ROS学习(六)——服务端Server的编程实现
申明:ROS学习参考了古月居老师的Blibli视频,强烈推荐大家看视频学习,本博客仅记录自己的学习经历和心得,欢迎大家一起讨论!
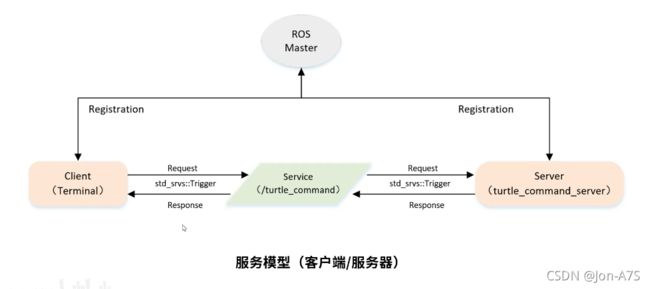
1 ROS服务模型
本节,首先定义一个服务模型。其中Client和Server是其下两个节点。Server (turtle_command _server)通过Topic向海龟发送运动指令,Client作为开关请求Server端指令的发送。用到的Service为/turtle_command,数据类型是std_srvs::Trigger
如何创建一个服务端?
- 初始化ROS节点
- 创建一个Server实例
- 循环等待服务请求,进入回调函数
- 在回调函数中完成服务功能的处理,并反馈应答数据
2 编写Server程序文件
在learning_service下的src文件夹下新建.cpp文件或.py文件,需要在此learning_service/src文件夹下运行:
2.1 C++文件
(1)创建C++文件
touch turtle_command_server.cpp
(2)编写.cpp文件内容
/**
* 该例程将执行/turtle_command服务,服务数据类型std_srvs/Trigger
*/
#include (3)配置CMakeLists.txt编译规则
- 设置需要编译的代码和生成的可执行文件;
- 设置链接库
add_executable(turtle_command_server src/turtle_command_server.cpp)#将程序文件生成可执行文件
target_link_libraries(turtle_command_server ${
catkin_LIBRARIES})#将可执行文件与ros库链接
(4)进入catkin_ws 进行可执行文件 turtle_command_server的编译,运行
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make#编译
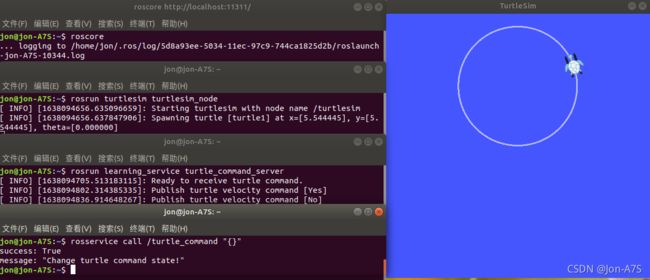
(5) 程序测试
roscore
rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node
rosrun learning_service turtle_command_server
rosservice call /turtle_command "{}"
2.2 python文件
(1) 创建.py文件
touch turtle_command_server.py
(2)编写.py文件内容
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 该例程将执行/turtle_command服务,服务数据类型std_srvs/Trigger
import rospy
import thread,time
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from std_srvs.srv import Trigger, TriggerResponse
pubCommand = False;
turtle_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=10)
def command_thread():
while True:
if pubCommand:
vel_msg = Twist()
vel_msg.linear.x = 0.5
vel_msg.angular.z = 0.2
turtle_vel_pub.publish(vel_msg)
time.sleep(0.1)
def commandCallback(req):
global pubCommand
pubCommand = bool(1-pubCommand)
# 显示请求数据
rospy.loginfo("Publish turtle velocity command![%d]", pubCommand)
# 反馈数据
return TriggerResponse(1, "Change turtle command state!")
def turtle_command_server():
# ROS节点初始化
rospy.init_node('turtle_command_server')
# 创建一个名为/turtle_command的server,注册回调函数commandCallback
s = rospy.Service('/turtle_command', Trigger, commandCallback)
# 循环等待回调函数
print "Ready to receive turtle command."
thread.start_new_thread(command_thread, ())
rospy.spin()
if __name__ == "__main__":
turtle_command_server()
pytion开头注释参考
(3) 给文件授权
PS:在ros下运行python文件一定要注意待执行的python文件有可执行权限。对着python文件右键→属性(Properties)→权限(Permissions)→Allow executing file as program打钩。
或者通过命令行修改:(进入learining_service/src/文件夹中)
chmod +x turtle_command_server.py
(4) 程序运行
roscore
rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node
rosrun learning_service turtle_command_server.py
rosservice call /turtle_command "{}"
本讲完,接下来会持续更新!