springboot实战电商项目mall4j (https://gitee.com/gz-yami/mall4j)
代码版本
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
2.2.0
既然是springboot 那么要想知道怎么运行的,有从三个地方入手
xxxAutoConfiguration- yml对应的配置文件(
xxxProperties) - 配置的注解
我们先来看三个类
1. MybatisAutoConfiguration 构造SqlSession
这个类通过dataSource的配置,构造出SqlSessionFactory 与 SqlSessionTemplate。如果以前使用spring相关的api的话,应该会比较熟悉 jdbcTemplate 与 redisTemplate 之类的。SqlSessionTemplate这个命名,就会让人联想到这个也是类似的功能。而session 这个词很明显就是与服务之间交互保存连接状态的东西。Factory是工厂模式。从而可以得出:SqlSessionFactory是用来创建SqlSession的,SqlSession可以打开或关闭与数据库的连接。SqlSessionTemplate 就是操作这些开关的关键。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
// 省略...
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
// 省略...
}
}2. MybatisProperties 读取配置信息
这个类主要是将配置文件里面的配置转成bean映射,配置文件类似这个样子
#mybatis的相关配置
mybatis:
#mapper配置文件
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml
type-aliases-package: com.frozen-watermelon.**.model
#开启驼峰命名
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = MybatisProperties.MYBATIS_PREFIX)
public class MybatisProperties {
public static final String MYBATIS_PREFIX = "mybatis";
}3. @MapperScan 扫描Mapper接口
我们通常为了确定被扫描的mapper所属的包,都会有这样一个配置
@Configuration
@MapperScan({ "com.frozen-watermelon.**.mapper" })
public class MybatisConfig {
}这里就有这个注解@MapperScan,那么这个注解是如何在源码中运用的呢?
我们先看下这个注解类
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
public @interface MapperScan {
String[] value() default {};
String[] basePackages() default {};
}这里面@Import 了 MapperScannerRegistrar.class ,也就是说这个类被实例化了。这个类同时实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,也就是说 registerBeanDefinitions()这个方法会被调用
public class MapperScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 获取@MapperScan的配置信息
AnnotationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
if (mapperScanAttrs != null) {
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, mapperScanAttrs, registry,
generateBaseBeanName(importingClassMetadata, 0));
}
}
void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annoMeta, AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName) {
// 准备构建MapperScannerConfigurer
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);
// 省略...
List basePackages = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取注解的配置的信息,
basePackages.addAll(
Arrays.stream(annoAttrs.getStringArray("value")).filter(StringUtils::hasText).collect(Collectors.toList()));
basePackages.addAll(Arrays.stream(annoAttrs.getStringArray("basePackages")).filter(StringUtils::hasText)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(basePackages));
// 构建对象
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
} 从上面的代码可以看出最终构建了一个MapperScannerConfigurer对象。那么MapperScannerConfigurer到底是干嘛用的呢?MapperScannerConfigurer实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,也就是说postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()这个方法创建完bean之后会被调用
public class MapperScannerConfigurer
implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
// 省略...
// 扫描basePackage
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
}4. 创建mapper代理对象
我们来看下扫描干了啥
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider {
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 真正的执行扫描 这里的doScan方法,调用的应该是ClassPathMapperScanner里面的扫描方法,上面new出来的
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
protected Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 将beanDefininition进行register操作,后面就可以创建这个bean了
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
} public class ClassPathMapperScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner {
private Class mapperFactoryBeanClass = MapperFactoryBean.class;
@Override
public Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
// 调用父类的构造方法`ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner` 这个是spring的方法,主要是用来构造一个bean,此时是构造 basePackage里面的各种mapper的定义信息
Set beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages)
+ "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
// 处理bean定义信息,将上面创建的bean定义信息传入
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set beanDefinitions) {
AbstractBeanDefinition definition;
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = getRegistry();
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (AbstractBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
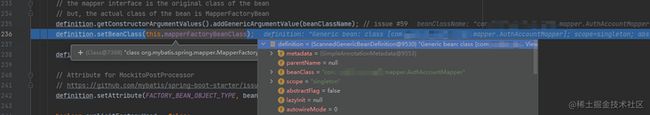
// 这里的mapperFactoryBeanClass是MapperFactoryBean,而原来的definition是basePackage里面的各种mapper的定义信息,神奇的操作
// 可以看下debugger的截图就可以看到这奇妙的信息,MapperFactoryBean这个东西很重要
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
// 下面添加了一堆sqlSessionFactory、sqlSessionTemplate,不过初始化的时候没有用到
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
}
}
} 将普通的mapper变成MapperFactoryBean
上面已经将bean的定义信息进行了registerBeanDefinition,而此时register的是MapperFactoryBean这个bean。而这个bean实现了FactoryBean的接口,那么我们就来看下MapperFactoryBean这个信息,顺便看下getObject()方法
public class MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
} 这个getSqlSession()就是用SqlSessionTemple啦,这里的getMapper又是什么呢?一路找下去就能发现,是mybatis在 MapperProxyFactory使用jdk动态代理生成的代理mapper
// SqlSessionTemple
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
// 往下找
// Configuration
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
// 往下找
// MapperRegistry
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 往下找
// MapperProxyFactory
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} 上面的一堆操作,通过FactoryBean的getObject() 只是将代理过后的mapper交给了spring去管理,那么mybatis是怎么管理的呢?我们继续回到MapperFactoryBean ,发现他也实现了InitializingBean接口。所以还有afterPropertiesSet()会被调用。
public abstract class DaoSupport implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// Let abstract subclasses check their configuration.
checkDaoConfig();
// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
}
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
notNull(this.sqlSessionTemplate, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
}
public class MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean {
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
// 代理的mapper放到mybatis的Configuration中
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
} 上面通过configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface); 将代理的mapper放到mybatis的Configuration中。上面的一切,都是对@MapperScan 扫描出来的接口创建动态代理的操作。
继续看下addMapper()方法
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 缓存mapper代理
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
} 最后看下解析的方法
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 这里面就会去解析与Mapper接口相同包名下面的xml文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
// 这里回去解析接口方法上的SQL注解
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}5. MapperProxy代理mapper接口的方法
我们已经知道mapper的所有的接口都会被代理,这个代理类是谁呢?显而易见的是MapperProxy
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} 假设我们有一个这样的mapper:
public interface UserMapper {
int getById(String userId);
}这个时候我们调用userMapper.getById("1")会发生什么呢?
由于被MapperProxy代理了,所以我们要看下代理的invoke()方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 缓存方法,并执行方法
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
// MapUtil.computeIfAbsent 如果存在就返回缓存对象,如果不存在再构造
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 缓存的方法
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}我们继续看PlainMethodInvoker这个类的invoke()方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}通过方法是增删改查(比如 标签判断出是查询),调用SqlSession增删改查对应的方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}