1.摘要
本次是第六篇,讲解V8中抽象语法树(abstract syntax code,AST)到字节码(bytecode)的翻译过程。AST是源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表示,是语法分析的输出结果,bytecode是一种体系结构无关的、在V8中可以运行的抽象机器码,不依赖指令集。本文中,我们以AST作为V8输入,从AST生成后开始调试(Debug),讲解bytecode生成过程,分析核心源码和重要数据结构,如图1所示。本文内容的组织方式:介绍字节码,讲解字节码原理,如何看懂字节码(章节2);AST到bytecode的翻译过程、源码分析(章节3)。 
2.字节码介绍
字节码是机器码的抽象表示,采用和物理CPU相同的计算模型进行设计。字节码是最小功能完备集,JavaScript源码的任何功能都可以等价转换成字节码的组合。V8有数以百计的字节码,例如Add和Sub等简单操作,还有LdaNamedProperty等属性加载操作。每个字节码都可以指定寄存器作为其操作数,生成字节码的过程中使用寄存器 r0,r1,r2,... 和累加寄存器(accumulator register)。累加器是和其它寄存器一样的常规寄存器,但不同的是累加器的操作没有显式给出指令,具体来说,Add r1将寄存器r1中的值和累加器中的值进行加法运算,在这个过程不需要显示指出累加器。字节码的定义在v8/src/interpreter/bytecodes.h中,下面展示一部分相关源码。
#define BYTECODE_LIST_WITH_UNIQUE_HANDLERS(V) \
/* Extended width operands */ \
V(Wide, ImplicitRegisterUse::kNone) \
V(ExtraWide, ImplicitRegisterUse::kNone) \
\
/* Debug Breakpoints - one for each possible size of unscaled bytecodes */ \
/* and one for each operand widening prefix bytecode */ \
V(DebugBreakWide, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(DebugBreakExtraWide, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(DebugBreak0, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(DebugBreak1, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg) \
V(DebugBreak2, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg) \
V(DebugBreak3, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg) \
V(DebugBreak4, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg, \
OperandType::kReg) \
V(DebugBreak5, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kRuntimeId, OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg) \
V(DebugBreak6, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kRuntimeId, OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kReg, \
OperandType::kReg) \
\
/* Side-effect-free bytecodes -- carefully ordered for efficient checks */ \
/* - [Loading the accumulator] */ \
V(Ldar, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kReg) \
V(LdaZero, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaSmi, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kImm) \
V(LdaUndefined, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaNull, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaTheHole, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaTrue, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaFalse, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator) \
V(LdaConstant, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kIdx) \
