重学前端,万字入门 HTML+CSS+响应式网页设计
响应式网页设计 认证 | freeCodeCamp.org
观前提醒:擅用
Ctrl+F,笔记不求详细,但求理解,部分难以理解的内容我给了实例或者文档的链接,还有一些我推荐的小游戏,希望能给个三连
文章目录
- Basic HTML
-
- DOCTYPE
- h1~h6 p img br comment
- a
- list
- input
- form button
- label radio checkbox div value
- Basic CSS
-
- style color
- class
- font
- size border
- id
- padding margin border
- attribute selectors
- em rem
- body class id important
- color hex
- var
- browser fallbacks
- :root
- @media
- Applied Visual Design
-
- text-align width height
- strong u em s
- rgba
- box-shadow opactiy
- text-transform
- font
- :hover
- position
-
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- float
- z-index
- center horizontally
- Color
-
- hsl
- linear-gradient
- background
- transform
-
- scale
- skewX skewY
- rotate
- Create Graphics
-
- Crescent Moon
- Heart
- Animation
-
- fill-mode
- iteration-count
- timing-function
- Applied Accessibility
-
- img alt
- Elements
-
- h1 ~ h6
- main
- article
- header
- nav
- footer
- audio
- figure figcaption
- label for
- fieldset legend
- input date
- time datetime
- ScreenReader-only
- High Contrast Text
- accesskey
- tabindex
- Responsive Web Design Principles
-
- @media
- Responsive Image
- Retina Image
- vw vh vmin vmax
- CSS Flexbox
-
- flex-direction
- justify-content
- align-items
- flex-wrap
- Child Elements
-
- flex-shrink
- flex-grow
- flex-basis
- order
- align-self
- CSS Grid
-
- grid-template
-
- rows columns
- fr
- grid-gap
- grid-column grid-row
- Cell Attr
-
- justify-self
- align-self
- justify-items
- align-items
- Areas
-
- grid-template-areas
- grid-area
- repeat minmax
- @media
- Grid within grid
Basic HTML
就此开始,不想看基础的 HTML 和 CSS 可以跳过。
DOCTYPE
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
h1~h6 p img br comment
<h1>Helloh1>
<h2>CatPhotoApph2>
<p>I'm a p tag!p>
<img src="https://www.bit.ly/fcc-relaxing-cat" alt="a cat">
<br>
<main>
<h1>Hello Worldh1>
<p>Hello Paragraphp>
main>
a
<a href="https://www.freecatphotoapp.com">cat photosa>
<a href="#contacts-header">Contactsa>
...
<h2 id="contacts-header">Contactsh2>
<p>Click here to view more
<a href="#">
<img src="https://www.bit.ly/fcc-relaxing-cat" alt="A cute orange cat.">
cat photos
a>
.
p>
list
<ul>
<li>milkli>
<li>cheeseli>
ul>
<ol>
<li>Garfieldli>
<li>Sylvesterli>
ol>
input
input为输入文本框,有不同的type属性,placeholder作为占位符在未输入时显示内容。
<input type="text">
<input type="text" placeholder="cat photo URL">
form button
form为发送数据给服务器的表单。
required表明必须填写后才能提交。
<form action="https://www.freecatphotoapp.com/submit-cat-photo">
<input type="text" placeholder="cat photo URL" required>
<button type="submit">submitbutton>
form>
label radio checkbox div value
按钮用
label包裹,需用for指明按钮id
radio代表单选,checked代表默认选中
<label for="indoor">
<input type="radio" id="indoor" name="indoor-outdoor" checked> Indoor
label>
<label for="outdoor">
<input type="radio" id="outdoor" name="indoor-outdoor"> Outdoor
label>
checkbox为多选框
div为内容划分元素,是一个包裹其他元素的通用容器。
<div>
<label for="1">
<input type="checkbox" name="personality" id="1"> 1
label>
<label for="2">
<input type="checkbox" name="personality" id="2"> 2
label>
<label for="3">
<input type="checkbox" name="personality" id="3"> 3
label>
div>
按钮被选中时,会在表单内提交
indoor-outdoor=indoor, 即value的数据
<label for="indoor">
<input id="indoor" type="radio" name="indoor-outdoor" value="indoor"> Indoor
label>
Basic CSS
style color
<style>
h2 {
color: red;
}
style>
<h2 style="color: red;">CatPhotoApph2>
class
一个HTML元素可以有多个class
<style>
.red-text {
color: red;
background-color: silver;
}
style>
<h2 class="red-text">CatPhotoApph2>
font
Browse Fonts - Google Fonts
<link
href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lobster"
rel="stylesheet"
type="text/css"
/>
<style>
p {
font-size: 16px;
font-family: monospace;
font-weight: 200;
}
h2 {
font-family: Lobster, "Open Sans";
}
style>
size border
<style>
.smaller-image {
width: 100px;
}
.thick-green-border {
border-color: green;
border-width: 10px;
border-style: solid;
border-radius: 10px; /* 50% */
}
style>
<img class = "smaller-image thick-green-border"
src="https://bit.ly/fcc-relaxing-cat"
alt="A cute orange cat."
