利用python语言进行图像特征匹配及地理标记图像匹配
利用python语言进行图像特征匹配及地理标记图像匹配
目录
- 利用python语言进行图像特征匹配及地理标记图像匹配
- 一、相关概念及原理流程
-
- 1.Harris角点检测
-
- ①Harris角点简介
- ②数学表达
- ③角点检测
- 2.SIFT算子
-
- 引言
- ①SIFT算子的特点
- ②SIFT可以解决的问题
- ③SIFT算法实现步骤(☆)
- 二、图像特征匹配
-
- (一)实现代码
- (二)运行结果
-
- 结果展示
-
- ①特征点检测
- ②特征匹配结果
- 二、地理标记图像匹配
-
- (一)实现代码
- (二)运行结果
- (三)结果分析
一、相关概念及原理流程
1.Harris角点检测
①Harris角点简介
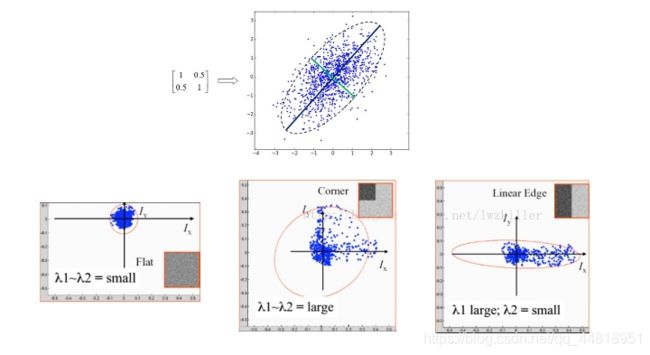
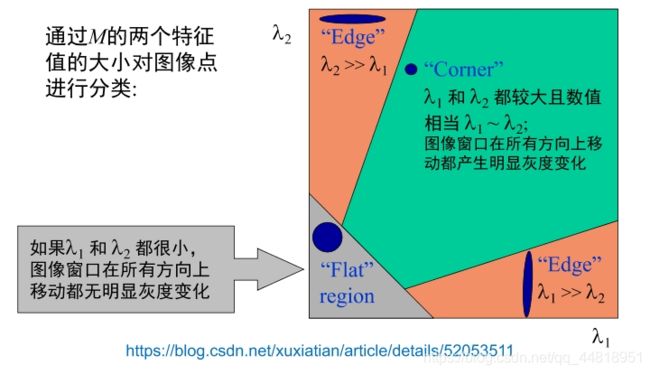
人眼对角点的识别通常是在一个局部的小区域或小窗口完成的。如果在各个方向上移动这个特征的小窗口,窗口内区域的灰度发生了较大的变化,那么就认为在窗口内遇到了角点。如果这个特定的窗口在图像各个方向上移动时,窗口内图像的灰度没有发生变化,那么窗口内就不存在角点;如果窗口在某一个方向移动时,窗口内图像的灰度发生了较大的变化,而在另一些方向上没有发生变化,那么,窗口内的图像可能就是一条直线的线段。

②数学表达
③角点检测
2.SIFT算子
引言
SIFT算子(尺度不变特征变换):SIFT特征是基于物体上的一些局部外观的兴趣点而与影像的大小和旋转无关。对于光线、噪声、微视角改变的容忍度也相当高。基于这些特性,它们是高度显著而且相对容易撷取,在母数庞大的特征数据库中,很容易辨识物体而且鲜有误认。使用SIFT特征描述对于部分物体遮蔽的侦测率也相当高,甚至只需要3个以上的SIFT物体特征就足以计算出位置与方位。在现今的电脑硬件速度下和小型的特征数据库条件下,辨识速度可接近即时运算。SIFT特征的信息量大,适合在海量数据库中快速准确匹配。
*尺度空间不变:即图像在进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示,实现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以满足特征点的尺度不变性。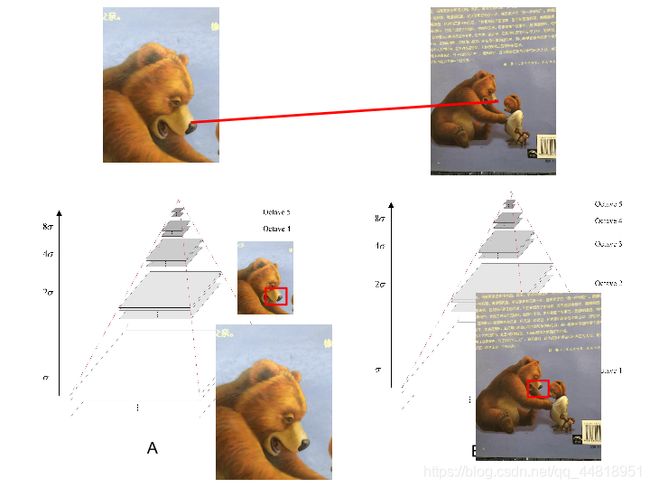
