运维实战 容器部分 Kubernetes存储
运维实战 容器部分 Kubernetes存储
- CoinfigMap配置管理
-
- 如何使用
- 分类实践及其特性
-
- 字面值方式创建
- 使用文件创建
- 使用目录创建
- 使用资源清单创建
- 如何使用ConfigMap
-
- 通过环境变量直接传递
- 设置命令行参数方式
- 通过数据卷挂载进行使用
-
- 数据卷模式下的ConfigMap热更新
- Secret配置管理
-
- 简单概念
- Service Account的默认设置
- Opaque Secret
-
- 文件方式创建
- 资源清单方式创建
- 将Secret挂载到Volume
-
- 向指定路径映射Secret密钥
- 将Secret设置为环境变量
- 存储Docker Registry的认证信息
- Volumes配置管理
-
- emptyDir卷
-
- 使用场景
- 缺点
- hostPath卷
-
- 使用场景
- 注意事项
- NFS挂载
- PV 持久卷
-
- 两种PV提供方式
- 使用说明
- 访问模式
- 回收策略
- StorageClass
-
- 属性
- NFS动态分配PV示例
- StatefulSet控制器
-
- 注意事项
-
- Kubectl弹缩
- 改变StatefulSet副本数量
- 资源清单相关方式
- 使用Kubectl Patch
CoinfigMap配置管理
在K8S中, CoinfigMap被用于保存配置信息.
其主要特点是以键值对方式存储.
通过CoinfigMap, K8S提供了向Pod中导入配置的方法.
这一操作结局了镜像与配置耦合度高的问题, 实现了镜像与配置的解耦, 同时也大大提高了镜像的复用性和可移植性.
通过导入配置, 镜像可以批量化的进行配置修改和迁移.
可能的应用场景
- 用于向容器内填充环境变量
- 设置容器内的命令行参数
- 作为容器内应用的配置文件存在
- 填充数据卷的配置文件
如何使用
常见的创建ConfigMap的方式有4种
CLI交互式创建, 即字面值方式创建- 使用文件进行创建
- 使用目录进行创建(实际就是批量文件创建)
- 通过编写
yaml资源清单创建
分类实践及其特性
字面值方式创建
##采用CLI方式交互式填写键值对
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl create configmap my-config --from-literal=key1=config1 --from-literal=key2=config2
configmap/my-config created
##查看创建的ConfigMap
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h31m
my-config 2 6s
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl describe cm my-config
Name: my-config
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
key1:
----
config1
key2:
----
config2
Events: <none>
##测试完成后清理环境
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl delete cm my-config
configmap "my-config" deleted
使用文件创建
默认情况下, 文件的名称会成为Key, 而文件的内容会成为对应的Value.
##使用DNS解析文件作为导入文件
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl create configmap my-config-2 --from-file=/etc/resolv.conf
configmap/my-config-2 created
##查看创建的ConfigMap
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h32m
my-config-2 1 5s
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl describe cm my-config-2
Name: my-config-2
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
resolv.conf:
----
nameserver 114.114.114.114
Events: <none>
##测试完成后清理环境
[root@Server2 YAML]# kubectl delete cm my-config-2
configmap "my-config-2" deleted
使用目录创建
##创建测试目录并导入用于测试的文件
[root@Server2 mnt]# mkdir configMap
[root@Server2 mnt]# cd configMap/
[root@Server2 configMap]# cp /etc/passwd .
[root@Server2 configMap]# cp /etc/resolv.conf .
[root@Server2 configMap]# cp /etc/hosts .
##通过目录方式创建ConfigMap
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl create configmap my-config-3 --from-file=/etc/configMap
##查看创建的ConfigMap
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h35m
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl create configmap my-config-3 --from-file=/mnt/configMap
configmap/my-config-3 created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h35m
my-config-3 3 3s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl describe cm my-config-3
Name: my-config-3
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
hosts:
----
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
172.25.5.250 foundation4.ilt.example.com
172.25.5.1 Server1 reg.westos.org
172.25.5.2 Server2
172.25.5.3 Server3
172.25.5.4 Server4
172.25.5.5 Server5
172.25.5.6 Server6
172.25.5.7 Server7
172.25.5.8 Server8
passwd:
----
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
systemd-network:x:192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
polkitd:x:999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
tss:x:59:59:Account used by the trousers package to sandbox the tcsd daemon:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
kubeadm:x:1000:1000::/home/kubeadm:/bin/bash
resolv.conf:
----
nameserver 114.114.114.114
Events: <none>
##测试完成后清理环境
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl delete cm my-config-3
configmap "my-config-3" deleted
使用资源清单创建
- 使用的
CM1.yaml文件内容
vim CM1.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cm1-config
data:
db_host: "172.25.0.250"
db_port: "3306"
- 创建一个简单的
ConfigMap
[root@Server2 configMap]# vim CM1.yaml
##导入资源清单
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f CM1.yaml
configmap/cm1-config created
##查看创建的ConfigMap
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
cm1-config 2 7s
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h37m
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl describe cm cm1-config
Name: cm1-config
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
db_host:
----
172.25.0.250
db_port:
----
3306
Events: <none>
如何使用ConfigMap
上文有提到, ConfigMap的用法之一就是导入Pod中, 那么如何在Pod中使用自然也有不同的用法了.
通过环境变量直接传递
Pod1.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod1
spec:
containers:
- name: pod1
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "env"]
env:
- name: key1
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: cm1-config
key: db_host
- name: key2
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: cm1-config
key: db_port
restartPolicy: Never
实现目的
通过使用Pod1.yaml, 可以创建一个自主式Pod, 名称为pod1,并将cm1-config中的db_host赋给了容器内的环境变量key1, db_port的值赋给了key2, 在容器运行后采用终端输出环境变量.
相当于只是传递数值而并没有直接引入变量.