V(LdaContextSlot, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kReg, \
OperandType::kIdx, OperandType::kUImm) \
V(LdaImmutableContextSlot, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kIdx, OperandType::kUImm) \
V(LdaCurrentContextSlot, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kIdx) \
V(LdaImmutableCurrentContextSlot, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kIdx) \
/* - [Register Loads ] */ \
V(Star, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadAccumulator, OperandType::kRegOut) \
V(Mov, ImplicitRegisterUse::kNone, OperandType::kReg, OperandType::kRegOut) \
V(PushContext, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadAccumulator, OperandType::kRegOut) \
V(PopContext, ImplicitRegisterUse::kNone, OperandType::kReg) \
/* - [Test Operations ] */ \
V(TestReferenceEqual, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kReg) \
V(TestUndetectable, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(TestNull, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(TestUndefined, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator) \
V(TestTypeOf, ImplicitRegisterUse::kReadWriteAccumulator, \
OperandType::kFlag8) \
//.........省略很多.....上面这段代码是字节码的宏定义,用语句V(Ldar, ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kReg)举例说明,Ldar是加载数据到累加器,ImplicitRegisterUse::kWriteAccumulator, OperandType::kReg说明了Ldar指令的源操作数和目的操作数,具体讲两条字节码的含义,如下:
(1) LdaSmi [1],这里的[1]是Smi小整型(small int)常量,加载到累加器中,如图2所示。 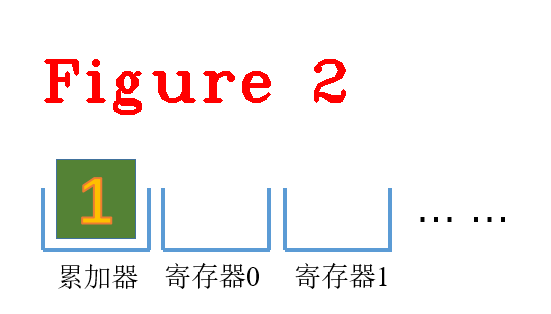
(2) Star r1,这里的r1是r1寄存器,把累加器中的值写入到r1寄存器,目前累加器的值为1,执行完后r1的值为1,如图3所示。 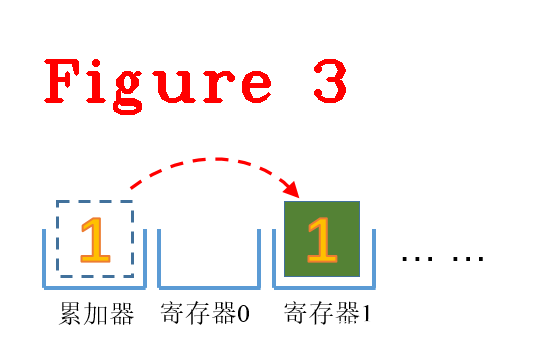
其它字节码指令参见V8的指令定义文件,这里不再赘述。V8为了提升性能,会把多次执行的字节码标记为热点代码,使用优化编译器(TurboFan)把热点代码翻译成机器相关的本地指令,达到提高运行效率的目的,如图4所示。 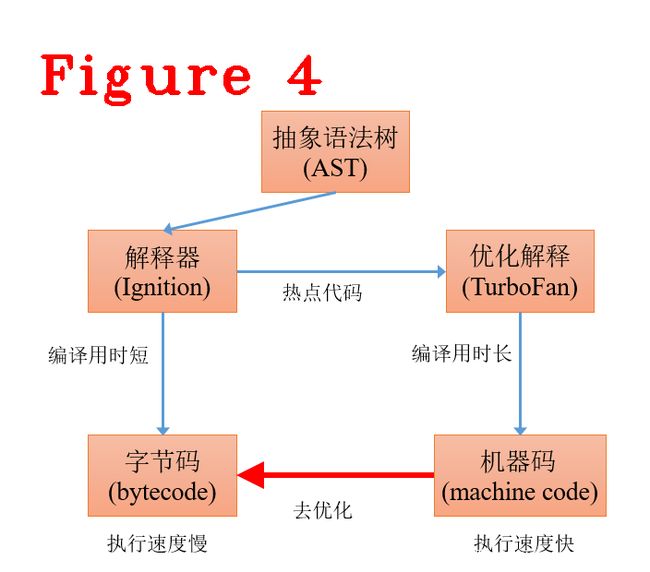
解释器将AST翻译成字节码比TurboFan用时更短,对于运行次数较少的代码非常合适,即不在运行次数较少的代码上付出更高的编译代价。TurboFan则是对常用代码(热点代码)进行本地化编译,生成体系结构相关的机器码,这需要更长的编译时间,换来的是更快的执行速度。
去优化,是将机器码转成字节码,为什么要这样做?原因有很多,详细原因参见TurboFan的定义文件。这里说一个与技术开发人员相关的原因:调试javascript源码,对源码进行调试时,需要转回字节码。
3.字节码生成
聊字节码生成之前,先要看明白AST树的结构,明白了AST树结构,也就知道了字节码生成其实是遍历树的过程,落地到程序上就是一个有限状态自动机,具体实现就是switch case配合一些预设的宏定义模板,图5给出了AST的数据结构。 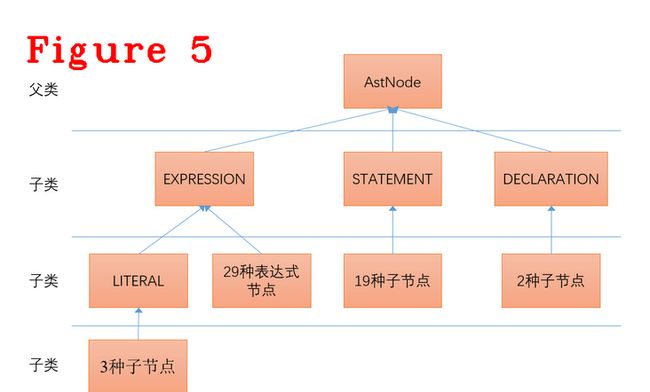
AST树的每个节点都继承自AstNode这个类,可以说一切皆“AstNode”。AstNode的成员方法是最多的,在众多方法中,AstNode的NodeType方法无疑是最重要的,因为把一个AstNode节点翻译成字节码时,首先,根据NodeType把父类AstNode转成具体的子类,比如,转成表达式(ExPRESSION)或语句(STATEMENT);其次,才能读取相应的数据、生成字节码,下面的代码是AstNode转成Assignment的具体实现。
void BytecodeGenerator::VisitAssignment(Assignment* expr) {
AssignmentLhsData lhs_data = PrepareAssignmentLhs(expr->target());
VisitForAccumulatorValue(expr->value());
