李沐《动手学深度学习v2》学习笔记(三):Fashion-MNIST 数据集
李沐《动手学深度学习v2》学习笔记(三):Fashion-MNIST 数据集
目录:
- 李沐《动手学深度学习v2》学习笔记(三):Fashion-MNIST 数据集
- 一、Fashion-MNIST 数据集简介
- 二、了解数据集
- 三、批量显示图像
一、Fashion-MNIST 数据集简介
图像分类数据集介绍:MNIST 数据集(手写数字数据集)是图像分类中广泛使用的数据集之一,但作为基准数据集过于简单,MNIST 数据集在简单的模型上都可以有比较高的 A c c u r a c y \tt Accuracy Accuracy,不便于模型的验证,因此我们将使用类似但更复杂的 Fashion-MNIST 数据集
先导入相关库:
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision # PyTorch 计算机视觉库
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms # 数据操作库
通过 t o r c h v i s i o n . t r a n s f o r m s \tt torchvision.transforms torchvision.transforms 中的内置函数将 Fashion-MNIST 数据集下载并读取到内存中,若已下载,则只读取:
trans = transforms.ToTensor()
将原始的 PILImage 格式或者 numpy.ndarray 格式(或 cv2 读取的图像也可以)的数据格式化为可被 PyTorch 处理的张量类型,即 32 位浮点数格式;
将 shape 为 ( H , W , C ) (H, W, C) (H,W,C) 的 numpy.ndarray 或 PILImage 转为 shape 为 ( C , H , W ) (C, H, W) (C,H,W) 的张量,其将每一个数值归一化到 [ 0 , 1 ] [0,1] [0,1];
其归一化方法比较简单,直接除以255即可
return得到一个转换对象
trans = transforms.ToTensor() # 将格式归一化为张量
# 如果没有,则下载训练集,root:选择下载/读取路径,传入 trans
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="./data", train=True,
transform=trans, download=True)
# 如果没有,则下载测试集,root:选择下载/读取路径,传入 trans
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="./data", train=False,
transform=trans, download=True)
# 显示训练集和测试集的大小
len(mnist_train), len(mnist_test)
![]()
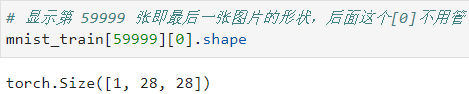
图片的形状 ( c h a n n e l , h e i g h t , w i d t h ) \tt(channel,\ height,\ width) (channel, height, width) 为 ( 1 , 28 , 28 ) (1,28,28) (1,28,28):
二、了解数据集
通过 d a t a . D a t a L o a d e r \tt data.DataLoader data.DataLoader 进行小批量划分,同时显示图像,进一步了解图像
train_iter = data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=18, shuffle=True)
image, label = next(iter(train_iter)) # 获得一个小批量
plt.imshow(image[0].squeeze()) # 显示批量中的图片[0]
print('label:', label[0]) # 显示标签
plt.imshow(image[1].squeeze()) # 显示批量中的图片[1]
print('label:', label[1]) # 显示标签
grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(tensor, nrow=8, padding=2, normalize=False,…) 将若干幅图像拼成一幅大图像,返回值是一个张量
tensor( b a t c h _ s i z e , c h a n n e l , h e i g h t , w i d t h ) \tt (batch\_size,\ channel,\ height,\ width) (batch_size, channel, height, width),即 ( 批 量 数 , 通 道 数 , 高 , 宽 ) (批量数,\ 通道数,\ 高,\ 宽) (批量数, 通道数, 高, 宽),通道数如果是 1 1 1,会变为 3 3 3
nrow每一行显示的图像数,default=8
padding子图像与子图像之间的间距,default=2
normalize是否归一化到 [ 0 , 1 ] [0, 1] [0,1] 之间,default=False
返回值张量, s h a p e = ( c h a n n e l , h e i g h t + 2 × p a d d i n g , w i d t h × b a t c h _ s i z e + ( b a t c h _ s i z e + 1 ) × p a d d i n g ) \tt shape=(channel,\ height+2×padding,\ width×batch\_size+(batch\_size+1)×padding) shape=(channel, height+2×padding, width×batch_size+(batch_size+1)×padding)
其中, 2 × p a d d i n g \tt2×padding 2×padding 表示上下边界; ( b a t c h _ s i z e + 1 ) × p a d d i n g \tt (batch\_size+1)×padding (batch_size+1)×padding 表示左右边界和中间边界
import numpy as np
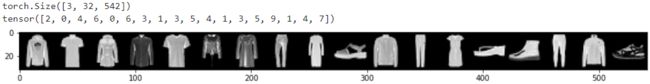
grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(image, nrow=18)
print(grid.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(np.transpose(grid, (1, 2, 0)))
print(label)
注意,由于 plt.imshow 输入的图像的格式为 ( h e i g h t , w i d t h , c h a n n e l ) \tt(height,\ width,\ channel) (height, width, channel),而我们的 grid 的格式为 ( c h a n n e l , h e i g h t , w i d t h ) \tt(channel,\ height,\ width) (channel, height, width),因此需要调用 np.transpose 来进行维度的转换,它的用法与我们在PyTorch基础与线性代数中讲的 torch.transpose() 类似,只不过后者只能进行两个维度间的互换
三、批量显示图像
定义一个函数,该函数可以根据 label 的数值返回该数值所指的名称:
def get_fashion_mnist_labels(labels):
"""返回Fashion-MNIST数据集的文本标签"""
text_labels = [
't-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover',
'dress', 'coat', 'sandal', 'shirt',
'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot']
return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]
Fashion-MNIST 数据集共有 10 10 10 种标签
批量显示图片,加上上一例中的一组,这里再额外增加三组:
for i in range(3):
temp_image, temp_label = next(iter(train_iter))
temp_grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(temp_image, nrow=18)
grid = torch.cat((grid, temp_grid), dim=1)
label = torch.cat((label, temp_label), dim=0)
plt.figure(figsize=(40, 8))
plt.imshow(np.transpose(grid, (1, 2, 0)))
print(get_fashion_mnist_labels(label))

改变 range(3) 的大小,可以显示更多的图像,这里不再展开
参考资料:
[1]Pytorch教程(十六):FashionMNIST数据集DataSet DataLoader
[2]np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0))的作用