①SIFT算子的特点
1.SIFT特征是图像的局部特征,其对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化保持不变性,对视角变化、仿射变换、噪声也保持一定程度的稳定性;
2. 区分性(Distinctiveness)好,信息量丰富,适用于在海量特征数据库中进行快速、准确的匹配;
3. 多量性,即使少数的几个物体也可以产生大量的SIFT特征向量;
4.高速性,经优化的SIFT匹配算法甚至可以达到实时的要求;
5.可扩展性,可以很方便的与其他形式的特征向量进行联合
②SIFT可以解决的问题
1.目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
2.图像仿射/投影变换
3.弱光照影响
4.部分目标遮挡
5.杂物场景
6.噪声
③SIFT算法实现步骤(☆)
1.提取关键点
2.对关键点附加详细的信息(局部特征)
3.通过特征点(附带上特征向量的关键点)的两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立景物间的对应关系
二、图像特征匹配
(一)实现代码
from PIL import Image
import numpy
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
# im1f = '../data/sf_view1.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/sf_view2.jpg'
im1f = r'D:\pythonCode\test\lubuilding1.jpg'
im2f = r'D:\pythonCode\test\lubuilding2.jpg'
# im1f = '../data/climbing_1_small.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/climbing_2_small.jpg'
im1 = numpy.array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = numpy.array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print ('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
