Python 正则表达式大全
1 前言
正则表达式是对字符串(包括普通字符(例如,a 到 z 之间的字母)和特殊字符(称为“元字符”))操作的一种逻辑公式,就是用事先定义好的一些特定字符、及这些特定字符的组合,组成一个“规则字符串”,这个“规则字符串”用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。正则表达式是一种文本模式,该模式描述在搜索文本时要匹配的一个或多个字符串。
上面都是官方的说明,博主自己的理解是(仅供参考):通过事先规定好一些特殊字符的匹配规则,然后利用这些字符进行组合来匹配各种复杂的字符串场景。比如现在的爬虫和数据分析,字符串校验等等都需要用到正则表达式来处理数据。
python的正则表达式则是re模块了:
-
re 模块使 Python 语言拥有全部的正则表达式功能。
-
re 模块也提供了与这些方法功能完全一致的函数,这些函数使用一个模式字符串做为它们的第一个参数。
2 基本语法
2.1 match函数
只从字符串的最开始与pattern进行匹配,下面是函数的语法 :
re.match(pattern, string, flags = 0)
这里是参数的描述 :
- p attern - 这是要匹配的正则表达式。
- string - 这是字符串,它将被搜索用于匹配字符串开头的模式。
- flags - 可以使用按位OR(|)指定不同的标志。这些是修饰符,如下表所列。
- re.match 函数在成功时返回匹配对象,失败时返回None。使用match(num)或groups函数匹配对象来获取匹配的表达式。
示例
#未从初始位置匹配,会返回None import re line = ‘i can speak good english’matchObj = re.match(r’s(w*)s(w*).*’,line)if matchObj:print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group)print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(1))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(2))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(3))else:print(‘no match!’)
#从初始位置开始匹配import re line = ‘i can speak good english’matchObj = re.match(r’(i)s(w*)s(w*).*’,line)if matchObj:print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group)print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(1))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(2))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(3))else:print(‘no match!’)
2.2 search 函数
与match工作的方式一样,但是search不是从最开始匹配的,而是从任意位置查找第一次匹配的内容。下面是这个函数的语法 :