- 验证效果
[root@Server2 configMap]# vim Pod1.yaml
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f Pod1.yaml
pod/pod1 created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 6s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl logs pod1
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT=443
KUBERNETES_PORT=tcp://10.96.0.1:443
HOSTNAME=pod1
SHLVL=1
HOME=/root
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_ADDR=10.96.0.1
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PORT=443
key1=172.25.0.250
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PROTO=tcp
key2=3306
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS=443
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP=tcp://10.96.0.1:443
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST=10.96.0.1
PWD=/
##进行环境清洁
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl delete -f Pod1.yaml
pod "pod1" deleted
env命令的效果为打印环境变量.
上文代码框中的环境变量含有key1和key2, 其内容取自ConfigMap的键.
另一种方式
当然, 也可以直接传递变量而不是赋值了.
Pod2.yaml内容
vim pod2.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod2
spec:
containers:
- name: pod2
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "env"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: cm1-config
restartPolicy: Never
- 检查结果
[root@Server2 configMap]# vim Pod2.yaml
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f Pod2.yaml
pod/pod2 created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl logs pod2
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT=443
KUBERNETES_PORT=tcp://10.96.0.1:443
HOSTNAME=pod2
SHLVL=1
db_port=3306
HOME=/root
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_ADDR=10.96.0.1
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PORT=443
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PROTO=tcp
KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP=tcp://10.96.0.1:443
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS=443
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST=10.96.0.1
PWD=/
db_host=172.25.0.250
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl delete -f Pod2.yaml
pod "pod2" deleted
设置命令行参数方式
- 修改过的
Pod2.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod1
spec:
containers:
- name: pod1
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo $(db_host) $(db_port)"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: cm1-config
restartPolicy: Never
不难看出, 这里是将变量的值在命令行中直接显示, 实际的实现与上面的方式并无二样.
[root@Server2 configMap]# vim Pod2.yaml
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f Pod2.yaml
pod/pod1 created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl logs pod1
172.25.0.250 3306
通过数据卷挂载进行使用
Pod3.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod3
spec:
containers:
- name: pod3
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "cat /config/db_host"]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: cm1-config
restartPolicy: Never
上面的资源清单做了以下几件事:
- 将
cm1-config作为数据卷config-volume - 将
config-volume挂载到/config下 - 在命令行中输出
/config/db_host的内容, 实际就是读取了db_host的值
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl delete -f Pod2.yaml
pod "pod1" deleted
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f Pod3.yaml
pod/pod3 created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod3 0/1 Completed 0 10s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl logs pod3
172.25.0.250[root@Server2 configMap]#
数据卷模式下的ConfigMap热更新
- 通过以下实验, 我们可以验证
ConfigMap热更新相关的问题 - 通过以下
YAML文件创建控制器并将配置文件作为数据卷挂载
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: nginxconf
- 使用的
nginx.conf内容
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
- 创建
ConfigMap并进行内容检测
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl create configmap nginxconf --from-file=nginx.conf
configmap/nginxconf created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get cm
kNAME DATA AGE
cm1-config 2 15m
kube-root-ca.crt 1 5h53m
nginxconf 1 10s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl describe cm nginxconf
Name: nginxconf
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
nginx.conf:
----
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
Events: <none>
- 不难发现, 此时
nginxconf中的nginx.conf的值中端口配置部分为listen 80 - 创建控制器并进行内容检测
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl apply -f Pod4.yaml
deployment.apps/my-nginx created
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl exec -it my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v -- bash
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/# cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/etc/nginx/conf.d# ls
nginx.conf
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/etc/nginx/conf.d# cat nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
##查看容器内挂载情况(此处节选有用部份)
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/etc/nginx/conf.d# mount
/dev/mapper/rhel-root on /etc/nginx/conf.d type xfs (ro,relatime,attr2,inode64,noquota)
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/etc/nginx/conf.d# exit
exit
- 测试
Nginx服务情况, 通过默认80端口可以访问
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v 1/1 Running 0 94s 10.244.141.201 server3 <none> <none>
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.141.201
