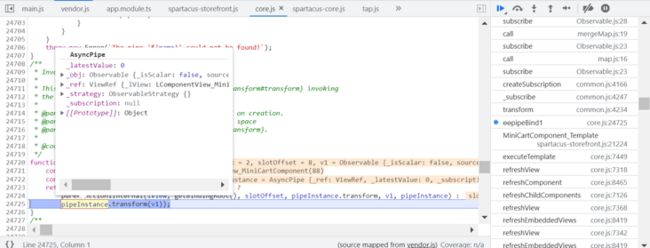
async pipe 的 transform 方法会调用 subscribe 方法: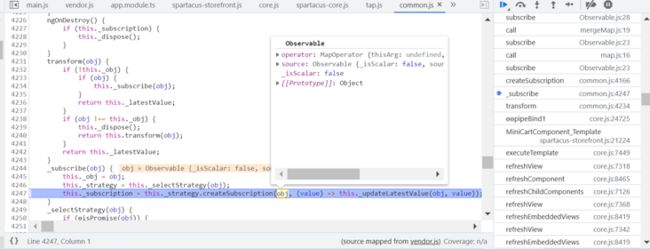
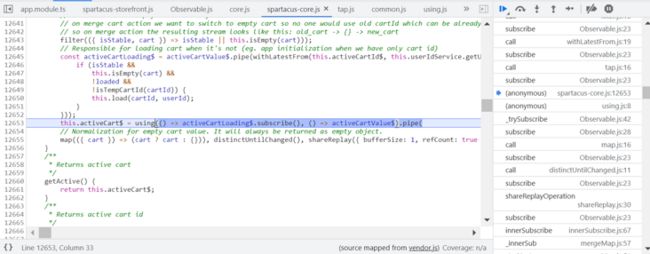
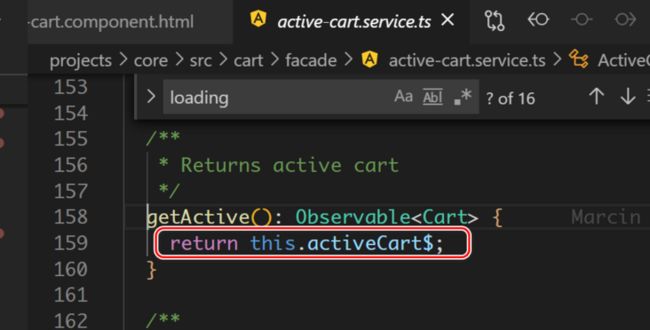
getActive 返回:
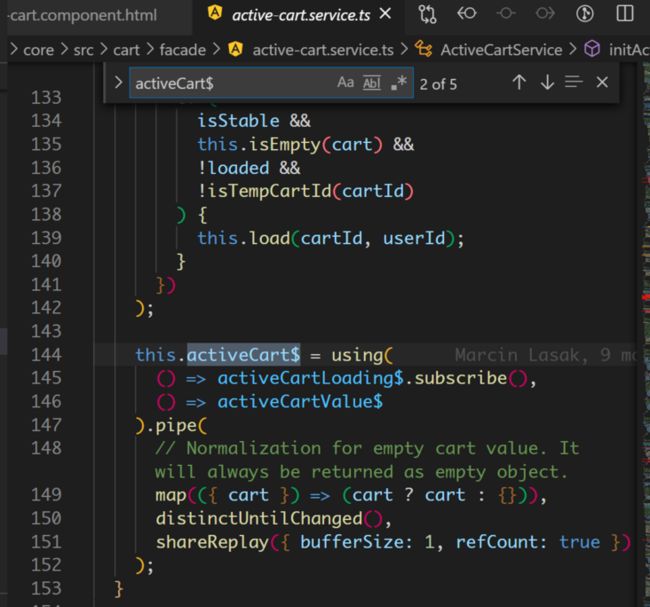
activeCart$ 的值来自 activeCartLoading$ 和 activeCartValue$ 两部分。
activeCartLoading$ 负责加载 cart,见代码第 139 行。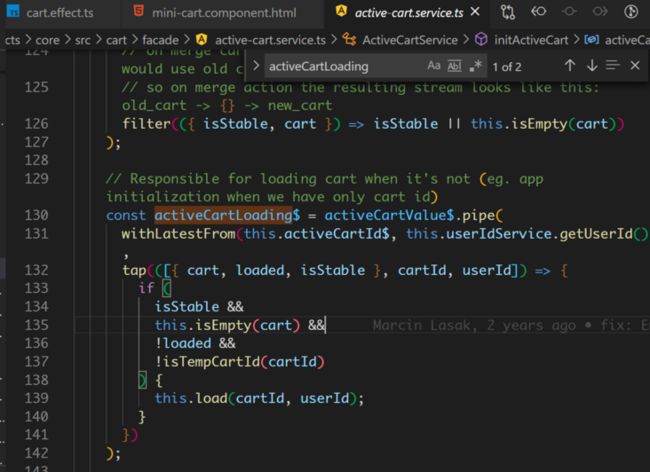
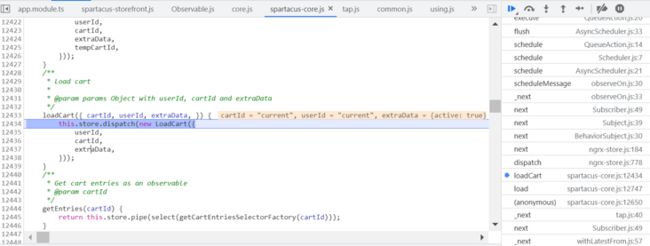
调用的是 ActiveCartService 的 loadCart 方法:
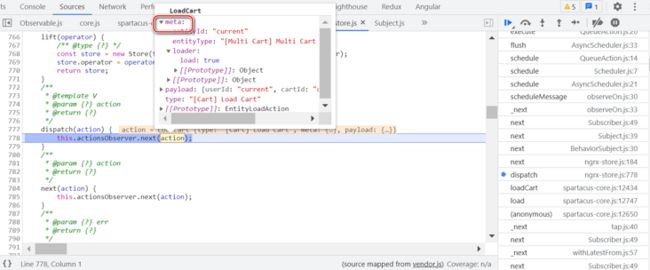
给 store 发送一个 action。
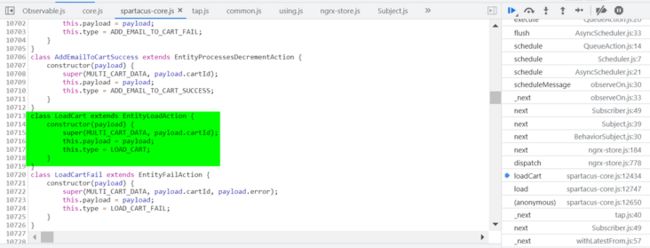
LoadCart 扩展自 EntityLoadAction,除了 payload 之外,定义了额外的字段:
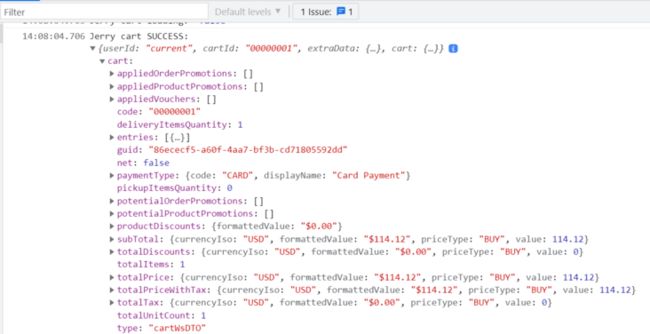
如果想打印出加载成功的购物车信息:
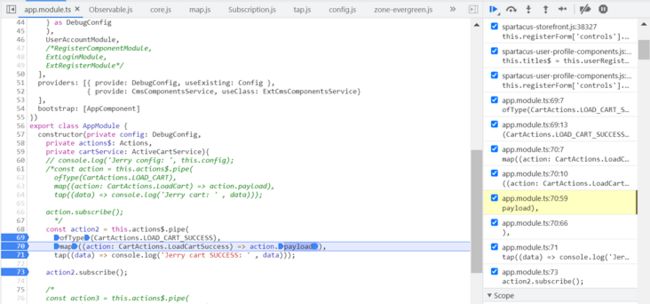
const action2 = this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(CartActions.LOAD_CART_SUCCESS),
