【Netty权威指南】04-TCP粘包/拆包问题的解决之道
1、TCP粘包/拆包
TCP是个“流”协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据。大家可以想想河里的流水它们是连成一片的,其间并没有分界线。TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分,所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也有可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP粘包和拆包问题。
1.1、TCP粘包/拆包问题说明
我们可以通过图解对TCP粘包和拆包问题进行说明,粘包问题示例如图4-1所示。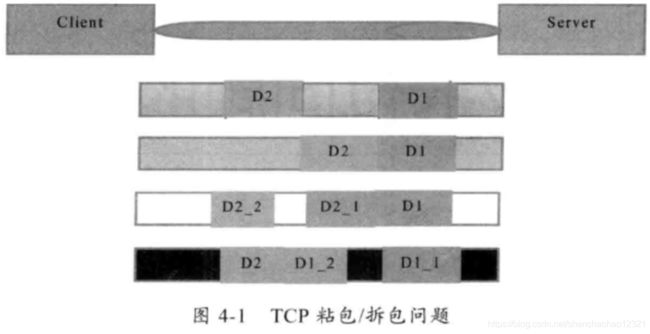
假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包D1和D2给服务端,由于服务端一次读取到的字节数是不确定的,故可能存在以下4种情况
- 服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,没有粘包和拆包
- 服务端一次接收到了两个数据包,D1和D2粘合在一起,被称为TCP粘包;
- 服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1包和D2包的部分内容,第二次读取到了D2包的剩余内容,这被称为TCP拆包;
- 服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了D1包的部分内容D1_1,第次读取到了D1包的剩余内容D1_2和D2包的整包
如果此时服务端TCP接收滑窗非常小,而数据包D1和D2比较大,很有可能会发生第5种可能,即服务端分多次才能将D1和D2包接收完全,期间发生多次拆包。
1.2、TCP粘包拆包发生的原因
问题产生的原因有三个,分别如下。
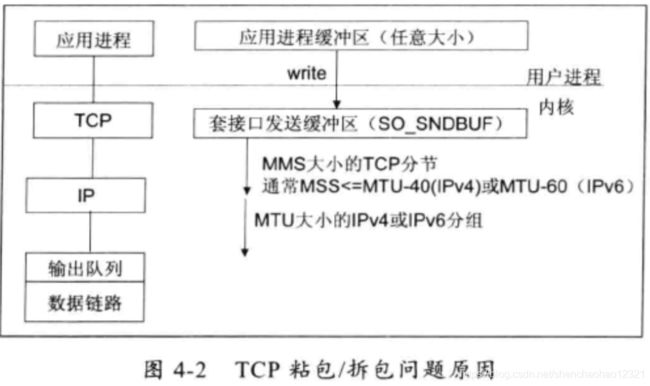
- 应用程序 write写入的字节大小大于套接口发送缓冲区大小;
- 进行MSS大小的TCP分段;
- 以太网帧的 payload大于MTU进行IP分片。
1.3、粘包问题的解决策略
由于底层的TCP无法理解上层的业务数据,所以在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层的应用协议栈设计来解决,根据业界的主流协议的解决方案,可以归纳如下。
- 消息定长,例如每个报文的大小为固定长度200字节,如果不够,空位补空格
- 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,例如FTP协议;
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示消息总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段,通常设计思路为消息头的第一个字段使用int32来表示消息的总长度;
- 更复杂的应用层协议。
介绍完了TCP粘包/拆包的基础知识,下面我们就通过实际例程来看看如何使用Netty提供的半包解码器来解决TCP粘包/拆包问题。
2、未考虑TCP粘包导致功能异常案例
在前面的时间服务器例程中,我们多次强调并没有考虑读半包问题,这在功能测试时往往没有问题,但是一旦压力上来,或者发送大报文之后,就会存在粘包/拆包问题。如果代码没有考虑,往往就会出现解码错位或者错误,导致程序不能正常工作。下面我们以下面代码为例,模拟故障场景,然后看看如何正确使用Netty的半包解码器来解决TCP粘包/拆包问题。
2.1、TimeServer的改造
package com.phei.netty.frame.fault;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8").substring(0, req.length
- System.getProperty("line.separator").length());
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body
+ " ; the counter is : " + ++counter);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}每读到一条消息后,就计一次数,然后发送应答消息给客户端。按照设计,服务端接收到的消息总数应该跟客户端发送的消息总数相同,而且请求消息删除回车换行符后应该为" QUERY TIME ORDER"。下面我们继续看下客户端的改造。
2.2、TimeClient的改造
package com.phei.netty.frame.fault;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger
.getLogger(TimeClientHandler.class.getName());
private int counter;
private byte[] req;
/**
* Creates a client-side handler.
