Spark源码阅读02-Spark核心原理之消息通信原理
Spark消息通信架构
在Spark中定义了通信框架接口,这些接口实现中调用了Netty的具体方法。通信框架使用了工厂设计模式,这种模式实现了对Netty的解耦,能够根据需要引入其他的消息通信工具。
Spark消息通信类图如下:

通信框架在上图中虚线的部分。其具体实现步骤为:
- ①定义RpcEnv和RpcEnvFactory两个抽象类,其中在RpcEnv中定义了RPC通信框架启动、停止和关闭等抽象方法;在RpcEnvFactory中定义了创建抽象方法
- ②在NettyRpcEnv和NettyRpcEnvFactory类中使用了Netty对继承的方法进行了实现
- ③在RpcEnv的object类中通过反射方法实现了创建RpcEnv的实例静态方法
上述Spark消息类图中各模块使用流程:
- ①使用RpcEnv的静态方法创建RpcEnv实例,实例化Master
- ②调用RpcEnv启动终端点方法,把Master的终端点和其对应的引用注册到RpcEnv中
- ③若其他对象获取了Master终端点的引用,就能够发消息给Master进行通信了。
Spark启动消息通信
Spark启动过程中主要是Master与Worker之间的通信。其过程如下:
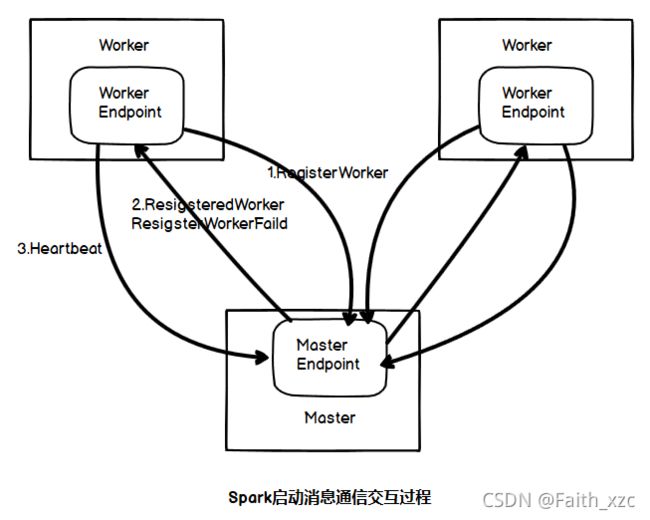
其详细过程及源代码如下:
(1)Work向Master发送注册Worker的消息
private def registerWithMaster() {
// onDisconnected may be triggered multiple times, so don't attempt registration
// if there are outstanding registration attempts scheduled.
registrationRetryTimer match {
case None =>
...
registerMasterFutures = tryRegisterAllMasters()
...
}
/
private def tryRegisterAllMasters(): Array[JFuture[_]] = {
...
//获取Master终端点的引用
val masterEndpoint = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(masterAddress, Master.ENDPOINT_NAME)
//调用sendRegisterMessageToMaster方法注册消息
sendRegisterMessageToMaster(masterEndpoint)
...
}
/
private def sendRegisterMessageToMaster(masterEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef): Unit = {
masterEndpoint.send(RegisterWorker(
workerId,
host,
port,
self,
cores,
memory,
workerWebUiUrl,
masterEndpoint.address))
}
/
case class RegisterWorker(
id: String,
host: String,
port: Int,
worker: RpcEndpointRef,
cores: Int,
memory: Int,
workerWebUiUrl: String,
masterAddress: RpcAddress)
extends DeployMessage {
Utils.checkHost(host)
assert (port > 0)
}
(2)Master收到消息后,需要对Worker发送的消息进行验证、记录。如果注册成功,发送注册成功消息;否则发送注册失败消息。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
...
case RegisterWorker(
...
