平衡二叉树(AVL树)Java语言实现
参考:《数据结构与算法分析》和《算法(第四版)》
文章目录
-
- 概述
- 旋转
-
- 左旋转
- 右旋转
- 右左双旋转(RL)
- 左右双旋转(LR)
- 判断是否平衡方法 balance
- 所有代码
概述
之前的二分搜索树可能会出现最坏的情况,如果添加的元素为:1,2,3,4,5 和 6 ,那么,二分搜索树就会像链表一样,插入速度没有影响,但是查询速度明显降低(因为需要依次比较),不能发挥 BST 的优势,因为每次还需要比较左子树,其查询速度比单链表还慢;
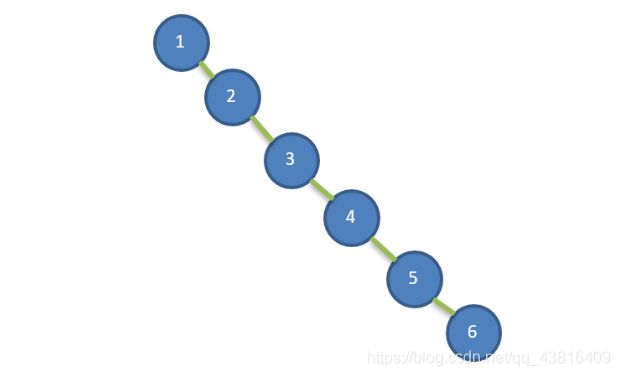
因此,需要使用 平衡二叉树来解决此问题:
- 平衡二叉树也叫平衡二叉搜索树(Self-balancing binary search tree)又被称为AVL树, 可以保证查询效率较高;
- 具有以下特点:它是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 ,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树;
在 AVLTree 中只要熟悉了它是如何将如上图的这样的情况转换成一个平衡的树,就基本掌握了 AVLTree ,因此接下来就看其转换平衡树的工作原理即可;
由于 AVLTree 最重要的是旋转和判断平衡的这些方法,其余方法和二分搜索树类似;
旋转
往往平衡二叉树中添加节点或者删除结点很可能会导致二叉树失去平衡,所以我们需要在每次插入节点或者删除结点后进行平衡的维护操作,因此就会出现四种情况;
左旋转
如果目前树为如下形状:

因此上图的结点1处就需要进行一次向左的旋转,左旋转:
执行 TreeNode y = x.rchild
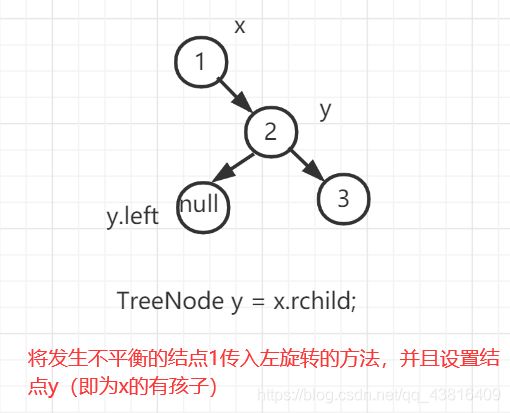
代码 x.rchild = y.lchild :

接着执行代码: y.lchild = x
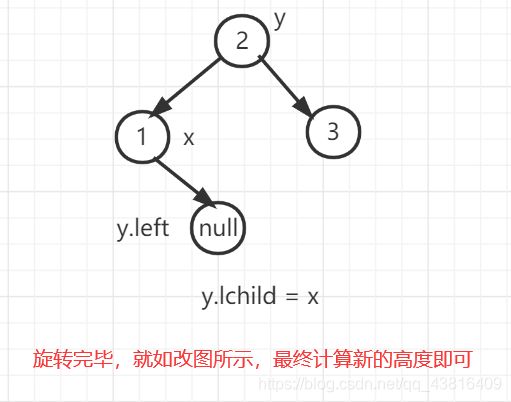
上述过程就是一次左旋转的情况,然后对应的就会出现右旋转(都是对应并相反的);
上述代码:
/**
* 左旋转
* @param x 产生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithLeft(TreeNode<E> x) {
//旋转
TreeNode y = x.rchild;
x.rchild = y.lchild;
y.lchild = x;
//重新计算结点 x 的高度
x.height = Math.max(height(x.lchild), height(x.rchild)) + 1;
//由于目前 x 被旋转到了 y 结点的左子树,因此比较y的右子树和x的高度即可
y.height = Math.max(height(y.rchild), x.height) + 1;
return y;
}
计算高度的话,在 TreeNode 内部类中的构造器中,每次创建一个结点,就默认该节点的高度为1即可,然后为了方便在这些方法中获取当前结点的高度时,就可以编写一个内部方法
height(TreeNode< E >) 即可,方法如下:
private int height(TreeNode<E> root) {
return root == null ? 0 : root.height;
}
然后将每个结点的高度统计?
