毕业设计 - 题目:基于单片机的智能温控农业大棚系统 - 物联网 嵌入式
文章目录
- 1 简介
- 2 绪论
-
- 2.1 课题背景与目的
- 3 系统设计
-
- 详细设计描述
- 3.2 硬件部分
-
- 温度测量电路
- 其他电路部分
- 3.3 软件部分
-
- 主程序
- 子系统程序
- 温湿度程序流程
- 键盘显示子程序
- 3.4 实现效果
- 3.5 部分相关代码
- 4 最后
1 简介
Hi,大家好,这里是丹成学长,今天向大家介绍一个 单片机项目
基于单片机的智能温控农业大棚系统
大家可用于 课程设计 或 毕业设计
技术解答、毕设帮助、开题指导
print("Q 746876041")
2 绪论
2.1 课题背景与目的
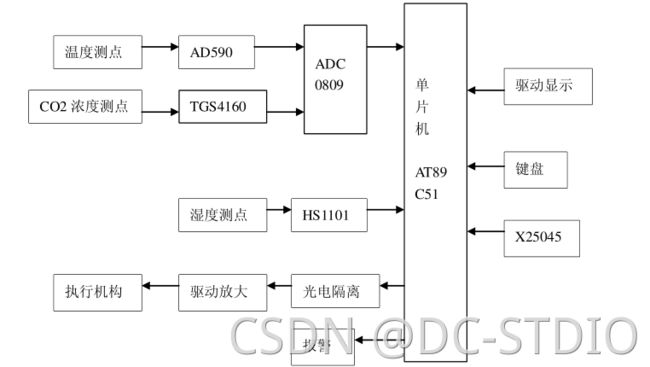
近年来我国的温室控制取得了 长足的进步, 首先在温室群控制方面, 进行了初步的探索和理论研究, 其次在温室控制中引入了 人工智能和先进的控制算法。 当前温室控制系统研究热点己由简单的DDC(直接数字控制) 发展到分布式控制系统, 如 DCS(分布式控制) 、 FCS(柔性控制) 等网络化的控制系统。实施远程控制。 虽然国内温室规模有限, 还没有形成规模经济, 另外构建的费用也较高, 但从长远来看,温室监控系统分布式和网络化将是一种必然的趋势。 本方案以 AT89C51 单片机系统为核心来对温度,湿度和二氧化碳浓度进行实时控制和检测。 检测单元能独立完成各自功能, 并根据单片机的指令对温度进行实时或定时采集。 单片机负责控制指令的发送, 并控制各机构进行温度采集, 手机测量数据, 同时对测量结果进行处理及显示。
3 系统设计
本设计是基于AT89C51单片机的温湿度智能控制采集系统,主要完成以下功能:
(1)选择AT89C51单片机,了解其基本特性和功能,使用AT89C51实现对温湿度及二氧化碳浓度的智能控制。
(2)使用温度传感器测量现场环境温度,进行数据的采集及传到单片机处理。
(3)使用湿度传感器对现场时读数据采集,由单片机进行数据处理和控制,实现范围为1%—99%RH的湿度控制。
(4)设计人机对话接口,键盘显示和报警系统。
(5)设计执行机构电路,是单片机能够自动控制执行机构工作。
(6)在完成以上功能时,要确保系统的可靠性和稳定性,是系统能够长期稳定的工
作。
详细设计描述
采用的芯片主要有:ATMEL公司生产的AT89C51单片机,AD公司生产的AD590集成温度传感器,电容式湿度传感器HS1101。
单片机通过AD0809A\D转换器把从传感器输出的模拟信号转换成数字信号,通过单片机对脉冲宽值的计算得到湿度值。
选用的二氧化碳传感器是FIGARO(弗加罗)公司生产的固态电化学型气体敏感元件TGS4160。通过监测S(+)、S(-)两个电极之间所产生的电势值EMF,就可以测量CO2的浓度值。
在这里温度及二氧化碳浓度需要模数转换。
在执行机构中,可以通过单片机直接控制来达到需要的数值。
显示部分由单片机分时把温度湿度及二氧化碳浓度值送到数码管显示。通过键盘可以设定参数的上限值下限值,当当前参数超过设定值时,由单片机控制报警电路报警。
同时单片机控制相应的执行机构运行相应的动作,使得温度湿度及二氧化碳浓度恢复到正常水平。
3.2 硬件部分
温度测量电路
AD590 封装图简介
温度测量电路
其他电路部分
非关键点,略
3.3 软件部分
主程序
主程序是整个测控系统中最重要的程序, 各个子程序都在主程序的协调指挥下运行, 是一个顺序执行的无限循环程序, 可以被任何优先级的中断请求所打断。
主程序的初始化工作主要完成对 X25045、 HS1101、 LED、 ADC0809、 测试数据寄存器、 串行口、 定时/计数器等的初始化。 在程序的开始, 编写一段简短的程序, 执行该程序并与预定结果进行比较, 如果不同, 则跳转到错误处理子程序;如果相同, 则证明 CPU 及其它部件工作正常, 程序继续向下执行。
子系统程序
温湿度程序流程
选用电容式传感器 HS1101, 根据其电容的改变而改变了 555 定时器的输出脉冲的宽度。
键盘显示子程序
3.4 实现效果
过热驱动风扇
换上LED屏,并且模拟温室环境(加上个盒子)
3.5 部分相关代码
/************************************************
作者:丹成学长,Q746876041
************************************************/
/*********************************************************************
* INCLUDES
*/
#include "ZComDef.h"
#include "OSAL.h"
#include "OSAL_Nv.h"
#include "OnBoard.h"
#include "ZMAC.h"
#ifndef NONWK
#include "AF.h"
#endif
/* Hal */
#include "hal_lcd.h"
#include "hal_led.h"
#include "hal_adc.h"
#include "hal_drivers.h"
#include "hal_assert.h"
#include "hal_flash.h"
/*********************************************************************
* MACROS
*/
/*********************************************************************
* CONSTANTS
*/
// Maximun number of Vdd samples checked before go on
#define MAX_VDD_SAMPLES 3
#define ZMAIN_VDD_LIMIT HAL_ADC_VDD_LIMIT_4
/*********************************************************************
* TYPEDEFS
*/
/*********************************************************************
* GLOBAL VARIABLES
*/
/*********************************************************************
* EXTERNAL VARIABLES
*/
/*********************************************************************
* EXTERNAL FUNCTIONS
*/
extern bool HalAdcCheckVdd (uint8 limit);
/*********************************************************************
* LOCAL VARIABLES
*/
/*********************************************************************
* LOCAL FUNCTIONS
*/
static void zmain_dev_info( void );
static void zmain_ext_addr( void );
static void zmain_vdd_check( void );
#ifdef LCD_SUPPORTED
static void zmain_lcd_init( void );
