【PyTorch基础教程15】循环神经网络RNN(学不会来打我啊)
学习总结
(1)RNN的激活函数一般用tanh(范围在-1到1之间),之前多分类问题的最后一层用的torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(注意已经包括softmax了),而前面的层使用relu。GoogleNet和ResNet我们也是用了relu作为激活函数。
(2)RNN实现我们分别用了三种方法:利用RNN Cell后面重写循环调用等过程;直接调用RNN网络;加上embedding部分的RNN网络(更快收敛)。要注意计算好输入输出的维度和参数准确。
(3)不止RNN能实现seq2seq任务(如NLP、天气数据、股市金融数据等序列数据等),还有LSTM、GRU、还有之前学的transformer等都是可以实现的。
PS:用pytorch的Embedding层的输入必须是要LongTensor类型
文章目录
- 学习总结
- 一、简单回顾
- 二、RNN算法
-
- 2.1 RNN Cell
- 2.2 文本转为向量
- 2.3 注意维度
- 2.4 输出是预测值
- 三、nn.RNN小栗子
-
- 3.1 如何使用RNNCell
- 3.2 如何使用RNN
- 四、RNNCell训练
- 五、用RNN模块训练
- 六、优化:Embedding
-
- 6.1 通过embedding降维
- 6.2 embedding改进的代码
- 七、LSTM网络
- 八、介于RNN和LSTM:GRU
- Reference
一、简单回顾
全连接被称为Dense或者Deep层。输入数据样本的不同特征。
CNN用了权重共享的概念,而全连接层的参数量是巨大的。所以使用RNN解决如下图(天气预报预测)这种带有序列模式的数据(如NLP、天气、股市金融数据等),并且使用权重共享的概念来减少参数量。
下图栗子简述:已知前三天的天气,并且每个样本有3个特征(天数、 温度、气压),label是是否下雨。

如果需要用图像生成文本,可以用CNN+FC层后的结果输入RNN。如果没有先验前置信息h0,就设置和h1一样的全0向量即可(维度要匹配)。
二、RNN算法
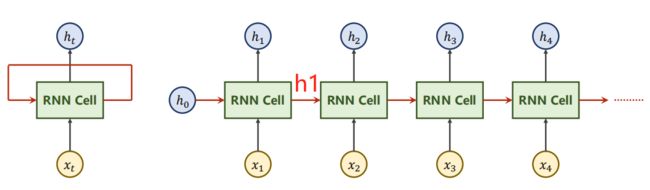
2.1 RNN Cell
RNN Cell本质上为一个线性层(共享权重的线性层,如上图),在t时刻的N维向量,经过RNN Cell后变为一个M维的向量 h t h_t ht。
W i h \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{ih}} Wih:和输入向量 x t x_t xt相乘的权重矩阵,维度大小为 h i d d e n _ s i z e × i n p u t _ s i z e hidden\_size \times input\_size hidden_size×input_size。
W h h \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{hh}} Whh:和隐层向量 h t − 1 h_{t-1} ht−1相乘的权重矩阵,维度大小为 h i d d e n _ s i z e × h i d d e n _ s i z e hidden\_size \times hidden\_size hidden_size×hidden_size。

几点注意:
(1)通过RNN Cell的维度和上一个hidden_size的维度相同。
(2)也可以将两个线性层的运算合并:

严谨写的矩阵运算形式是: W h h h t − 1 + W i h x t = [ W h h W i h ] [ h x ] \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{hh}} \mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{t}-1}+\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{ih}} \mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{t}}=\left[\begin{array}{ll} \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{hh}} & \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{ih}} \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} \mathrm{h} \\ \mathrm{x} \end{array}\right] Whhht−1+Wihxt=[WhhWih][hx]
(3)维度的要求:
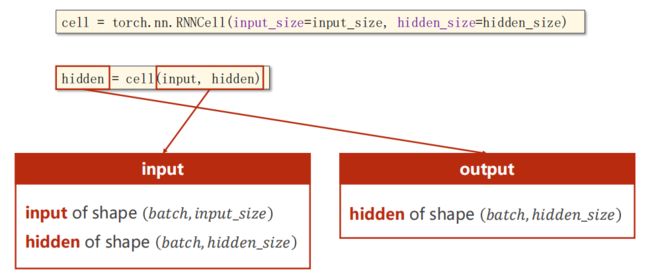
seqLen = 3指序列长度为3,每个样本里有x1,x2,x3。
(4)一个batch中,各个元素之间是并行计算;输入数据是按批次来的,每一批3个。