>
id
一个HTML元素只能有一个id
<style>
#cat-photo-form {
background-color: green;
}
style>
<form action="https://freecatphotoapp.com/submit-cat-photo" id="cat-photo-form">
<button type="submit">Submitbutton>
form>
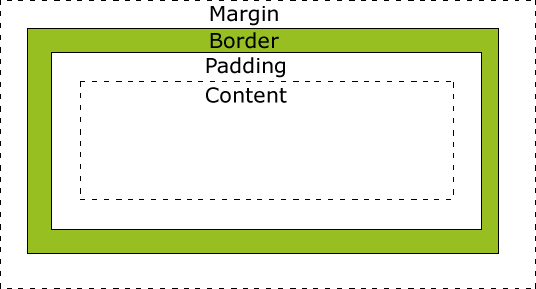
padding margin border
每个 HTML 元素所占有的矩形空间由这三个重要的属性来控制:内边距
padding、外边距margin、边框border。
padding用来控制着元素内容与border之间的空隙大小。
margin用来控制元素的边框与其他元素之间的border距离。
margin设置为负值,元素会变得占用更多空间。
.red-box {
padding-top: 40px;
padding-right: 20px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-left: 40px;
/* 顺时针指定 */
padding: 20px 40px 20px 40px;
}
.blue-box {
margin-top: 40px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
margin-left: 40px;
margin: 20px 40px 20px 40px;
}
attribute selectors
/* [attr=value] */
[type='radio'] {
margin-top: 10px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
em rem
相对单位长度,它们的实际值会依赖其他长度的值而决定。
em相对于当前对象内文本的字体尺寸。
rem相对的只是HTML根元素。px、em、rem区别介绍 (runoob.com)
.red-box {
background-color: red;
margin: 20px 40px 20px 40px;
padding: 1.5em;
}
body class id important
可以从
body继承样式
<style>
body {
background-color: black;
color: green;
font-family: monospace;
}
style>
<h1>Hello Worldh1>
class 会覆盖
body的 CSS 样式。在
transform
当使用伪类选取元素的指定状态(如
:hover)时,我们可以通过transform属性非常方便地给元素添加交互。scale
用来改变元素的显示比例。
<style> div { width: 70%; height: 100px; margin: 50px auto; background: linear-gradient( 53deg, #ccfffc, #ffcccf ); } div:hover { transform: scale(1.1); } style> <div>div>skewX skewY
skewX():使选择的元素沿着 X 轴(横向)翻转指定的角度。
skewY():使元素沿 Y 轴(垂直方向)翻转指定角度。#top { background-color: red; transform: skewY(-10deg); } #bottom { background-color: blue; transform: skewX(24deg); }rotate
旋转元素,正为顺时针,负则为逆时针。
.heart { background-color: pink; height: 50px; width: 50px; transform: rotate(-45deg); }Create Graphics
Crescent Moon
创建一个圆的、透明的图形,它具有模糊阴影并略微向两边递减。
如你所见,这个阴影就是新月形狀。
<style> .center { position: absolute; margin: auto; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: transparent; border-radius: 50%; box-shadow: 25px 10px 0 0 blue; } style> <div class="center">div>Heart
伪元素
::before和::after可以在所选元素之前或之后添加一些内容。必须配合
content来使用,这个属性通常用来给元素添加内容诸如图片或者文字。
content属性仍然是必需的,用来实现形状时它的值可以是空字符串。<style> .heart { position: absolute; margin: auto; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; background-color: pink; height: 50px; width: 50px; transform: rotate(-45deg); } .heart::after { content: ""; background-color: pink; border-radius: 50%; position: absolute; width: 50px; height: 50px; top: 0; left: 25px; } .heart::before { content: ""; background-color: pink; border-radius: 50%; position: absolute; width: 50px; height: 50px; top: -25px; left: 0; } style> <div class="heart">div>Animation
给元素添加动画:animation 属性控制动画的外观,