(二)运行结果
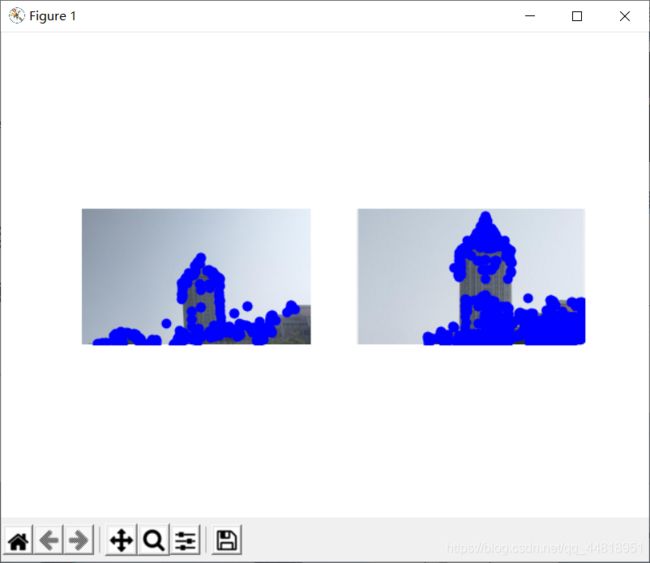
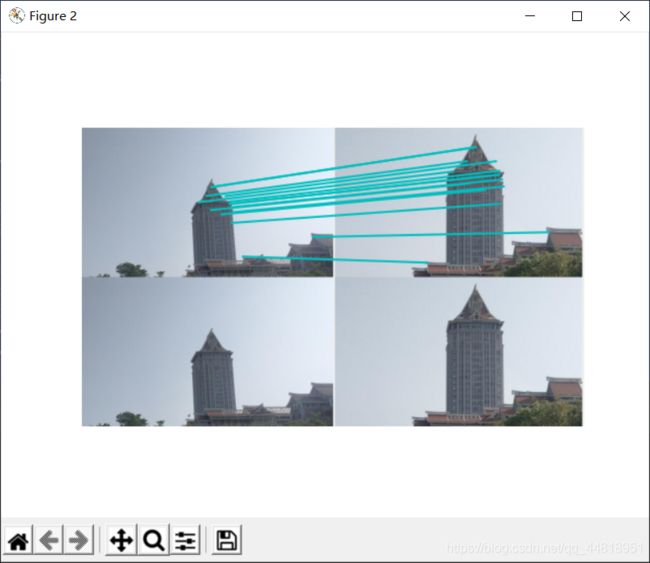
结果展示
①特征点检测
②特征匹配结果
二、地理标记图像匹配
(一)实现代码
代码
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
download_path = "D:/pythonCode/test/testimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "D:/pythonCode/test/testimages" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('whitehouse.png')
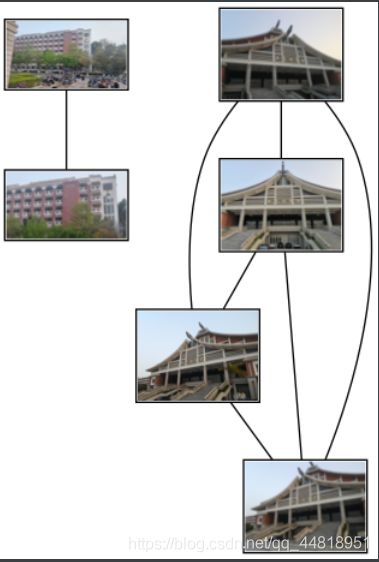
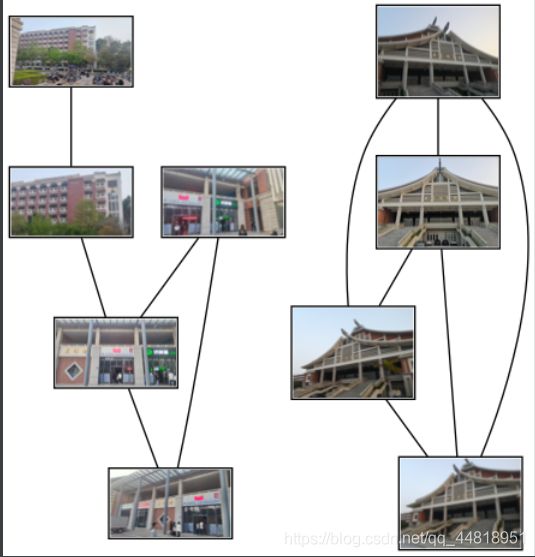
(二)运行结果
(三)结果分析
在进行地理标记匹配的过程中,当测试图片为6张时,可以从结果看出很好的匹配得到了对应的图片,原因可能是两组图片的差别较大,特征点差异明显,而同组之间的图片在进行拍摄时所选角度以及亮度差别较小,所以匹配结果较好。
当测试图片为9张时,可以发现,相同组图片还是可以很好的对应,但不同组图片有出现误判的情况。原因可能是因为不同组的某两张图片的特征点在图片中对应的位置想似,由于SIFT算法是匹配特征点的位置,可能导致即使是不同图片,但特征点位置在图片上的位置相同数量较多,也会导致程序误判两张图片相同。
总体来看,SIFT算法有较好的适用性,可以得出基本吻合的结果。对于旋转、尺度缩放保持不变性,对视角变化、噪声也保持一定程度的稳定性。但也有需要改进的地方,如:匹配特征点位置时是否需要根据特征点的特征进行再特征化从而从多方面(不单纯是位置)来匹配图像从而区别有较多想似特征点位置的不同图片。