(5)注意输入的hidden有参数numLayers(如上图,每种颜色是一个线性层),指RNN的层数。可以发现输入和输出的2个参数之间,不同的只有input_size变为hidden_size。

2.2 文本转为向量
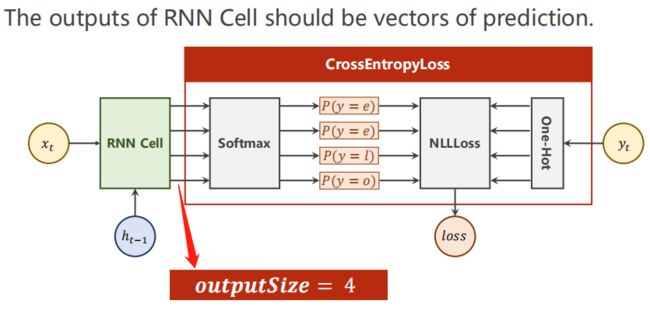
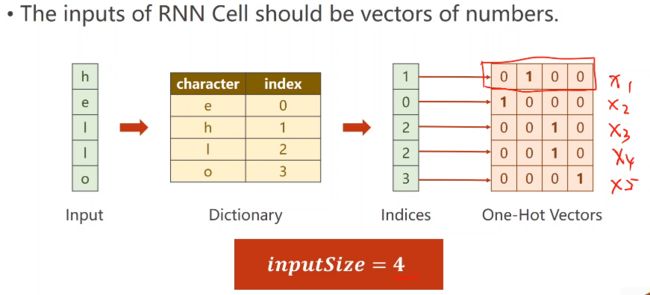
(1)将单词转成one-hot编码,注意下面的input_size为4。
2.3 注意维度
注意训练部分的内层for循环的input和inputs的维度:

另外label和labels的维度:

# 训练模型
for epoch in range(15):
loss = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 初始化h0
hidden = net.init_hidden()
print('Predicted string:', end = '')
# input是(seq × batch × inputsize) 依次拿x1,x2..x5
for input, label in zip(inputs, labels):
# zip函数是沿着第一个维度拼接
hidden = net(input, hidden)
# 没用item,因为整个序列的loss之和才是损失(要构建计算图)
loss += criterion(input, hidden)
_, idx = hidden.max(dim = 1)
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end = '')
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.4f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
2.4 输出是预测值
三、nn.RNN小栗子
3.1 如何使用RNNCell
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Oct 23 09:07:58 2021
@author: 86493
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3 # x1, x2, x3
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 2
cell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size = input_size,
hidden_size = hidden_size)
# (seq, batch, features)
dataset = torch.randn(seq_len,
batch_size,
input_size)
hidden = torch.zeros(batch_size,
hidden_size)
# 分别读x1, x2, x3
for idx, input in enumerate(dataset):
print('=' * 20, idx, '=' * 20)
# Input size: torch.Size([1, 4])
print('Input size:', input.shape)
hidden = cell(input, hidden)
# outputs size: torch.Size([1, 2])
print('outputs size:', hidden.shape)
print(hidden)
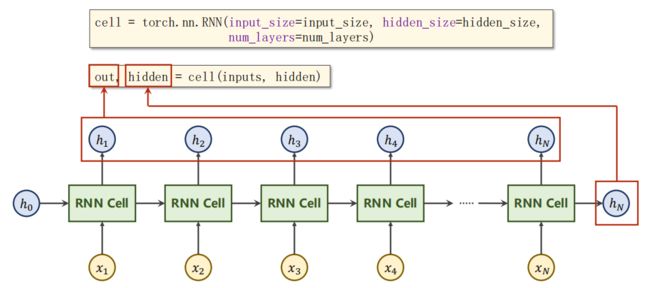
3.2 如何使用RNN
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Oct 23 09:07:58 2021
@author: 86493
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
batch_size = 1
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 2
num_layers = 1
cell = torch.nn.RNN(input_size = input_size,
hidden_size = hidden_size,
num_layers = num_layers)
# (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize)
inputs = torch.randn(seq_len,
batch_size,
input_size)
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers,
batch_size,
hidden_size)
out, hidden = cell(inputs, hidden)
print('Output size:', out.shape)
print('Output:', out)
print('Hidden size:', hidden.shape)
print('Hidden:', hidden)
结果为:
Output size: torch.Size([3, 1, 2])
Output: tensor([[[-0.2704, -0.7284]],
[[-0.4312, 0.0836]],
[[ 0.6894, -0.9946]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward>)
Hidden size: torch.Size([1, 1, 2])
Hidden: tensor([[[ 0.6894, -0.9946]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward>)
四、RNNCell训练
在(四)中我们是先实现RNN Cell,再手动写循环调用训练等逻辑;在(五)中我们可以直接调用RNN网络(代码会少很多)。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Oct 23 09:17:10 2021
@author: 86493
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
losslst = []
# 准备数据
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2]
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1,
batch_size,
input_size)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1)
# 模型设计
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnncell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size = self.input_size,
hidden_size = self.hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
hidden = self.rnncell(input, hidden)
return hidden
# 生成默认的初始隐层h0,batch_size也仅为了构造h0
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size,
hidden_size,
batch_size)
# loss函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),
lr = 0.1)
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(15):
loss = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 初始化h0
hidden = net.init_hidden()
print('Predicted string:', end = '')
# input是(seq × batch × inputsize) 依次拿x1,x2..x5
for input, label in zip(inputs, labels):
# zip函数是沿着第一个维度拼接
hidden = net(input, hidden)
# 没用item,因为整个序列的loss之和才是损失(要构建计算图)
loss += criterion(hidden, label)
# hidden是四维的(e h l o),找出概率值最大的数的下标
_, idx = hidden.max(dim = 1)
# 每一轮训练能输出的预测字符串
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end = '')
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losslst.append(loss.item())
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.4f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
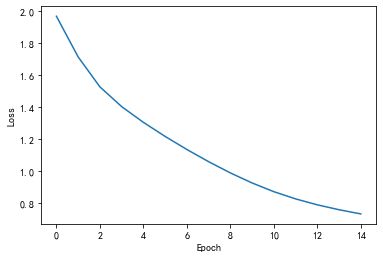
plt.plot(range(15), losslst)
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.show()

同时从预测的字符串结果看,当趋于收敛时,字符串是ohlol:
Predicted string:hhhhh, Epoch [1/15] loss = 6.2508
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [2/15] loss = 4.9792
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [3/15] loss = 4.2028
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [4/15] loss = 3.7331
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [5/15] loss = 3.3555
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss = 3.0020
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss = 2.6944
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 2.4562
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 2.2846
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 2.1613
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 2.0679
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 1.9959
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 1.9450
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 1.9128
Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 1.8900
五、用RNN模块训练
用RNN模块训练就简化很多:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Oct 23 09:17:10 2021
@author: 86493
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
num_layers = 1
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
# 准备数据
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2]
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len,
batch_size,
input_size)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# 模型设计
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size = self.input_size,
hidden_size = self.hidden_size,
num_layers = num_layers)
def forward(self, input):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers,
self.batch_size,
self.hidden_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(input, hidden)
# 输出要变成两维的,用交叉熵的时候变成一个矩阵
return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size,
hidden_size,
batch_size)
# loss函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),
lr = 0.05)
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 向前传播
outputs = net(inputs)
# labels的shape是 seq×B×1
# outputs的shape是 seq×B×H
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim = 1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted:', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end = '')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
Predicted: lhhhh, Epoch [1/15] loss = 1.481
Predicted: lhlhh, Epoch [2/15] loss = 1.360
Predicted: lhlll, Epoch [3/15] loss = 1.244
Predicted: lhlll, Epoch [4/15] loss = 1.132
Predicted: lhlll, Epoch [5/15] loss = 1.026
Predicted: ohlll, Epoch [6/15] loss = 0.931
Predicted: ohlll, Epoch [7/15] loss = 0.852
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 0.791
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 0.744
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 0.706
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 0.675
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 0.649
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 0.626
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 0.605
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 0.588
六、优化:Embedding
6.1 通过embedding降维

