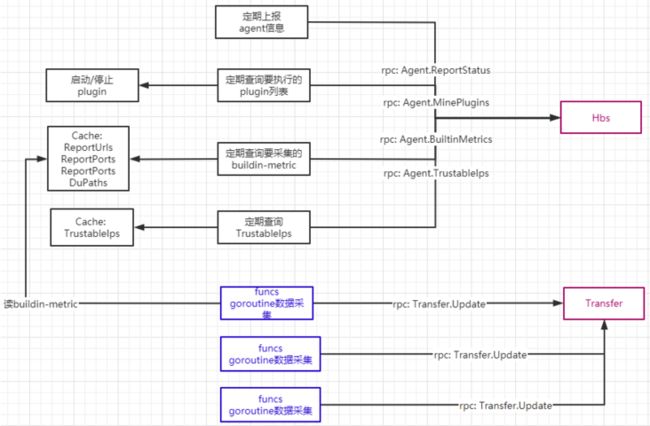
agent是指标采集模块,仅关注linux本身的监控指标,主要负责:
- 定期进行指标采集,然后通过RPC上报给Transfer;
- 向hbs发送heartbeat,同时从hbs获取要监听的process、port和要执行的plugin信息;
- 定期执行plugin,将plugin的指标结果发送给Transfer;
1. 指标采集
代码入口:
func main() {
......
cron.Collect()
......
}
//modules/agent/cron/collector.go
func Collect() {
.....
for _, v := range funcs.Mappers {
go collect(int64(v.Interval), v.Fs)
}
}其中funcs.Mappers是采集函数的集合,agent为每一类采集启动了一个goroutine,有几种分类就有几个goroutine:
//modules/agent/funcs/funcs.go
var Mappers []FuncsAndInterval
func BuildMappers() {
interval := g.Config().Transfer.Interval
Mappers = []FuncsAndInterval{
{
Fs: []func() []*model.MetricValue{
AgentMetrics,
CpuMetrics,
NetMetrics,
KernelMetrics,
LoadAvgMetrics,
......
},
Interval: interval,
},
{
Fs: []func() []*model.MetricValue{
DeviceMetrics,
},
Interval: interval,
},
......
}
}具体的采集过程,执行每个采集函数,将采集的指标汇集起来,发送给transfer:
// modules/agent/cron/collector.go
func collect(sec int64, fns []func() []*model.MetricValue) {
t := time.NewTicker(time.Second * time.Duration(sec))
defer t.Stop()
for {
<-t.C
hostname, err := g.Hostname()
if err != nil {
continue
}
mvs := []*model.MetricValue{}
ignoreMetrics := g.Config().IgnoreMetrics
for _, fn := range fns {
items := fn()
for _, mv := range items {
mvs = append(mvs, mv)
......
}
}
......
g.SendToTransfer(mvs)
}
}2. 指标上报Transfer
agent与Transfer之间是TCP RPC通道,agent配置了多个transfer的地址,上报时随机选一个地址,只要上报成功就退出,不再尝试其他的transfer地址:
func SendMetrics(metrics []*model.MetricValue, resp *model.TransferResponse) {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
for _, i := range rand.Perm(len(Config().Transfer.Addrs)) {
addr := Config().Transfer.Addrs[i]
c := getTransferClient(addr)
if c == nil {
c = initTransferClient(addr)
}
if updateMetrics(c, metrics, resp) {
break
}
}
}agent与transfer之间维持一个TCP长连接,由SingleConnRpcClient来维护:
type SingleConnRpcClient struct {
sync.Mutex
rpcClient *rpc.Client
RpcServer string
Timeout time.Duration
}SingleConnRpcClient包装了rpc.Client,调用rpc.Client.Call("Transfer.Update")完成最终的方法调用;
- 首先确保有1个TCP rpc长连接到Transfer;
- 调用rpc.Client.Call()方法进行实际的rpc调用;
- rpc调用放在goroutine内执行,外面使用select进行超时判断;
func (this *SingleConnRpcClient) Call(method string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) error {
this.Lock()
defer this.Unlock()
err := this.serverConn()
if err != nil {
return err
}
timeout := time.Duration(10 * time.Second)
done := make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
err := this.rpcClient.Call(method, args, reply)
done <- err
}()
select {
case <-time.After(timeout):
this.close()
return errors.New(this.RpcServer + " rpc call timeout")
case err := <-done:
if err != nil {
this.close()
return err
}
}
return nil
}3. 指标类型:GUAGE与COUNTER
GAUGE与COUNTER类型,与Prometheus的类型语义相同:
- GAUGE表示有实际意义的立即数,比如内存用量;
- COUNTER表示递增的计数,比如cpu使用时间的计数;
agent用cpu在user模式下的使用计数差值 / 总模式的计数差值,得到cpu.user.percent(GAUGE类型),具体来看一下代码;
agent使用1个goroutine来定期采集/proc/stat下各种cpu的使用计数:
//modules/agent/cron/collector.go
func InitDataHistory() {
for {
funcs.UpdateCpuStat()
time.Sleep(g.COLLECT_INTERVAL)
}
}由于要计算统计时间间隔内的差值,故保存了2份数据,上一次统计和本次统计的:
//modules/agent/funcs/cpustat.go
const (
historyCount int = 2
)
func UpdateCpuStat() error {
ps, err := nux.CurrentProcStat()
if err != nil {
return err
}
psLock.Lock()
defer psLock.Unlock()
for i := historyCount - 1; i > 0; i-- {
procStatHistory[i] = procStatHistory[i-1]
}
procStatHistory[0] = ps
return nil
}cpu指标数据的来源,是读取/proc/stats文件:
//github.com/toolkits/nux/cpustat.go
func CurrentProcStat() (*ProcStat, error) {
f := Root() + "/proc/stat"
bs, err := ioutil.ReadFile(f)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
ps := &ProcStat{Cpus: make([]*CpuUsage, NumCpu())}
reader := bufio.NewReader(bytes.NewBuffer(bs))
for {
line, err := file.ReadLine(reader)
if err == io.EOF {
err = nil
break
} else if err != nil {
return ps, err
}
parseLine(line, ps)
}
return ps, nil
}最后看下cpu.user.percent指标如何计算的,其计算公式为:
(cpu.user2 - cpu.use1) / (cpu.total2 - cpu.total1)//modules/agent/funcs/cpustat.go
func CpuMetrics() []*model.MetricValue {
user := GaugeValue("cpu.user", CpuUser())
return []*model.MetricValue{user, ....}
}
func CpuUser() float64 {
psLock.RLock()
defer psLock.RUnlock()
dt := deltaTotal()
if dt == 0 {
return 0.0
}
invQuotient := 100.00 / float64(dt)
return float64(procStatHistory[0].Cpu.User-procStatHistory[1].Cpu.User) * invQuotient
}
func deltaTotal() uint64 {
if procStatHistory[1] == nil {
return 0
}
return procStatHistory[0].Cpu.Total - procStatHistory[1].Cpu.Total
}4. agent与hbs
agent定期向hbs发送heartbeat,上报时调用hbs的RPC方法(Agent.ReportStatus)实现的:
func reportAgentStatus(interval time.Duration) {
for {
hostname, err := g.Hostname()
req := model.AgentReportRequest{
Hostname: hostname,
IP: g.IP(),
AgentVersion: g.VersionMsg(),
PluginVersion: g.GetCurrPluginVersion(),
}
var resp model.SimpleRpcResponse
err = g.HbsClient.Call("Agent.ReportStatus", req, &resp)
time.Sleep(interval)
}
}agent还会定期向hbs查询自己要执行的plugin名称及版本信息,通过调用hbs的RPC方法(Agent.MinePlugins)实现:
// modules/agent/cron/plugin.go
func syncMinePlugins() {
duration := time.Duration(g.Config().Heartbeat.Interval) * time.Second
for {
time.Sleep(duration)
hostname, err := g.Hostname()
req := model.AgentHeartbeatRequest{
Hostname: hostname,
}
var resp model.AgentPluginsResponse
err = g.HbsClient.Call("Agent.MinePlugins", req, &resp)
......
}
}5. 执行plugin
plugin即采集的插件或脚本,通常是shell或py,该脚本执行后通常会输出特定格式的指标信息,agent读取该执行结果,发送到transfer;比如:
[root@host01:/path/to/plugins/plugin/sys/ntp]#./600_ntp.py
[{"endpoint": "host01", "tags": "", "timestamp": 1431349763, "metric": "sys.ntp.offset", "value": 0.73699999999999999, "counterType": "GAUGE", "step": 600}]上一步讲到,agent向hbs查询要执行的plugin list,跟本地执行的plugin list进行比对,若有新的plugin则执行:
//modules/agent/plugins/plugins.go
func AddNewPlugins(newPlugins map[string]*Plugin) {
for fpath, newPlugin := range newPlugins {
if _, ok := Plugins[fpath]; ok && newPlugin.MTime == Plugins[fpath].MTime {
continue
}
Plugins[fpath] = newPlugin
sch := NewPluginScheduler(newPlugin)
PluginsWithScheduler[fpath] = sch
sch.Schedule()
}
}每个plugin是定期被执行的:
func (this *PluginScheduler) Schedule() {
go func() {
for {
select {
case <-this.Ticker.C:
PluginRun(this.Plugin)
case <-this.Quit:
this.Ticker.Stop()
return
}
}
}()
}plugin的执行,实际上是执行cmd命令,然后读取cmd命令的输出结果,解析后发送给transfer:
func PluginRun(plugin *Plugin) {
var cmd *exec.Cmd
if args == "" {
cmd = exec.Command(fpath)
} else {
arg_list := PluginArgsParse(args)
cmd = exec.Command(fpath, arg_list...)
}
//执行cmd命令
err, isTimeout := sys.CmdRunWithTimeout(cmd, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Millisecond)
// exec successfully
data := stdout.Bytes()
//发送到transfer
var metrics []*model.MetricValue
err = json.Unmarshal(data, &metrics)
g.SendToTransfer(metrics)
}plugin的执行有个风险,由于goroutine执行cmd会进入SYSCALL阻塞,也就是其对应的G和M一起被阻塞,若阻塞较多的话,会有较多的M被阻塞,M是对应系统线程,较多的M被创建并阻塞,会导致系统的性能下降。
参考:
1.Open-falcon docs: https://book.open-falcon.org/...