@keyframes规则控制动画中各阶段的变化。
@keyframes通过给持续时间内的特定帧(从 0% 到 100%)加上 CSS 规则设置动画效果。
8个属性值 说明 animation-name 用来设置动画的名称,也就是在 @keyframes里用到的名称。animation-duration 动画指定需要多少秒或毫秒完成 animation-timing-function 设置动画将如何完成一个周期 animation-delay 设置动画在启动前的延迟间隔 animation-iteration-count 定义动画的播放次数 animation-direction 指定是否应该轮流反向播放动画 animation-fill-mode 规定当动画不播放时(当动画完成时,或当动画有一个延迟未开始播放时),要应用到元素的样式 animation-play-state 指定动画是否正在运行或已暂停 <style> div { height: 40px; width: 70%; background: black; margin: 50px auto; border-radius: 5px; position: relative; } #rect { animation-name: rainbow; animation-duration: 4s; } @keyframes rainbow { 0% { background-color: blue; top: 0; left: 0; } 50% { background-color: green; top: 50px; left: 25px; } 100% { background-color: yellow; top: 0; left: -25px; } } style> <div id="rect">div>fill-mode
值 描述 none 不改变默认行为。 forwards 当动画完成后,保持最后一个属性值(在最后一个关键帧中定义)。 backwards 在 animation-delay 所指定的一段时间内,在动画显示之前,应用开始属性值(在第一个关键帧中定义)。 both 向前和向后填充模式都被应用。 <style> button { border-radius: 5px; color: white; background-color: #0F5897; padding: 5px 10px 8px 10px; } button:hover { animation-name: background-color; animation-duration: 500ms; } @keyframes background-color { 100% { background-color: #4791d0; } } style> <button>Registerbutton>iteration-count
nimation-iteration-count 描述 n 定义动画播放次数的数值。 infinite 规定动画应该无限次播放。 <style> .back { position: fixed; padding: 0; margin: 0; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; background: white; animation-name: backdiv; animation-duration: 1s; animation-iteration-count: infinite; } .heart { position: absolute; margin: auto; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; background-color: pink; height: 50px; width: 50px; transform: rotate(-45deg); animation-name: beat; animation-duration: 1s; animation-iteration-count: infinite } .heart:after { background-color: pink; content: ""; border-radius: 50%; position: absolute; width: 50px; height: 50px; top: 0; left: 25px; } .heart:before { background-color: pink; content: ""; border-radius: 50%; position: absolute; width: 50px; height: 50px; top: -25px; left: 0; } @keyframes backdiv { 50% { background: #ffe6f2; } } @keyframes beat { 0% { transform: scale(1) rotate(-45deg); } 50% { transform: scale(0.6) rotate(-45deg); } } style> <div class="back">div> <div class="heart">div>timing-function
✿ cubic-bezier.com
使用名为三次贝塞尔(Cubic Bezier)函数的数学函数,来生成速度曲线。
值 描述 linear 动画从头到尾的速度是相同的。 ease 默认。动画以低速开始,然后加快,在结束前变慢。 ease-in 动画以低速开始,以高速结束。 ease-out 动画以高速开始,以低速结束。 ease-in-out 动画以低速开始和结束。 cubic-bezier(n,n,n,n) 在 cubic-bezier 函数中自己的值。可能的值是从 0 到 1 的数值。
cubic-bezier函数包含了 1 * 1 网格里的4个点:p0、p1、p2、p3。其中
p0和p3是固定值,代表曲线的起始点和结束点,坐标值依次为 (0, 0) 和 (1, 1)。你只需设置另外两点的 x 值和 y 值,设置的这两点确定了曲线的形状从而确定了动画的速度曲线。
