MySQL必知必会语法和基础知识大总结
概述
主键:唯一区分表中每个行(不可重复,不允许null
mysql:基于客户-服务器的数据库系统
使用mysql
mysql是部署在主机上的,可以通过ssh建立mysql连接
# 显示数据库
show databases;
# 选择数据库
use databases;
# 显示库中的表
show tables;
# 显示表中的列
show columns from [table];
# 显示状态信息
show status;
# 显示用户
show grants;
# 显示错误和警告
show errors;
show warnings;
关于表
default可以给列赋一个默认值- 这个默认值不允许是函数
not或者not null表明插入数据时是否允许该列为null值,默认情况下为null- 默认的存储引擎为
innoDB
# 创建表
create table student(
student_id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null default '张大炮'
)engine=innoDB;
# 使用复合主键
create test(
test_id int auto_increment,
math int,
chinese int,
primary key(math,test_id)
);
外键约束
外键经常应用的地方为以下两种情况:
-
父表更新时子表也更新,父表删除时如果子表有匹配的项,删除失败;
-
父表更新时子表也更新,父表删除时子表匹配的项也删除。
注意:只有innoDB支持外键,MyISAM不支持外键
# 基本格式
constraint (key_name) foreign key(column) references table(column)
on delete/update (触发语句)
on delete和on update表示事件触发,触发操作有以下几种:
- RESTRICT(限制外表中的外键改动,默认值)
- CASCADE(跟随外键改动)
- SET NULL(设空值)
- SET DEFAULT(设默认值)
- NO ACTION(无动作,默认的)
# 建立外键约束
# 外键关联的表的元素改地,则这个表里面的关联元素也会改动
create table test(
test_id int auto_increment,
subject varchar(10),
date date,
student_id int,
constraint stu_fk foreign key(student_id) references student(student_id)
on update cascade,
primary key(test_id)
)engine=InnoDB;
关于引擎
InnoDB:可靠事务处理引擎,但不支持全文本搜索
MyISAM:性能高,但不支持事务处理
Memory:功能等同MyISAM,但数据存储在内存,很快但不能永久保存,适合临时表
修改表
使用alter table来修改修改表,一般是add操作和rename操作
add:可以添加新列和键约束
# 添加列
alter table student add
class int not null;
# 添加外键约束
alter table student add
constraint st_fk foreign key(student_id) references test(student_id)
on update cascade;
删除表
drop table student;
数据检索
基本格式如下
select [column...] from [table];
column可以选择多个列,也可用通配符*表示所有列
去除重复行:使用distinct关键字,distinct作用于所有列
# 两个列都一样才会认为是重复
select distinct student_id,student_name form student;
使用limit限制结果
注意:行号从0开始
# 返回前5行
# 相当于 limit 0,5
select student_id form student limit 5;
# 返回行5开始的后5行(包括第5行
select student_id form student limit 5,5;
使用.来表示全限名
# 表示从school库的student表查student_name这个列
select student.student_name from school.student;
数据排序
使用order by字句选择按照哪个列来进行排序
默认顺序:A—>Z,0—>∞,使用DESC指定为降序排列(必须指定在每个列上
可指定多个列
# 结果通过名字排序
select name from student order by name;
# 优先按照name排序,相同则按照number排序;降序
select name from student order by name DESC,number DESC;
数据过滤
使用where字句
使用where字句限定条件
| 运算符 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| = | 等于 |
| !=或<> | 不等于 |
| > | 大于 |
| < | 小于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| between | 限定在两个值之间 |
- 匹配字符串需要单引号,匹配数值则不需要
- 使用
and和or连接多个条件,and运算优先级高于or - 使用
is null检查空值 - 使用
in来限定范围,范围是一个离散值的集合,离散值用,隔开 - 使用
not来否定限定范围
# 按照id和grade两个条件进行限定
select name from student where id='0000' and grade=100;
# 空值检查
select name from student where id is null;
# 使用between限定范围,下面2个语句等价
select name from student where id between '0000' and '1000';
select name from student where id >= '0000' and id <= '1000';
# 使用in限定范围,下面2个语句等价
select name from student where id in (1,2);
select name from student where id = 1 or id = 2;
# 使用not取限定范围以外的值
select name from student where id not in (1,2);
使用通配符
使用like操作符来进行模糊匹配