builder()->SetExpressionPosition(expr);
BuildAssignment(lhs_data, expr->op(), expr->lookup_hoisting_mode());
}在这段代码中,计算expr->target(),expr->value(),expr->op()时可能会发生递归调用,因为表达式内可以包含多个子表达式。
void BytecodeGenerator::GenerateBytecodeBody() {
// Build the arguments object if it is used.
VisitArgumentsObject(closure_scope()->arguments());
// Build rest arguments array if it is used.
Variable* rest_parameter = closure_scope()->rest_parameter();
VisitRestArgumentsArray(rest_parameter);
// Build assignment to the function name or {.this_function}
// variables if used.
VisitThisFunctionVariable(closure_scope()->function_var());
VisitThisFunctionVariable(closure_scope()->this_function_var());
// Build assignment to {new.target} variable if it is used.
VisitNewTargetVariable(closure_scope()->new_target_var());
// Create a generator object if necessary and initialize the
// {.generator_object} variable.
FunctionLiteral* literal = info()->literal();
if (IsResumableFunction(literal->kind())) {
BuildGeneratorObjectVariableInitialization();
}
// Emit tracing call if requested to do so.
if (FLAG_trace) builder()->CallRuntime(Runtime::kTraceEnter);
// Emit type profile call.
if (info()->flags().collect_type_profile()) {
feedback_spec()->AddTypeProfileSlot();
int num_parameters = closure_scope()->num_parameters();
for (int i = 0; i < num_parameters; i++) {
Register parameter(builder()->Parameter(i));
builder()->LoadAccumulatorWithRegister(parameter).CollectTypeProfile(
closure_scope()->parameter(i)->initializer_position());
}
}
// Increment the function-scope block coverage counter.
BuildIncrementBlockCoverageCounterIfEnabled(literal, SourceRangeKind::kBody);
// Visit declarations within the function scope.
if (closure_scope()->is_script_scope()) {
VisitGlobalDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
} else if (closure_scope()->is_module_scope()) {
VisitModuleDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
} else {
VisitDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
}
// Emit initializing assignments for module namespace imports (if any).
VisitModuleNamespaceImports();
// The derived constructor case is handled in VisitCallSuper.
if (IsBaseConstructor(function_kind())) {
if (literal->class_scope_has_private_brand()) {
BuildPrivateBrandInitialization(builder()->Receiver());
}
if (literal->requires_instance_members_initializer()) {
BuildInstanceMemberInitialization(Register::function_closure(),
builder()->Receiver());
}
}
// Visit statements in the function body.