在 CSS 里面通过
(x1, y1, x2, y2)来确定p1和p2。通俗的讲,将一条直线放在范围只有 1 的坐标轴中,并从中间拿
p1和p2两个点来拉扯(X 轴的取值区间是 [0, 1],Y 轴任意)<style> .balls { border-radius: 50%; position: fixed; width: 50px; height: 50px; top: 60%; animation-name: jump; animation-duration: 2s; animation-iteration-count: infinite; } #red { background: red; left: 25%; /*animation-timing-function: linear;*/ animation-timing-function: cubic-bezier(0.25, 0.25, 0.75, 0.75); } #blue { background: blue; left: 50%; animation-timing-function: ease-out; } #green { background: green; left: 75%; animation-timing-function: cubic-bezier(0.311, 0.441, 0.444, 1.649); } @keyframes jump { 50% { top: 10%; } } style> <div class="balls" id="red">div> <div class="balls" id="blue">div> <div class="balls" id="green">div>Applied Accessibility
img alt
alt属性可以帮助用户在图片加载失败或者不可见的情况下理解图片内容, 搜索引擎也通过它来理解图片内容,并将其加入到搜索结果中。屏幕阅读器可以识别
alt属性,朗读其中的内容,来告知视觉障碍用户图片包含的关键信息。在图片已经有了文字说明,或者仅仅为了美化页面,
img仍然需要一个alt属性,但可以设置为空字符串。对于有标题的图片,依然需要添加
alt文本,这样有助于搜索引擎记录图片内容。<img src="importantLogo.jpeg" alt="Company logo">Elements
HTML5 引入了诸如
main、header、footer、nav、article、section等大量新标签,给予开发者更多的选择,也包含辅助功能。默认情况下,浏览器呈现这些元素的方式类似于普通的
div。 但是,在适当的地方使用它们会让标记文本具有更多的含义。h1 ~ h6
每个页面应只有一个
h1标签,用来概括说明页面的主题。六个标题标签可以让搜索引擎获取页面的大纲。
main
main标签用于呈现网页的主体内容,且每个页面应只有一个。它有一个内嵌的特性,以便辅助技术快速定位到页面的主体。
如果在页面顶部看到过“跳转到主要内容”链接,那么使用
main标签会自动让辅助设备具有这个跳转的功能。article
article是一个分段标签,用于呈现独立及完整的内容。 这个标签适用于博客、论坛帖子或者新闻文章。删除了所有周围的上下文,这个内容仍然有意义,确定内容可以单独作为一部分。
article用于独立且完整的内容,而section用于对与主题相关的内容进行分组,可以根据需要来嵌套使用。举个例子:如果一本书是一个
article的话,那么每个章节就是section。当内容组之间没有联系时,我们可以使用
div。header
header可以为父级标签呈现简介信息或者导航链接,适用于那些在多个页面顶部重复出现的内容。
header应当在 HTML 文档的body标签内使用,与包含页面标题、元信息的head标签不同。nav
nav也是一个具有语义化特性的 HTML5 标签。它可以使屏幕阅读器快速识别出页面中的导航信息。 它用于呈现页面中的主导航链接。
footer
footer元素也具有语义化的特性,可以让辅助工具快速定位到它。它位于页面底部,用于呈现版权信息或者相关文档链接。
audio
audio标签用于呈现音频内容或音频流,它也具有语义化特性。 音频内容也需要备用文本,供聋哑人或听力困难的人使用。
audio标签支持controls属性, 用于显示浏览器默认播放、停止和其他控制,以及支持键盘功能。注意: 音频片段的播放速度可能会快到难以理解,但是对于屏幕阅读器用户来说这是正常速度。
<audio controls> <source src="https://s3.amazonaws.com/freecodecamp/screen-reader.mp3" type="audio/mpeg"> audio>figure figcaption
figure标签以及figcaption标签一起用于展示可视化信息(如:图片、图表)及其标题。<figure> <img src="roundhouseDestruction.jpeg" alt="Photo of Camper Cat executing a roundhouse kick"> <br> <figcaption> Master Camper Cat demonstrates proper form of a roundhouse kick. figcaption> figure>label for
label标签的文本内容通常会是表单组件的名称或标签。这些文本表明了组件的意义,也提升了表单的可访问性。
label标签的for属性将标签与表单组件绑定,屏幕阅读器也会读取for属性的属性值。为了让标签可以在点击的时候也选中输入框,可以将单选按钮 input 标签嵌套在了
label标签里面。 或者使用for属性,使其与表单组件的id属性值相同。<label for="email">Email:label> <input type="text" id="email" name="email"> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">fieldset legend
