javaSE基础之对象操作流
课程笔记Day20
- 对象操作流
- 属性集Properties
第一章 对象操作流
第01节 ObjectOutputStream
快速入门
//目标:学习对象操作流的快速入门(对象序列化操作)
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件01.txt";
//1.创建对象
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path));
//2.读写数据
oos.writeObject(1314);
//3.释放资源
oos.close();
}
}
//小结:将对象,保存到本地文件当中,序列化操作。 对象 --> 文件。
常见问题
1. 为什么序列化接口 Serializable 当中没有任何方法呢?
序列化接口 Serializable 称之为 "标记型接口" (标记型接口:没有任何方法的接口)
他只是给出一个标记,用于给 ObjectOuputStream 进行识别的。
2. 异常问题:
A. 未序列化的异常 NotSerializableException
原因: 我们的类,没有实现标识接口 Serializable
解决:类上限需要实现序列化接口 Serializable
第02节 ObjectInputStream
快速入门
//目标:学习ObjectInputStream 读取数据的操作
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件01.txt";
//1.创建对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
//2.读写数据
Object o = ois.readObject();
//3.释放资源
ois.close();
System.out.println(o);
}
}
常见问题
1. 异常:InvalidClassException
A. 原因: 当我们先采用 writeObject 写对象,然修改了 类文件信息,再次 readObject 就会出现此异常。因为字节码变化了。
B. 解决: 需要告诉字节码无论怎么改变,我就是我。 需要添加序列化的 ID 证明我就是我
C. 例如: private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
2. 不想被序列化怎么办?
可以采用 瞬态关键字,给成员变量,添加瞬态。
例如: transient int age;
举例: java.util.Date 类底层有一个 fastTime
3. 出现异常 EOFException
原因: 写对象 writeObject() 的次数和读对象 readObject() 的次数不一致。
解决: 我们的对象只写一次,我们的对象只读一次即可。
第03节 标准写法
汽车类
import java.io.Serializable;
//汽车类
//1. 需要实现序列化的接口
//2. 需要添加序列化的ID
//3. 可以添加瞬态关键字
public class Car implements Serializable {
private String brand;
private transient int price;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 10L;
public Car(String brand, int price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
测试类
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//写数据
//writeData();
//读数据
readData();
}
//写数据的方法
public static void writeData() throws Exception{
ArrayList<Car> array = new ArrayList<>();
array.add(new Car("五菱宏光",3));
array.add(new Car("劳斯莱斯",3000));
//写数据的操作
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件03.txt";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path));
oos.writeObject(array);
oos.close();
}
//读数据的方法
public static void readData() throws Exception{
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件03.txt";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
Object o = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
ArrayList<Car> array = (ArrayList<Car>) o;
array.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
第04节 深浅克隆
基础理论
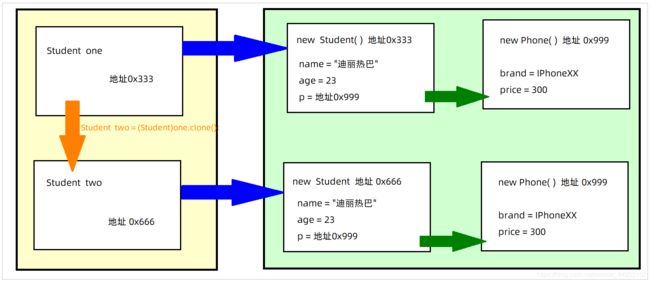
对象的拷贝复制是不可以使用 等号的。例如:
Student one = new Student("迪丽热巴",23);
Student two = one; //这里叫做把 one的地址赋值给two 指向是相同的堆内存空间。
采用 等号赋值的模型图。两个引用one和two指向相同的内存地址
浅克隆
手机类
//手机类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Phone {
private String brand;
private int price;
public Phone(String brand, int price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
学生类
//学生类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Student implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private Phone p;
//重写方法。来自于Object类的克隆 clone方法,快捷键 Ctrl+o (欧)
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
public Student(String name, int age, Phone p) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.p = p;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Phone getP() {