re.match(pattern, string, flags = 0)
这里是参数的描述 :
- pattern - 这是要匹配的正则表达式。
- string - 这是字符串,它将被搜索用于匹配字符串开头的模式。
- flags - 可以使用按位OR(|)指定不同的标志。这些是修饰符,如下表所列。
- re.search函数在成功时返回匹配对象,否则返回None。使用match对象的group(num)或groups函数来获取匹配的表达式。最后,如果你的时间不是很紧张,并且又想快速的python提高,最重要的是不怕吃苦,建议你可以架微♥信:762459510 ,那个真的很不错,很多人进步都很快,需要你不怕吃苦哦!大家可以去添加上看一下~
示例
import re line = ‘i can speak good english’matchObj = re.search(’(.) (.?) (.*)’,line)if matchObj:print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group)print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(1))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(2))print(‘matchObj.group :’,matchObj.group(3))else:print(‘no match!’)
2.3 sub 函数
使用正则表达式re模块中的最重要的之一是sub。
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, max=0)
此方法使用repl替换所有出现在RE模式的字符串,替换所有出现,除非提供max。此方法返回修改的字符串。
示例
import re line = ‘i can speak good english’speak = re.sub(r’can’,‘not’,line)print(speak)speak1 = re.sub(r’s’,’’,line) #替换所有空格print(speak1)
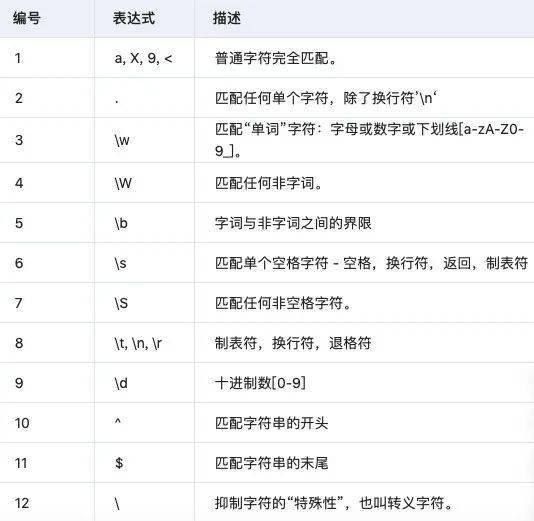
3 特殊类语法
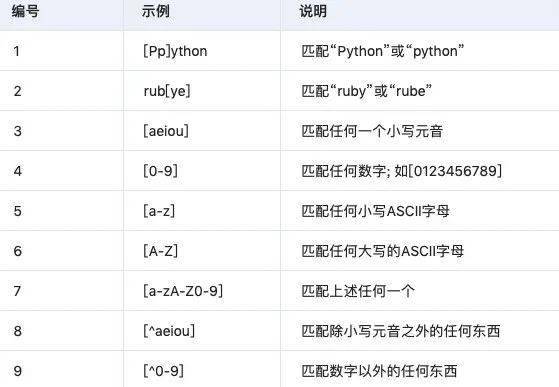
3.1 字符类
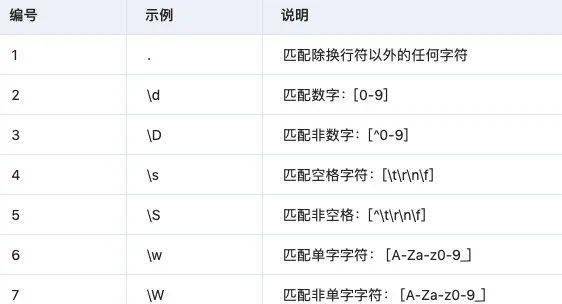
3.2 特殊字符类
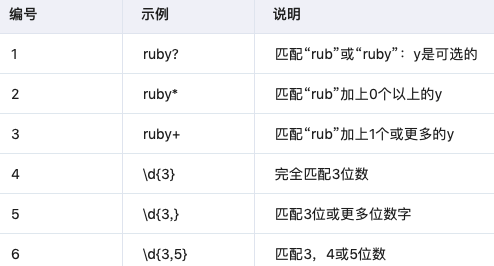
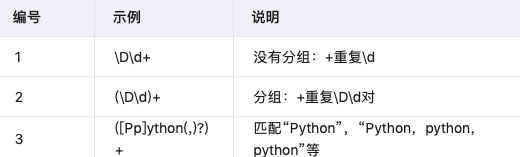
3.3 重复匹配
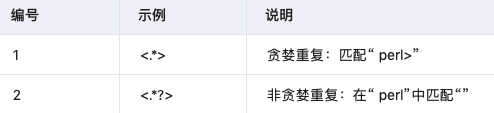
3.4 非贪婪重复
这匹配最小的重复次数:
3.5 圆括号分组
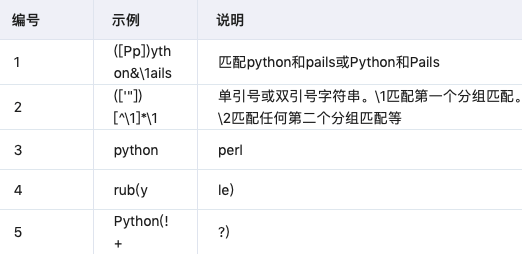
3.6 反向引用
与以前匹配的组再次匹配
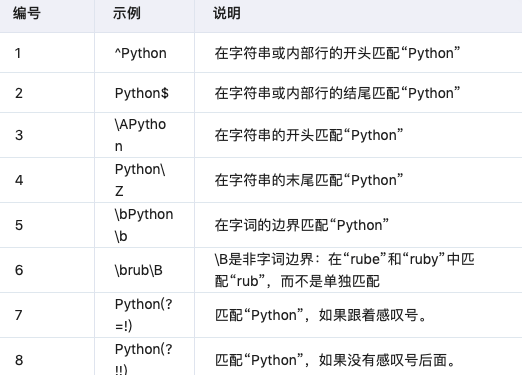
3.7 锚点
需要指定匹配位置。
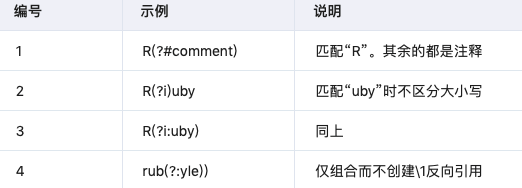
3.8 带括号的特殊语法
python福利教程领取方式:
1、点赞+评论(勾选“同时转发”)
2、关注小编。并私信回复关键字【19】
(一定要私信哦~点击我的头像就能看到私信按钮了)