fieldset标签包裹整组单选按钮,使用legend标签来提供分组的描述,以便屏幕阅读器用户会阅读fieldset元素中的每个选项。而当选项的含义很明确时,如“性别选择”,使用包含
for属性的label标签就足够了。<form> <fieldset> <legend>Choose one of these three items:legend> <input id="one" name="items" type="radio" value="one"> <label for="one">Choice Onelabel> <br> <input id="two" name="items" type="radio" value="two"> <label for="two">Choice Twolabel> <br> <input id="three" name="items" type="radio" value="three"> <label for="three">Choice Threelabel> fieldset> form>input date
<label for="pickdate">Enter a date: label> <input type="date" id="pickdate" name="date">time datetime
<p> Thank you to everyone for responding to Master Camper Cat's survey. The best day to host the vaunted Mortal Kombattournament is <time datetime="2016-09-15">Thursday, September 15<sup>thsup>time> . May the best ninja win! p>ScreenReader-only
添加一些只对屏幕阅读器可见的内容,可以用 CSS 来实现。
注意:
display: none;或visibility: hidden;会把内容彻底隐藏起来,屏幕阅读器也无法获取这些内容。- 如果把值设置为 0px,如
width: 0px; height: 0px;,意味着让元素脱离文档流,这样做同样也会让屏幕阅读器忽略此元素。.sr-only { position: absolute; left: -10000px; width: 1px; height: 1px; top: auto; overflow: hidden; }High Contrast Text
Web 内容无障碍指南(WCAG)建议正常文本的对比度至少为 4.5 : 1。
对比度是通过比较两种颜色的相对亮度值来计算的。
对比度的范围是从相同颜色的 1:1(无对比度)到白色与黑色的最高对比度 21:1。
可以通过将较暗的颜色变暗、将较淡的颜色变淡的方法来使对比度达到 4.5:1。
在色轮中,较暗的颜色通常是蓝色、紫色、洋红和红色,而较淡的颜色通常是橙色、黄色、绿色和蓝绿色。
accesskey
HTML 提供
accesskey属性,用于指定激活元素或者使元素获得焦点的快捷键。添加
accesskey属性可以让使用键盘的用户更高效率地导航。HTML5 允许在任何标签上使用这个属性。 该属性尤其适用于链接、按钮、表单组件等元素。
tabindex
当用户使用键盘浏览页面时,诸如链接、表单控件等元素可以自动获得焦点,获得焦点的顺序与它们出现在 HTML 文档流中的顺序一致。当然可以通过将其他标签(如
div、span、p等)的tabindex属性值设为 0 来让它们实现类似的效果。注意:
tabindex属性值为负整数(通常为 -1)的标签也是可以获得焦点的,只是不可以通过键盘操作(如 tab 键)来获得焦点。使用tabindex属性还可以让 CSS 伪类:focus在p标签上生效。<div tabindex="0">I need keyboard focus!div>给元素设置
tabindex="1",键盘将首先把焦点放在这个元素上。然后它按照指定的
tabindex值(2、3 等等)顺序循环,再移动到默认值和tabindex="0"项目。<input type="search" name="search" id="search" tabindex="1"> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" id="submit" tabindex="2">Responsive Web Design Principles
@media
可以根据不同的视口大小调整内容的布局。
视口是指浏览器中,用户可见的网页内容。 视口会随访问网站的设备不同而改变。
p { font-size: 20px; } @media (max-height: 800px) { p { font-size: 10px; } }Responsive Image
使图片自适应设备尺寸:
- 设置
max-width值为100%可确保图片不超出父容器的范围。- 设置
height属性为auto可以保持图片的原始宽高比。<style> .responsive-img { max-width: 100%; height: auto; } img { width: 600px; } style> <img class="responsive-img" src="https://s3.amazonaws.com/freecodecamp/FCCStickerPack.jpg" alt="freeCodeCamp stickers set"> <img src="https://s3.amazonaws.com/freecodecamp/FCCStickerPack.jpg" alt="freeCodeCamp stickers set">Retina Image
针对高分辨率屏幕应使用视网膜图片:由于“视网膜显示屏”和“非视网膜显示屏”显示器之间像素密度的不同,某些未考虑高分辨率显示器的图像在高分辨率显示器上渲染时,可能因出现“像素化”而不够清晰。
让图像正确出现在高分辨率显示器上的最简单方式, 是定义它们的
