SpringBoot重点详解--操作多数据源(JPA+JdbcTemplate)
目录
添加依赖与配置
配置数据源与JdbcTemplate
使用JdbcTemplate操作数据源
配置JPA
使用JPA操作数据源
启动类中测试
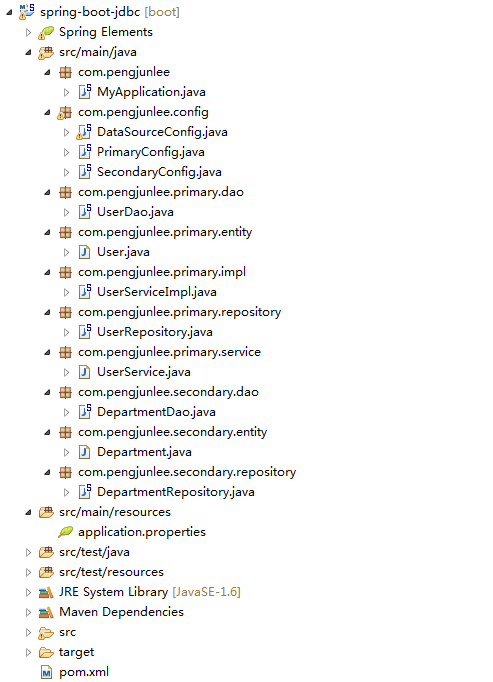
本文仅对如何在Springboot中使用Spring Data JPA和JdbcTemplate去操作多个HikariCP数据源进行简单示例和介绍,项目的完整目录层次如下图所示。
添加依赖与配置
为了使用Spring Data JPA和HikariCP数据源,需要在工程POM文件中引入它们的Maven依赖。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.4.1.RELEASE
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.apache.tomcat
tomcat-jdbc
com.zaxxer
HikariCP
在application.properties核心配置文件中除了要定义MYSQL数据库连接信息外,还需要添加如下JPA相关配置。
#########################################################
### Primary DataSource -- DataSource 1 configuration ###
#########################################################
primary.datasource.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
primary.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
primary.datasource.username=root
primary.datasource.password=123456
#########################################################
### Secondary DataSource -- DataSource 2 configuration ##
#########################################################
secondary.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
secondary.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
secondary.datasource.username=root
secondary.datasource.password=123456
secondary.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
#########################################################
### Java Persistence Api -- Spring jpa configuration ###
#########################################################
# Specify the DBMS
spring.jpa.database = MYSQL
# Show or not log for each sql query
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# Naming strategy
#[org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy #org.hibernate.cfg.DefaultNamingStrategy]
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
# stripped before adding them to the entity manager)
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect配置数据源与JdbcTemplate
首先,在DataSourceConfig配置类中定义两个数据源,同时为每一个数据源创建一个JdbcTemplate。
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
/**
* 数据源 1
*/
@Primary
@Bean(name = "primaryDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "primary.datasource")
public DataSource primaryDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "secondaryDataSourceProperties")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "secondary.datasource")
public DataSourceProperties secondaryDataSourceProperties() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
}
/**
* 数据源 2
*/
@Bean(name = "secondaryDataSource")
public DataSource thirdDataSource(
@Qualifier("secondaryDataSourceProperties") DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties) {
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
/**
* 数据源 1 的 JdbcTemplate
*/
@Bean(name = "primaryJdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate primaryJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("primaryDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
/**
* 数据源 2 的 JdbcTemplate
*/
@Bean(name = "secondaryJdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate secondaryJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("secondaryDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}使用JdbcTemplate操作数据源
在Dao层中通过注入不同的JdbcTemplate来操作对应的数据源。
/**
* 使用 JdbcTemplate 操作数据源 1
*/
@Repository
public class UserDao {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("primaryJdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional
public void addUser(Integer userAge, String userName) {
String sql = "insert into tbl_user (age,name) values ('" + userAge + "','" + userName + "');";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
}
}
/**
* 使用 JdbcTemplate 操作数据源 2
*/
@Repository
public class DepartmentDao {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("secondaryJdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional
public void addDept(String userName) {
String sql = "insert into tbl_dept (name) values ('" + userName + "');";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
}
}
配置JPA
通过注解@EnableJpaRepositories来为不同包下的Repository分别创建不同TransactionManager和EntityManagerFactory,用来操作不同的数据源。
/**
* 数据源 1 JPA配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(entityManagerFactoryRef = "primaryEntityManagerFactory", transactionManagerRef = "primaryTransactionManager", basePackages = {
