Netty学习(二)- TCP粘包/拆包
一、TCP 粘包/拆包介绍
1、什么是粘包、拆包
首先只有TCP数据传输才会存在是粘包、拆包现象。
假设客户端分别发送两个数据包D1和D2给服务器,由于TCP是面向流的协议,TCP把客户端传过来的数据看成是一连串的无结构的字节流,且服务端一次读取到的数据是不确定的,所以可能会出现下面几种情况。
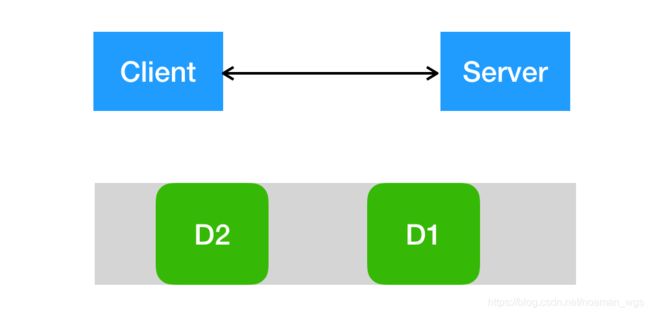
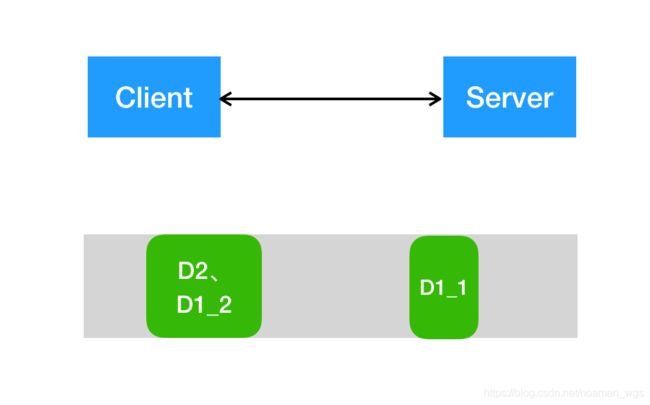
(1)服务端分两次接收到D1和D2数据包,没有发生粘包/拆包。
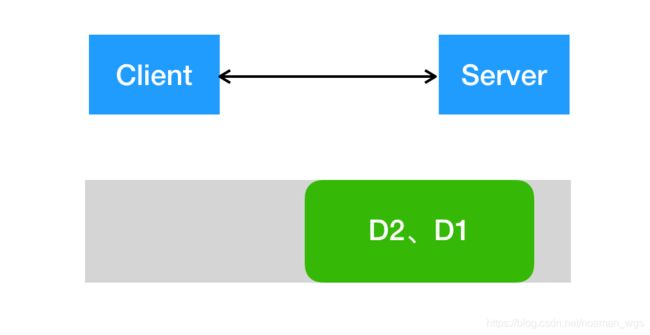
(2)服务端一次接收了两个数据包,D1和D2粘在一起,发生TCP粘包。
如:客户端第一次发送"Hello,Netty",第二次发送"Time out"数据包,发生粘包后,数据就会合并一起"Hello,NettyTime out"发送至服务端。
(3)服务端分两次读取,第一次读取完整D1包+不完整D2包;第二次读取D2包剩下内容。
如:服务端第一次接收到"Hello,NettyTi",第二次接收"me out",第一次即发生TCP拆包。
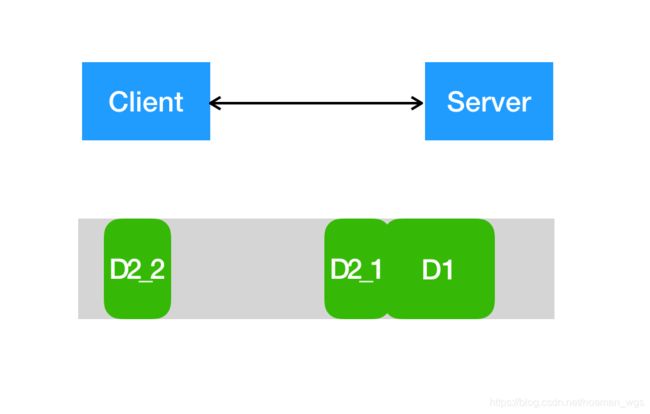
(4)同样,服务端也可能第一次读取不完整D1包;第二次读取到剩下的D1包和D2包。
2、粘包/拆包产生的原因
首先我们需要知道UDP协议中不存在粘包、拆包现象**,因为UDP是面向报文的**,应用层发送给UDP多长报文,UDP在加上UDP首部后就原封不动发送出去;接收方UDP对接收到的数据报文去除首部后再原装不动地交付给上层的应用进程。即UDP一次交付一个完整的报文,所以不存在粘包、拆包现象。
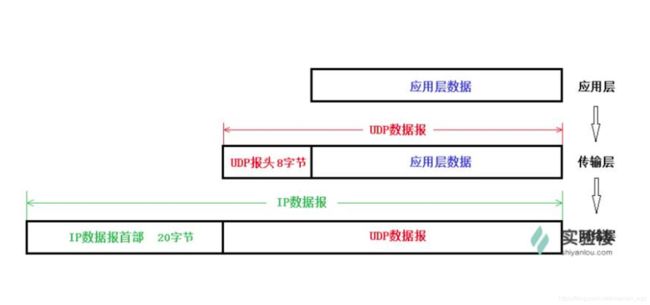
TCP数据传输是以流的形式进行传输。
一个完整的数据包会被拆分成多个小包进行发送;
也可能多个小包被封装成一个大的数据包进行发送。
这就涉及到了TCP的粘包/拆包问题。
TCP传输产生粘包/拆包问题的原因:
- 应用程序写入的字节大小大于套接口发送缓冲区大小(即一次发送的内容过多,导致产生拆包);
- 进行MSS大小的TCP分端;
- 以太网诊的payload大小大于MTU进行IP分片。
3、解决办法
- 消息定长:如可以设定每个报文的长度为200个字节,如果不够,空位补空格;
- 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,如FTP协议;
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中至少标识消息总长度,这样接收端在接收到数据后就可以知道每一个数据包实际长度(Dubbo采用该方案进行编解码);
- 更复杂的应用协议;
二、代码演示TCP 粘包/拆包现象
下面用代码演示什么是示TCP 粘包/拆包。
1、服务端
服务端的作用就是读取客户端发送的指令,每读取一次计数器就+1;根据指令做出响应,并将响应发送给客户端。
代码:
package com.wgs.netty.demo2_packet;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by wanggenshen
* Date: on 2019/7/12 23:41.
* Description: TCP粘包演示服务端
*/
public class TcpPacketServer {
public static void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup parentGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(parentGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler() {
// 计数器
private int counter;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 读取内容
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()];
byteBuf.readBytes(req);
// 接收客户端消息后换行
String bodyFromClient = new String(req, "UTF-8")
.substring(0, req.length - System.getProperty("line.separator").length());
System.out.println("【Receive from client, msg is 】: " + System.getProperty("line.separator")
+ bodyFromClient
+ ", the counter is:" + ++counter);
// 收到客户端指令后, 将响应返回给客户端
String currentTime = "";
if ("QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(bodyFromClient)) {
currentTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
} else {
currentTime = "BAD ORDER";
}
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
// 将响应放到缓冲区
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(resp);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
parentGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TcpPacketServer.bind(8080);
}
}
2、客户端
客户端的作用:
首先客户端循环发送100条指令,将指令写入到channel中;
然后监听channel,读取服务端的响应,并将响应内容打印出来。
代码:
package com.wgs.netty.demo2_packet;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
/**
* Created by wanggenshen
* Date: on 2019/7/13 00:17.