在每次添加元素或者删除元素时都会去判断目前结点的树是否平衡,而在该判断是否平衡的方法中,每次去计算当前结点的高度即可。(判断平衡的方法在下面)
右旋转
右旋转和左旋转其实是相反的;
/**
* 右旋转
* 右旋转和左旋转是相反的
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithRight(TreeNode<E> x) {
TreeNode<E> y = x.lchild;
x.lchild = y.rchild;
y.rchild = x;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.lchild), height(x.rchild)) + 1;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.lchild), x.height) + 1;
return y;
}
右左双旋转(RL)
如下情况:
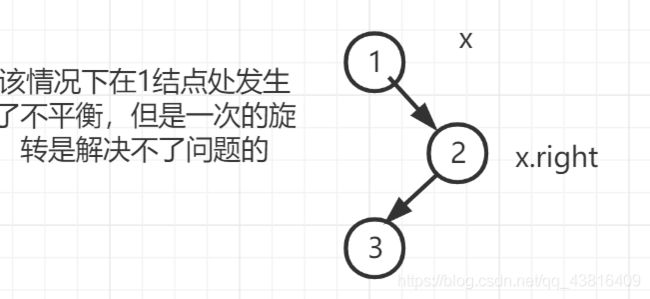
因此,我们可以先将3结点元素旋转至,能够进行左旋转解决时的情况,也就是说,先在结点2的地方进行一次右旋转,结果如下:
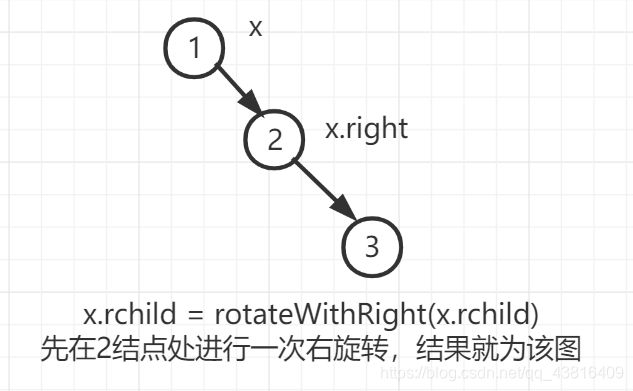
此时,可以很明显的看出,只要在x结点(1结点)处再进行一次简单的左旋转即可解决问题,左旋转就和之前的介绍一样;
右左双旋转:
/**
* 右左双旋转
* 先进行一次右旋转,让其构成可以进行左旋转的条件
*
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithRightLeft(TreeNode<E> x) {
//先进行右旋转
x.rchild = rotateWithRight(x.rchild);
//接着进行左旋转
return rotateWithLeft(x);
}
左右双旋转(LR)
该旋转和右左双旋转的套路是一样的,也就是说,之前的左旋转和右旋转也都是相反的,我们只需要牢记“一组”旋转即可(如,左旋转和右左双旋转,因为,这两个旋转都是出现在当前结点的右子树);
代码:
/**
* 左右双旋转
* 先进性左旋转,接着右旋转
*
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithLeftRight(TreeNode<E> x) {
x.lchild = rotateWithLeft(x.lchild);
return rotateWithRight(x);
}
判断是否平衡方法 balance
该方法只负责去判断当前结点的左右子树是否平衡;
-
如果当前结点的左右子树高度差超过允许值,且左子树较高,即在左子树插入时导致的不平衡;
– 然后需要再次进行判断:在左节点的左子树插入导致不平衡时,就要进行一次右旋转;
– 而如果是在左节点的右子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先左旋,再右旋; -
相反,如果是当前结点的右子树较高,那么就和上面的步骤类似;
– 然后需要再次进行判断:在右节点的右子树插入导致不平衡时,就要进行一次左旋转;
– 而如果是在右节点的左子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先右旋转,再左旋转,也就是之前图中的情况;
/**
* 判断传入的结点的左右子树是否是平衡的,如果不平衡那么判断采用哪种旋转方式
* @param root 传入将要判断是否平衡的结点
* @return 返回一个“根结点”,最终被删除或添加方法中的引用链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> balance(TreeNode<E> root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//左右子树高度差超过允许值,且左子树较高,即在左子树插入时导致的不平衡
if (height(root.lchild) - height(root.rchild) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
//在左(L)节点的左(L)子树插入导致不平衡,进行右旋转
if (height(root.lchild.lchild) >= height(root.lchild.rchild)) {
root = rotateWithRight(root);
} else {
//在左(L)节点的右子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先左旋,再右旋
root = rotateWithLeftRight(root);
}
//左右子树高度差超过允许值,且右子树较高,即在右子树插入导致不平衡
} else if (height(root.rchild) - height(root.lchild) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
//在右(R)节点的右(R)子树插入导致不平衡,单旋转调整, 左旋转
if (height(root.rchild.rchild) >= height(root.rchild.lchild)) {
root = rotateWithLeft(root);
} else {