//Master处于STANDBY状态,返回“MASTER处于STANDBY状态”
if (state == RecoveryState.STANDBY) {
workerRef.send(MasterInStandby)
} else if (idToWorker.contains(id)) {
workerRef.send(RegisterWorkerFailed("Duplicate worker ID"))
} else {
val worker = new WorkerInfo(id, workerHost, workerPort, cores, memory,
workerRef, workerWebUiUrl)
//registerWorker方法中注册Worker,该方法中会把Worker放到列表中
//用于后续运行任务时使用
if (registerWorker(worker)) {
persistenceEngine.addWorker(worker)
workerRef.send(RegisteredWorker(self, masterWebUiUrl, masterAddress))
schedule()
} else {
val workerAddress = worker.endpoint.address
logWarning("Worker registration failed. Attempted to re-register worker at same " +
"address: " + workerAddress)
workerRef.send(RegisterWorkerFailed("Attempted to re-register worker at same address: "
+ workerAddress))
}
}
...
}
(3)当Worker接受到注册后,会定时发送心跳信息Heartbeat给Master,使得Master能了解Worker的实时状态。
private def handleRegisterResponse(msg: RegisterWorkerResponse): Unit = synchronized {
msg match {
case RegisteredWorker(masterRef, masterWebUiUrl, masterAddress) =>
if (preferConfiguredMasterAddress) {
logInfo("Successfully registered with master " + masterAddress.toSparkURL)
} else {
logInfo("Successfully registered with master " + masterRef.address.toSparkURL)
}
....
//如果设置清理以前应用使用的文件夹,则进行该动作
if (CLEANUP_ENABLED) {
logInfo(
s"Worker cleanup enabled; old application directories will be deleted in: $workDir")
forwordMessageScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
self.send(WorkDirCleanup)
}
}, CLEANUP_INTERVAL_MILLIS, CLEANUP_INTERVAL_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
//向Master汇报Worker中Executor最新状态
val execs = executors.values.map {
e =>
new ExecutorDescription(e.appId, e.execId, e.cores, e.state)
}
masterRef.send(WorkerLatestState(workerId, execs.toList, drivers.keys.toSeq))
case RegisterWorkerFailed(message) =>
if (!registered) {
logError("Worker registration failed: " + message)
System.exit(1)
}
case MasterInStandby =>
// Ignore. Master not yet ready.
}
}
/
private[deploy] object DeployMessages {
...
case object SendHeartbeat
}
Spark运行时消息消息通信
Spark运行消息通信的交互过程如下图:
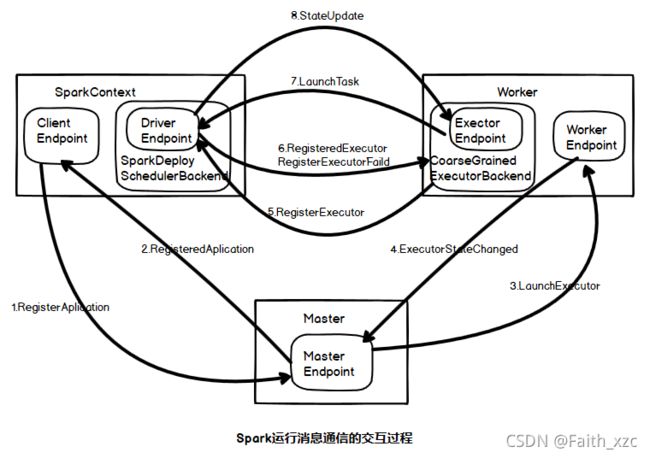
其详细过程及源代码如下:
(1)执行应用程序需要启动SparkContext,在SparkContext的启动过程中,会先实例化SchedulerBackend对象(上图中创建的是SparkDeploySchedulerBackend对象,因为是独立运行模式),在该对象的启动中会继承DriverEndpoint和创建Appclient的ClientEndpoint的两个终端点。
在ClientEndpoint的tryRegisterAllMasters方法中创建注册线程池registerMasterThreadPool,在该线程池中启动注册线程并向Master发送RegisterApplication注册应用的消息。
private def tryRegisterAllMasters(): Array[JFuture[_]] = {
//由于HA等环境有多个Master,需要遍历所有的Master发送消息
for (masterAddress <- masterRpcAddresses) yield {
//向线程池中启动注册线程,当该线程读到应用注册成功标志registered=ture时,退出注册线程
registerMasterThreadPool.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = try {
if (registered.get) {
return
}
logInfo("Connecting to master " + masterAddress.toSparkURL + "...")