- 不能匹配null
- 注意:通配符时间开销大,能采用其他操作符尽量采用其他操作符
| 操作符 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| % | 匹配任意多个字符 |
| _ | 匹配单个字符 |
# 多字符匹配
select name from student where id like '%00%';
# 单字符匹配
select name from student where id like '_00';
创建计算字段
字段:多个列的值合成而成
拼接字段
使用Concat()来拼接多个列
# 拼接name、=以及grade
select Concat(name,'=',grade) from student;
-
使用
RTrim()和LTrim()分别去除左右多余空格,Trim()直接去除两边空格 -
使用
as为列赋别名用以显示# 赋name别名为姓名 select name as 姓名 from student;
算数运算
| 操作符 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| + | 加 |
| - | 减 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
# 计算学号000开头的学生总成绩
select Chinese+Math+English as 总成绩 from student where id = '000_';
函数
sql支持以下函数类型:
- 处理文本串
- 算术操作
- 处理日期
- 系统函数(返回登录信息,检查版本等
文本处理函数
| 函数 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| Left() | 返回左边的字符 |
| Length() | 返回串长度 |
| Locate(subStr,string) | 找出字串出现的位置 |
| Lower() | 转换小写 |
| LTrim() | 去除左边空格 |
| RTrim() | 去除右边空格 |
| Right() | 返回右边的字符 |
| Soundex() | 匹配发音类似的值 |
| SubString(string,position,length) | 返回字串 |
| Upper() | 转换大写 |
# 匹配发音类似Y Lei的值
select grade from student where Soundex(name) = Soundex('Y Lei');
日期处理函数
日期时间满足yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:SS形式
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AddDate() | 增加一个日期(天、周 |
| AddTime() | 增加一个时间(时、分 |
| CurDate() | 返回当前日期 |
| CurTime() | 返回当前时间 |
| Date() | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
| DateDiff() | 计算日期之差 |
| Date_Add() | 日期运算 |
| Date_Format() | 返回格式化的日期和时间串 |
| Day() | 返回日期的天数 |
| DayOfWeek() | 返回日期对应的星期几 |
| Hour() | 返回时间的小时部分 |
| Minute() | 返回时间的分钟部分 |
| Month() | 返回日期的月份 |
| Now() | 返回当前日期和时间 |
| Second() | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
| Time() | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
| Year() | 返回日期的年份 |
常见情况:Date数据类型的字段值存入了yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:SS形式的字段值,但匹配时只想要日期或者时间
# 只需要日期值进行比较
select id from student where Date(register_time)='2001-2-3';
# 取出某年某月的数据
select id from student where Year(register_time)=2005 and Month(register_time)=6
数值处理函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Abs() | 返回绝对值 |
| Cos() | 返回余弦值 |
| Exp() | 返回指数值 |
| Mod() | 返回余数 |
| Pi() | 返回圆周率Π |
| Rand() | 返回随机数 |
| Sin() | 返回正弦值 |
| Sqrt() | 返回数的平方根 |
| Tan() | 返回角度的正切值 |
# 返回一个余数值
select Mod(55,33);
数据汇总函数
聚焦函数:确定行数、列数或者找其中某特定值(如最大值、最小值…)
- 使用聚焦函数处理列不能离开
group by字句
| 函数 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| AVG() | 返回平均值 |
| COUNT() | 返回某列的行数 |
| MAX() | 返回该列最大值 |
| MIN() | 返回该列最小值 |
| SUM() | 列求和 |
注意:count(*)多所有行进行计数,count(column)对该列为null的行不计数
可以和distinct关键词搭配使用,去除重复值
使用distinct必须指定列名,也就是说不能和count(*)搭配使用
# 求平均值,每个值只计算一次
select AVG(DISTINCT grade) from student;
# 都整一遍
select AVG(grade) as 平均成绩,
MAX(grade) as 最大值,
MIN(grade) as 最小值
from student;
数据分组
涉及group by和having两个字句
group by:按照某个属性分组计算,相当于是对每个分组单独进行一次sql语句的执行
- 必须出现在
where之后,order by之前 - 可指定多个,但最后会汇总到最后指定的属性进行分组
- 除去聚焦函数(子句中不允许包含聚焦函数),
select语句中出现的所有列都必须在group by中给出
# 求业务员分别卖出了多少物品
select id,name,count(*) from kpi
group by id;