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
- 修改
nginxconf中的监听端口部分
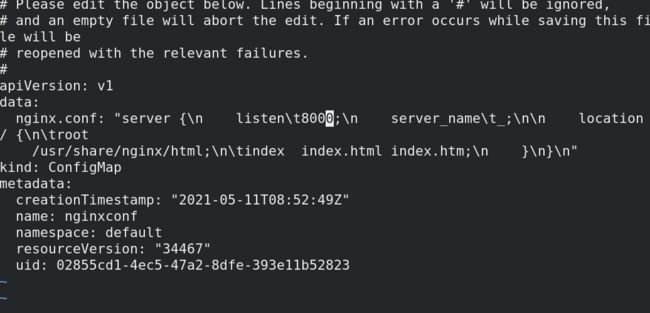
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl edit cm nginxconf
configmap/nginxconf edited
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl exec -it my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v -- bash
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
root@my-nginx-86d5ccb8db-zsl8v:/# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx.conf
server {
listen 8000;
server_name _;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
- 等待一段时间后, 会发现容器内的文件内容也变化了, 即完成了文件的热更新
- 但是稍加测试就会发现, 文件修改了, 服务却没有重载, 访问依旧是
80端口而不没有变成8000端口
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.141.201
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.141.201:8000
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.244.141.201:8000; Connection refused
- 服务重载的正确方式: 打补丁
kubectl patch deployments.apps my-nginx --patch '{"spec": {"template":{"metadata": {"annotations": {"version/config": "2021051102"}}}}}'
deployment.apps/my-nginx patched
- 在进行
patch后,80端口无法正常访问而8000畅通
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.22.5
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.244.22.5:80; Connection refused
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.22.5:8000
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
- 尝试修改回去
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl edit cm nginxconf
configmap/nginxconf edited
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl patch deployments.apps my-nginx --patch '{"spec": {"template":{"metadata": {"annotations": {"version/config": "2021051101"}}}}}'
deployment.apps/my-nginx patched
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
my-nginx-687ccbd4f6-79cr9 1/1 Terminating 0 88s 10.244.22.5 server4 <none> <none>
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 0 4s 10.244.141.202 server3 <none> <none>
[root@Server2 configMap]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 0 6s 10.244.141.202 server3 <none> <none>
[root@Server2 configMap]# curl 10.244.141.202
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
- 不难发现, 提交补丁的过程实际上就是控制器完成了一次滚动更新的操作
Secret配置管理
简单概念
- 与
ConfigMap类似,Secret也是一种对象存储, 区别在于Secret对象性质的卷常被用来保存敏感信息, 如密码/OAuth认证令牌等等 - 比起
CpnfigMap, 将这些信息存储在Secret重命更加安全和灵活
常见的两种使用方式
- 作为数据卷中的文件挂载入
Pod进行使用 - 当作
Pod从私有仓库拉取镜像时的认证必需品使用
Secret的类型
| 类型 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| Service Account | K8S会自动创建包含访问 API 凭据的Secret, 并自动修改 pod 以使用此类型的Secret, 如果没有API凭证则Pod无法与管理节点交互 |
| Opaque | 使用base64编码存储信息, 可以通过base64 --decode解码获得原始数据, 因此安全性弱, 常用于文件挂载入Pod时使用 |
| kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson | 用于存储Docker Registry的认证信息, 当需要拉取私有仓库的镜像时使用 |
Service Account的默认设置
-
Service Account创建时Kubernetes会默认创建对应的Secret -
对应的
Secret会自动挂载到Pod的/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount目录中
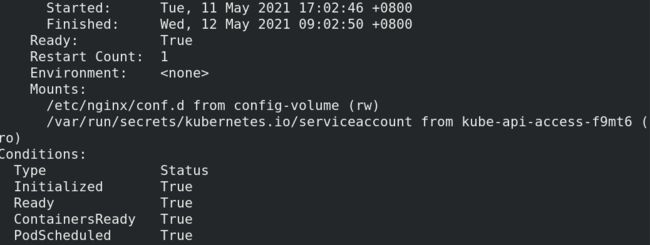
通过describe方式可以查看Pod挂载情况
kubectl describe pod my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8
可以看到, Mounts信息中有Service Account, 挂载位置为/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
进入容器查看其内部内容, 可以看到包含命名空间, CA证书, token
[root@Server2 ~]# kubectl exec my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 -- ls /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
ca.crt
namespace
token
每个Namespace下有一个名为default的默认的Service Account对象
上方在内部文件中看到的token起到的作用时, 当Pod启动后用来协助完成Pod中的进程访问API Server时的身份鉴权过程
也就是说, 缺少了这部分文件, Pod将无法有效的与MASTER节点进行交互
Opaque Secret
交互式方式此处不列举, 但有一条需要注意的
- 如果密码具有特殊字符, 则需要使用
\字符对其进行转义
文件方式创建
[root@Server2 Secret]# echo -n 'westos' > ./Password.txt
[root@Server2 Secret]# echo -n 'NeuWings' > ./Username.txt
[root@Server2 Secret]# ls
Password.txt Username.txt
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl create secret generic db-user-pass --from-file=./Username.txt --from-file=./Password.txt
secret/db-user-pass created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get secrets
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
db-user-pass Opaque 2 13s
default-token-5rnvk kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 22h
同时可看到了上文所述的default
资源清单方式创建
- 获取编码转化文字内容的方式
echo -n 'admin' | base64
YWRtaW4=
$ echo -n 'westos' | base64
d2VzdG9z
- 使用的
Mysecret.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysecret
type: Opaque
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
password: d2VzdG9z
- 操作过程
[root@Server2 Secret]# vim Mysecret.yaml
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl delete secrets db-user-pass
secret "db-user-pass" deleted
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl apply -f Mysecret.yaml
secret/mysecret created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get secrets
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
default-token-5rnvk kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 23h
mysecret Opaque 2 15s
默认情况下kubectl get和kubectl describe为了安全是不会显示密码的内容, 只会显示长度
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl describe secrets mysecret
Name: mysecret
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data
====
password: 6 bytes
username: 5 bytes
如果需要查看内容可以附加-o yaml参数, 使其以yaml格式输出.