width和height值为原始值的一半。<style> img { /* 原尺寸宽高为200px */ height: 100px; width: 100px; } style> <img src="https://s3.amazonaws.com/freecodecamp/FCCStickers-CamperBot200x200.jpg" alt="freeCodeCamp sticker that says 'Because CamperBot Cares'">vw vh vmin vmax
视窗单位是相对于设备的视窗尺寸(宽度或高度),百分比是相对于父级元素的大小。
个不同的视窗单位分别是:
vw:如10vw的意思是视窗宽度的 10%。vh:如3vh的意思是视窗高度的 3%。vmin:如70vmin的意思是视窗的高度和宽度中较小一个的 70%。vmax:如100vmax的意思是视窗的高度和宽度中较大一个的 100%。<style> h2 { width: 80vw; background-color: pink; } p { width: 75vmin; background-color: pink; } style> <h2>Importantus Ipsumh2> <p> Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus quis tempus massa. Aenean erat nisl, gravida vel vestibulum cursus, interdum sit amet lectus. Sed sit amet quam nibh. Suspendisse quis tincidunt nulla. In hac habitasse platea dictumst. Ut sit amet pretium nisl. Vivamus vel mi sem. Aenean sit amet consectetur sem. Suspendisse pretium, purus et gravida consequat, nunc ligula ultricies diam, at aliquet velit libero a dui. p>CSS Flexbox
Play Flex Box Adventure – CSS Game to Learn Flexbox (codingfantasy.com)
Knights of the Flexbox table
Flexbox Froggy - A game for learning CSS flexbox
Flexbox Defense
Flexbox Zombies (mastery.games)
给元素添加
display: flex属性可以让它变成 flex 容器, 然后可以让元素的项目排列成行或列。flex-direction
属性值设置为 row 或 column,即可横向排列或纵向排列它的所有子元素。
值 描述 row 默认值。flex 项目将水平显示,正如一个行一样。 row-reverse 与 row 相同,但是以相反的顺序。 column 灵活的项目将垂直显示,正如一个列一样。 column-reverse 与 column 相同,但是以相反的顺序。 justify-content
flex 子元素有时不能充满整个 flex 容器, 可以通过
justify-content属性的不同值来实现告诉 CSS 以什么方式排列 flex 子元素。子元素排列的方向被称为 main axis(主轴)。 对于行,主轴水平贯穿每一个项目; 对于列,主轴垂直贯穿每一个项目。
值 描述 Playit (runoob.com) flex-start 默认值。从 flex 容器的起始位置开始排列项目。 对行来说是把项目移至左边, 对于列是把项目移至顶部。 flex-end 从 flex 容器的终止位置开始排列项目。 对行来说是把项目移至右边, 对于列是把项目移至底部。 center flex 子元素在 flex 容器中居中排列。 space-between 项目间保留一定间距地沿主轴居中排列。 第一个和最后一个项目被放置在容器边沿。 例如,在行中第一个项目会紧贴着容器左边,最后一个项目会紧贴着容器右边,然后其他项目均匀排布。 space-around 与 space-between相似,但头尾两个项目不会紧贴容器边缘,所有项目之间的空间均匀排布。space-evenly 头尾两个项目不会紧贴容器边缘,所有项目之间的空间均匀排布。 align-items
Flex 容器中,与主轴垂直的叫做 cross axis(交叉轴)。 行的交叉轴是垂直的,列的交叉轴是水平的。
align-items属性用来定义 flex 子元素沿交叉轴的对齐方式。对行来说,定义的是元素的上下对齐方式; 对列来说,是定义元素的左右对齐方式。
Attributes Description Playit (runoob.com) stretch 默认值。拉伸项目,填满 flex 容器。 例如,排成行的项目从容器顶部拉伸到底部。 center 把项目居中放置。 对行来说,垂直居中(项目距离顶部和底部的距离相等); 对列来说,水平居中(项目距离左边和右边的距离相等)。 flex-start 从 flex 容器的起始位置开始对齐项目。 对行来说,把项目移至容器顶部; 对列来说,是把项目移至容器左边。 flex-end 从 flex 容器的终止位置开始对齐项目。 对行来说,把项目移至容器底部; 对列来说,把项目移至容器右边。 baseline 沿基线对齐。 基线是文本相关的概念,可以认为它是字母排列的下端基准线。 flex-wrap
以我的理解就是截断,如同 JetBrains 的软件设置里通常会有的 Hard-wrap ,用来设置每行最多有多少字符,会在你格式化代码 Ctrl+Alt+L 的时候强制插入换行符,形成显示效果上的换行。
默认情况下,flex 容器会调整项目大小,把它们都塞到一起。 对于行来说,所有项目都会在一条直线上。
使用
flex-wrap属性可以使项目换行展示。 这意味着多出来的子元素会被移到新的行或列。 换行发生的断点由子元素和容器的大小决定。
值 描述 nowrap 默认值,不换行。 wrap 如果排列以行为基准,就将行从上往下排列;