having:起过滤作用,和where类似。但where过滤的是行,having过滤的是分组
# 求除了id为1的业务员分别卖出了多少物品
select id,name,count(*) from kpi
group by id
having id!=1;
不要依赖group by产生的顺序
要正确排序还是应该使用order by字句,该字句一般放在最后
# 顺序求除id为1的每个业务员卖出物品的总价值
select id,sum(price) from kpi
group by id
having id!=1
order by sum(price);
select字句顺序
| select
| from
| where
| group by
| having
↓ limit
多表查询
子查询
主要用途:查询多个表
子查询的执行顺序是从内向外的
原理:select语句的查询结果可以提供给其他select语句作为条件
可以嵌套,但一般不建议超过3层
# 联结两个表,查询数学成绩
select student_id from student where grade in(
select grade from test where subject='数学');
# 对每个学生单独计算成绩总和
select student_id,(select sum(grade) from test where test.student_id=student.student_id) as sum
from student order by grade DESC;
联结表
外键:将一个表的主键放在其他表作为外键,加强数据一致性
外键的字段值依赖于所连接的表的主键,会对插入、删除等操作做检查
联结表设定的条件一般是外键
# 联结多表进行查询
select name,math
from student,test
where student.student_id=test.student_id;
# 使用表别名缩短sql语句
select name,math
from student as s,test as t
where s.student_id=t.student_id;
不使用where字句做限定的话会返回一个笛卡尔积
内部联结
联结表这种基于两个表之间相等测试的方法也称为内部联结
可以使用join...on...达到相同目的
inner/outer:表示内联结或者外联结
join:使用join加入表
on:条件
# JOIN...ON...
select name,math
from student inner join test
on student.student_id=test.student_id;
高级联结
自联结
一张表自己联结自己
使用场景:前一次查到这张表的数据作为后一次查询这张表的条件的时候
为了避免二义性,列采用全限定名
# 首先根据test_id=4查到student_id,再根据student_id查到语文成绩
select t2.chinese from
test as t1,test as t2
where t1.student_id=t2.student_id
and t1.test_id=4;
# 等效子查询
select chinese from test
where student_id = (select student_id from test where test_id=4);
自然联结
避免多表查询中相同的列多次出现
注意:这是一种规范,不是某种特定的用法
实现:自己刻意避免出现相同列
外部联结
虽然是两个有关联的表进行联结,但其中一个表不一定所有数据在另外一个表都有对应数据
left outer join:左边的表的所有行加入进来,若右边没有对应的则显示null
right outer join:右边的表的所有行加入进来,若左边没有对应的则显示null
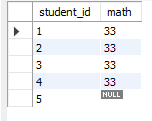
# 使用左联结
select s.student_id,t.math
from student as s left join test as t
on s.student_id = t.student_id
student_id=5在右边表中是没有对应数据的,但还是会予以显示
组合查询
含义:执行多条sql语句,但将结果作为一个结果集返回
- 每个查询中的内容相同(列、函数
- 默认返回的是并集,使用
union all会出现重复结果 - 使用
order by排序时只需要写在最后一条sql语句上即可 - 相当于
where子句中使用or
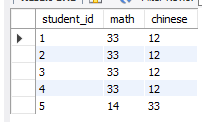
# 简单测试
select student_id,math,chinese from test
where math > 20
union
select student_id,math,chinese from test
where chinese >20
全文本搜索
不是所有存储引擎都支持全文本搜索
InnoDB不支持,MyISAM支持
启动全文本查询支持
在创建表的时候使用fulltext()索引可以被全文本搜索的列
同时指定引擎为MyISAM
create table article(
article_id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
student_id int,
component text,
fulltext(component)
)engine=MyISAM;
进行全文本搜索
match():指定被搜索的列
against():指定搜索表达式
# 搜索带有When的文本
select component from article
where match(component) against('When');
数据插入
插入完整行
使用insert into来插入数据
# 基本格式
insert into [table](columns1,columns2,...) values(...);
可以不带column,但是就需要记住列的顺序按序插入
数据约束为null的列可以插入null值
使用;分隔多行插入,如果数据一致也可以使用,分隔多行数据
# 插入多行
insert into student(name) values('袁瑞通过');
insert into student(name) values('赎金小松');
# 如果插入是相同列的数据,也可以这样
insert into student(name) values('打字话'),('大选呀'),('大批及')
插入搜索行
可以插入其他行中搜索出来的结果
插入数据时通过select字句返回的顺序来匹配
# 插入select结果
insert into article(name,student_id)
select name,student_id from student where student_id=3;