将Secret挂载到Volume
- 修改后的
Mysecret.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mysecret
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets
mountPath: "/secret"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: secrets
secret:
secretName: mysecret
- 操作记录
[root@Server2 Secret]# vim Mysecret.yaml
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl apply -f Mysecret.yaml
pod/mysecret created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 17h
mysecret 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 17h
mysecret 1/1 Running 0 8s
向指定路径映射Secret密钥
- 使用到的
v2.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mysecret
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets
mountPath: "/secret"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: secrets
secret:
secretName: mysecret
items:
- key: username
path: my-group/my-username
- 操作流程
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl apply -f v2.yaml
pod/mysecret created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 17h
mysecret 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl describe pod mysecret
将Secret设置为环境变量
- 使用到的
v3.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: secret-env
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
env:
- name: SECRET_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: username
- name: SECRET_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: password
上面的资源清单做到了
- 从
mysecret中分别读取两个key对应的value存储到两个对应的环境变量中
环境变量读取Secret是一种很方便好用的方法, 但是其无法动态更新Secret
存储Docker Registry的认证信息
- 创建一个包含私有仓库认证信息的
Secret, 并创建对应的私有仓库
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl create secret docker-registry myregistrykey --docker-server=reg.westos.org --docker-username=admin --docker-password=westos [email protected]
secret/myregistrykey created
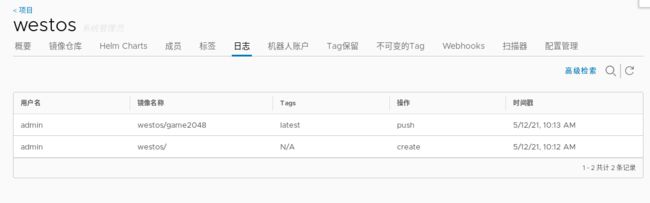
- 实验开始前私有仓库
westos的日志情况
- 实验用到的
TestPod.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: game2048
image: reg.westos.org/westos/game2048
- 由于镜像拖取是从私有仓库, 而上面的资源清单没有做登陆验证, 镜像是无法拉取的
[root@Server2 Secret]# vim TestPod.yaml
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl apply -f TestPod.yaml
pod/mypod created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 17h
mypod 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 4s
mysecret 1/1 Running 0 9m46s
secret-env 1/1 Running 0 6m38s
- 修改构建, 增加
imagePullSecrets
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: game2048
image: reg.westos.org/westos/game2048
imagePullSecrets:
- name: myregistrykey
[root@Server2 Secret]# vim TestPod.yaml
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl apply -f TestPod.yaml
pod/game2048 created
[root@Server2 Secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
game2048 1/1 Running 0 6s
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 17h
mysecret 1/1 Running 0 13m
secret-env 1/1 Running 0 9m58s
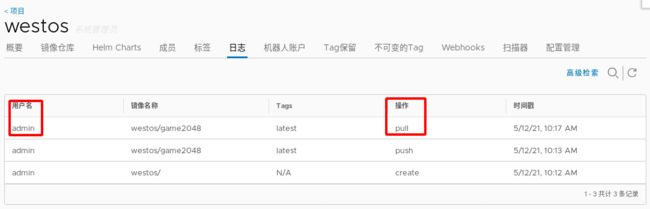
- 查看私有仓库日志, 可以看到一条登录后的
pull, 证明mypod确实用到了引入的认证
Volumes配置管理
- 默认情况下, 容器中的文件是临时存放在磁盘上的
- 如果容器崩溃,
kubelet将尝试重启容器, 容器重建后恢复初始状态, 而这将导致容器内的文件丢失 - 而且在生产环境中, 一个
Pod内经常存在多个容器, 各个容器间还需要共享文件/资源
这些问题该如何解决
K8S中的卷具有明确的生命周期, 与包裹它的Pod相同.
这也就意味着, 卷比Pod中运行的任何容器的存活时间都要长.这样即使容器重建, 数据也不会丢失.
当然, 如果Pod被摧毁, 卷自然也就不复存在了.
卷不能挂载到其他卷, 也不能与其他卷有硬链接. Pod 中的每个容器必须独立地指定每个卷的挂载位置.
emptyDir卷
Pod被调度到某一节点后, 首先会创建一个emptyDir卷- 只要
Pod不被调度到其他节点, 该emptyDir卷就会一直存在 - 之所以叫
emptyDir, 是因为在建立时卷最初是空的 Pod中的各个容器都可以挂载这个emptyDir卷, 即使挂载的路径不同也不影响对于emptyDir卷中文件的读写- 当
Pod被从节点上调度走/删除时,emptyDir卷中的数据也会被删除
使用场景
-
缓存空间, 例如基于磁盘的归并排序.
-
为耗时较长的计算任务提供检查点, 以便任务能方便地从崩溃前状态恢复执行.
-
在 Web 服务器容器服务数据时, 保存内容管理器容器获取的文件.
默认情况下, emptyDir卷使用固态硬盘/磁盘/网络存储进行数据存储, 但可以通过将emptyDir.medium字段设置为Memory,以告诉 Kubernetes为您安装tmpfs(基于内存的文件系统)
需要注意的是虽然tmpfs速度非常快, 但是要注意它与磁盘不同. tmpfs在节点重启时会被清除, 并且您所写入的所有文件都会计入容器的内存消耗, 受容器内存限制约束
emptyDir示例
MemoryType.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol1
spec:
containers:
- image: busyboxplus
name: vm1
command: ["sleep", "300"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /cache
name: cache-volume
- name: vm2
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: cache-volume
volumes:
- name: cache-volume
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 100Mi
- 实验流程
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl apply -f MemoryType.yaml
pod/vol1 created
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h
vol1 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 3s
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h
vol1 2/2 Running 0 7s
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl describe pod vol1
Name: vol1
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: server4/172.25.5.4
Start Time: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:07:00 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: cni.projectcalico.org/podIP: 10.244.22.11/32
cni.projectcalico.org/podIPs: 10.244.22.11/32
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.22.11
IPs:
IP: 10.244.22.11
Containers:
vm1:
Container ID: docker://c07a426ba156670207c5dbd6a5a279691cbf10164b5ac6b5a5803f2998bc037b
Image: busyboxplus
Image ID: docker-pullable://busyboxplus@sha256:9d1c242c1fd588a1b8ec4461d33a9ba08071f0cc5bb2d50d4ca49e430014ab06
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
sleep
300
State: Running
Started: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:07:02 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/cache from cache-volume (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-sp8tb (ro)
vm2:
Container ID: docker://37870d781896e385d006f0d26ab90344e3f2762ac168ddc5cad66520d3351f88