//获取Master终端点的引用,发送注册应用的消息
val masterRef = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(masterAddress, Master.ENDPOINT_NAME)
masterRef.send(RegisterApplication(appDescription, self))
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // Cancelled
case NonFatal(e) => logWarning(s"Failed to connect to master $masterAddress", e)
}
})
}
}
当Master接收到注册应用的消息时,在registerApplication方法中记录应用消息并把该消息加入到等待运行应用列表中,注册完毕发送RegisteredApplication给ClientEndpoint,同时调用startExecutorOnWorker方法运行应用,通知Worker启动Executor。
private def startExecutorsOnWorkers(): Unit = {
// Right now this is a very simple FIFO scheduler. We keep trying to fit in the first app
// in the queue, then the second app, etc.
//使用FIFO调度算法运行应用,先注册的应用先运行
for (app <- waitingApps) {
val coresPerExecutor = app.desc.coresPerExecutor.getOrElse(1)
// If the cores left is less than the coresPerExecutor,the cores left will not be allocated
if (app.coresLeft >= coresPerExecutor) {
// Filter out workers that don't have enough resources to launch an executor
val usableWorkers = workers.toArray.filter(_.state == WorkerState.ALIVE)
.filter(worker => worker.memoryFree >= app.desc.memoryPerExecutorMB &&
worker.coresFree >= coresPerExecutor)
.sortBy(_.coresFree).reverse
//确定运行在哪些Worker上和每个Worker分配用于运行的核数,分配算法有两种,一种时把应用
//运行在尽可能多的Worker上,相反,另一种是运行在尽可能少的Worker上
val assignedCores = scheduleExecutorsOnWorkers(app, usableWorkers, spreadOutApps)
// Now that we've decided how many cores to allocate on each worker, let's allocate them
//通知分配的Worker,启动Worker
for (pos <- 0 until usableWorkers.length if assignedCores(pos) > 0) {
allocateWorkerResourceToExecutors(
app, assignedCores(pos), app.desc.coresPerExecutor, usableWorkers(pos))
}
}
}
}
(2)ApplicationClientEndpoint接收到Master发送RegisteredApplication消息,需要把注册表示registered改为true,Master注册线程获取状态变化后,完成注册Application。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
//Master注册线程获取状态变化后,完成注册Application进程
case RegisteredApplication(appId_, masterRef) =>
// FIXME How to handle the following cases?
// 1. A master receives multiple registrations and sends back multiple
// RegisteredApplications due to an unstable network.
// 2. Receive multiple RegisteredApplication from different masters because the master is
// changing.
appId.set(appId_)
registered.set(true)
master = Some(masterRef)
listener.connected(appId.get)
...
}
(3)在Master类的startExecutorOnWorker方法中分配资源运行应用程序时,调用allocationWorkerResourceToExecutor方法实现Worker启动Executor。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = synchronized {
...
case LaunchExecutor(masterUrl, appId, execId, appDesc, cores_, memory_) =>
...
//创建Executor执行目录
val executorDir = new File(workDir, appId + "/" + execId)
if (!executorDir.mkdirs()) {
throw new IOException("Failed to create directory " + executorDir)
}
//通过SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS环境变量,在Worker中创建Executor中创建Executor执行目录,
//当程序执行完后由Worker进行删除
val appLocalDirs = appDirectories.getOrElse(appId, {
val localRootDirs = Utils.getOrCreateLocalRootDirs(conf)
val dirs = localRootDirs.flatMap {
dir =>
try {
val appDir = Utils.createDirectory(dir, namePrefix = "executor")
Utils.chmod700(appDir)
Some(appDir.getAbsolutePath())
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
logWarning(s"${e.getMessage}. Ignoring this directory.")
None
}
}.toSeq
if (dirs.isEmpty) {
throw new IOException("No subfolder can be created in " +
s"${localRootDirs.mkString(",")}.")
