南方的朋友请回避一下,我给北方的朋友介绍一下我们南方的臭豆腐 ——《带头双向循环链表》
文章目录
-
-
- 一、南北大战
- 二、前言
- 三、函数各接口的实现
-
- malloc空间
- 初始化数据1
- 初始化数据2
- 尾插数据
- 头插数据
- 判空链表
- 尾删数据
- 头删数据
- 查找数据
- pos位置之前插入数据
- pos位置删除数据
- 链表的长度
- 打印数据
- 销毁动态内存开辟的空间
- 四、完整代码
-
- List.h
- List.c
- Test.c
-
一、南北大战
1️⃣ 北方代表首先给我们展示了当地特色——大耗子

2️⃣ 南方人表示不服,抬出了老鼠界的扛把子

接着就进入了南北大混战
1️⃣ 北方的消防员

2️⃣ 南方的牛肉面

1️⃣ 北方的鸭血

2️⃣南方的话梅

1️⃣北方的裤衩

2️⃣ 南方的显卡

但当我们遇见外人时总是意料之中的团结
还有我国的珍稀品种——狗雀
二、前言
实际中链表的结构非常多样,组合起来共有8种结构,但是最常用的只有2种:
1️⃣ 无头单向非循环链表
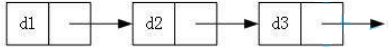
无头单向非循环链表,结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2️⃣ 带头双向循环链表
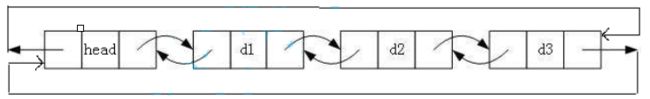
带头双向循环链表,结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了(果真闻起来臭吃起来香)。
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
struct ListNode* prev;//前驱指针
struct ListNode* next;//后驱指针
LTDataType data;//值
}LTNode;
三、函数各接口的实现
malloc空间
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
LTNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
LTNode* node = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
//malloc失败
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//malloc成功
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
node->data = x;
//返回起始地址
return node;
}
初始化数据1
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListInit1(LTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//据析,这里需要传二级指针,因为它要改变plist本身(NULL->0x...)
*pphead = BuyListNode(-1);
//初始化前驱指针和后驱指针(一开始同时指向自己)
(*pphead)->next = *pphead;
(*pphead)->prev = *pphead;
}
初始化数据2
为了接口的一致性
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
LTNode* ListInit2()
{
LTNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);
//初始化前驱指针和后驱指针(一开始同时指向自己)
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
//返回哨兵位的地址
return phead;
}
尾插数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
据析,这里不需要对plist变量改变,所以不用传二级指针
assert(phead);
tail记录尾地址
//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
//LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
原尾和新尾相互链接
//tail->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = tail;
哨兵位和新尾相互链接
//newnode->next = phead;
//phead->prev = newnode;
//当实现了ListInser,ListPushBack就可以复用了
ListInser(phead, x);
}
头插数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
tail记录第一个有效节点
//LTNode* tail = phead->next;
newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
//LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
头和新节点相互链接
//phead->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = phead;
新节点和旧节点相互链接
//newnode->next = tail;
//tail->prev = newnode;
//当实现了ListInser,ListPushFront就可以复用了
ListInser(phead->next, x);
}
判空链表
当链表为空时,不能尾删、头删,所以先实现ListEmpty
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
bool ListEmpty(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//链表为空返回true
return phead->next == phead;
}
尾删数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//空链表需要报错,调用ListEmpty:不为空时返回false,再!为真;为空时返回true,再!为假
assert(!ListEmpty(phead));
tail记录尾
//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
cur记录尾的前一个
//LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;
释放尾
//free(tail);
重新链接
//phead->prev = tailPrev;
//tailPrev->next = phead;
//当实现了ListErase,ListPopBack就可以复用了
ListErase(phead->prev);
}
头删数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
空链表报错,调用ListEmpty:不为空时返回false,再!为真;为空时返回true,再!为假
//assert(!ListEmpty(phead));
tail记录第一个有效节点的后一个节点
//LTNode* tail = phead->next->next;
释放第一个有效节点
//free(phead->next);
头和第一个有效节点相互链接
//phead->next = tail;
//tail->prev = phead;
//当实现了ListErase,ListPopFront就可以复用了
ListErase(phead->next);
}
查找数据
要实现在某个位置之前插入数据或某个位置删除数据就要先实现ListFind
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
//从第一个有效节点开始
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//一直找到哨兵位的头
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
printf("找到了\n");
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("没找到\n");
return NULL;
}
pos位置之前插入数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListInser(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
//newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//posPrev记录pos的前一个地址
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
//posPrev和新节点相互链接
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
//pos和新节点相互链接
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
pos位置删除数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListErase(LTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
//记录pos的前一个和后一个位置的地址
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* posNext = pos->next;
//释放空间
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
//pos的前一个和后一个相互链接
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
}
链表的长度
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
size_t ListLen(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//cur记录第一个有效节点
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//len记录长度
size_t len = 0;
//cur指向哨兵位的头时则停止
while (cur != phead)
{
len++;
//迭代
cur = cur->next;
}
return len;
}
打印数据
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListPrint(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//cur记录第一个有效节点
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//cur指向哨兵位的头时则停止
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
//迭代
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
销毁动态内存开辟的空间
函数原型
![]()
函数实现
void ListDestory(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//从有效节点开始释放
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//循环结束后,哨兵位的头节点还未释放
while (cur != phead)
{
//记录cur下一个节点的地址
LTNode* curNext = cur->next;
//释放