Image: nginx
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:42bba58a1c5a6e2039af02302ba06ee66c446e9547cbfb0da33f4267638cdb53
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:07:03 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/usr/share/nginx/html from cache-volume (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-sp8tb (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
cache-volume:
Type: EmptyDir (a temporary directory that shares a pod's lifetime)
Medium: Memory
SizeLimit: 100Mi
kube-api-access-sp8tb:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 21s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/vol1 to server4
Normal Pulling 19s kubelet Pulling image "busyboxplus"
Normal Pulled 19s kubelet Successfully pulled image "busyboxplus" in 172.941458ms
Normal Created 19s kubelet Created container vm1
Normal Started 19s kubelet Started container vm1
Normal Pulling 19s kubelet Pulling image "nginx"
Normal Pulled 19s kubelet Successfully pulled image "nginx" in 143.30415ms
Normal Created 18s kubelet Created container vm2
Normal Started 18s kubelet Started container vm2
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h 10.244.141.205 server3 <none> <none>
vol1 2/2 Running 0 42s 10.244.22.11 server4 <none> <none>
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl exec -it vol1 -c vm1 -- sh
/ # cd /cache/
/cache # ls
/cache # echo www.westos.org > index.html
/cache # cat index.html
www.westos.org
/cache # curl localhost
www.westos.org
vm1和vm2同用一个emptyDir卷, 在vm1中创建文件并访问locolhost, curl正确返回; vm2的nginx也正确接受了发布页面
缺点
- 不能及时禁止用户使用内存. 虽然过1-2分钟
kubelet会将Pod挤出, 但是这个时间内,Node一就要承担风险 - 会影响
K8S调度, 因为emptyDir并不涉及Node的resources, 这样会造成Pod“偷偷”使用了Node的内存, 但是调度器并不知晓, 用户y也不能及时感知到内存不可用
hostPath卷
- 主要作用是能将主机节点文件目录的文件/目录挂载进
Pod - 虽然并不是大多数
Pod的需求, 但却是可以为一些应用服务提供强大的逃生舱
使用场景
- 运行一个需要访问
Docker引擎内部机制的容器,挂载/var/lib/docker路径 - 在容器中运行
cAdvisor时, 以hostPath方式挂载/sys - 允许
Pod指定给定的hostPath在运行Pod之前是否应该存在, 是否应该创建以及应该以什么方式存在
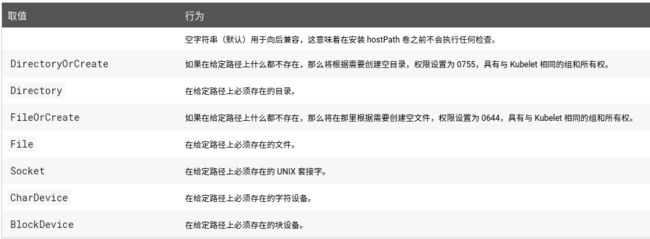
除了必需的path属性之外, 用户可以选择性地为hostPath卷指定type
注意事项
-
具有相同配置(例如从
podTemplate创建)的多个Pod会由于节点上文件的不同而在不同节点上有不同的行为 -
当
Kubernetes按照计划添加资源感知的调度时, 这类调度机制将无法考虑由hostPath使用的资源 -
基础主机上创建的文件或目录只能由
root用户写入. 您需要在 特权容器 中以root身份运行进程, 或者修改主机上的文件权限以便容器能够写入hostPath卷 -
HostPath.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pd
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: test-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /test-pd
name: test-volume
volumes:
- name: test-volume
hostPath:
path: /data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
- 实验操作流程
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl apply -f HostPath.yaml
pod/test-pd created
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h
test-pd 1/1 Running 0 5s
vol1 2/2 Running 1 8m12s
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl exec -it test-pd -- sh
# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
overlay 17811456 3496292 14315164 20% /
tmpfs 65536 0 65536 0% /dev
tmpfs 507372 0 507372 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/rhel-root 17811456 3496292 14315164 20% /test-pd
shm 65536 0 65536 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 507372 12 507360 1% /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
tmpfs 507372 0 507372 0% /proc/acpi
tmpfs 507372 0 507372 0% /proc/scsi
tmpfs 507372 0 507372 0% /sys/firmware
# cd /test-pd
# ls
# exit
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl describe pod test-pd
Name: test-pd
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: server3/172.25.5.3
Start Time: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:15:06 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: cni.projectcalico.org/podIP: 10.244.141.208/32
cni.projectcalico.org/podIPs: 10.244.141.208/32
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.141.208
IPs:
IP: 10.244.141.208
Containers:
test-container:
Container ID: docker://91534a1a06226d91272c431b8ad1be8eea2890d16804483639ac5f9a5b122035
Image: nginx
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:42bba58a1c5a6e2039af02302ba06ee66c446e9547cbfb0da33f4267638cdb53
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:15:08 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/test-pd from test-volume (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-6g66k (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
test-volume:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /data
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
kube-api-access-6g66k:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 108s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/test-pd to server3
Normal Pulling 108s kubelet Pulling image "nginx"
Normal Pulled 108s kubelet Successfully pulled image "nginx" in 148.025546ms
Normal Created 108s kubelet Created container test-container
Normal Started 107s kubelet Started container test-container
NFS挂载
NFS.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-nfs
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: test-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: test-volume
volumes:
- name: test-volume
nfs:
server: 172.25.5.2
path: /NFS
- 实验操作流程
##首先在所有需要用到NFS和提供NFS的节点安装nfs-utils
[root@Server2 Volumes]# yum install nfs-utils
##在NFS服务端创建共享目录并创建规则
[root@Server2 Volumes]# mkdir -m 777 /NFS
[root@Server2 Volumes]# vim /etc/exports
/NFS *(rw,sync,no_root_squash)
[root@Server2 Volumes]# systemctl enable --now rpcbind
[root@Server2 Volumes]# systemctl enable --now nfs
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service.