独热编码向量:维度会太高、向量系数、硬编码。
通过embedding将向量编码为低维、稠密的向量(从data中学习)。
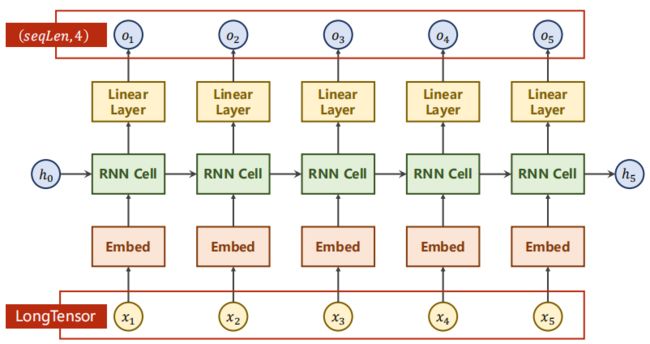
nn.Embedding的shape:

6.2 embedding改进的代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Oct 23 19:12:40 2021
@author: 86493
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
num_class = 4
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 8
embedding_size = 10
num_layers = 2
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
# 准备数据
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
# (batch, seq_len)
x_data = [[1, 0, 2, 2, 3]]
# (batch * seq_len)
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2]
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
inputs = torch.LongTensor(x_data)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# 模型设计
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.emb = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size = embedding_size,
hidden_size = hidden_size,
num_layers = num_layers,
batch_first = True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_class)
def forward(self, x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, x.size(0), hidden_size)
# (batch, seqLen, embeddingSize)
x = self.emb(x)
x, _ = self.rnn(x, hidden)
x = self.fc(x)
return x.view(-1, num_class)
net = Model(input_size,
hidden_size,
batch_size)
# loss函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),
lr = 0.05)
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
# labels的shape是 seq×B×1
# outputs的shape是 seq×B×H
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim = 1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted:', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end = '')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
这次可以看到第6个epoch就收敛到ohlol了,上次是第8个epoch才收敛到这个单词。
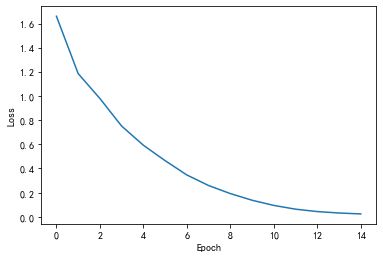
Predicted: oeeol, Epoch [1/15] loss = 1.371
Predicted: ollll, Epoch [2/15] loss = 1.122
Predicted: ollll, Epoch [3/15] loss = 0.980
Predicted: ollll, Epoch [4/15] loss = 0.849
Predicted: ohlll, Epoch [5/15] loss = 0.703
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss = 0.543
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss = 0.386
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 0.269
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 0.180
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 0.113
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 0.075
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 0.051
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 0.036
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 0.026
Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 0.019
七、LSTM网络

初学LSTM可以先不理很多教程说的××门(可解释性问题)。
可以参考nn.LSTM官方文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#lstm
八、介于RNN和LSTM:GRU
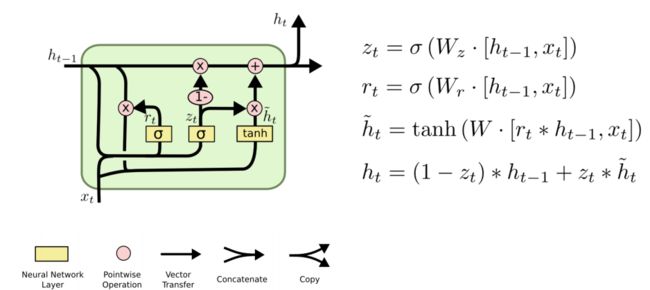
可以参考nn.LSTM官方文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#gru
Reference
(1)https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?p=12
(2)pytorch官方文档embedding类