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
//迭代
cur = curNext;
}
//释放哨兵位的头 - 其实phead置不置空都无所谓,因为它出了ListDestory就销毁了,其次就是phead的置空不会影响外面的实参
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
四、完整代码
这里需要三个文件
1️⃣ List.h,用于函数的声明
2️⃣ List.c,用于函数的定义
3️⃣ Test.c,用于测试函数
List.h
#pragma once
//头
#includeList.c
#include"List.h"
LTNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
LTNode* node = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
//malloc失败
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//malloc成功
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
node->data = x;
//返回起始地址
return node;
}
void ListInit1(LTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//据析,这里需要传二级指针,因为它要改变plist本身(NULL->0x...)
*pphead = BuyListNode(-1);
//初始化前驱指针和后驱指针(一开始同时指向自己)
(*pphead)->next = *pphead;
(*pphead)->prev = *pphead;
}
LTNode* ListInit2()
{
LTNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);
//初始化前驱指针和后驱指针(一开始同时指向自己)
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
//返回哨兵位的地址
return phead;
}
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
据析,这里不需要对plist变量改变,所以不用传二级指针
assert(phead);
tail记录尾地址
//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
//LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
原尾和新尾相互链接
//tail->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = tail;
哨兵位和新尾相互链接
//newnode->next = phead;
//phead->prev = newnode;
//当实现了ListInser,ListPushBack就可以复用了
ListInser(phead, x);
}
void ListPrint(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//cur记录第一个有效节点
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//cur指向哨兵位的头时则停止
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
//迭代
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//空链表需要报错,调用ListEmpty:不为空时返回false,再!为真;为空时返回true,再!为假
assert(!ListEmpty(phead));
tail记录尾
//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
cur记录尾的前一个
//LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;
释放尾
//free(tail);
重新链接
//phead->prev = tailPrev;
//tailPrev->next = phead;
//当实现了ListErase,ListPopBack就可以复用了
ListErase(phead->prev);
}
bool ListEmpty(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//链表为空返回true
return phead->next == phead;
}
size_t ListLen(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//cur记录第一个有效节点
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//len记录长度
size_t len = 0;
//cur指向哨兵位的头时则停止
while (cur != phead)
{
len++;
//迭代
cur = cur->next;
}
return len;
}
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
tail记录第一个有效节点
//LTNode* tail = phead->next;
newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
//LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
头和新节点相互链接
//phead->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = phead;
新节点和旧节点相互链接
//newnode->next = tail;
//tail->prev = newnode;
//当实现了ListInser,ListPushFront就可以复用了
ListInser(phead->next, x);
}
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
空链表报错,调用ListEmpty:不为空时返回false,再!为真;为空时返回true,再!为假
//assert(!ListEmpty(phead));
tail记录第一个有效节点的后一个节点
//LTNode* tail = phead->next->next;
释放第一个有效节点
//free(phead->next);
头和第一个有效节点相互链接
//phead->next = tail;
//tail->prev = phead;
//当实现了ListErase,ListPopFront就可以复用了
ListErase(phead->next);
}
LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
//从第一个有效节点开始
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//一直找到哨兵位的头
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
printf("找到了\n");
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("没找到\n");
return NULL;
}
void ListInser(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
//newnode接收malloc空间的起始地址
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//posPrev记录pos的前一个地址
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
//posPrev和新节点相互链接
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
//pos和新节点相互链接
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
void ListErase(LTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
//记录pos的前一个和后一个位置的地址
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* posNext = pos->next;
//释放空间
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
//pos的前一个和后一个相互链接
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
}
void ListDestory(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//从有效节点开始释放
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
//循环结束后,哨兵位的头节点还未释放
while (cur != phead)
{
//记录cur下一个节点的地址
LTNode* curNext = cur->next;
//释放
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
//迭代
cur = curNext;
}
//释放哨兵位的头 - 其实phead置不置空都无所谓,因为它出了ListDestory就销毁了,其次就是phead的置空不会影响外面的实参
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
Test.c
#include"List.h"
void TestList()
{
LTNode* plist = NULL;
//初始化
//ListInit1(&plist);
plist = ListInit2();
//尾插+打印
ListPushBack(plist, 1);
ListPushBack(plist, 2);
ListPushBack(plist, 3);
ListPushBack(plist, 4);
ListPrint(plist);
//尾删+打印
ListPopBack(plist);
ListPrint(plist);
//链表的长度
printf("%d\n", ListLen(plist));
//头插+打印
ListPushFront(plist, -1);
ListPushFront(plist, -2);
ListPushFront(plist, -3);
ListPushFront(plist, -4);
ListPrint(plist);
//头删+打印
ListPopFront(plist);
ListPrint(plist);
//查找+pos前插入+打印(如果查找失败返回空,ListInser里也会报错)
LTNode* pos = ListFind(plist, 1);
ListInser(pos, 0);
ListPrint(plist);
//查找+pos位置删除+打印(如果查找失败返回空,ListErase里也会报错)
pos = ListFind(plist, 0);
ListErase(pos);
ListPrint(plist);
//销毁 - 当ListDestory函数结束时,plist就是一个野指针,因为ListDestory的参数是值传递的形式
//但其实各有优劣:1、用一级指针,会存在野指针问题,但是它保持接口的一致性;2、用二级指针虽然解决了野指针问题,但从接口设计的角度来看会造成混乱
//用二级指针可以自己在函数内部解决;用一级指针就是交给用的人解决(ListDestory后你知道它是一级,并主动释放)
ListDestory(plist);
plist = NULL;
}
int main()
{
TestList();
return 0;
}