return p;
}
public void setP(Phone p) {
this.p = p;
}
//定义普通方法
public void show(){
System.out.println("p = " + p);
System.out.println("p.getBrand() = " + p.getBrand());
System.out.println("p.getPrice() = " + p.getPrice());
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
}
}
测试类
//测试类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建学生类的对象
Student one = new Student("迪丽热巴",23,new Phone("IPhoneXX",300));
//克隆对象
Student two = (Student) one.clone();
System.out.println("one = " + one);
System.out.println("two = " + two);
System.out.println("=============");
one.show();
System.out.println("-------");
two.show();
}
}
运行效果
深克隆
手机类
//手机类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Phone implements Serializable {
private String brand;
private int price;
public Phone(String brand, int price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
学生类
//学生类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Student implements Serializable,Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private Phone p;
//重写方法。来自于Object类的克隆 clone方法,快捷键 Ctrl+o (欧)
//深克隆的方式:
//将对象 ---写入到内存---> 内存 ---读取处理---> 新的对象
//ByteArrayOutputStream 和 ByteArrayInputStream
//ByteArrayOutputStream --> 写数据到数组里面(存在于内存当中)
//ByteArrayInputStream ---> 读取上面数组的内容即可
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//定义对象的引用
Student stu = null;
try {
//1.将当前的对象,写入到内存当中。
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
//写对象,谁调用 clone()方法,我就写谁。
oos.writeObject(this);
//2.重新读取数据,读取写入的内存数据,数据来自于 bos
//在 bos 当中保存的就是 oos 里面写的对象 this
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Object o = ois.readObject();
//3. 强制类型转换
stu = (Student)o;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//直接返回
return stu;
}
public Student(String name, int age, Phone p) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.p = p;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Phone getP() {
return p;
}
public void setP(Phone p) {
this.p = p;
}
//定义普通方法
public void show(){
System.out.println("p = " + p);
System.out.println("p.getBrand() = " + p.getBrand());
System.out.println("p.getPrice() = " + p.getPrice());
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
}
}
测试类
//测试类
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建学生类的对象
Student one = new Student("迪丽热巴",23,new Phone("IPhoneXX",300));
//克隆对象
Student two = (Student) one.clone();
System.out.println("one = " + one);
System.out.println("two = " + two);
System.out.println("=============");
one.show();
System.out.println("-------");
two.show();
}
}
运行效果
第05节 标准IO流异常处理
以前的写法
//目标:ObjectOuputStream写数据的方法(标准处理异常的代码)以前写法
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1.创建对象
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件04.txt";
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//2.读写数据
oos.writeObject("川哥,你是真的帅炸啦");
//3.释放资源
fos.close();
oos.close();
}
}
标准IO流处理异常的方式
//目标:ObjectOuputStream写数据的方法(标准处理异常的代码) 标准写法
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
FileOutputStream fos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//...