数据更新
使用update...set...来更新数据
ignore关键字:默认更新多行数据如果发生错误,则之前更新过的数据恢复原来值;使用ignore后不会恢复
# 更新多个数据
update ignore article set name='大花衣',
component='bilibili'
where article_id=3;
数据删除
delete关键字删除整行的数据
# 删除一行数据
delete from article where article_id=3;
视图
视图是虚拟的表,包含的是动态的sql查询的结果
建立视图后,可以进行和表一样的查询操作
视图不能索引,不能有关联触发器
创建
# 建立视图
create view exam as
select student.student_id,name,subject,date
from student,test;
视图直接组合各个表中的列,在某些特定情况下非常方便
# 和查询一般的表无异
select * from exam;
select * from exam where date between '2020-1-3' and '2021-3-4';
视图的更新
视图是可以更新的,但有很多的限制。一般只用视图来做数据检索。
存储过程
方便后续使用的一条或多条sql语句集合
变量必须以@开头
使用call来调用存储过程
# 括号里面的是参数
call product(@low,@high);
创建存储过程
# 遵顼以下格式
create procedure grade_avg()
begin
select avg(grade) as 平均成绩
from test;
end;
注意:mysql应用程序中会出现;冲突,使用delimiter来定义一个分隔符使用
# 定义分隔符为 //
DELIMITER //
create procedure grade_avg()
begin
select avg(grade) as 平均成绩
from test;
end //
使用drop删除存储过程
drop procedure grade_avg();
使用参数
参数:
IN: 表示输入参数,可以携带数据带存储过程中
OUT: 表示输出参数,可以从存储过程中返回结果
INOUT: 表示输入输出参数,两者结合
使用set为变量赋值
使用into把查询结果赋给变量
# 携带输入参数的存储过程
DELIMITER //
create procedure search(in sid int)
begin
select * from student where student_id=sid;
end //
# 使用带内部参数的存储过程:直接传入参数值
call search(10);
# 携带输出参数的存储过程
DELIMITER //
create procedure stu_out(out str varchar(20))
begin
set str='123123';
end //
# 使用外部参数的存储过程:先获得这个外部变量值,再进行操作
call stu_out(@name);
select @name;
# 使用select into
delimiter //
create procedure stu_into(in id int,out str varchar(20))
begin
select name into str
from student where student_id=id;
end //
# 使用该存储过程
call stu_into(5,@name);
select @name as 名字;
使用分支控制语句
if...then...elseif...else...end if的格式
# 使用分支控制
delimiter //
create procedure weekday(in input int,out output varchar(10))
begin
if input=1 then set output='星期一';
elseif input=2 then set output='星期二';
else set output='其他日子';
end if;
end //
# 使用该存储过程
call weekday(2,@day);
select @day;
使用循环控制语句
通过declare定义存储过程的内部变量(也可叫局部变量、临时变量
采用while...do...end while的格式
# 使用循环控制
# 计算1到某个数值的和
delimiter //
create procedure stu_while(in input int,out output int)
begin
declare i int default 0;
declare result int default 0;
while i<=input
do
set result=result+i;
set i=i+1;
end while;
set output=result;
end //
# 使用该存储过程
call stu_while(4,@res);
select @res as 和;
还可以采用repeat...until...end repeat语句
# 修改上面例子的循环部分
repeat
set result=result+i;
set i=i+1;
until i>input end repeat;
游标
场景:为了在检索出来的行中前进后者后退几行
只能用在存储过程
- 在存储过程中用
declare声明游标,游标的变量名是cursor - 使用
for来使游标关联select语句 - 创建好过后,还要使用
open来打开游标;并且不使用的话还要使用close关闭游标释放资源 - 一般游标用在循环语句,为了使游标可以正常退出,一般需要绑定一个对应的错误处理
异常处理
exit handler:出现某种异常后退出
continue handler:出现某种异常后继续
应用场景:事务出现错误时进行回滚
游标中的使用:游标检索完时设置退出标志
使用游标
fetch...into...将游标值赋给变量
# 使用游标
delimiter //
create procedure cursor_test()
begin
declare done boolean default 0;
declare str varchar(20);
declare ct cursor for
select name from student;
declare continue handler for not found set done=1;
open ct;
repeat
fetch ct into str;
until done end repeat;
close ct;
end //
一个使用场景
涉及到数据迁移,使用游标循环将数据转移非常的方便
# 将多行数据转移创建一个新的表
delimiter //
create procedure new_test()