#endif
/*********************************************************************
* @fn main
* @brief First function called after startup.
* @return don't care
*/
int main( void )
{
// Turn off interrupts
osal_int_disable( INTS_ALL );
// Initialization for board related stuff such as LEDs
HAL_BOARD_INIT();
// Make sure supply voltage is high enough to run
zmain_vdd_check();
// Initialize board I/O
InitBoard( OB_COLD );
// Initialze HAL drivers
HalDriverInit();
// Initialize NV System
osal_nv_init( NULL );
// Initialize the MAC
ZMacInit();
// Determine the extended address
zmain_ext_addr();
// Initialize basic NV items
zgInit();
#ifndef NONWK
// Since the AF isn't a task, call it's initialization routine
afInit();
#endif
// Initialize the operating system
osal_init_system();
// Allow interrupts
osal_int_enable( INTS_ALL );
// Final board initialization
InitBoard( OB_READY );
// Display information about this device
zmain_dev_info();
/* Display the device info on the LCD */
#ifdef LCD_SUPPORTED
zmain_lcd_init();
#endif
#ifdef WDT_IN_PM1
/* If WDT is used, this is a good place to enable it. */
WatchDogEnable( WDTIMX );
#endif
osal_start_system(); // No Return from here
return 0; // Shouldn't get here.
} // main()
/*********************************************************************
* @fn zmain_vdd_check
* @brief Check if the Vdd is OK to run the processor.
* @return Return if Vdd is ok; otherwise, flash LED, then reset
*********************************************************************/
static void zmain_vdd_check( void )
{
uint8 vdd_passed_count = 0;
bool toggle = 0;
// Repeat getting the sample until number of failures or successes hits MAX
// then based on the count value, determine if the device is ready or not
while ( vdd_passed_count < MAX_VDD_SAMPLES )
{
if ( HalAdcCheckVdd (ZMAIN_VDD_LIMIT) )
{
vdd_passed_count++; // Keep track # times Vdd passes in a row
MicroWait (10000); // Wait 10ms to try again
}
else
{
vdd_passed_count = 0; // Reset passed counter
MicroWait (50000); // Wait 50ms
MicroWait (50000); // Wait another 50ms to try again
}
/* toggle LED1 and LED2 */
if (vdd_passed_count == 0)
{
if ((toggle = !(toggle)))
HAL_TOGGLE_LED1();
else
HAL_TOGGLE_LED2();
}
}
/* turn off LED1 */
HAL_TURN_OFF_LED1();
HAL_TURN_OFF_LED2();
}
/**************************************************************************************************
* @fn zmain_ext_addr
*
* @brief Execute a prioritized search for a valid extended address and write the results
* into the OSAL NV system for use by the system. Temporary address not saved to NV.
*
* input parameters
*
* None.
*
* output parameters
*
* None.
*
* @return None.
**************************************************************************************************
*/
static void zmain_ext_addr(void)
{
uint8 nullAddr[Z_EXTADDR_LEN] = {
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF};
uint8 writeNV = TRUE;
// First check whether a non-erased extended address exists in the OSAL NV.
if ((SUCCESS != osal_nv_item_init(ZCD_NV_EXTADDR, Z_EXTADDR_LEN, NULL)) ||
(SUCCESS != osal_nv_read(ZCD_NV_EXTADDR, 0, Z_EXTADDR_LEN, aExtendedAddress)) ||
(osal_memcmp(aExtendedAddress, nullAddr, Z_EXTADDR_LEN)))
{
// Attempt to read the extended address from the location on the lock bits page
// where the programming tools know to reserve it.