* Description: TCP粘包演示客户端
*/
public class TcpPacketClient {
public static void connect(int port, String host) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
private int counter;
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler() {
/**
* 读取来自服务端的响应
*
* @param channelHandlerContext
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()];
byteBuf.readBytes(req);
// 读取来自服务端的响应内容
String bodyFromServer = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now time is " + bodyFromServer
+ ", counter is : " + ++counter);
}
/**
* 发送消息到服务端
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
String command = "QUERY TIME ORDER" + System.getProperty("line.separator");
byte[] commandReq = command.getBytes();
// 循环发送100条带有换行的 "QUERY TIME ORDER"指令
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(commandReq.length);
message.writeBytes(commandReq);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port);
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TcpPacketClient.connect(8080, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
3、运行与测试
分别运行服务端和客户端,按照预我们期望看到的结果是:
(1)客户端发送100条"QUERY TIME ORDER"的指令;
(2)服务端接收到这100条"QUERY TIME ORDER"指令,打印在控制台上;并且根据指令查询当前时间,发送100条响应给客户端;
(3)客户端接收到服务端发送的100条响应内容,打印在控制台上。
下面来看看实际的运行效果。
服务端:
- 【Receive from client, msg is 】:
- QUERY TIME ORDER
- QUERY TIME ORDER
- ===此处省略56行【QUERY TIME ORDER】
- QUERY TIME ORDER
- QUE, the counter is:1
- 【Receive from client, msg is 】:
- Y TIME ORDER
- QUERY TIME ORDER
- ===此处省略37行【QUERY TIME ORDER】
- QUERY TIME ORDER, the counter is:2
可以看到,在第1行接收到来自客户端的第一条指令,该指令内容包含60行"QUERY TIME ORDER"(而我们预想的效果是每一条指令对应一行"QUERY TIME ORDER"),说明发生了TCP粘包现象。
同时,第6与8行我们可以看到,同一个指令被分割成"QUE" 和 "Y TIME ORDER"两段,说明发生了TCP拆包现象。
客户端:
- Now time is BAD ORDER
- BAD ORDER
- , counter is : 1
可以看到,客户端接收到了一条来自服务端的消息,该消息包含两条"BAD ORDER"指令;实际上服务端发送了2条响应内容,而客户端也应该分别收到该两条响应内容,这就说明发生了TCP粘包现象。
三、使用LineBasedFrameDecoder + StringDecoder 文本解码器解决粘包/拆包问题
Netty提供了多种编解码器解决TCP粘包/拆包问题。
下面看看如何使用用Netty提供的LineBasedFrameDecoder + StringDecoder API。
1、服务端改造
package com.wgs.netty.demo2_packet;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by wanggenshen
* Date: on 2019/7/13 13:24.
* Description: 解决粘包问题的服务端demo
*/
public class TcpPacketServer2 {
public static void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup parentGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(parentGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
private int counter;
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
// 换行解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
// 将接收到的对象转为字符串后再调用handler
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 读取客户端指令
String bodyFromClient = (String) msg;
System.out.println("【Receive from client, msg is 】: "
+ System.getProperty("line.separator")
+ bodyFromClient
+ ", the counter is " + ++counter
);
// 发送响应内容
String currentTime = null;
if ("QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(bodyFromClient)) {
currentTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
} else {
currentTime = "BAD ORDER";
}
// 加上换行符
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
// 写入缓冲区
ByteBuf response = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
});
// 绑定端口同步等待
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务监听端口关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
parentGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TcpPacketServer2.bind(8080);
}
}
服务端加了编解码器:
socketChannel.pipeline()
// 换行解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
// 将接收到的对象转为字符串后再调用handler
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
2、客户端改造
package com.wgs.netty.demo2_packet;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* Created by wanggenshen
* Date: on 2019/7/13 13:54.