[root@Server2 Volumes]# cd /NFS/
[root@Server2 Volumes]# echo www.westos.org > index.html
[root@Server2 Volumes]# ssh Server3 yum install nfs-utils -y
[root@Server2 Volumes]# ssh Server4 yum install nfs-utils -y
##实验流程
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl apply -f NFS.yaml
pod/test-nfs created
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h
test-nfs 1/1 Running 0 3s
vol1 2/2 Running 3 20m
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl describe pod test-nfs
Name: test-nfs
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: server3/172.25.5.3
Start Time: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:27:17 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: cni.projectcalico.org/podIP: 10.244.141.209/32
cni.projectcalico.org/podIPs: 10.244.141.209/32
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.141.209
IPs:
IP: 10.244.141.209
Containers:
test-container:
Container ID: docker://cde7eee713b2ead825af1ddb3f0a3ef6b6077dd12dee55dea4a5f2188663536f
Image: nginx
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:42bba58a1c5a6e2039af02302ba06ee66c446e9547cbfb0da33f4267638cdb53
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Wed, 12 May 2021 11:27:19 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/usr/share/nginx/html from test-volume (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-75w98 (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
test-volume:
Type: NFS (an NFS mount that lasts the lifetime of a pod)
Server: 172.25.5.2
Path: /NFS
ReadOnly: false
kube-api-access-75w98:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 10s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/test-nfs to server3
Normal Pulling 9s kubelet Pulling image "nginx"
Normal Pulled 8s kubelet Successfully pulled image "nginx" in 163.869214ms
Normal Created 8s kubelet Created container test-container
Normal Started 8s kubelet Started container test-container
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
my-nginx-759cdbfbdc-f6jx8 1/1 Running 1 18h 10.244.141.205 server3 <none> <none>
test-nfs 1/1 Running 0 41s 10.244.141.209 server3 <none> <none>
vol1 1/2 CrashLoopBackOff 3 20m 10.244.22.11 server4 <none> <none>
##可以看到Pod被调度到了server3上
##跳转到server3检查挂载情况
[root@Server3 ~]# mount | grep NFS
172.25.5.2:/NFS on /var/lib/kubelet/pods/dce71d95-0de0-4930-9ebb-13741ef5081a/volumes/kubernetes.io~nfs/test-volume type nfs4 (rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=172.25.5.3,local_lock=none,addr=172.25.5.2)
##进入Pod内部进行发布页访问测试
[root@Server2 Volumes]# kubectl exec -it test-nfs -- sh
# ls
bin docker-entrypoint.d home media proc sbin tmp
boot docker-entrypoint.sh lib mnt root srv usr
dev etc lib64 opt run sys var
# curl localhost
www.westos.org
PV 持久卷
PersistentVolume(持久卷, 简称PV)是集群内, 由管理员提供的网络存储的一部分.
就像集群中的节点一样, PV也是集群中的一种资源.
像Volume一样, 是一种volume插件, 但是它的生命周期却是和使用它的Pod相互独立的.
PV这个API对象, 捕获了诸如NFS, ISCSI, 或其他云存储系统的实现细节.
也就是说, 可以使用网络存储来创建PV, 并且能实现持久化存储
PersistentVolumeClaim(持久卷声明, 简称PVC)是用户的一种存储请求.
和Pod类似, Pod消耗Node资源, 而PVC消耗PV资源.
Pod能够请求特定的资源(如CPU和内存). PVC能够请求指定的大小和访问的模式(可以被映射为一次读写或者多次只读).
两种PV提供方式
静态PV: 集群管理员创建多个PV, 它们携带着真实存储的详细信息, 这些存储对于集群用户是可用的. 它们存在于Kubernetes API中, 并可用于存储使用.
动态PV: 当管理员创建的静态PV都不匹配用户的PVC时, 集群可能会尝试专门地供给volume给PVC. 这种供给基于StorageClass.
PVC与PV的绑定是一对一的映射.
如果找不到匹配的PV, PVC会无限期得处于unbound(未绑定)状态.
使用说明
使用
Pod使用PVC就像使用volume一样- 集群检查
PVC, 查找绑定的PV, 检查到后映射PV给Pod - 对于支持多种访问模式的
PV, 用户可以指定想用的模式 - 一旦用户拥有了一个
PVC, 并且PVC被绑定, 那么只要用户还需要,PV就一直属于这个用户 - 当用户调度
Pod时, 通过在Pod的volume块中包含PVC来访问PV
释放
- 当用户使用
PV完毕后, 他们可以通过API来删除PVC对象 - 当
PVC被删除后, 对应的PV状态会变更为released, 但仍不能再给另外一个PVC使用 - 前一个
PVC的关联关系还存在于该PV中, 必须根据策略来处理掉 - 根据策略处理完成后, 就可以提供给新的
PVC使用了
回收
PV回收策略的作用在于, 在PV被释放之后集群应该如何处理该PV- 目前支持被Retained(保留), Recycled(再利用)或者Deleted(删除)三种处理方式
- 对于支持删除操作的
PV卷, 删除操作会从Kubernetes中移除PV对象, 还有对应的外部存储(如AWS EBS, GCE PD, Azure Disk, 或者Cinder volume). 动态供给的卷总是会被删除.
访问模式
| 参数 | 模式 |
|---|---|
| ReadWriteOnce | 该volume只能被单个节点以读写的方式映射 |
| ReadOnlyMany | 该volume可以被多个节点以只读方式映射 |
| ReadWriteMany | 该volume可以被多个节点以读写的方式映射 |
在命令行中可以使用简写
| 简写 | 全称 |
|---|---|
| RWO | ReadWriteOnce |
| ROX | ReadOnlyMany |
| RWX | ReadWriteMany |
回收策略
| 参数 | 策略含义 |
|---|---|
| Retain | 保留, 需要手动回收 |
| Recycle | 回收, 自动删除卷中数据 |
| Delete | 删除, 相关联的存储资产/卷都会被删除 |
当前, 只有NFS和HostPath支持回收利用
常见的云计算存储, 如AWS EBS, GCE PD, Azure Disk, OpenStack Cinder卷支持删除操作
PV.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: nfs
mountOptions:
- hard
- nfsvers=4.1
nfs:
path: /NFS
server: 172.25.5.2
- 实验操作流程
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl apply -f PV.yaml
persistentvolume/pv1 created
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pv1 1Gi RWO Recycle Available nfs 5s
PVC.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc1
spec:
storageClassName: nfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
- 实验操作流程
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl apply -f PVC.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc1 created
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc1 Bound pv1 1Gi RWO nfs 8s
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pv1 1Gi RWO Recycle Bound default/pvc1 nfs 2m54s
可以看到PV的状态改变了
-
创建
Pod并挂载PV -
Pod.yaml内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod1
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: pv1
volumes:
- name: pv1
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc1
- 实验操作流程
##之前已经在NFS共享目录中放过发布文件了
##创建Pod
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl apply -f Pod.yaml
pod/pod1 created
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod1 1/1 Running 0 5s
##测试发布情况
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl exec -it pod1 -- bash
root@pod1:/# curl localhost
www.westos.org
##使用ClusterIP进行测试
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod1 1/1 Running 0 2m22s 10.244.141.210 server3 <none> <none>
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# curl 10.244.141.210
www.westos.org
##删除Pod不会影响PV和PVC的状态, 确实做到了持续化存储
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl delete -f Pod.yaml
pod "pod1" deleted
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pod
No resources found in default namespace.