VisitStatements(literal->body());
// Emit an implicit return instruction in case control flow can fall off the
// end of the function without an explicit return being present on all paths.
if (!builder()->RemainderOfBlockIsDead()) {
builder()->LoadUndefined();
BuildReturn(literal->return_position());
}
}上面的函数是生成bytecode的入口,最终进入VisitStatements(literal->body());,从这里开始生成bytecode,在生成byteocde之前要先使用AstNode->XXXtype()获取子类的具体类型,下面给出XXXtype的具体实现。
#define DECLARATION_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(VariableDeclaration) \
V(FunctionDeclaration)
#define ITERATION_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(DoWhileStatement) \
V(WhileStatement) \
V(ForStatement) \
V(ForInStatement) \
V(ForOfStatement)
#define BREAKABLE_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(Block) \
V(SwitchStatement)
#define STATEMENT_NODE_LIST(V) \
ITERATION_NODE_LIST(V) \
BREAKABLE_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(ExpressionStatement) \
V(EmptyStatement) \
V(SloppyBlockFunctionStatement) \
V(IfStatement) \
V(ContinueStatement) \
V(BreakStatement) \
V(ReturnStatement) \
V(WithStatement) \
V(TryCatchStatement) \
V(TryFinallyStatement) \
V(DebuggerStatement) \
V(InitializeClassMembersStatement) \
V(InitializeClassStaticElementsStatement)
#define LITERAL_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(RegExpLiteral) \
V(ObjectLiteral) \
V(ArrayLiteral)
#define EXPRESSION_NODE_LIST(V) \
LITERAL_NODE_LIST(V) \
V(Assignment) \
V(Await) \
V(BinaryOperation) \
//............代码太长,省略很多
V(YieldStar)
#define FAILURE_NODE_LIST(V) V(FailureExpression)
#define AST_NODE_LIST(V) \
DECLARATION_NODE_LIST(V) \
STATEMENT_NODE_LIST(V) \
EXPRESSION_NODE_LIST(V)
//=========分隔线===============================
#define GENERATE_VISIT_CASE(NodeType) \
case AstNode::k##NodeType: \
return this->impl()->Visit##NodeType(static_cast(node));
#define GENERATE_FAILURE_CASE(NodeType) \
case AstNode::k##NodeType: \
UNREACHABLE();
//=========分隔线===============================
#define GENERATE_AST_VISITOR_SWITCH() \
switch (node->node_type()) { \
AST_NODE_LIST(GENERATE_VISIT_CASE) \
FAILURE_NODE_LIST(GENERATE_FAILURE_CASE) \
}
#define DEFINE_AST_VISITOR_SUBCLASS_MEMBERS() \
public: \
void VisitNoStackOverflowCheck(AstNode* node) { \
GENERATE_AST_VISITOR_SWITCH() \
} \
\
void Visit(AstNode* node) { \
if (CheckStackOverflow()) return; \
VisitNoStackOverflowCheck(node); \
} \ 上述代码中,隔开的三部分代码,组成了AstNode中所有类型(NodeType)的switch语句,第一部分代码和图5的节点类型一一对应。
void BytecodeGenerator::VisitStatements(
const ZonePtrList* statements) {
for (int i = 0; i < statements->length(); i++) {
// Allocate an outer register allocations scope for the statement.
RegisterAllocationScope allocation_scope(this);
Statement* stmt = statements->at(i);
Visit(stmt);
if (builder()->RemainderOfBlockIsDead()) break;
}
} 上述代码是bytecode生成的入口,请读者使用图1的样例代码自行跟踪,图6给出VisitStatements的函数调用堆栈。 
V8中AST到字节码的翻译过程,与编译LLVM中AST到三地址码的翻译相似,读者可自行查阅编译技术相关资料。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
恳请读者批评指正、提出宝贵意见
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流 邮箱:[email protected]