"com.pengjunlee.primary.repository" }) // 设置Repository所在位置
public class PrimaryConfig {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("primaryDataSource")
private DataSource primaryDataSource;
@Autowired
private JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Primary
@Bean(name = "primaryEntityManager")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return primaryEntityManagerFactory(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "primaryEntityManagerFactory")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean primaryEntityManagerFactory(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder.dataSource(primaryDataSource).properties(getVendorProperties(primaryDataSource))
.packages("com.pengjunlee.primary.entity") // 设置实体类所在位置
.persistenceUnit("primaryPersistenceUnit").build();
}
private Map getVendorProperties(DataSource dataSource) {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(dataSource);
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "primaryTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager primaryTransactionManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(primaryEntityManagerFactory(builder).getObject());
}
} /**
* 数据源 2 JPA配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(entityManagerFactoryRef = "secondaryEntityManagerFactory", transactionManagerRef = "secondaryTransactionManager", basePackages = {
"com.pengjunlee.secondary.repository" }) // 设置Repository所在位置
public class SecondaryConfig {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("secondaryDataSource")
private DataSource secondaryDataSource;
@Autowired
private JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Bean(name = "secondaryEntityManager")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return secondaryEntityManagerFactory(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Bean(name = "secondaryEntityManagerFactory")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean secondaryEntityManagerFactory(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder.dataSource(secondaryDataSource).properties(getVendorProperties(secondaryDataSource))
.packages("com.pengjunlee.secondary.entity") // 设置实体类所在位置
.persistenceUnit("secondaryPersistenceUnit").build();
}
private Map getVendorProperties(DataSource dataSource) {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "secondaryTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager secondaryTransactionManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(secondaryEntityManagerFactory(builder).getObject());
}
} 使用JPA操作数据源
由于是通过包名来区分哪些Repository用来操作哪个数据源,故而需要将不同数据源的Entity和Repository类放入不同的包中。
此处定义了User(用户)和Department(部门)两个实体类,分别对应数据源一和数据源二。
@Entity
@Table(name = "tbl_user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
// 此处省略get和set方法
}
@Entity
@Table(name = "tbl_dept")
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
// 此处省略get和set方法
}
/**
* 使用 JPA 操作数据源 1
*/
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository {
} /**
* 使用 JPA 操作数据源 2
*/
@Repository
public interface DepartmentRepository extends CrudRepository {
}
启动类中测试
在启动类中进行数据源测试,并分别向两个数据库中添加记录。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement // 只会回滚运行期异常
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
Object ds1 = context.getBean("primaryDataSource");
System.out.println(ds1.getClass().getName());
Object ds2 = context.getBean("secondaryDataSource");
System.out.println(ds2.getClass().getName());
UserRepository userRepository = context.getBean(UserRepository.class);
User user1 = new User();
user1.setAge(21);
user1.setName("Tracy");
userRepository.save(user1);
DepartmentRepository deptRepository = context.getBean(DepartmentRepository.class);
Department dept1 = new Department();
dept1.setName("集团事业部");
deptRepository.save(dept1);
UserDao userDao = context.getBean(UserDao.class);
userDao.addUser(30, "pengjunlee");
DepartmentDao deptDao = context.getBean(DepartmentDao.class);
deptDao.addDept("总裁办公室");
}
}
启动程序,两个数据库中的用户表和部门表中数据都能正常添加成功。
在实际项目中我们一般都会将定义好的Repository自动装配到Service层进行调用,此时要格外注意事务。
@Service
@Transactional("primaryTransactionManager")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public void deleteUserById(Long id) {
userRepository.delete(id);
}
}
本文项目源码已上传至CSDN,资源地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/pengjunlee/10382622