HalFlashRead(HAL_FLASH_IEEE_PAGE, HAL_FLASH_IEEE_OSET, aExtendedAddress, Z_EXTADDR_LEN);
if (osal_memcmp(aExtendedAddress, nullAddr, Z_EXTADDR_LEN))
{
// Attempt to read the extended address from the designated location in the Info Page.
if (!osal_memcmp((uint8 *)(P_INFOPAGE+HAL_INFOP_IEEE_OSET), nullAddr, Z_EXTADDR_LEN))
{
osal_memcpy(aExtendedAddress, (uint8 *)(P_INFOPAGE+HAL_INFOP_IEEE_OSET), Z_EXTADDR_LEN);
}
else // No valid extended address was found.
{
uint8 idx;
#if !defined ( NV_RESTORE )
writeNV = FALSE; // Make this a temporary IEEE address
#endif
/* Attempt to create a sufficiently random extended address for expediency.
* Note: this is only valid/legal in a test environment and
* must never be used for a commercial product.
*/
for (idx = 0; idx < (Z_EXTADDR_LEN - 2);)
{
uint16 randy = osal_rand();
aExtendedAddress[idx++] = LO_UINT16(randy);
aExtendedAddress[idx++] = HI_UINT16(randy);
}
// Next-to-MSB identifies ZigBee devicetype.
#if ZG_BUILD_COORDINATOR_TYPE && !ZG_BUILD_JOINING_TYPE
aExtendedAddress[idx++] = 0x10;
#elif ZG_BUILD_RTRONLY_TYPE
aExtendedAddress[idx++] = 0x20;
#else
aExtendedAddress[idx++] = 0x30;
#endif
// MSB has historical signficance.
aExtendedAddress[idx] = 0xF8;
}
}
if (writeNV)
{
(void)osal_nv_write(ZCD_NV_EXTADDR, 0, Z_EXTADDR_LEN, aExtendedAddress);
}
}
// Set the MAC PIB extended address according to results from above.
(void)ZMacSetReq(MAC_EXTENDED_ADDRESS, aExtendedAddress);
}
/**************************************************************************************************
* @fn zmain_dev_info
*
* @brief This displays the IEEE (MSB to LSB) on the LCD.
*
* input parameters
*
* None.
*
* output parameters
*
* None.
*
* @return None.
**************************************************************************************************
*/
static void zmain_dev_info(void)
{
#ifdef LCD_SUPPORTED
uint8 i;
uint8 *xad;
uint8 lcd_buf[Z_EXTADDR_LEN*2+1];
// Display the extended address.
xad = aExtendedAddress + Z_EXTADDR_LEN - 1;
for (i = 0; i < Z_EXTADDR_LEN*2; xad--)
{
uint8 ch;
ch = (*xad >> 4) & 0x0F;
lcd_buf[i++] = ch + (( ch < 10 ) ? '0' : '7');
ch = *xad & 0x0F;
lcd_buf[i++] = ch + (( ch < 10 ) ? '0' : '7');
}
lcd_buf[Z_EXTADDR_LEN*2] = '\0';
HalLcdWriteString( "IEEE: ", HAL_LCD_LINE_1 );
HalLcdWriteString( (char*)lcd_buf, HAL_LCD_LINE_2 );
#endif
}
#ifdef LCD_SUPPORTED
/*********************************************************************
* @fn zmain_lcd_init
* @brief Initialize LCD at start up.
* @return none
*********************************************************************/
static void zmain_lcd_init ( void )
{
#ifdef SERIAL_DEBUG_SUPPORTED
{
HalLcdWriteString( "TexasInstruments", HAL_LCD_LINE_1 );
#if defined( MT_MAC_FUNC )
#if defined( ZDO_COORDINATOR )
HalLcdWriteString( "MAC-MT Coord", HAL_LCD_LINE_2 );
#else
HalLcdWriteString( "MAC-MT Device", HAL_LCD_LINE_2 );
#endif // ZDO
#elif defined( MT_NWK_FUNC )
#if defined( ZDO_COORDINATOR )
HalLcdWriteString( "NWK Coordinator", HAL_LCD_LINE_2 );
#else
HalLcdWriteString( "NWK Device", HAL_LCD_LINE_2 );
#endif // ZDO
#endif // MT_FUNC
}
#endif // SERIAL_DEBUG_SUPPORTED
}
#endif
/*********************************************************************
*********************************************************************/
/*******************************************************************
篇幅有限,只展示部分代码
作者:丹成学长,Q746876041
********************************************************************/
4 最后
技术解答、毕设帮助、开题指导
print("Q 746876041")
![]()
单片机毕设项目大全:
https://blog.csdn.net/huawei123444/article/details/119822845