//在右(R)节点的左(L)子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先右旋,再左旋
root = rotateWithRightLeft(root);
}
}
//重新计算当前 root 结点的高度
root.height = Math.max(height(root.lchild), height(root.rchild)) + 1;
return root;
}
所有代码
/**
* @author 七夏
* @create 2020-06-25
*/
public class AVLTree<E extends Comparable<? super E>> {
private TreeNode root;
private static final int ALLOWED_IMBALANCE = 1;
//获取当前结点的高度
private int height(TreeNode<E> root) {
return root == null ? 0 : root.height;
}
public void insert(E e) {
root = insert(e, root);
}
public void remove(E e) {
root = remove(e, root);
}
public E findMin() {
return (E) findMin(root).data;
}
private TreeNode<E> findMin(TreeNode<E> root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else if (root.lchild == null) {
return root;
}
return findMin(root.lchild);
}
public E findMax(){
return (E) findMax(root).data;
}
private TreeNode<E> findMax(TreeNode<E> root){
if(root == null){
return null;
}else if (root.rchild == null){
return root;
}
return findMax(root.rchild);
}
private TreeNode<E> remove(E e, TreeNode<E> root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
int compareRes = e.compareTo(root.data);
if (compareRes < 0) {
root = remove(e, root.lchild);
} else if (compareRes > 0) {
root = remove(e, root.rchild);
} else if (root.lchild != null && root.rchild != null) {
//如果删除的该结点的左右子树都不为空,那么将找寻到该结点的右子树的最小结点来覆盖要删除的结点root
root.data = findMin(root.rchild).data;
//上步被覆盖之后,就继续递归地删除该root结点的右子树的最小结点
root.rchild = remove(root.data, root);
}else{
//删除的root结点的左右子树可能有一个为空,或者都为空
//如果左子树不为空,那么就直接让左子树去链接要删除的结点,否则就使用右子树
root = (root.lchild != null) ? root.lchild : root.rchild;
}
return balance(root);
}
private TreeNode<E> insert(E e, TreeNode<E> root) {
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode(e);
}
int compareRes = e.compareTo(root.data);
if (compareRes < 0) {
root.lchild = insert(e, root.lchild);
} else if (compareRes > 0) {
root.rchild = insert(e, root.rchild);
} else {
//已经存在该元素 e
}
return balance(root);
}
/**
* 判断传入的结点的左右子树是否是平衡的,如果不平衡那么判断采用哪种旋转方式
*
* @param root 传入将要判断是否平衡的结点
* @return 返回一个“根结点”,最终被删除或添加方法中的引用链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> balance(TreeNode<E> root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//左右子树高度差超过允许值,且左子树较高,即在左子树插入时导致的不平衡
if (height(root.lchild) - height(root.rchild) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
//在左(L)节点的左(L)子树插入导致不平衡,进行右旋转