map((action: CartActions.LoadCartSuccess) => action.payload),
tap((data) => console.log('Jerry cart SUCCESS: ' , data)));
action2.subscribe();
const action3 = this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(CartActions.LOAD_CARTS_SUCCESS),
map((action: CartActions.LoadCartsSuccess) => action.payload),
tap((data) => console.log('Jerry carts SUCCESS: ' , data)));
action3.subscribe();结果:
那么,这个加载成功的 Cart 数据,是如何通过 action 实例 subscribe 之后被读取出来的呢?
显然,单步调试第73行代码,并不会看到我们想了解的明细。因为 subscribe 只是触发 cart 的加载,而后者是一个异步过程。
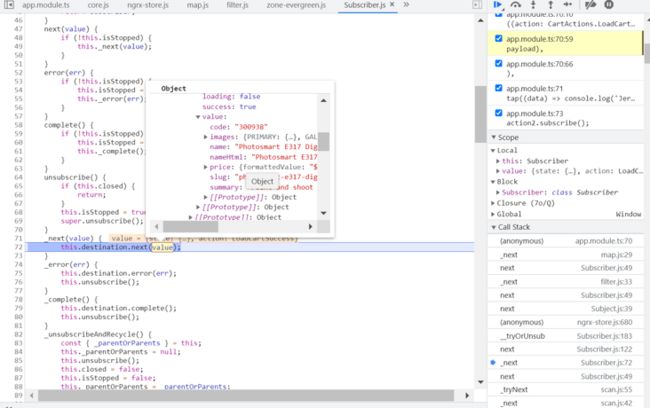
F8之后断点再次触发时,cart 数据已经出现在 payload 里了。但是我们不知道是谁从哪里通过什么样的方式进行的回调。
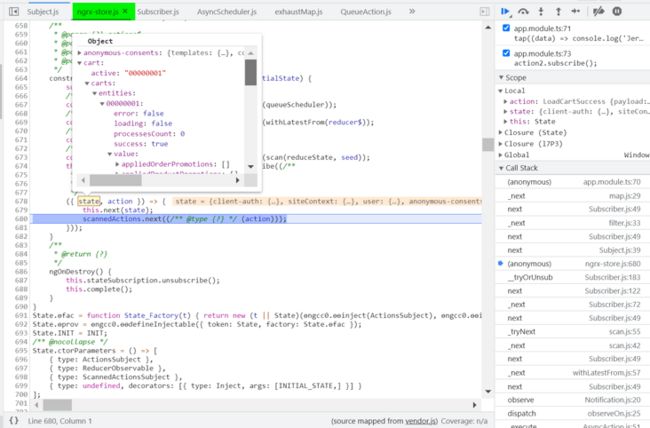
在 subscriber 的实现里,能看到当前已经 ready 的 state 值:
ngrx-store.js 在这里将 state 片段的 carts 传入 map 回调函数里:
更多Jerry的原创文章,尽在:"汪子熙":![]()