如果排列以列为基准,就将列从左往右排列。wrap-reverse 如果排列以行为基准,就将行从下往上排列;
如果排列以列为基准,就将列从右往左排列。Child Elements
以上提到的属性都应用于 flex 容器(flex 子元素的父元素),下面讲一些子元素的实用属性。
flex-shrink
使用之后,如果 flex 容器太小,则子元素会自动缩小。
当容器的宽度小于里面所有子元素的宽度之和时,所有子元素都会自动压缩。
子元素的
flex-shrink接受数值作为属性值。 数值越大,则该元素与其他元素相比会被压缩得更厉害。比如,一个项目的
flex-shrink属性值为 1,另一个项目的flex-shrink属性值为 3 ,那么后者相比前者会受到 3 倍压缩。flex-grow
flex-shrink会在容器太小时对子元素作出调整。相应地,
flex-grow会在容器太大时对子元素作出调整。如果一个项目的
flex-grow属性值为 1,另一个项目的flex-grow属性值为 3,那么值为 3 的一个会较另一个扩大 3 倍。flex-basis
flex-basis属性定义了在使用 CSS 的flex-shrink或flex-grow属性对元素进行调整前,元素的初始大小。
flex-basis属性的单位与其他表示尺寸的属性的单位一致(px、em、%等)。 如果值为auto,则项目的尺寸随内容调整。可以三种属性值一起设置:例如,
flex: 1 0 10px;会把项目属性设为
flex-grow: 1;、flex-shrink: 0;以及flex-basis: 10px;。默认设置是
flex: 0 1 auto;。order
默认情况下,项目排列顺序与源 HTML 文件中顺序相同。
order属性表明 CSS flex 容器里子元素的顺序。接受数字作为参数,可以使用负数。align-self
align-self允许你调整单个子元素自己的对齐方式,而不会影响到全部子元素。可设置的值与
align-items的一样,并且它会覆盖align-items所设置的值。因为
float、clear和vertical-align等调整对齐方式的属性都不能应用于 flex 子元素,所以这个属性显得十分有用。CSS Grid
Grid Garden - A game for learning CSS grid (cssgridgarden.com)
Play Grid Attack – CSS Game to learn CSS Grid (codingfantasy.com)
CSS Grid Cheat Sheet (alialaa.github.io)
通过将属性
display的值设为grid,HTML 元素就可以变为网格容器。在 CSS 网格中,父元素称为容器(container),它的子元素称为项(items)。
grid-template
rows columns
.container { display: grid; /* 在网格容器中添加两列,宽度均为50px */ grid-template-columns: 50px 50px; /* 在网格容器中添加两行,宽度均为50px */ grid-template-rows: 50px 50px; }fr
在 CSS 网格中,可以使用绝对单位(如
px)或相对单位(如em)来定义行或列的大小。下面的单位也可以使用:
fr:设置列或行占剩余空间的比例。auto:设置列宽或行高自动等于它的内容的宽度或高度。%:将列或行调整为它的容器宽度或高度的百分比。.container { font-size: 40px; width: 100%; background: LightGray; display: grid; /* 第一列的宽与它的内容宽度相等; 第二列宽 50px;第三列宽是它容器的 10%; 最后两列,将剩余的宽度平均分成三份,第四列占两份,第五列占一份。 */ grid-template-columns: auto 50px 10% 2fr 1fr; }grid-gap
.container { display: grid; width: 100%; /* 所有列之间都添加 10px 的空白间距 */ grid-column-gap: 10px; /* 所有行添加高度为 5px 的间距 */ grid-row-gap: 5px; /* 第一个值表示行间距,第二个值表示列间距 */ grid-gap: 10px 20px; /* 只有一个值表示均为这个值 */ grid-gap: 10px; }grid-column grid-row
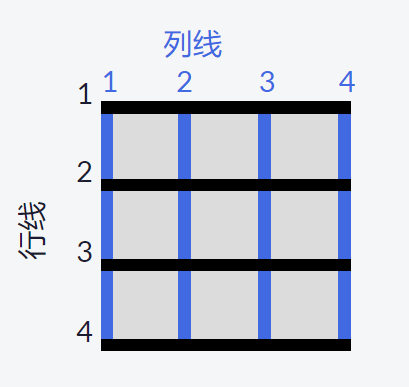
以上所有的讨论都是围绕网格容器的。
grid-column和grid-row属性是用于网格项本身的属性。网格中,假想的水平线和垂直线被称为线(lines),这些线在网格的左上角从 1 开始编号,垂直线向右、水平线向下累加计数。
.item5 { background: PaleGreen; /* 占据网格的后两列,即列线2~4的部分 */ grid-column: 2 / 4; /* 占用最后两行 */ grid-row: 2 / 4; }Cell Attr
在 CSS 网格中,每个网格项的内容分别位于被称为单元格(cell)的框内。
以下四种元素属性值可被 共用:
值 描述 stretch 默认值,内容将占满整个单元格的宽度 center 使内容在单元格居中对齐 start 使内容在单元格左侧对齐 end 使内容在单元格右侧对齐 justify-self
CSS / justify-self — DevDocs
使用网格项的
justify-self属性,设置其内容的位置在单元格内沿水平轴的对齐方式。align-self
CSS / align-self — DevDocs
对网格项使用
align-self属性来设置网格项沿竖直方向的对齐方式。justify-items
CSS / justify-items — DevDocs
对网格容器使用
justify-items可以让网格中所有的网格项沿水平方向对齐。将网格中 所有 的网格项按所设置的方式对齐。