if (height(root.lchild.lchild) >= height(root.lchild.rchild)) {
root = rotateWithRight(root);
} else {
//在左(L)节点的左(右)子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先左旋,再右旋
root = rotateWithLeftRight(root);
}
//左右子树高度差超过允许值,且右子树较高,即在右子树插入导致不平衡
} else if (height(root.rchild) - height(root.lchild) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
//在右(R)节点的右(R)子树插入导致不平衡,单旋转调整, 左旋转
if (height(root.rchild.rchild) >= height(root.rchild.lchild)) {
root = rotateWithLeft(root);
} else {
//在右(R)节点的左(L)子树插入导致不平衡,双旋转调整,先右旋,再左旋
root = rotateWithRightLeft(root);
}
}
//重新计算当前 root 结点的高度
root.height = Math.max(height(root.lchild), height(root.rchild)) + 1;
return root;
}
/**
* 左旋转
*
* @param x 产生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithLeft(TreeNode<E> x) {
//旋转
TreeNode y = x.rchild;
x.rchild = y.lchild;
y.lchild = x;
//重新计算结点 x 的高度
x.height = Math.max(height(x.lchild), height(x.rchild)) + 1;
//由于目前 x 被旋转到了 y 结点的左子树,因此比较y的右子树和x的高度即可
y.height = Math.max(height(y.rchild), x.height) + 1;
return y;
}
/**
* 右左双旋转
* 先进行一次右旋转,让其构成可以进行左旋转的条件
*
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithRightLeft(TreeNode<E> x) {
//先进行右旋转
x.rchild = rotateWithRight(x.rchild);
//接着进行左旋转
return rotateWithLeft(x);
}
/**
* 右旋转
* 右旋转和左旋转是相反的
*
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithRight(TreeNode<E> x) {
TreeNode<E> y = x.lchild;
x.lchild = y.rchild;
y.rchild = x;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.lchild), height(x.rchild)) + 1;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.lchild), x.height) + 1;
return y;
}
/**
* 左右双旋转
* 先进性左旋转,接着右旋转
*
* @param x 发生不平衡的结点
* @return 返回旋转好的结点,然后被调用者链接上
*/
private TreeNode<E> rotateWithLeftRight(TreeNode<E> x) {
x.lchild = rotateWithLeft(x.lchild);
return rotateWithRight(x);
}
//层序遍历
public void print(){
Queue<TreeNode<E>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.add(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode<E> current = queue.poll();
System.out.println(current.data);
if(current.lchild != null){
queue.add(current.lchild);
}
if(current.rchild != null){
queue.add(current.rchild);
}
}
}
private class TreeNode<E> {
private TreeNode<E> lchild;
private TreeNode<E> rchild;
private E data;
private int height;
private TreeNode(E data) {
this(data, null, null);
}
//创建结点的构造函数
private TreeNode(E data, TreeNode lchild, TreeNode rchild) {
this.data = data;
this.lchild = lchild;
this.rchild = rchild;
this.height = 1;
}
}
}