begin
declare name varchar(20);
declare id int;
declare grade int;
declare subject varchar(20);
declare done boolean default 0;
declare cs cursor for
select student.name,student.student_id,test.grade,test.subject from student,test where student.student_id=test.student_id;
declare continue handler for not found set done=1;
create table if not exists grades(
grades_id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
student_id int,
grade int,
subject varchar(20)
);
open cs;
repeat
fetch cs into name,id,grade,subject;
insert into grades(name,student_id,grade,subject) values(name,id,grade,subject);
until done end repeat;
close cs;
end //
触发器
触发器是某张表执行某一类型的语句后,表自动去执行某一存储过程
比如:某一张表的数据有修改,另一张表跟着也要修改
响应语句类型:delete,insert,update
- 触发器只能绑定到表,不能绑定到视图
mysql的触发器不能调用存储过程
删除和创建
创建触发器给出四条信息:
- 触发器名
- 关联表名
- 响应活动(delete、insert、update)
- 响应时间(before、after)
# 创建触发器
create trigger ct after insert on student
for each row
select 'balbala';
# 删除触发器
drop trigger ct;
insert触发器
new可以访问最新插入的行before insert触发器中new的值可以更改,即把将要插入的值更改了再插入
# 创建一个insert触发器
create trigger ct after insert on student
for each row
select new.student_id into @id;
# 执行insert语句后可以访问@id
insert into student(name) values('asduh');
select @id;
delete触发器
old访问被删除的行,里面的数据是只读的
# 创建一个delete触发器
create trigger ct after delete on grades
for each row
select old.student_id,old.name into @id,@name;
# 执行delete语句后可以访问参数
delete from grades where grades_id=1;
select @id as id,@name as name;
update触发器
old访问该行更新前的数值,new访问该行更新后的数值before update触发器可以更改new中的值old都是只读的
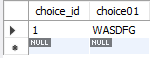
# 创建update触发器,将更新值全部换成大写
create trigger ct4 before update on choice
for each row
set new.choice01=upper(new.choice01);
# 查看结果
update choice set choice01='wasdfg' where choice_id=1;
select * from choice;
事务处理
- 使用
InnoDB,MyISAM不支持事务处理 - mysql默认的事务处理是每条sql语句自动提交
# autocommit为0:不自动提交
set autocommit=0;
事务:一组sql语句
回滚:撤销指定sql语句
提交:将未存储的sql语句提交到数据库,也就是执行
保留点:临时占位符,可以发布回退
开始事务处理
使用start transaction标志事务的开始
使用commit提交事务,事务中的多条sql语句是被一起提交的
使用rollback撤销事务,只能在一个事务内使用
# 提交事务
start transaction;
delete from student where name='打字话';
insert into student(name) values('asd');
commit;
# 撤销事务
start transaction;
delete from student where name='打字话';
insert into student(name) values('asd');
rollback;
使用保留点
rollback事务回滚是直接回滚到transaction还没开始的地方
保留点用在部分回滚的场景
使用savepoint...设置保留点
# 设置保留点,部分回退
start transaction;
delete from student where name='打字话';
savepoint sv1;
insert into student(name) values('asd');
rollback to sv1;
安全管理
管理用户
名为mysql的数据库中存储了数据库设置等信息,可以在里面的user表查看信息
# 查看用户
use mysql;
select user from user;
创建和删除用户
identified by设置密码
# 创建用户
create user xt identified by '123456';
# 修改用户名
rename user xt to xtbro;
# 删除用户
drop user xtbro;
# 更新密码,需要加密入表
set password for xt = Password('1234567');
赋予权限
show grants for...查看权限- 使用
grant赋予权限
# 赋予school数据库下的所有表的insert权限
grant insert on school.* to xt;
# 查看权限
show grant for xt;
# 撤销权限
revoke insert on school.* from xt;
权限的层次:
整个服务器:grant all
整个数据库:on database.*
特定的表:on database.table
特定的列:on database.table.column
特定的存储过程