//1.创建对象
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件05.txt";
fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
// System.out.println(3/0);
//2.读写数据
oos.writeObject("川哥,你是真的帅炸啦");
} catch (IOException e) {
//出现异常之后的处理的代码。
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//不管你最后走的是 try...还是 catch... 始终都会执行 finally
if(fos!=null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (oos!=null){
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("我执行了。。finally");
}
}
}
第二章 属性集Properties
第01节 基础理论
说明
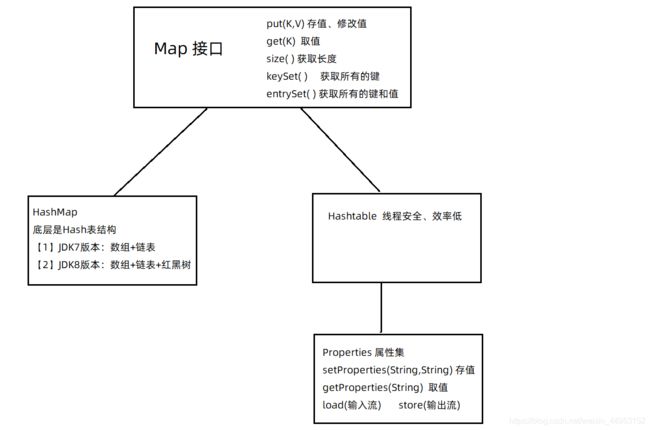
Hashtable 在JDK1.0版本出现。Hashtable 目前已经不适用了。被 HashMap取代了。(原因:HashMap效率高)
但是 Hashtable 他的儿子 Properties 依然在使用。(原因:Properties可以和IO结合使用)
说到 Hashtable 需要注意和 HashMap的小区别:能否存放 空值空键的问题。

第02节 快速入门
作为集合的常用方法
//目标: 学习属性集 Properties的快速入门
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Properties pp = new Properties();
//存放数据
pp.setProperty("萧峰", "阿朱");
pp.setProperty("段誉", "语嫣");
pp.setProperty("虚竹", "梦姑");
//取值操作
String value1 = pp.getProperty("西门庆");
System.out.println("value1 = " + value1);
String value2 = pp.getProperty("段誉");
System.out.println("value2 = " + value2);
//遍历集合 stringPropertyNames()获取到所有的键,类似于keySet()
Set<String> keys = pp.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = pp.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "," + value);
}
}
}
作为与IO结合的方法
//存数据
public static void method1() throws IOException {
Properties pp = new Properties();
pp.setProperty("username", "张三");
pp.setProperty("password", "123456");
//需要将上述的数据,存储到文件当中。
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件07.properties");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "UTF-8");
//将Properties的数据通过流保存到文件当中
pp.store(osw, "chuan ge a wo zhe ci yi ding yao chao shen");
//释放资源
fos.close();
osw.close();
}
//取数据
public static void method2() throws IOException {
//创建对象
Properties pp = new Properties();
pp.load(new FileReader("JavaSEDay20\\dir\\文件07.properties"));
Set<String> keys = pp.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = pp.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "," + value);
}
}
第03节 程序次数
需求
编写一个程序,统计该程序运行的次数。
如果程序第 1次运行,则展示 "第1次使用本软件"。
如果程序第 2次运行,则展示 "第2次使用本软件"。
如果程序第 3次运行,则展示 "第3次使用本软件"。
如果程序第 4次运行,则展示 "您的试用次数已经达到上限,请给我的支付宝充值200元"。
如果程序第 5次运行,则展示 "您的试用次数已经达到上限,请给我的支付宝充值200元"。
。。。。。。。
代码
//练习:程序次数
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pp = new Properties();
//定义路径
String path = "JavaSEDay20\\dir\\次数.properties";
//将路径,封装成为File对象,用于判断文件是否存在
File f = new File(path);
//判断文件是否存在
if (!f.exists()) {
//第一次出现,直接向文件当中,保存数据。
pp.setProperty("number", "1");
//将数据写入到文件当中
pp.store(new FileWriter(path),null);
System.out.println("第1次使用本软件");
} else {
//去加载数据
pp.load(new FileReader(path));
//不是第一次出现。取出数据
String countStr = pp.getProperty("number");
int count = Integer.parseInt(countStr);
count++;
//说明:这里加上双引号的原因是 setProperty方法的参数是字符串类型
pp.setProperty("number",count+"");
//将数据写入到文件当中
pp.store(new FileWriter(path),null);
//判断是否达到了上限
if (count<=3){
System.out.println("第"+count+"次使用本软件");
}else{
System.out.println("您的试用次数已经达到上限,请给我的支付宝充值200元");
}
}
}
}
今日总结:
好好复习,javaSE资料全部看完,明天大复习,阶段性考试!冲冲冲