*/
public TimeClientHandler() {
req = ("QUERY TIME ORDER" + System.getProperty("line.separator"))
.getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf message = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is : " + body + " ; the counter is : "
+ ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpected exception from downstream : "
+ cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}主要的修改点就是代码第33~38行,客户端跟服务端链路建立成功之后,循环发送100条消息,每发送一条就刷新一次,保证每条消息都会被写入 Channel中。按照我们的设计,服务端应该接收到100条查询时间指令的请求消息。第48~49行,客户端每接收到服务端一条应答消息之后,就打印一次计数器。按照设计初衷,客户端应该打印100次服务端的系统时间。
2.3、运行结果
服务端运行结果表明它只接收到了两条消息,第一条包含57条“ QUERY TIMEORDER”指令,第二条包含了43条“ QUERY TIME ORDER”指令,总数正好是100条。我们期待的是收到100条消息,每条包含一条“ QUERY TIME ORDER”指令。这说明发生了TCP粘包。
客户端运行结果如下。
按照设计初衷,客户端应该收到100条当前系统时间的消息,但实际上只收到了一条。这不难理解,因为服务端只收到了2条请求消息,所以实际服务端只发送了2条应答,由于请求消息不满足查询条件,所以返回了2条“ BAD ORDER”应答消息。但是实际上客户端只收到了一条包含2条“ BAD ORDER”指令的消息,说明服务端返回的应答消息也发生了粘包。
由于上面的例程没有考虑TCP的粘包拆包,所以当发生TCP粘包时,我们的程序就不能正常工作。
3、利用 LineBasedFrameDecoder解决TCP粘包问题
为了解决TCP粘包拆包导致的半包读写问题,Nety默认提供了多种编解码器用于处理半包,只要能熟练掌握这些类库的使用,TCP粘包问题从此会变得非常容易,你甚至不需要关心它们,这也是其他NO框架和JDK原生的 NIO API所无法匹敌的下面我们就以修正时间服务器为目标进行开发和讲解,通过对实际代码的讲解让大家能够尽快熟悉和掌握半包解码器的使用。
3.1、支持TCP粘包的TimeServer
package com.phei.netty.frame.correct;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel arg0) throws Exception {
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
new TimeServer().bind(port);
}
} 重点看45~47行,在原来的 TimeServerHandler之前新增了两个解码器:LineBasedFrameDecoder和StringDecoder。这两个类的功能后续会进行介绍,下面继续看TimeServerHandler的代码修改。
package com.phei.netty.frame.correct;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
String body = (String) msg;
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body
+ " ; the counter is : " + ++counter);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}直接看19~21行,可以发现接收到的msg就是删除回车换行符后的请求消息,不需要额外考虑处理读半包问题,也不需要对请求消息进行编码,代码非常简洁。读者可能会质疑这样是否可行,不着急,我们先继续看看客户端的类似改造,然后运行程序看执行结果,最后再揭开其中的奥秘。
3.2、支持TCP粘包的TimeClient
package com.phei.netty.frame.correct;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// 当代客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
new TimeClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
} 31~34行与服务端类似,直接在 TimeClientHandler之前新增 LineBasedFrameDecoder和 StringDecoder解码器,下面我们继续看 TimeClientHandler的代码修改。
package com.phei.netty.frame.correct;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @version 1.0
* @date 2014年2月14日
*/
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger
.getLogger(TimeClientHandler.class.getName());
private int counter;
private byte[] req;
/**
* Creates a client-side handler.
*/
public TimeClientHandler() {
req = ("QUERY TIME ORDER" + System.getProperty("line.separator"))
.getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf message = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
String body = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Now is : " + body + " ; the counter is : "
+ ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpected exception from downstream : "
+ cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}3.3、LineBasedFrameDecoder和 StringDecoder的原理分析
LineBasedFrameDecoder的工作原理是它依次遍历ByteBuf中的可读字节,判断看是否有“\n”或者“\r\n”,如果有,就以此位置为结束位置,从可读索引到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。它是以换行符为结束标志的解码器,支持携带结束符或者不携带结束符两种解码方式,同时支持配置单行的最大长度。如果连续读取到最大长度后仍然没有发现换行符,就会抛岀异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流。
StringDecoder的功能非常简单,就是将接收到的对象转换成字符串,然后继续调用后面的 Handler。LineBasedFrameDecoder+StringDecoder组合就是按行切换的文本解码器,它被设计用来支持TCP的粘包和拆包。
可能读者会提出新的疑问:如果发送的消息不是以换行符结束的,该怎么办呢?或者没有回车换行符,靠消息头中的长度字段来分包怎么办?是不是需要自己写半包解码器?
答案是否定的, Netty提供了多种支持TCP粘包/拆包的解码器,用来满足用户的不同诉求。