}
dirs
})
appDirectories(appId) = appLocalDirs
//在ExecutorRunner中创建CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend对象,创建的是使用应用信息中的
//command,而command在SparkDeploySchedulerBackend的start方法中构建
val manager = new ExecutorRunner(
appId,
execId,
appDesc.copy(command = Worker.maybeUpdateSSLSettings(appDesc.command, conf)),
cores_,
memory_,
self,
workerId,
host,
webUi.boundPort,
publicAddress,
sparkHome,
executorDir,
workerUri,
conf,
appLocalDirs, ExecutorState.RUNNING)
executors(appId + "/" + execId) = manager
manager.start()
coresUsed += cores_
memoryUsed += memory_
//向Master发送消息,表示Executor状态已经被更改ExecutorState.RUNNING
sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, manager.state, None, None))
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logError(s"Failed to launch executor $appId/$execId for ${appDesc.name}.", e)
if (executors.contains(appId + "/" + execId)) {
executors(appId + "/" + execId).kill()
executors -= appId + "/" + execId
}
sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, ExecutorState.FAILED,
Some(e.toString), None))
}
}
...
}
在Executor创建中调用了fetchAndRunExecutor方法进行实现。
private def fetchAndRunExecutor() {
try {
// Launch the process
val subsOpts = appDesc.command.javaOpts.map {
Utils.substituteAppNExecIds(_, appId, execId.toString)
}
val subsCommand = appDesc.command.copy(javaOpts = subsOpts)
//通过应用程序的信息和环境配置创建构造器builder
val builder = CommandUtils.buildProcessBuilder(subsCommand, new SecurityManager(conf),
memory, sparkHome.getAbsolutePath, substituteVariables)
val command = builder.command()
val formattedCommand = command.asScala.mkString("\"", "\" \"", "\"")
logInfo(s"Launch command: $formattedCommand")
//在构造器builder中添加执行目录信息
builder.directory(executorDir)
builder.environment.put("SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS", appLocalDirs.mkString(File.pathSeparator))
// In case we are running this from within the Spark Shell, avoid creating a "scala"
// parent process for the executor command
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LAUNCH_WITH_SCALA", "0")
// Add webUI log urls
//在构造器builder中添加监控页面输入日志地址信息
val baseUrl =
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.reverseProxy", false)) {
s"/proxy/$workerId/logPage/?appId=$appId&executorId=$execId&logType="
} else {
s"http://$publicAddress:$webUiPort/logPage/?appId=$appId&executorId=$execId&logType="
}
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDERR", s"${baseUrl}stderr")
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDOUT", s"${baseUrl}stdout")
//启动构造器,创建CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend实例
process = builder.start()
val header = "Spark Executor Command: %s\n%s\n\n".format(
formattedCommand, "=" * 40)
// Redirect its stdout and stderr to files
//输出创建CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend实例运行信息
val stdout = new File(executorDir, "stdout")
stdoutAppender = FileAppender(process.getInputStream, stdout, conf)
val stderr = new File(executorDir, "stderr")
Files.write(header, stderr, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
stderrAppender = FileAppender(process.getErrorStream, stderr, conf)
// Wait for it to exit; executor may exit with code 0 (when driver instructs it to shutdown)
// or with nonzero exit code
//等待CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend运行结束,当结束时,向Worker发送退出状态信息
val exitCode = process.waitFor()
state = ExecutorState.EXITED
val message = "Command exited with code " + exitCode
worker.send(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, state, Some(message), Some(exitCode)))
} catch {
case interrupted: InterruptedException =>
logInfo("Runner thread for executor " + fullId + " interrupted")
state = ExecutorState.KILLED
killProcess(None)
case e: Exception =>
logError("Error running executor", e)
state = ExecutorState.FAILED
killProcess(Some(e.toString))
}
}
}
(4)Mater接收到Worker发送的ExecutorStateChanged消息
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
...
case ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, state, message, exitStatus) =>
val execOption = idToApp.get(appId).flatMap(app => app.executors.get(execId))
execOption match {
case Some(exec) =>
val appInfo = idToApp(appId)
val oldState = exec.state
exec.state = state
if (state == ExecutorState.RUNNING) {
assert(oldState == ExecutorState.LAUNCHING,
s"executor $execId state transfer from $oldState to RUNNING is illegal")
appInfo.resetRetryCount()
}
//向Driver发送ExecutorUpdated消息
exec.application.driver.send(ExecutorUpdated(execId, state, message, exitStatus, false))
if (ExecutorState.isFinished(state)) {
// Remove this executor from the worker and app
logInfo(s"Removing executor ${exec.fullId} because it is $state")
// If an application has already finished, preserve its
// state to display its information properly on the UI
if (!appInfo.isFinished) {
appInfo.removeExecutor(exec)
}
exec.worker.removeExecutor(exec)
val normalExit = exitStatus == Some(0)
// Only retry certain number of times so we don't go into an infinite loop.