* Description: 解决粘包问题的客户端
*/
public class TcpPacketClient2 {
public static void connect(int port, String host) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
private int counter;
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler() {
/**
* 监听channel, 读取服务端响应
*
* @param channelHandlerContext
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object msg) throws Exception {
String bodyFromServer = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Now time is : " + bodyFromServer + "; the counter is : " + ++counter);
}
/**
* 发送指令给服务端
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf msg = null;
// 循环发送100条带有换行的 "QUERY TIME ORDER"指令
String command = "QUERY TIME ORDER" + System.getProperty("line.separator");
byte[] commandReq = command.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
msg = Unpooled.buffer(commandReq.length);
msg.writeBytes(commandReq);
ctx.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TcpPacketClient2.connect(8080, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
客户端也加了编解码器:
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
3、运行与测试
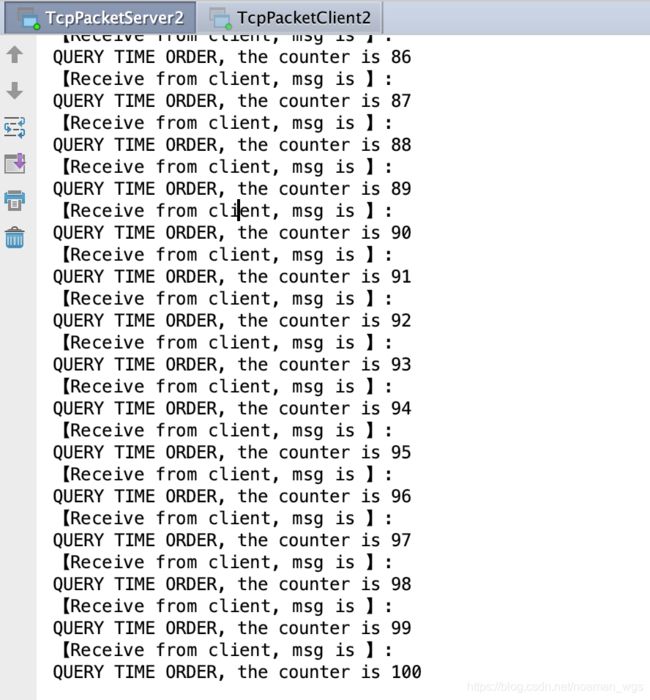
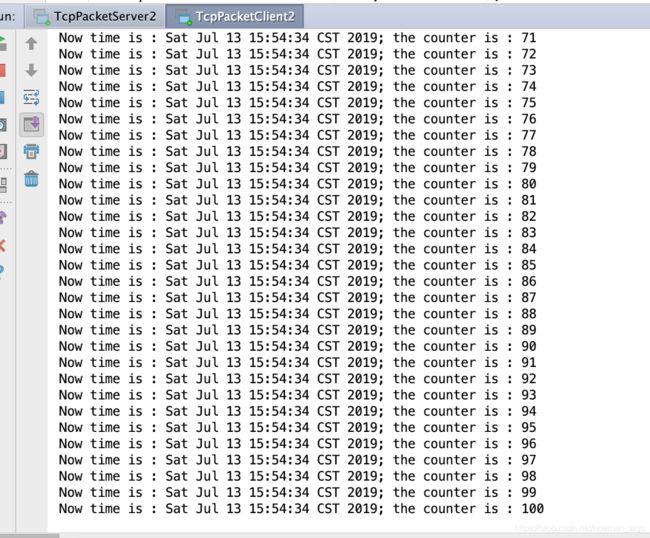
可以看到,客户端发送了100条指令,服务端接收到并且打印在控制台上;同时服务端发送的100条响应客户端均接收到,并且打印在控制台上,证明了没有发生TCP粘包/拆包现象。
4、LineBasedFrameDecoder和StringDecoder原理分析
LineBasedFrameDecode的工作原理是从ByteBuf遍历可读字节,如果发现是以’\n’或’\r\n’(换行或回车换行)就将这些字节当做一行;
StringDecoder是将接收到的对象转换成字符串,再继续调用后面的Handler。
LineBasedFrameDecoder + StringDecoder 的组合就是按行切换的文本解码器,用来解决TCP粘包和拆包问题。
参考:
《TCP权威指南》