align-items
CSS / align-items — DevDocs
可以让网格中所有的网格项沿竖直方向对齐。
Areas
grid-template-areas
可以将网格中的一些单元格组合成一个区域(area),并为该区域指定一个自定义名称。
通过给容器加上
grid-template-areas来实现:.container { font-size: 40px; min-height: 300px; width: 100%; background: LightGray; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-gap: 10px; /* 每个单词代表一个单元格,每对引号代表一行 */ grid-template-areas: "header header header" "advert content content" "footer footer footer"; }grid-area
对网格项使用
grid-area,通过引用你所定义的区域的名称,将元素放入相应的区域。.item5 { background: PaleGreen; grid-area: footer; }
grid-area: n/n/n/n: 分别代表水平网格线的起始和垂直网格线的起始。.item5 { background: PaleGreen; /* 放置在第 3 条和第 4 条水平网格线 以及第 1 条和第 4 条垂直网格线之间的区域内 */ grid-area: 3/1/4/4; }repeat minmax
使用
grid-template-columns或grid-template-rows定义网格结构时,你需要为添加的每一行或每一列都输入一个值。
repeat方法指定行或列的重复次数,后面加上逗号以及需要重复的值。
minmax作用是在网格容器改变大小时限制网格项的大小,需要指定网格项允许的尺寸范围。repeat 方法带有
auto-fill功能:是根据容器的大小,尽可能多地放入指定大小的行或列。 你可以通过结合 auto-fill 和 minmax 来更灵活地布局。
auto-fit效果几乎和auto-fill一样。 不同点仅在于,当容器的大小大于各网格项之和时,auto-fill会持续地在一端放入空行或空列,这样就会使所有网格项挤到另一边;而auto-fit则不会在一端放入空行或空列,而是会将所有网格项拉伸至合适的大小。如果容器宽度不足以将所有网格项放在同一行,余下的网格项将会移至新的一行。
.container { font-size: 40px; min-height: 300px; width: 100%; background: LightGray; display: grid; /* grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; */ grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fill, minmax(90px, 1fr)); /* grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr; */ grid-template-rows: repeat(3, 1fr); grid-gap: 10px; }@media
@media (min-width: 300px){ .container{ grid-template-columns: auto 1fr; grid-template-rows: auto 1fr auto; grid-template-areas: "advert header" "advert content" "advert footer"; } } @media (min-width: 400px){ .container{ grid-template-areas: "header header" "advert content" "footer footer"; } }Grid within grid
将元素转换为网格只会影响其子元素(即直接后代元素 direct descendants),因此把某个子元素设置为网格,就会得到一个嵌套的网格。
<style> .container { font-size: 1.5em; min-height: 300px; width: 100%; background: LightGray; display: grid; grid-template-columns: auto 1fr; grid-template-rows: auto 1fr auto; grid-gap: 10px; grid-template-areas: "advert header" "advert content" "advert footer"; } .item1 { background: LightSkyBlue; grid-area: header; } .item2 { background: LightSalmon; grid-area: advert; } .item3 { background: PaleTurquoise; grid-area: content; display: grid; grid-template-columns: auto 1fr; } .item4 { background: lightpink; grid-area: footer; } .itemOne { background: PaleGreen; } .itemTwo { background: BlanchedAlmond; } style> <div class="container"> <div class="item1">headerdiv> <div class="item2">advertdiv> <div class="item3"> <div class="itemOne">paragraph1div> <div class="itemTwo">paragraph2div> div> <div class="item4">footerdiv> div>