// Important note: this code path is not exercised by tests, so be very careful when
// changing this `if` condition.
if (!normalExit
&& appInfo.incrementRetryCount() >= MAX_EXECUTOR_RETRIES
&& MAX_EXECUTOR_RETRIES >= 0) {
// < 0 disables this application-killing path
val execs = appInfo.executors.values
if (!execs.exists(_.state == ExecutorState.RUNNING)) {
logError(s"Application ${appInfo.desc.name} with ID ${appInfo.id} failed " +
s"${appInfo.retryCount} times; removing it")
removeApplication(appInfo, ApplicationState.FAILED)
}
}
}
schedule()
case None =>
logWarning(s"Got status update for unknown executor $appId/$execId")
}
...
}
(5)在DriverEndpoint终端点进行注册Executor。(在步骤(3)CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend启动方法Onstart中,会发送注册Executor消息给RegisterExecutor给DriverEndpoint)
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
executorRef.send(RegisterExecutorFailed("Duplicate executor ID: " + executorId))
context.reply(true)
}
...
//记录executor的编号,以及该executor使用的核数
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorAddress, hostname,
cores, cores, logUrls)
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
//创建executor编号和其具体信息的键值列表
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {
currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt
}
if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {
numPendingExecutors -= 1
logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")
}
}
//回复executor完成注册消息
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))
//分配运行任务资源并发送LaunchTask消息执行任务
makeOffers()
}
...
}
(6)当CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend接收到Executor注册成功的RegisteredExecutor消息时,在CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend容器中实例化Executor对象。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
try {
//根据环境变量的参数,启动Executor,在Spark中,它是真正任务的执行者
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}
...
}
实例化的Executor对象会定时向Driver发送心跳信息,等待Driver下发任务。
private val heartbeater = ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadScheduledExecutor("driver-heartbeater")
/
private def startDriverHeartbeater(): Unit = {
//设置间隔时间
val intervalMs = HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL_MS
// Wait a random interval so the heartbeats don't end up in sync
//等待随机时间间隔,这样心跳不会在同步中结束
val initialDelay = intervalMs + (math.random * intervalMs).asInstanceOf[Int]
val heartbeatTask = new Runnable() {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.logUncaughtExceptions(reportHeartBeat())
}
//发送心跳信息给Driver
heartbeater.scheduleAtFixedRate(heartbeatTask, initialDelay, intervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
}
(7)CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的Executor启动后,接收到从DriverEndpoint终端点发送的LaunchTask执行任务消息,任务执行是在Executor的launchTask方法实现的。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
...
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
//当Executor没有成功启动时,输出异常日志并关闭Executor
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = TaskDescription.decode(data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
//启动TaskRunner进程执行任务
executor.launchTask(this, taskDesc)
}
...
}
调用executor的launchTask方法,在该方法中创建TaskRunner进程,然后把该进程加入到threadPool中,由Executor统一调度。
def launchTask(context: ExecutorBackend, taskDescription: TaskDescription): Unit = {
val tr = new TaskRunner(context, taskDescription)
runningTasks.put(taskDescription.taskId, tr)
threadPool.execute(tr)
}
(8)在TaskRunner执行任务完成时,会由向DriverEndpoint终端点发送状态变更StatusUpdate消息。
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) =>
//调用TaskSchedulerImpl的statusUpdate方法,根据任务执行不同结果继续处理
scheduler.statusUpdate(taskId, state, data.value)
if (TaskState.isFinished(state)) {
executorDataMap.get(executorId) match {
case Some(executorInfo) =>
//任务执行成功后,回收该Executor运行该任务的CPU,再根据实际情况分配任务
executorInfo.freeCores += scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASK
makeOffers(executorId)
case None =>
// Ignoring the update since we don't know about the executor.
logWarning(s"Ignored task status update ($taskId state $state) " +
s"from unknown executor with ID $executorId")
}
}
...
}