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pv1 1Gi RWO Recycle Bound default/pvc1 nfs 8m55s
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc1 Bound pv1 1Gi RWO nfs 6m32s
由此可见, 做到了集群内部可访问
删除Pod后, PVC和PV依然存在
删除PVC, PV状态转变为Released
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl delete -f PVC.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim "pvc1" deleted
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pvc
No resources found in default namespace.
[root@Server2 PersistentVolume]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pv1 1Gi RWO Recycle Released default/pvc1 nfs 10m
上述的方法都是**静态PV**的范畴, 依旧存在实用性上的问题
- 每次使用
PVC就得手动创建PV, 这不合适 - 各种应用对
PV的需求不同, 有的要求高并发有的要求高读写, 手动来挨个分配显然是不现实的 - 对于
StatefulSet类型的应用, 简单的来使用静态的PV也很不合适
因此需要使用 **动态PV**来实现自动分配, 这就涉及StorageClass了
StorageClass
StorageClass提供了一种描述存储类(class)的方法, 不同的class可能会映射到不同的服务质量等级和备份策略或其他策略等.
每个StorageClass都包含provisioner, parameters和reclaimPolicy字段, 这些字段会在StorageClass需要动态分配 PersistentVolume时会使用到.
属性
Provisioner(存储分配器)
- 决定使用哪个卷插件分配
PV, 该字段必须指定 - 可以指定内部分配器, 也可以指定外部分配器
- 外部分配器的代码地址为
kubernetes-incubator/external-storage, 其中包括NFS和Ceph等 Ceph是目前也比较流行
Reclaim Policy(回收策略)
reclaimPolicy字段用于指定创建的Persistent Volume的回收策略, 回收策略包括:Delete或者Retain- 当没有指定回收策略时默认为
Delete
NFS Client Provisioner是一个automatic provisioner, 使用NFS作为存储, 自动创建PV和对应的PVC
本身不提供NFS存储, 需要外部先有一套NFS存储服务
PV以${namespace}-${pvcName}-${pvName}的命名格式提供
PV回收的时候以archieved-${namespace}-${pvcName}-${pvName}的命名格式存储
NFS动态分配PV示例
nfs-client-provisioner.yaml文件内容- 包含对于
SA,RBAC,SC的创建
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.0
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: westos.org/nfs
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 172.25.5.2
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /NFS
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 172.25.5.2
path: /NFS
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
provisioner: westos.org/nfs
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true"
- 测试用的
PVC.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc1
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "managed-nfs-storage"
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc2
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "managed-nfs-storage"
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadOnlyMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc3
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "managed-nfs-storage"
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 3Gi
- 实验测试流程
[root@Server2 mnt]# mkdir StorageClass
[root@Server2 mnt]# cd StorageClass/
##创建实验用的Namespace
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl create ns nfs-client-provisioner
namespace/nfs-client-provisioner created
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 28h
ingress-nginx Active 27h
kube-node-lease Active 28h
kube-public Active 28h
kube-system Active 28h
metallb-system Active 27h
nfs-client-provisioner Active 4s
- 创建
StorageClass并进行RBAC授权
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# vim nfs-client-provisioner.yaml
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl apply -f nfs-client-provisioner.yaml
serviceaccount/nfs-client-provisioner created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nfs-client-provisioner-runner created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/run-nfs-client-provisioner created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner created
deployment.apps/nfs-client-provisioner created
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/managed-nfs-storage created
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
managed-nfs-storage westos.org/nfs Delete Immediate false 11s
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl -n nfs-client-provisioner get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nfs-client-provisioner-dbd6bcd94-4h6xh 1/1 Running 0 43s
- 创建
PVC并进行测试
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# vim PVC.yaml
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl apply -f PVC.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc1 created
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc1 Bound pvc-ae2cf8bc-3258-4eaf-a92e-6690bc65db3f 1Gi RWX managed-nfs-storage 11s
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-ae2cf8bc-3258-4eaf-a92e-6690bc65db3f 1Gi RWX Delete Bound default/pvc1 managed-nfs-storage 35s
##可以看到创建PVC时,自动创建了PV并绑定
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl delete -f PVC.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim "pvc1" deleted
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pvc
No resources found in default namespace.
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pv
No resources found
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# ls /NFS/
archived-pvc-ae2cf8bc-3258-4eaf-a92e-6690bc65db3f
##删除PVC时,PV也自动销毁
##同时在NFS主机的目录下自动完成打包
- 尝试批量创建
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# vim PVC.yaml
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl apply -f PVC.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc1 created
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc2 created
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc3 created
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc1 Bound pvc-550246e2-5ecc-4bee-a98b-e1cb00fc0a02 1Gi RWX managed-nfs-storage 4s
pvc2 Bound pvc-34bc7e52-3277-461a-8628-ec694f2b51cd 2Gi ROX managed-nfs-storage 4s
pvc3 Bound pvc-07e73d54-5101-4107-b84d-9fb0d583a1c4 3Gi RWO managed-nfs-storage 4s
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-07e73d54-5101-4107-b84d-9fb0d583a1c4 3Gi RWO Delete Bound default/pvc3 managed-nfs-storage 7s
pvc-34bc7e52-3277-461a-8628-ec694f2b51cd 2Gi ROX Delete Bound default/pvc2 managed-nfs-storage 7s
pvc-550246e2-5ecc-4bee-a98b-e1cb00fc0a02 1Gi RWX Delete Bound default/pvc1 managed-nfs-storage 7s
- 创建测试
Pod - 测试用的
Pod.yaml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-pod
image: busyboxplus
command:
- "/bin/sh"
args:
- "-c"
- "touch /mnt/SUCCESS && exit 0 || exit 1"
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-pvc
mountPath: "/mnt"
restartPolicy: "Never"
volumes:
- name: nfs-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc1
- 测试流程
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# vim Pod.yaml
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pod -n nfs-client-provisioner
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nfs-client-provisioner-dbd6bcd94-4h6xh 1/1 Running 0 15m
test-pod 0/1 Pending 0 2m23s
##因为没有绑定SC因此会Pending
##这里为managed-nfs-storage添加默认属性, 这样即使不绑定SC也会使用默认的
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl patch storageclass managed-nfs-storage -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/managed-nfs-storage patched
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
managed-nfs-storage (default) westos.org/nfs Delete Immediate false 16m
总结上面的问题
- 当
PVC不设定SC, 且没有默认的SC时, 会无法动态分配资源 - 只能有一个默认
StorageClass - 默认的
StorageClass将被用于动态的为没有特定SC需求的PersistentVolumeClaims配置存储
设置方法
##交互式
kubectl patch storageclass <SC名称> -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
##配置文件中直接添加
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
annotations:
"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "true"
provisioner: westos.org/nfs
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true"
既然刚才已经指定了default, 现在不附加annotations创建PVC4试试
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl apply -f DefaultCheck.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc4 created
[root@Server2 StorageClass]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc4 Bound pvc-b08608ad-c7a4-4c4f-a528-c0a53f90aa3d 4Gi RWO managed-nfs-storage 5s
可以看到, PVC4也绑定到了默认的sc: managed-nfs-storage上
StatefulSet控制器
在集群中, Pod可能会迁移, 如何保证稳定存储和网络标识就是一种客观需求了
StatefulSet控制器可以通过Headless Service维持Pod的拓扑状态
- 净化环境并开辟新目录
kubectl delete -f [需要删除的]
- 创建无头服务
Headless service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-svc
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
- 创建需要的
StatefulSet控制器
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "nginx-svc"
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
apiVersion: apps/v1
- 环境部署结束
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2d20h
nginx-svc ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 14s
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
web-0 1/1 Running 0 7s 10.244.1.122 server2
web-1 1/1 Running 0 6s 10.244.2.113 server3
web-2 1/1 Running 0 5s 10.244.0.62 server1
StatefulSet将应用状态抽象成了两种情况
拓扑状态: 应用实例必须按照某种顺序启动. 新创建的Pod必须和原来Pod的网络标识一样
存储状态: 应用的多个实例分别绑定了不同存储数据
StatefulSet给所有的Pod进行了编号, 编号规则是$(statefulset名称)-$(序号), 从0开始
这也是上面kubectl get pod看到名称的原因
Pod被删除后重建, 重建Pod的网络标识也不会改变,Pod的拓扑状态按照Pod的名字+编号的方式固定下来,并且为每个Pod提供了一个固定且唯一的访问入口, 即Pod对应的DNS记录.
##查看内部DNS解析
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# dig -t A web-0.nginx-svc.default.svc.cluster.local
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
web-0 1/1 Running 0 21m 10.244.1.122 server2
web-1 1/1 Running 0 2m21s 10.244.2.114 server3
web-2 1/1 Running 0 21m 10.244.0.62 server1
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# kubectl delete pod --all
pod "web-0" deleted
pod "web-1" deleted
pod "web-2" deleted
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
web-0 1/1 Running 0 16s 10.244.1.123 server2
web-1 1/1 Running 0 14s 10.244.2.115 server3
web-2 1/1 Running 0 12s 10.244.0.63 server1
##会发现解析依旧存在
[root@Server2 StatefulSet]# dig -t A web-0.nginx-svc.default.svc.cluster.local
又因为PV和PVC的设计属性, 使得StatefulSet对存储状态的管理成为了可能
- 根据
StatefulSet的属性要求, 上上一个Pod创建成功就绪前, 不会创建下一个Pod StatefulSet还会为每一个Pod分配并创建一个同样编号的PVC- 通过这种方式, 就可以通过
Persistent Volume机制为这个PVC绑定对应的PV, 从而保证每一个Pod都拥有一个独立的Volume
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "nginx-svc"
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
storageClassName: nfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
注意事项
尽管StatefulSet创建时有序, 但如果使用kubectel delete则不会遵循顺序
因此想要删除Pod时应当使用弹缩的方式来改变副本数
Kubectl弹缩
首先,想要弹缩的StatefulSet. 需先清楚是否能弹缩该应用
kubectl get statefulsets <stateful-set-name>
改变StatefulSet副本数量
kubectl scale statefulsets <stateful-set-name> --replicas=<new-replicas>
资源清单相关方式
如果是通过资源清单方式创建的, 就更简单了, 只需要更改replicas的value后重新kubectl apply即可
也可以通过命令kubectl edit直接编辑该字段
kubectl edit statefulsets <stateful-set-name>
使用Kubectl Patch
kubectl patch statefulsets <stateful-set-name> -p '{"spec":{"replicas":}}'